Well sampling system incorporating corrugated and slotted injection system and method of use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
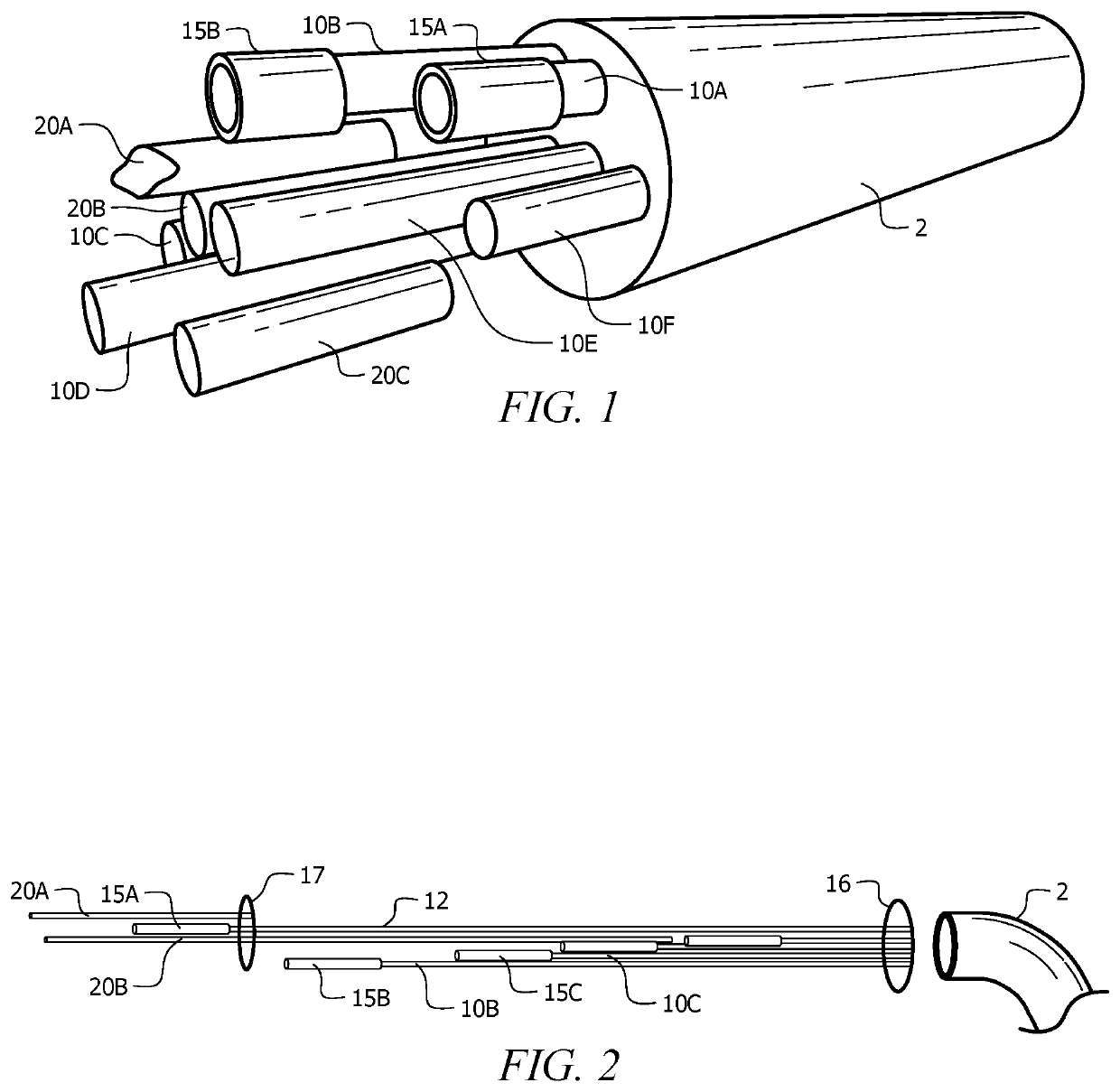
[0048]Sampling system 1 comprises a plurality of sampling well 10, designated 10A and 10B, with each sampling well terminating in a sampling mesh 15, such as sampling mesh 15A on a first end of sampling well 10A, sampling mesh 15B on a first end of sampling well 10B, and sampling mesh 15C on a first end of sampling well 10C. The sampling mesh covers a first end of the sampling well, designed to collect material from a matrix for sampling, and was formed of a corrugated and slotted sampling system, as described in U.S. application Ser. No. 15 / 066,811. Briefly, a corrugated conduit with a sampling channel formed from the removal of corrugation ribs was inserted over the sampling end of a sample well tube. The corrugated conduit was capped, and covered in a sieve. A grout spacer was disposed between sampling mesh 15A and sampling mesh 15B, preventing bleed over of analytes between the two sampling regions.
[0049]In preferred embodiments, sampling system 1 comprises a large number of sam...
example 2
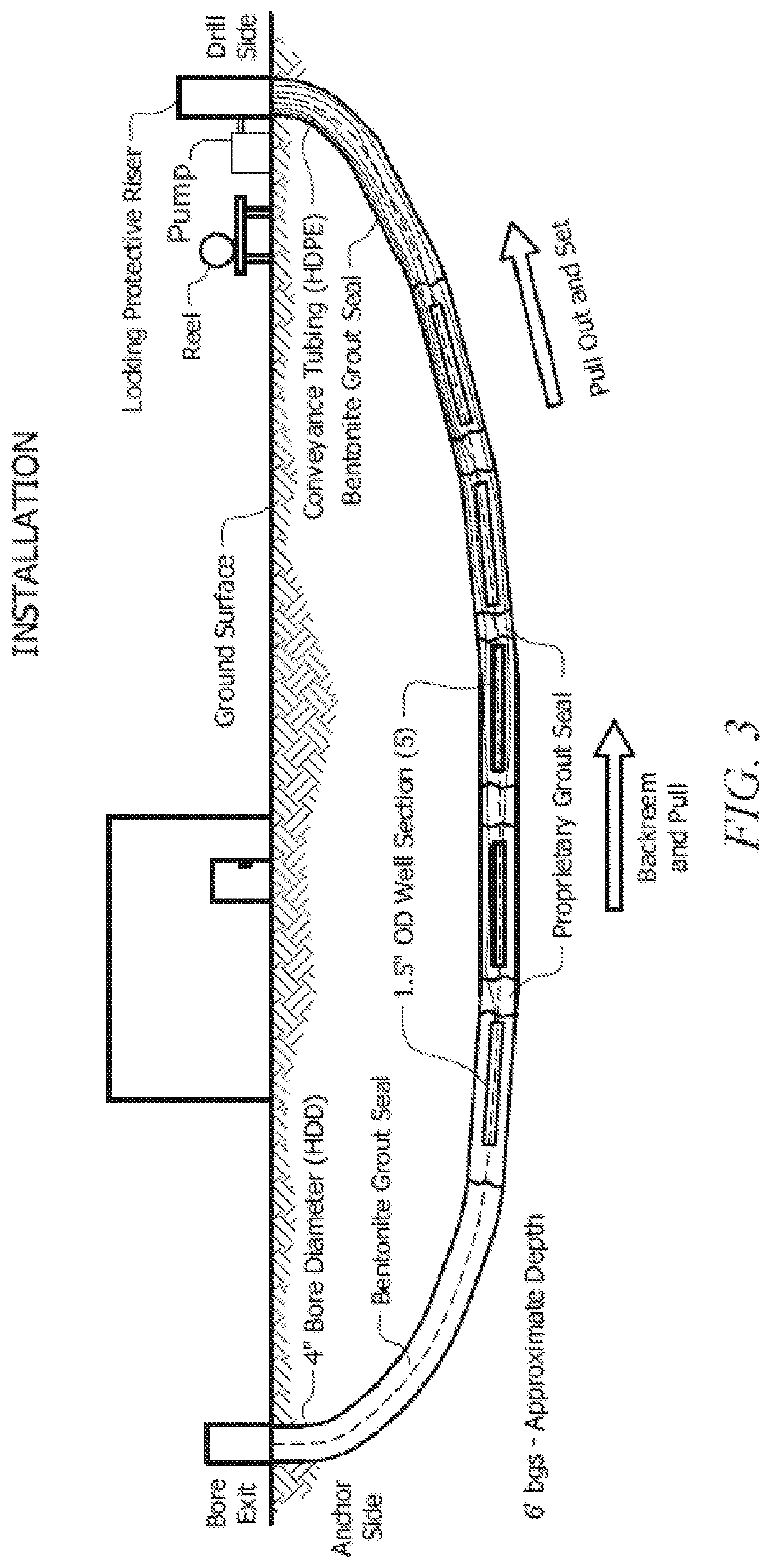
[0050]Sampling system 1 was prepared by inserting a sampling mesh 15, formed of tubular mesh or corrugated filter as described in Example 1 with a 1.25-inch outer diameter, on a first end of a high density polypropylene tubing having a 0.5-inch OD and ⅜-inch ID. The tubes form a channel for sampling wells 10. This process was repeated with tubing of various lengths, such as each tube differing by 10 feet. The plurality of tubes were aligned with the second end of each tube aligned with the other tubes, as seen in FIG. 2. The longest tube was designated the anchor sampling well 12. The remaining tubes were tacked to anchor sampling well 12 at sample well tacking 16, forming a sampling well bundle. Methods of tacking the sampling wells to the anchor sampling well would be evident to one of skill in the art upon review of this disclosure. Non-limiting examples include adhesive tape, a pull line, pull ties, mill tape, liquid adhesives, screws, binding straps, or rope / twine.
[0051]At leas...
example 3
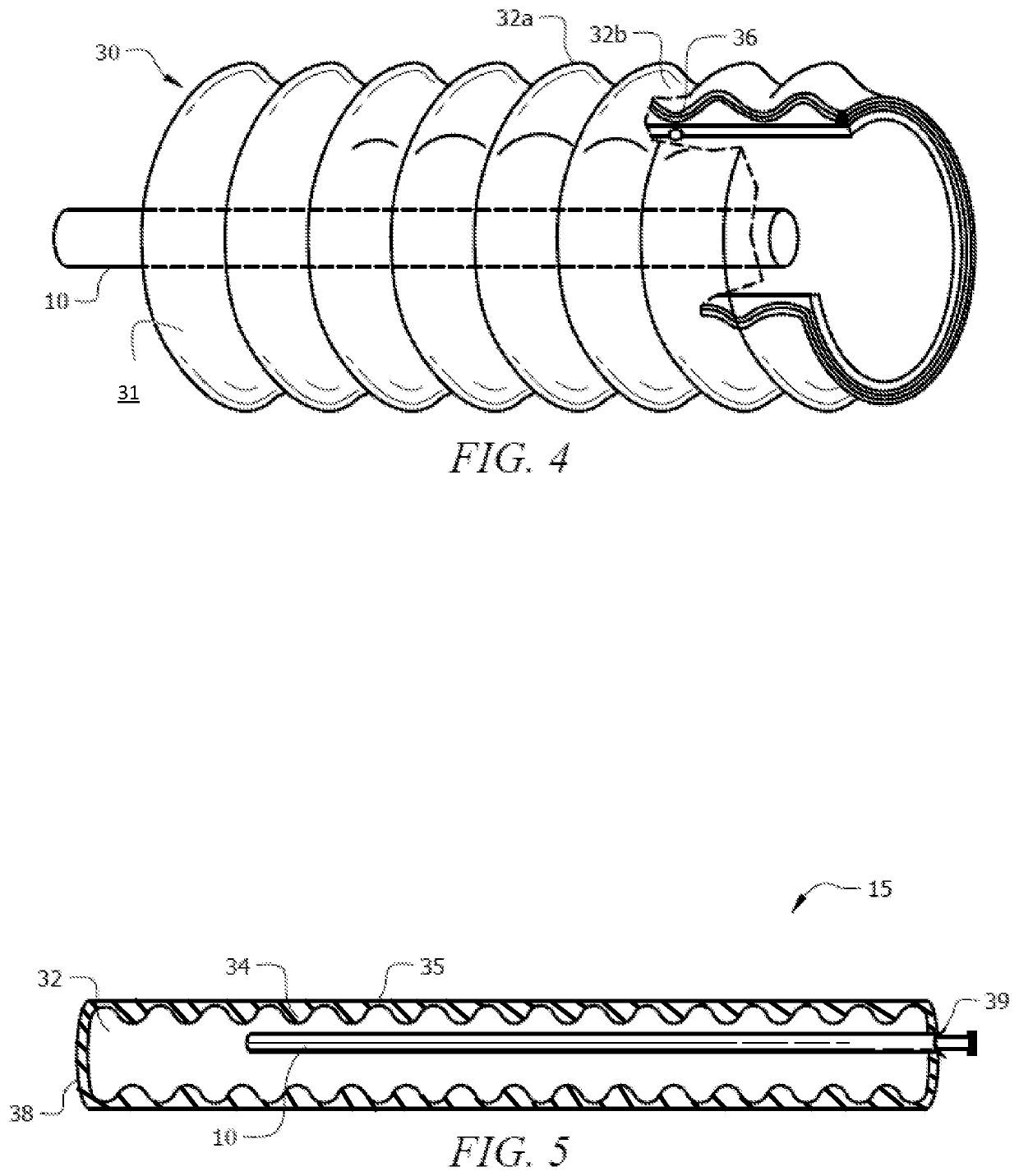
[0061]Sampling mesh 15 was optionally formed of corrugated conduit 30, which comprises a plurality of corrugated ridges formed of trough 34 and peak 35 disposed perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of corrugated conduit 30, as seen in FIG. 4. The corrugated conduit was formed of low density polyethylene (LDPE) tubing. Sample well tubing 40 ran parallel to the longitudinal axis of corrugated conduit 30, and terminates in the interior of corrugated conduit 30. Sampling channel 36 was formed on outer surface 31 of corrugated conduit 30 from the partial removal of the corrugated conduit, i.e. external rib 32b, while retaining the remainder of the corrugated conduit, i.e. internal rib 32a. As an example, a circular saw can be used to remove external rib 32b while retaining internal rib 32a, and allow the conduit's internal rib to collect liquids in the ground for matrix sampling or leak the fluid uniformly over the body length for remediation. The remaining portions of the external rib...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com