Nonlinear ultrasonic diagnostic imaging using intermodulation product signals
An intermodulation component and non-linear technology, applied in the field of medical diagnostic imaging systems, can solve problems such as reducing image diagnostic quality and reducing echo signal-to-noise characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
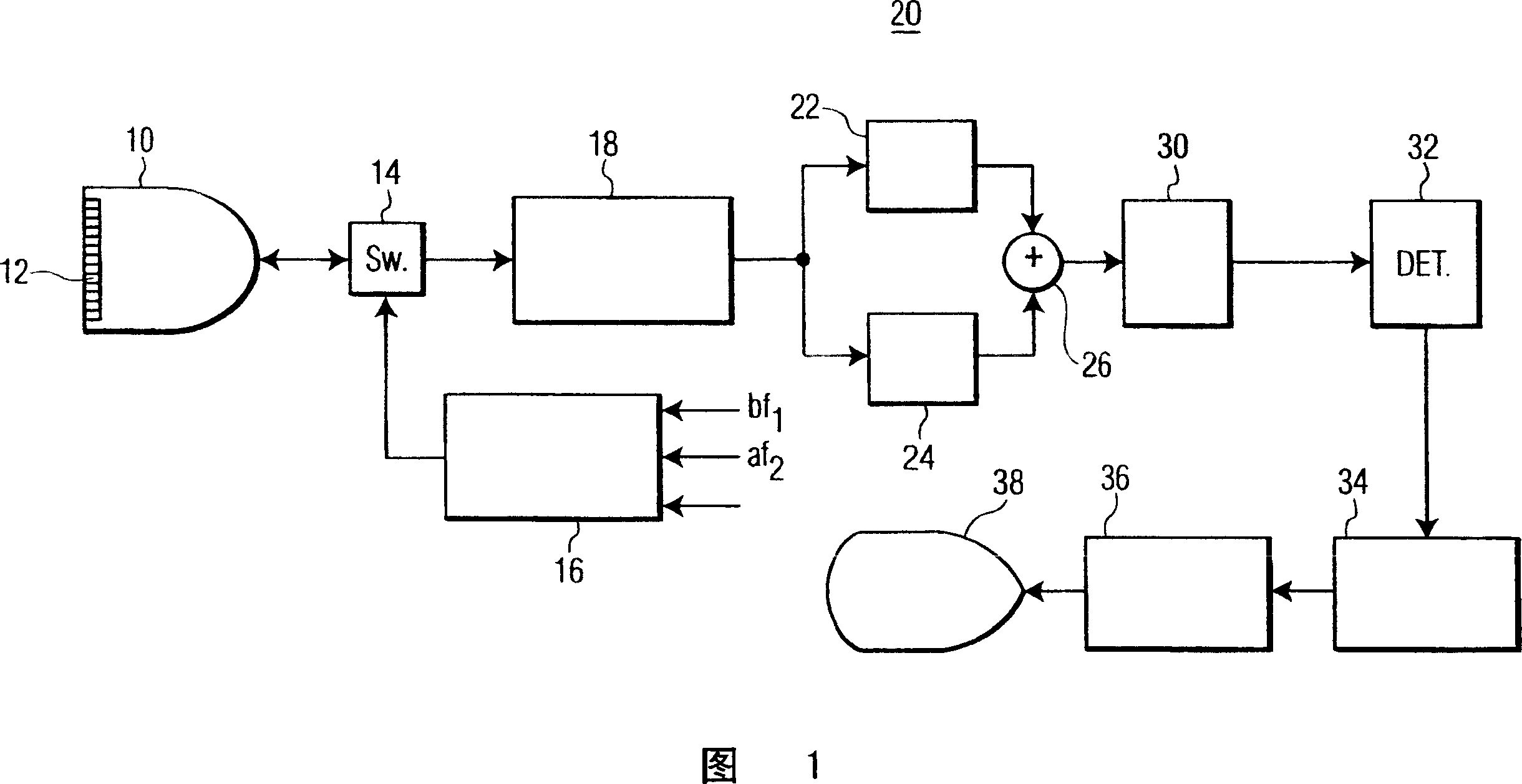
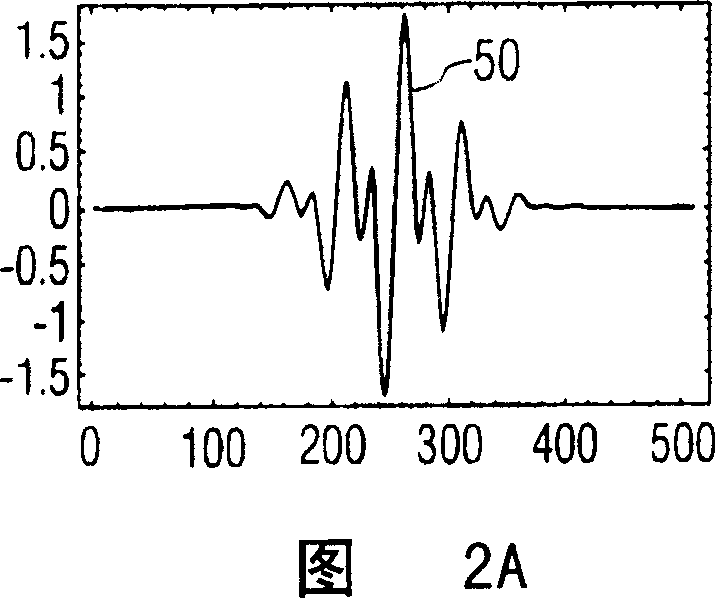
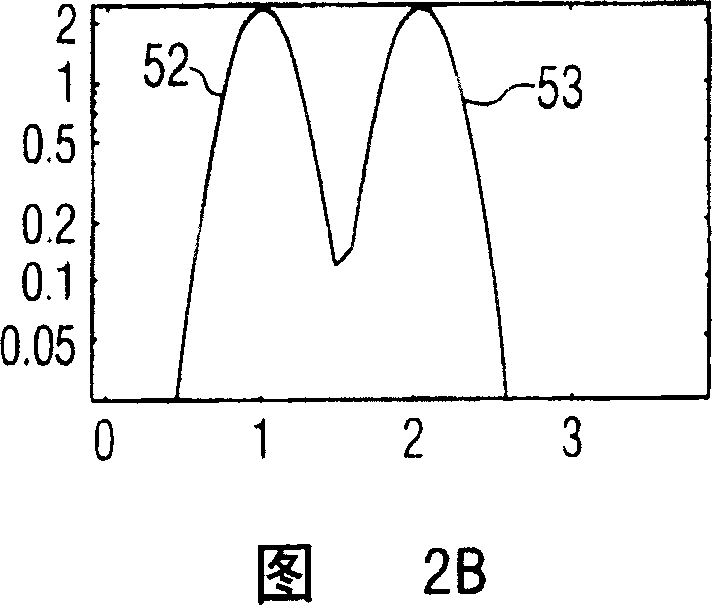
[0013] Referring first to Figure 1, there is shown an ultrasonic diagnostic imaging system constructed in accordance with the principles of the present invention. The ultrasound system of FIG. 1 utilizes a transmitter 16 that transmits a multi-frequency beam for non-linear generation of a difference frequency signal within an object to be imaged. The transmitter is coupled to elements of the array transducer 12 of the scan head 10 through a transmit / receive switch 14 . The transmitter responds to a number of control parameters that determine the characteristics of the transmit beam, as shown. Controlling the two main frequencies f of the multi-frequency beam 1 and f 2 , the two frequencies determine the difference (f 1 -f 2 ) The frequency at which the frequency component is located. Also controlled are the amplitudes or intensities a and b of the two transmit frequency components such that the transmit beam has (bsin(2πf 1 t)+asin(2πf 2 t)) form. However, as a differe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com