Ambient light adaptation for dynamic foil displays
A display and optical display technology, used in static indicators, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in providing images, limited number of gray levels, and inability to provide image quality, and achieve the effect of reducing motion artifacts and improving image quality.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0042] Figure 11 An embodiment of a dynamic foil display 1100 of the present invention is schematically represented. The display 1100 comprises a driver circuit 1102 for driving a display panel 1101, means 1104 for switching between modes of operation and a detector 1103 for detecting ambient light levels. The switching device 1104 is interconnected with the detector 1103 and the driving circuit 1102 .
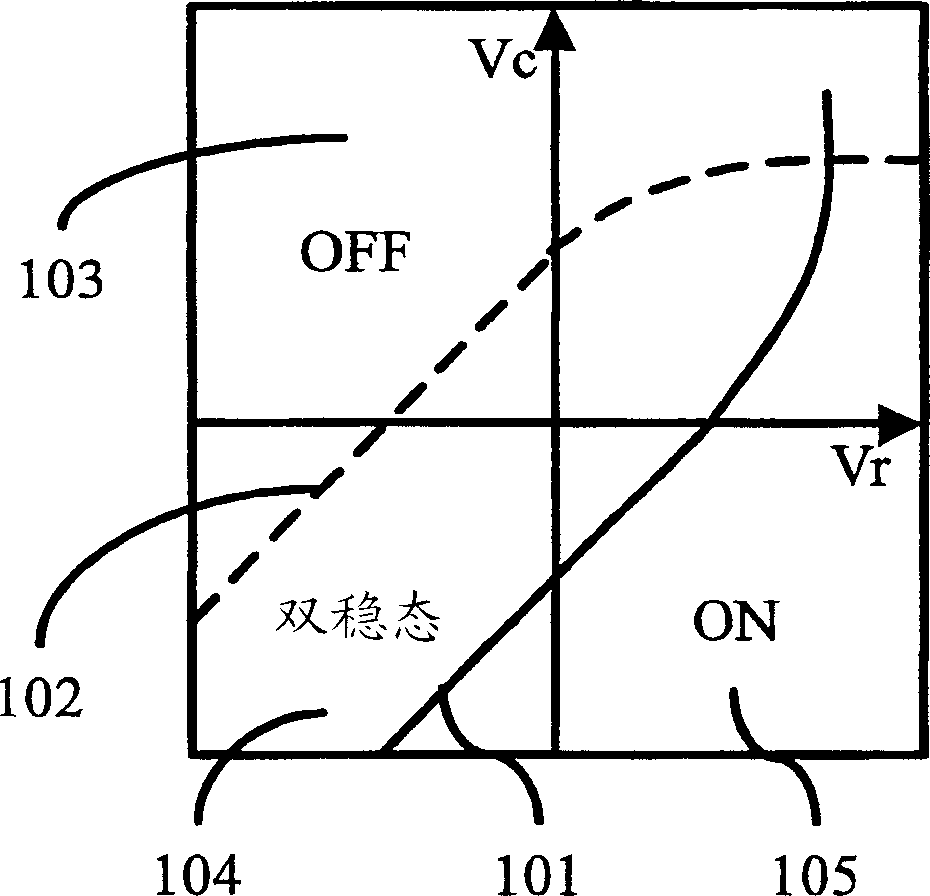
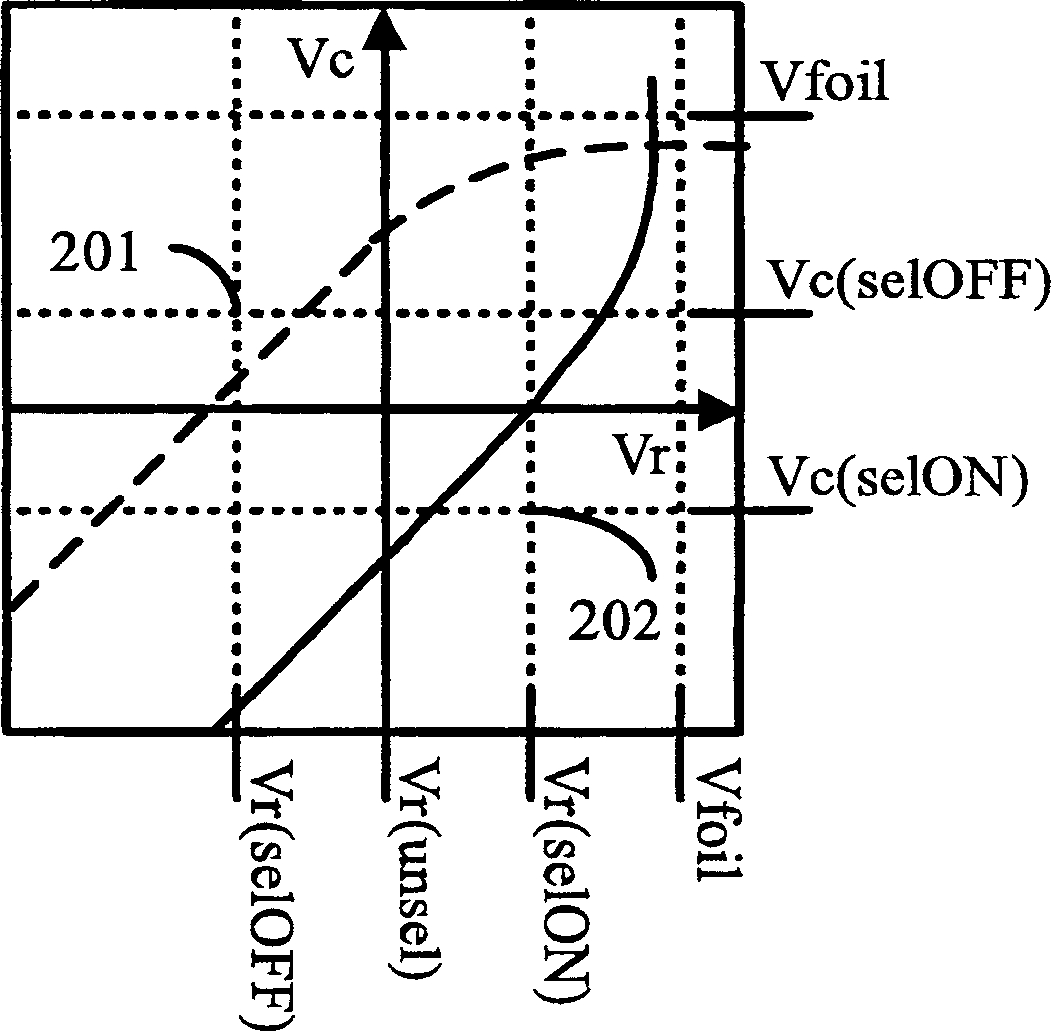
[0043] The driving of dynamic foil displays relies on bistability and hysteresis. A pixel is addressed by voltages applied to row and column electrodes associated with the pixel. The voltage applied to the electrodes can be divided into three distinct regions, the ON region where the pixel is in its ON state, the OFF region where the pixel is in its OFF-state and the intermediate bistable region where the pixel remains in its current state. figure 1 Schematic representation of the relevant voltages that can be applied to a pixel. The x-axis corresponds to the row electrod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com