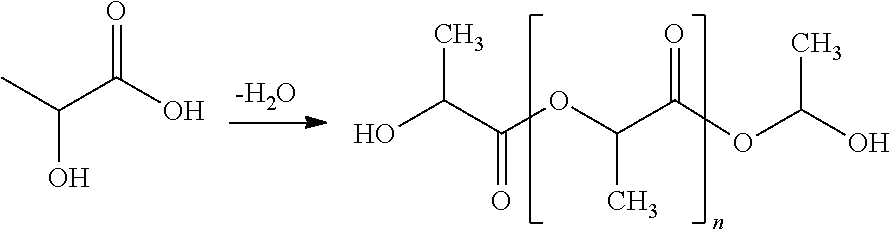
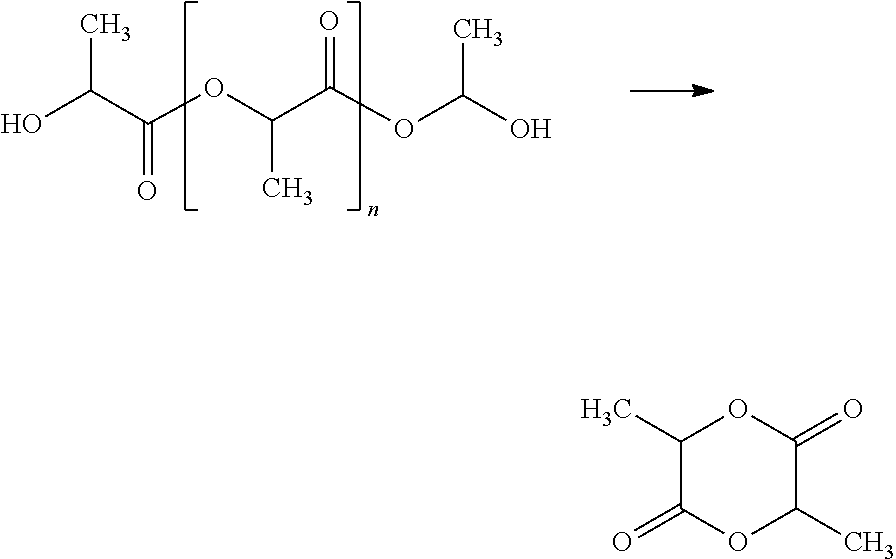
Method for synthesizing lactide by means of catalysis of lactid acid
a technology of lactid acid and catalysis method, which is applied in the field of biodegradable polymers, can solve the problems of reducing the efficiency of synthesis and separation, and reducing the production yield of lactide (70%), so as to improve the catalytic efficiency and the synthesis efficiency. , the effect of increasing the surface area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0030]1. Raw Material
[0031]In this example, commercial lactic acid (86%, 50 ml per group) supplied by Sigma is used as a raw material.
[0032]2. Catalyst
[0033]The catalyst used in each example is shown in Table 1. In Example 1, a group without a catalyst is set as a control group. The addition amounts of tin(II) 2-ethylhexanoate (also known as stannous octoate) in Examples 2 and 3 are respectively 0.3 wt % and 0.6 wt % of the weight of the raw material. 0.3 wt % and 0.6 wt % of a zinc oxide nanoparticle (30-40 nm) aqueous dispersion (20 wt %, US Research Nanomaterials) are respectively used as catalysts in Examples 4 and 5.
[0034]All chemicals are used directly without pretreatment.
[0035]
TABLE 1Catalysts used in Examples 1-5Example No.CatalystCatalyst amount A (wt %)1None—2Tin(II) 2-ethylhexanoate0.330.64zinc oxide nanoparticle0.3aqueous dispersion5(30-40 nm, 20 wt %)0.6
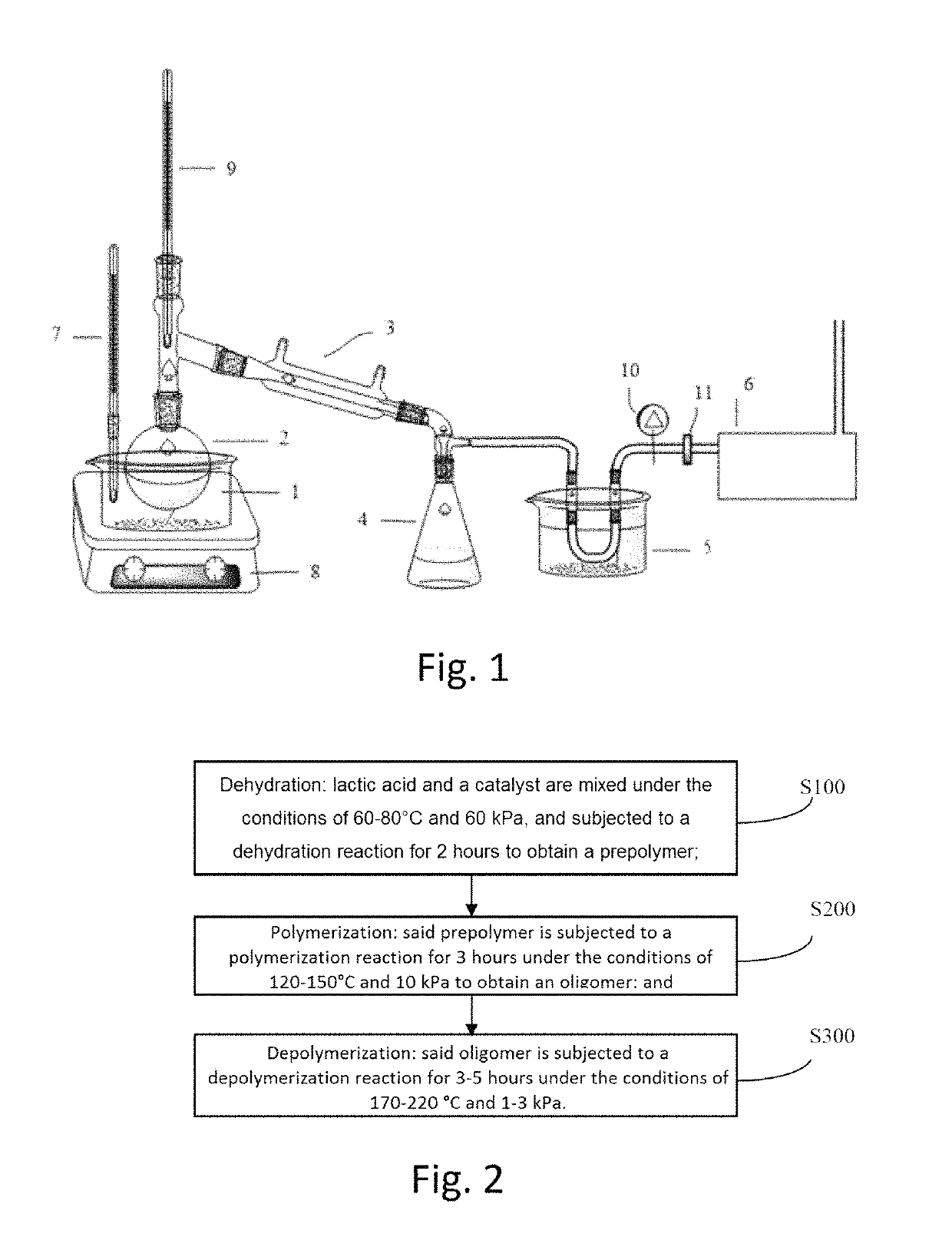
[0036]3. Reaction Process
[0037]FIG. 2 shows a process flow chart of the process for the catalytic synthesis lactide f...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com