Magnetoresistive effect element, magnetic head, magnetic storage device and magnetic memory device
A magnetoresistance effect element and magnetoresistance effect technology, which are used in the manufacture of magnetic flux sensitive magnetic heads, information storage, electrical components, etc., and can solve the problems of difficult rotation of magnetization, reduction of substantial changes in magnetoresistance, and decline in output of magnetoresistance elements.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
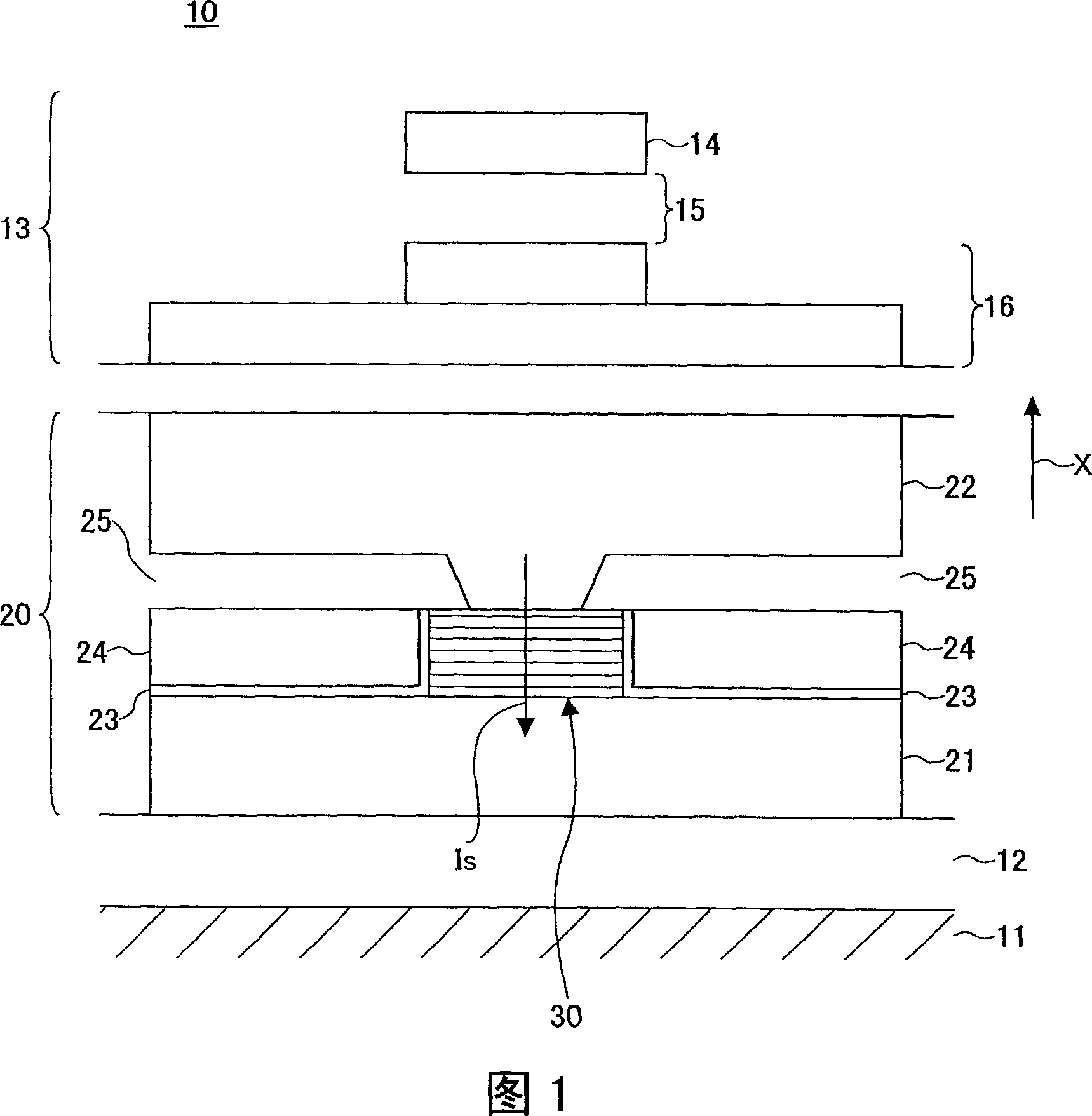
[0043] A composite type magnetic head having the magnetoresistive effect element and the inductive recording element according to the first embodiment of the present invention will be described below. FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram showing a part of the composite type magnetic head. In FIG. 1, arrow X indicates the moving direction of the magnetic recording medium facing the magnetoresistive effect element.
[0044] 1, the composite magnetic head 10 includes: a planar ceramic substrate 11, which is made of Al 2 O 3 -TiC is formed and used as a head slider; a magnetoresistance effect element 20 is formed on the ceramic substrate 11 ; and an inductive recording element 13 is formed on the magnetoresistance effect element 20 .
[0045] The inductive recording element 13 includes: an upper magnetic pole 14, facing the magnetic recording medium and having a width corresponding to the track width of the magnetic recording medium; a recording gap layer 15; a lower magnetic pole 16, ...
Embodiment 1
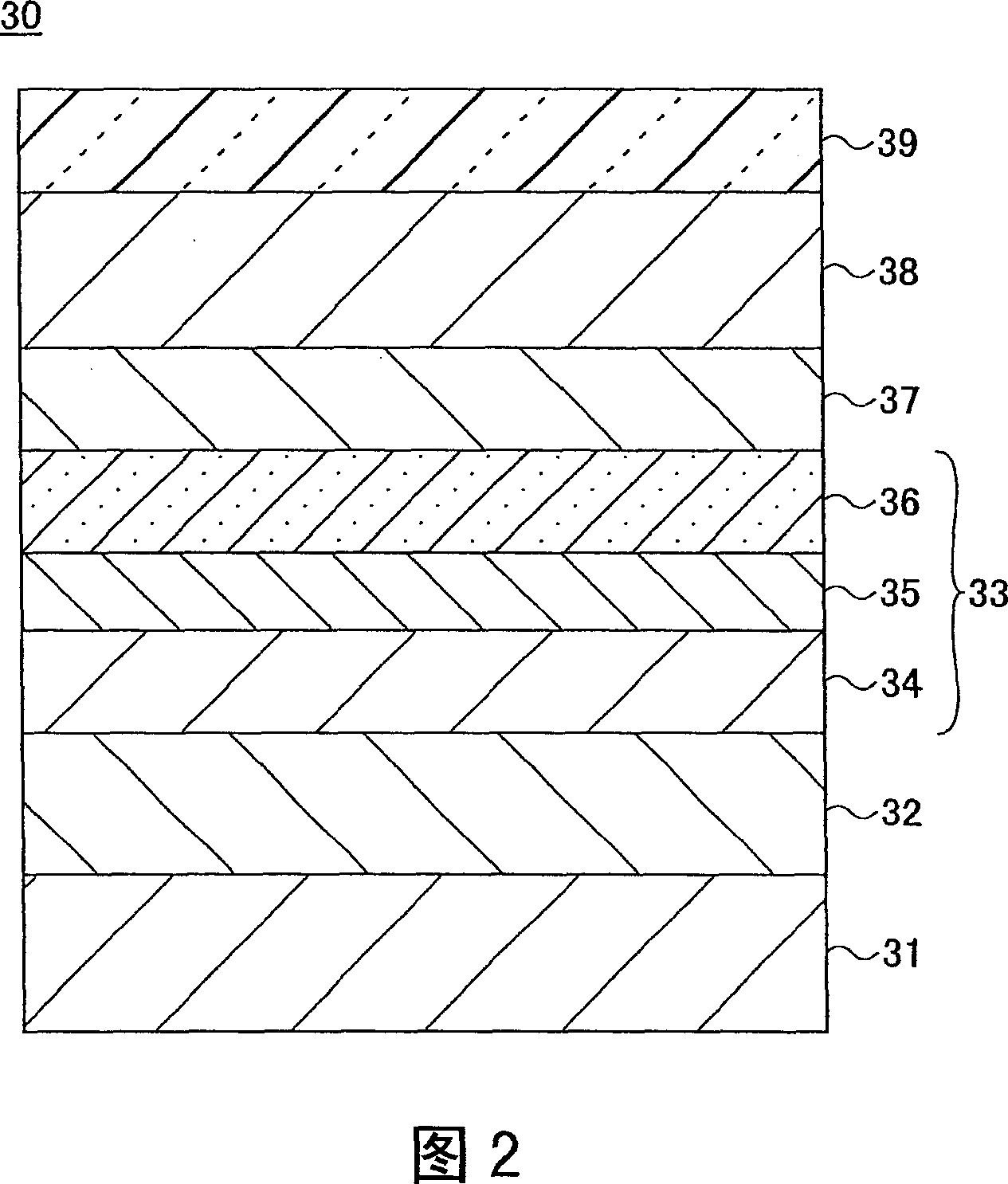
[0098] In Example 1, a magnetoresistance effect element having the GMR film structure of the second example shown in FIG. 3 was fabricated.
[0099] 7 is a graph showing the composition, coercive force, and magnetoresistance variation ΔRA of the free magnetization layer and the upper and lower second fixed magnetization layers in Embodiment 1. FIG.
[0100] Referring to FIG. 7, CoFeAl compositions for the lower second fixed magnetization layer, the free magnetization layer, and the upper second fixed magnetization layer in samples No. 1 to No. 27 were changed. The sample of Example 1 was prepared by the following method.
[0101] A laminated film of Cu (250 nm) / NiFe (50 nm) was formed as a lower electrode on a silicon substrate on which a thermally oxidized film was formed. Then, without heating the substrate, in an ultra-vacuum atmosphere (vacuum degree: equal to or lower than 2×10 -6 In Pa) each layer from the base layer to the protective layer of the lower laminate was fo...
Embodiment 2
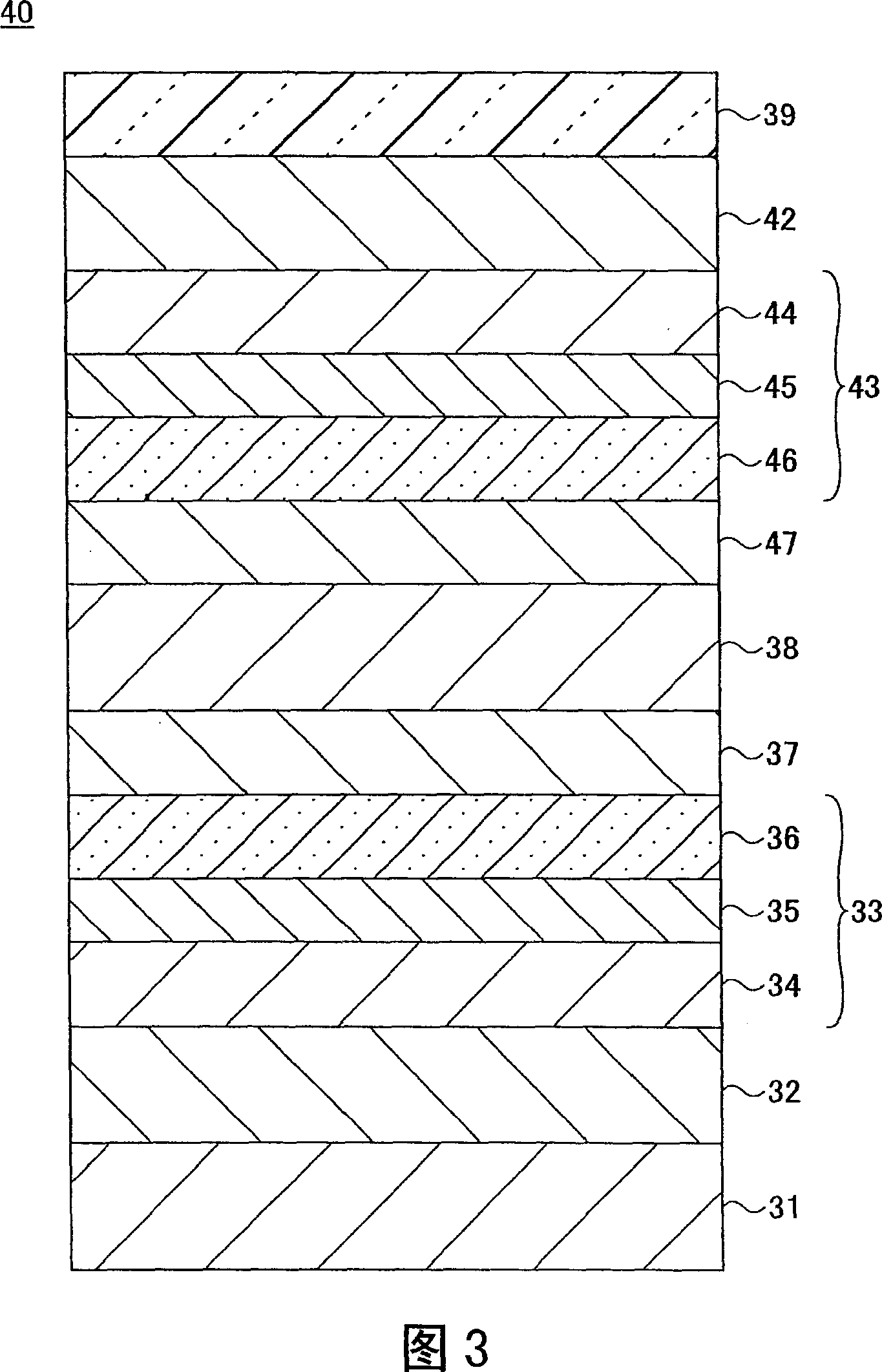
[0127] In Example 2, a magnetoresistive effect element having the GMR film structure of the fifth example according to the first embodiment shown in FIG. 6 was fabricated. In this embodiment, the composition of the free magnetization layer is fixed to Co 50 Fe 20 Al 30 , while changing the CoFeAl composition of the lower second fixed magnetization layer and the upper second fixed magnetization layer to form the magnetoresistive effect elements of the samples Nos. 31 to 37. The composition range of samples Nos. 31 to 37 is the range CHIDC in FIG. 8 . The range CHIDC is defined by a plurality of straight lines successively connecting the points C, H, I, D and C, wherein the point H is (40, 30, 30) and the point I is (50, 30, 20). The coordinates of the components are represented by (Co content, Fe content, Al content). Note that the lower second pinned magnetization layer and the upper second pinned magnetization layer in the same sample are set to have the same composition....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com