Array for the illumination of an object
A single-emission, planar technology, applied in projection devices, color photography, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve problems such as complex residual gaps in mechanical fixation, and achieve the effect of large color space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
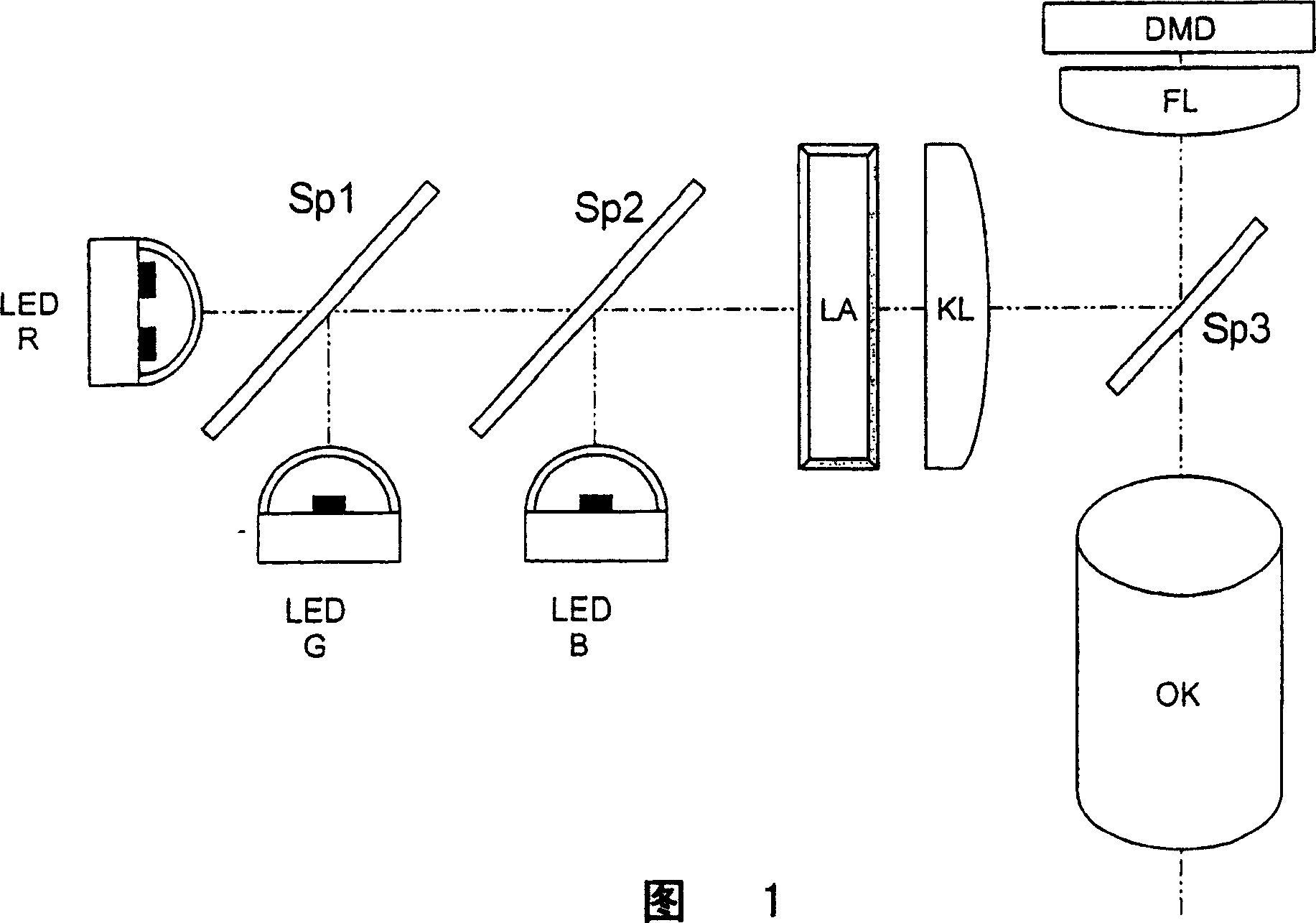
[0030] FIG. 1 shows a device for lighting as described above as prior art, for example on a projector with a DMD matrix.
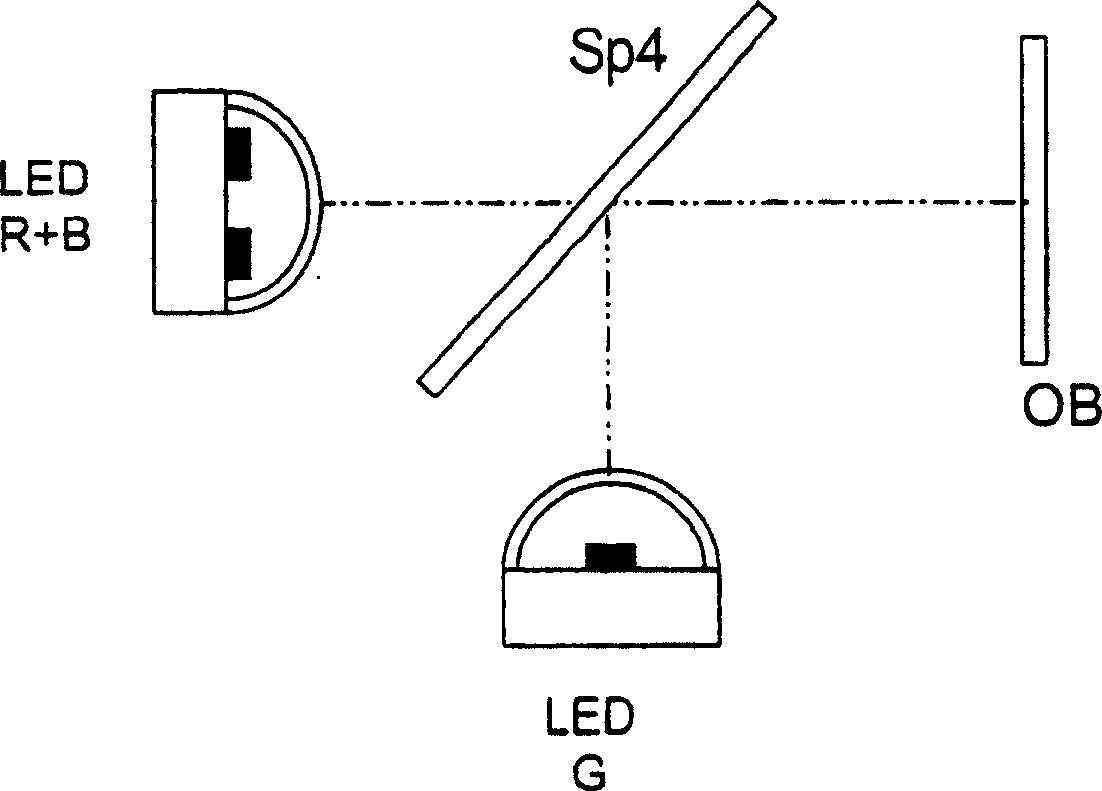
[0031] figure 2 Shown is a single-emitter planar arrangement in the example of a division into two LED modules LED R+B and LED G, whose emitted light components are spatially superimposed via a dichroic beamsplitter Sp4. The superimposed light components are used to illuminate the object OB.
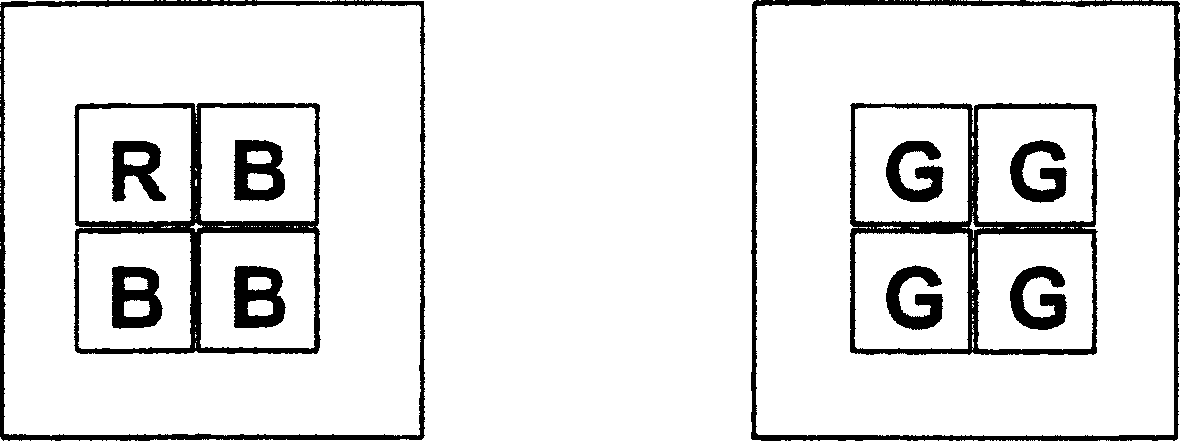
[0032] The first LED module LED R+B comprises three individual emitters for blue and one individual emitter for red. The second LED-module LED G consists of four single emitters of green color (see image 3 ). Currently available LED power ratios are, for example, red:green:blue=6:1:2. Green is the restricted color channel. Three blue emitters and one red emitter are used in one module while maintaining a balanced output power for white light generation. This results in two LED modules with three colors in the appropriate power class, which produce a power rati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com