Wearable action-assist device, and method and program for controlling wearable action-assist device
A motion assisting device and motion technology, which are applied in the directions of appliances, applications, and manufacturing tools that help people to move around, and can solve problems such as the wearer's sense of incongruity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0076] (A) Composition of wearable motion assistance device
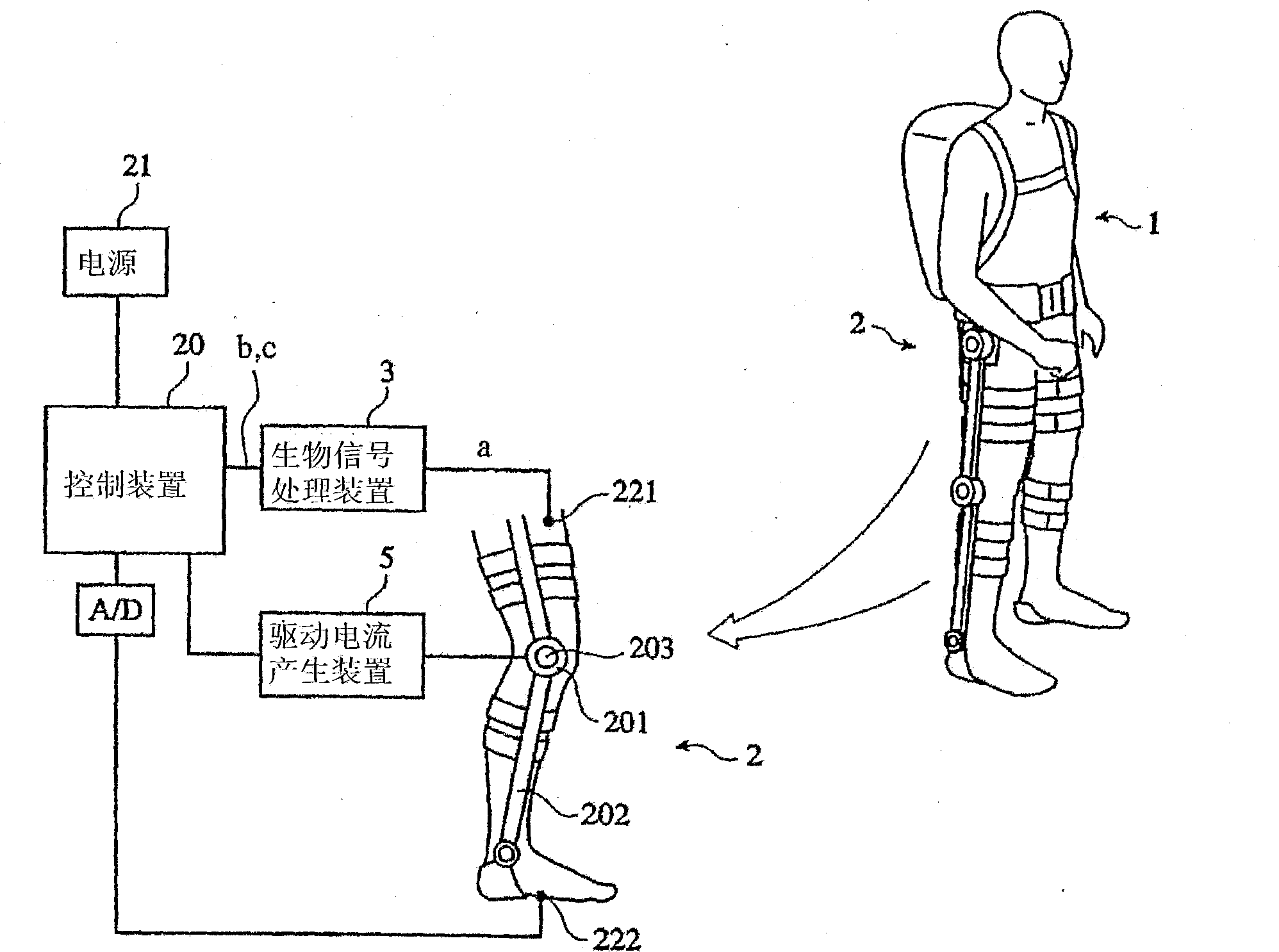
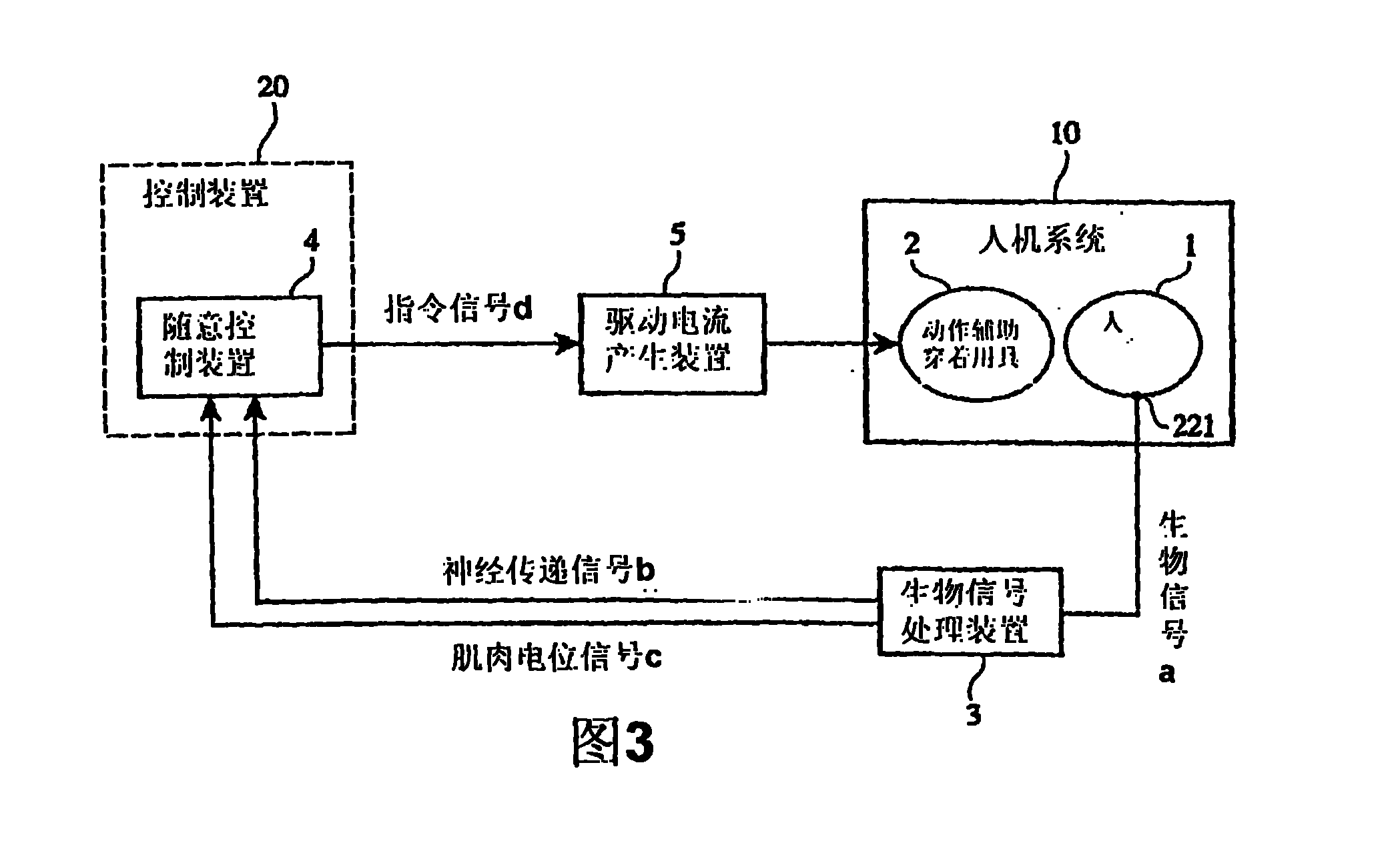
[0077] The wearable motion assisting device of the first embodiment includes: a motion assisting wearer having an actuator; a biosignal sensor for detecting biosignals of the wearer; and a biosignal processing device for obtaining nerve transmission signals and muscle potential signals from the biosignals ; The voluntary control device, which uses the nerve transmission signal and the muscle potential signal to generate an instruction signal for causing the actuator to generate power following the wearer's will; The current corresponding to the signal and the myoelectric signal is transmitted and supplied to the actuator. Among them, in the case where the actuator is to generate a power assist rate corresponding to the state of the task to be performed by the wearer, it is also necessary to set the physical quantity related to the wearer's motion in the wearable motion assisting device. A physical quantity sensor f...
no. 2 approach
[0119] (A) Composition of wearable motion assistance device
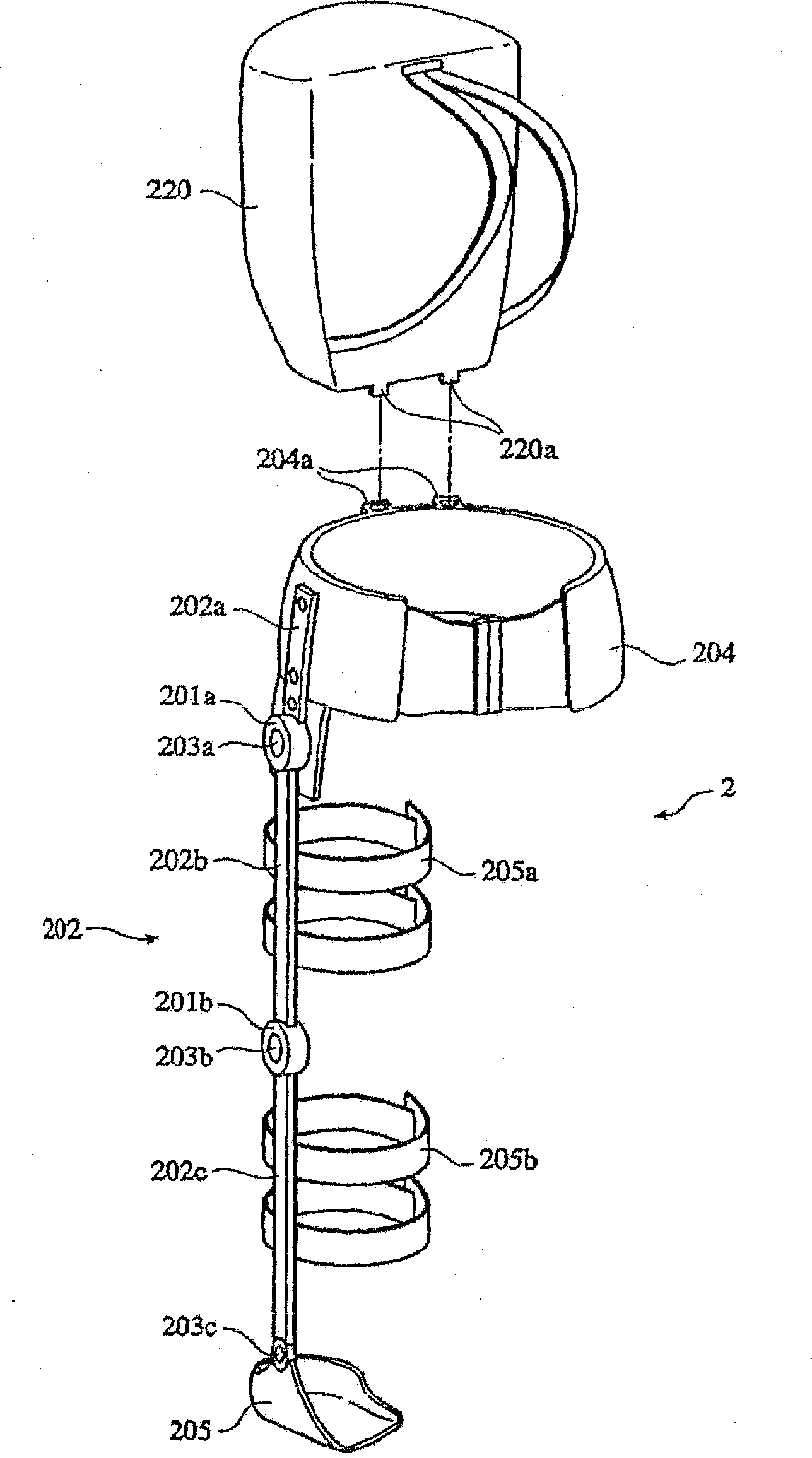
[0120] Such as Figure 13 As shown, the wearable motion assisting device of the second embodiment includes: a motion assisting wearer 2 with an actuator 201; a biological signal sensor 221 for detecting the biological signal a of the wearer 1; A physical quantity sensor 13; and a voluntary control device 14 that generates a command signal d (voluntary command signal d1) for causing the actuator 201 to generate power following the will of the wearer 1 using the biosignal a detected by the physical quantity sensor 13. In addition, it also includes: a database 6, storing each reference parameter of a series of minimum action units (states) constituting each action figure of the wearer 1 classified as a task; The physical quantity and the reference parameters stored in the database 6 estimate the state of the task of the wearer 1, and generate a command signal d (self-discipline command signal d2) for causing the actua...
no. 1 example
[0143] Figure 19 Graphs showing experimental results in the case of adding a pulse current corresponding to a nerve transmission signal in the first embodiment, the graph of (a) shows a change in the rotation angle θ of the knee, the graph of (b) Showing the variation of the amplified biosignal, the graph of (c) shows the torque of the knee actuator. Figure 20 The graph of (a) shows the experimental results in the case of not adding the pulse current corresponding to the nerve transmission signal in the first embodiment, the graph of (a) shows the change of the rotation angle θ of the knee, and the graph of (b) Showing the variation of the amplified biosignal, the graph of (c) shows the torque of the knee actuator.
[0144]This example is an example for illustrating the effects of the first embodiment. When the wearer starts to perform the knee joint stretching action from the state of relaxing on the chair, the condition where the nerve transmission signal b is used as th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com