Timing synchronization of mesh points in a wireless communication network
A timing synchronization function, grid point technology, applied in the field of wireless networks, can solve problems such as classification of difficult grid devices, and achieve the effect of easy implementation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
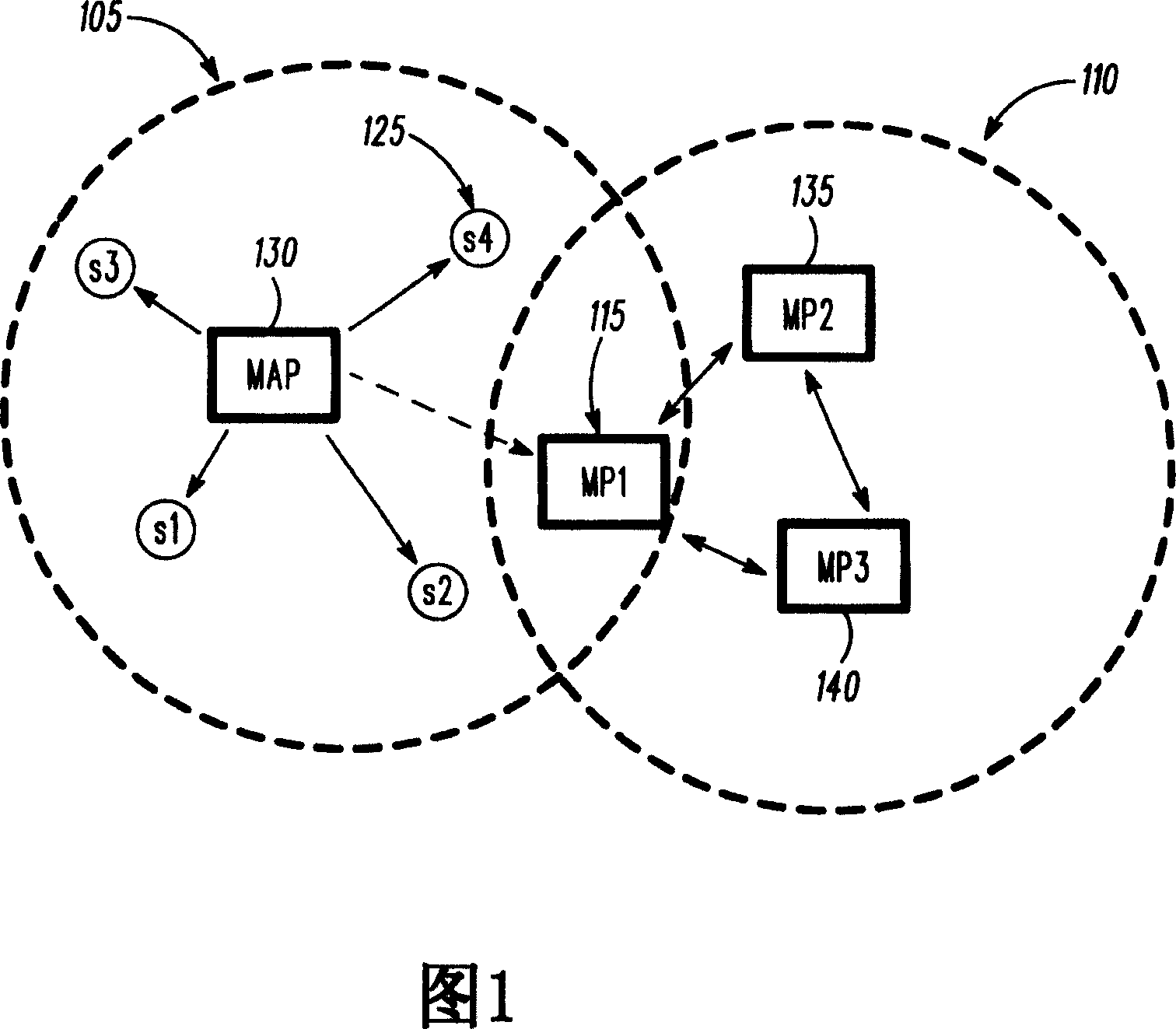
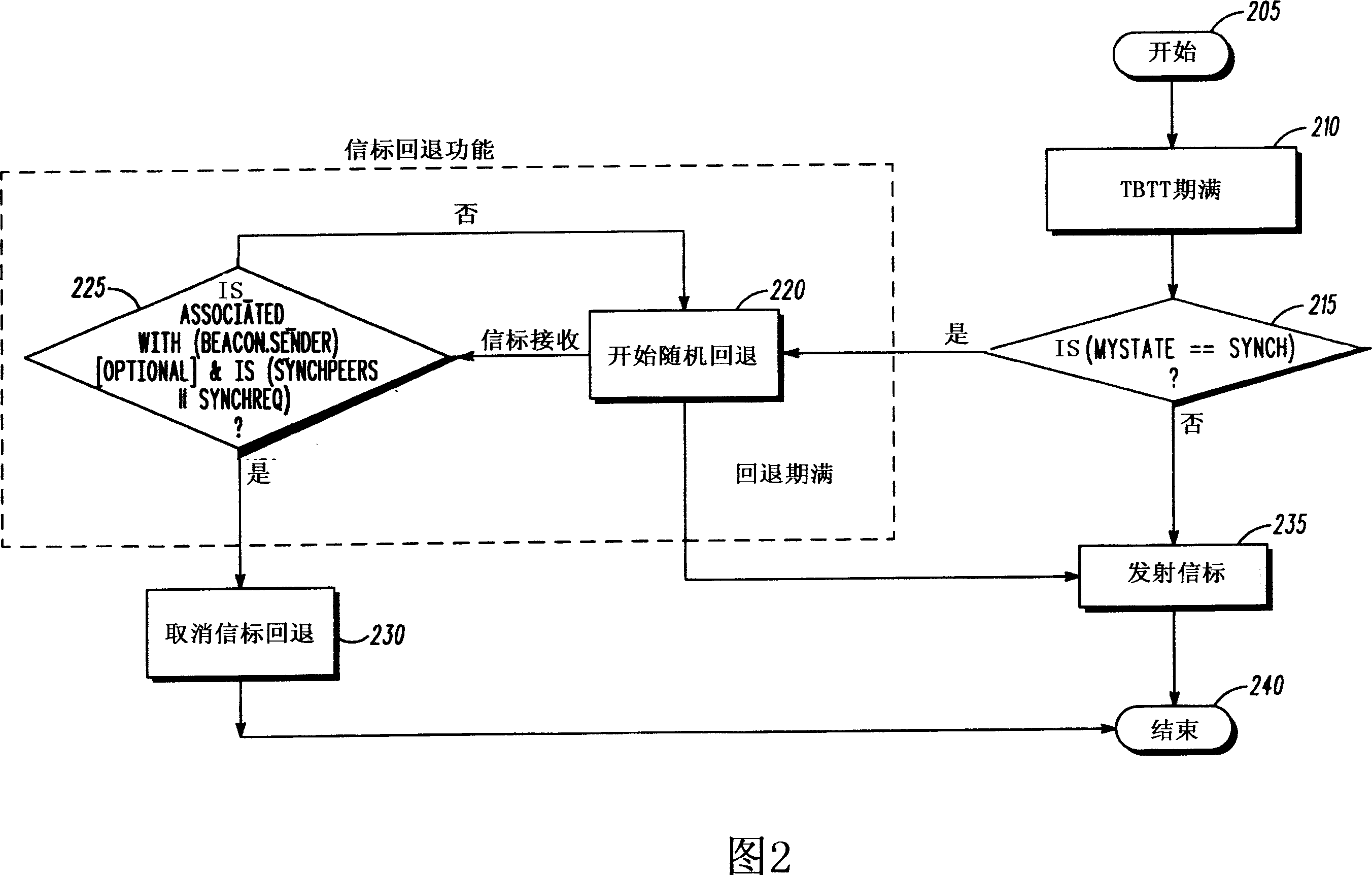
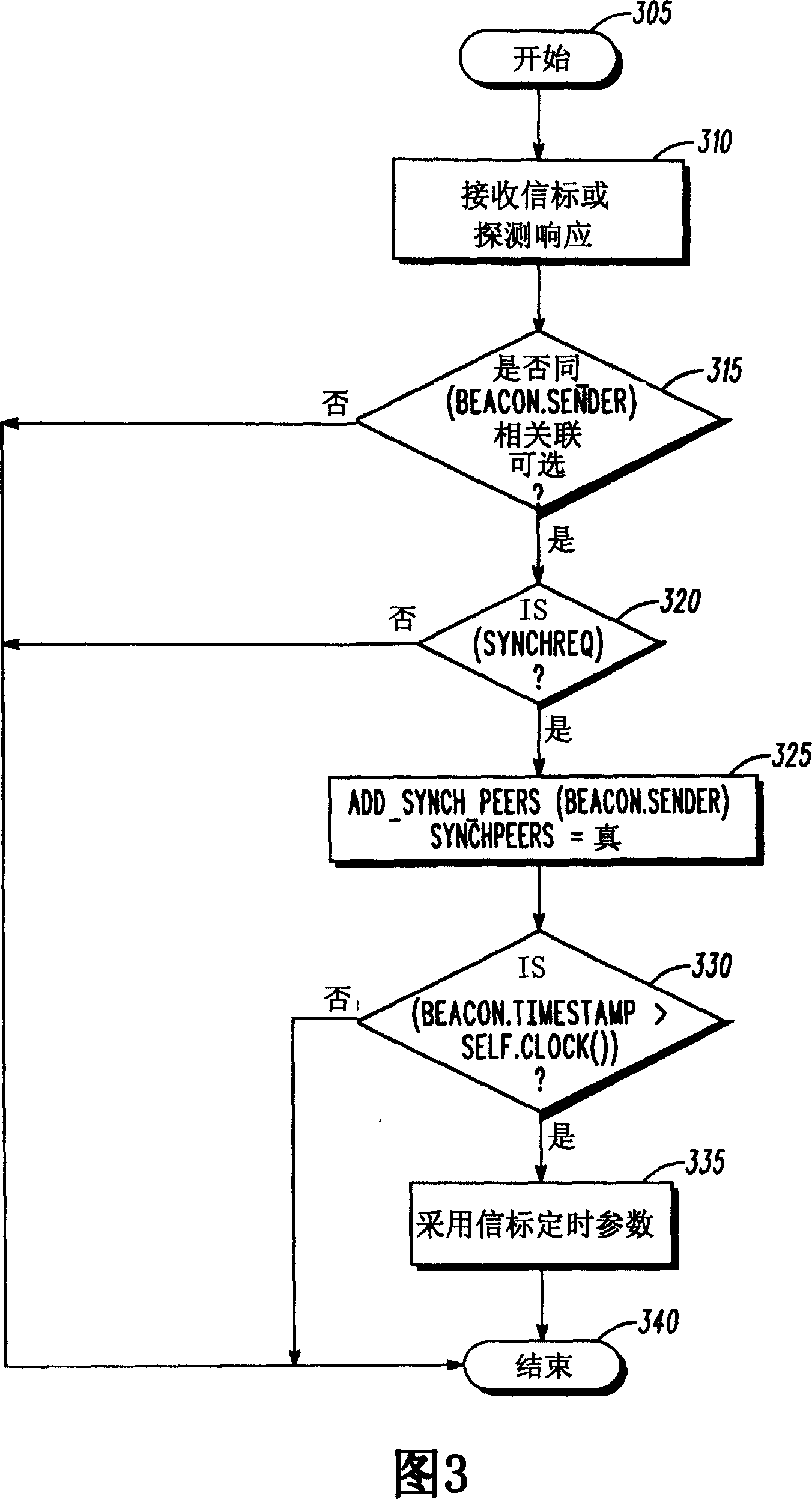
[0013] The proposed beacon generation algorithm for mesh networks includes elements of the IEEE 802.11 standard. For example, MAP follows the beacon generation algorithm of the infrastructure mode. This provides enough flexibility for the MAP to choose its own BSS parameters so that it can transmit beacons every beacon interval and avoid frequency synchronization with other MPs. Non-AP mesh devices, on the other hand, follow the IBSS mode of operation regarding beacon generation when synchronizing with other MPs.
[0014] Referring to FIG. 1 , a system diagram illustrates electronic devices operating in a mesh cluster 110 and an infrastructure network 105 in accordance with some embodiments of the present invention. Operating in the infrastructure network 105 is a MAP 130, and a plurality of basic service set stations s1...s4, including s4 125, which may be legacy stations (legacy stations may also be referred to herein as STAs). Operating in the mesh cluster 110 are a numbe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com