Method and system for compressing motion image information
a motion image and information technology, applied in the field of motion image information data compression methods and systems, can solve the problems of large amount of redundancy in the code, difficult to achieve both a high compression ratio and a high speed in the predictive compression coding of image data or audio data, and limited temporal change, so as to reduce the redundancy of information and reduce the redundant information between frames
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
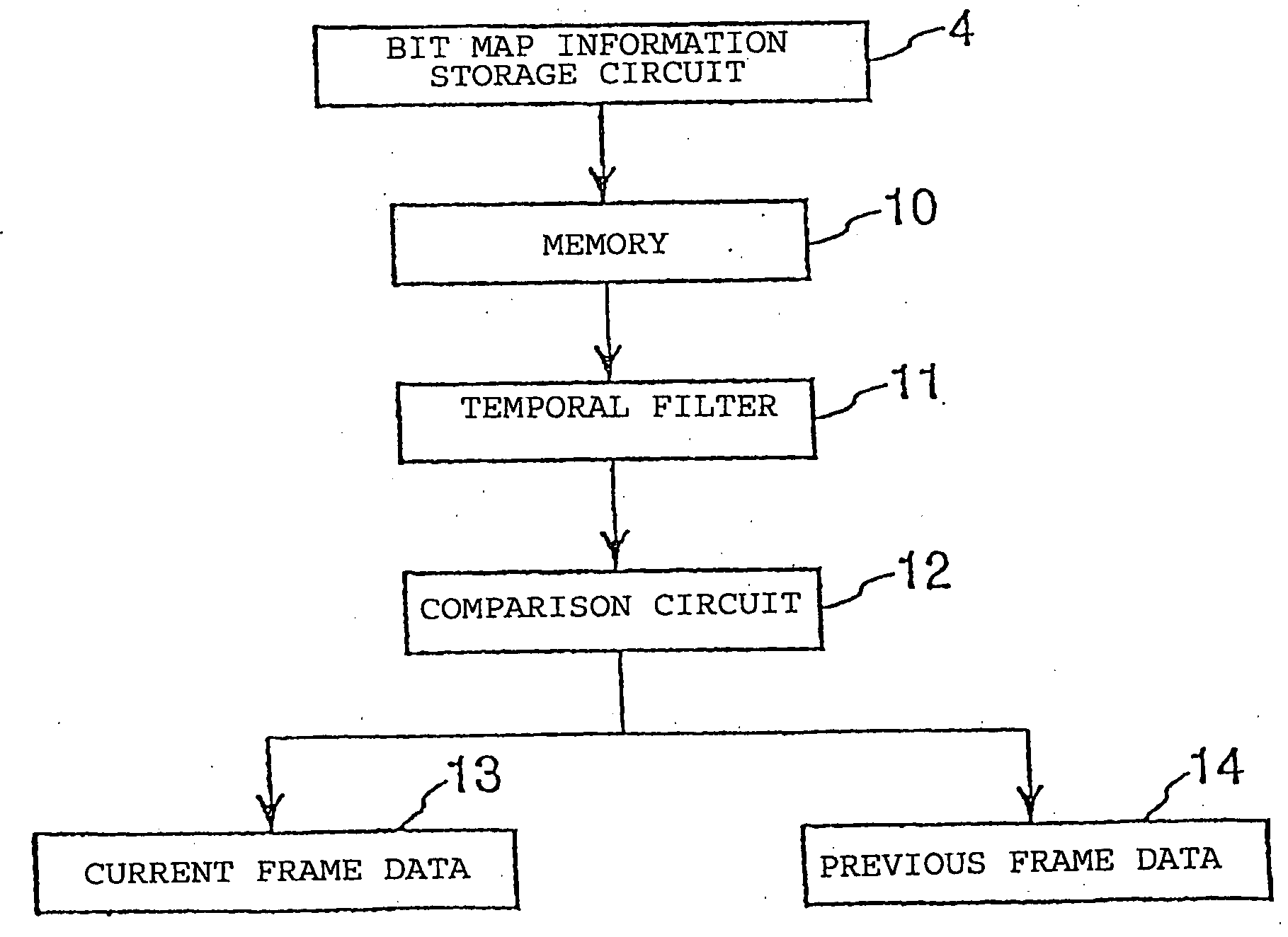
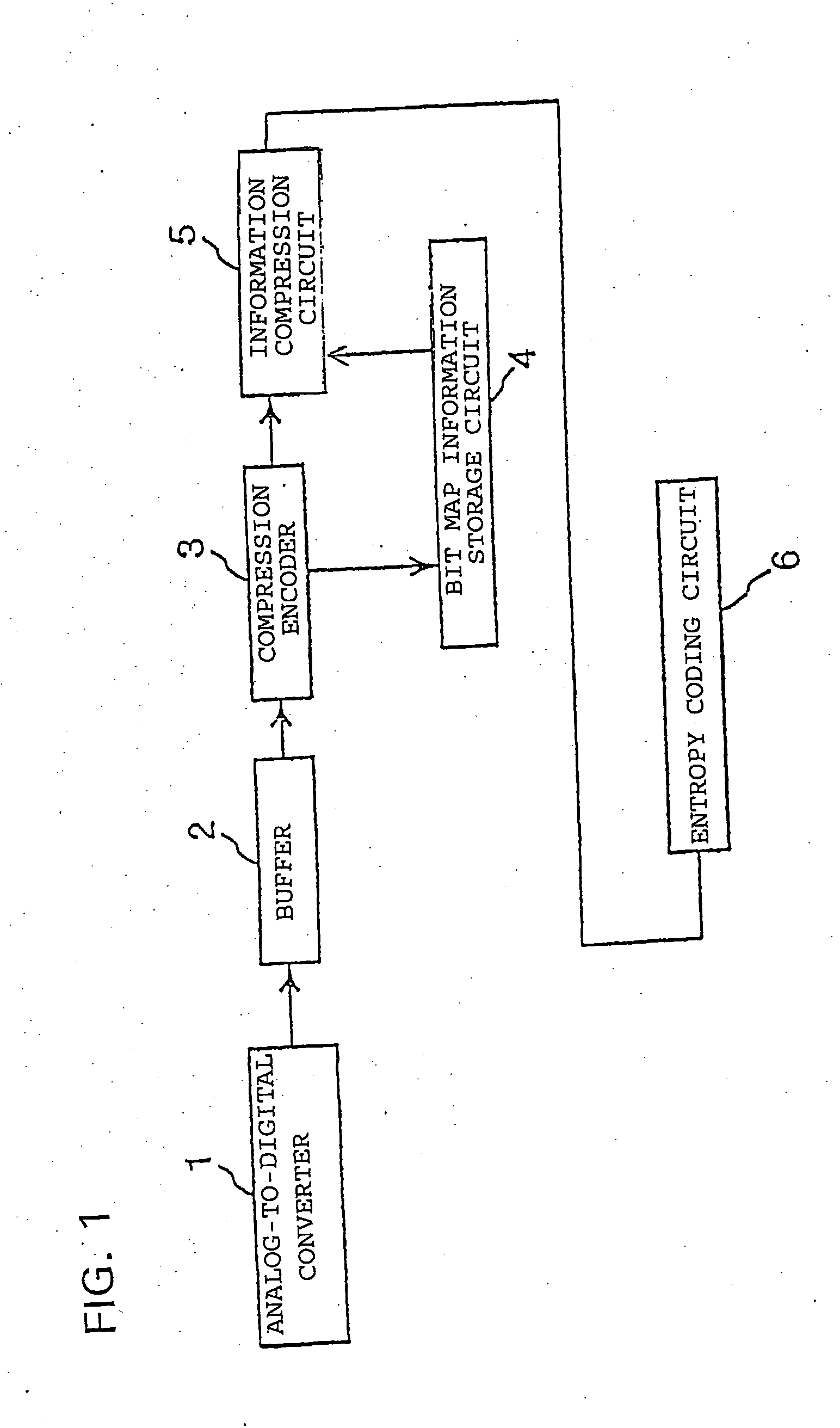
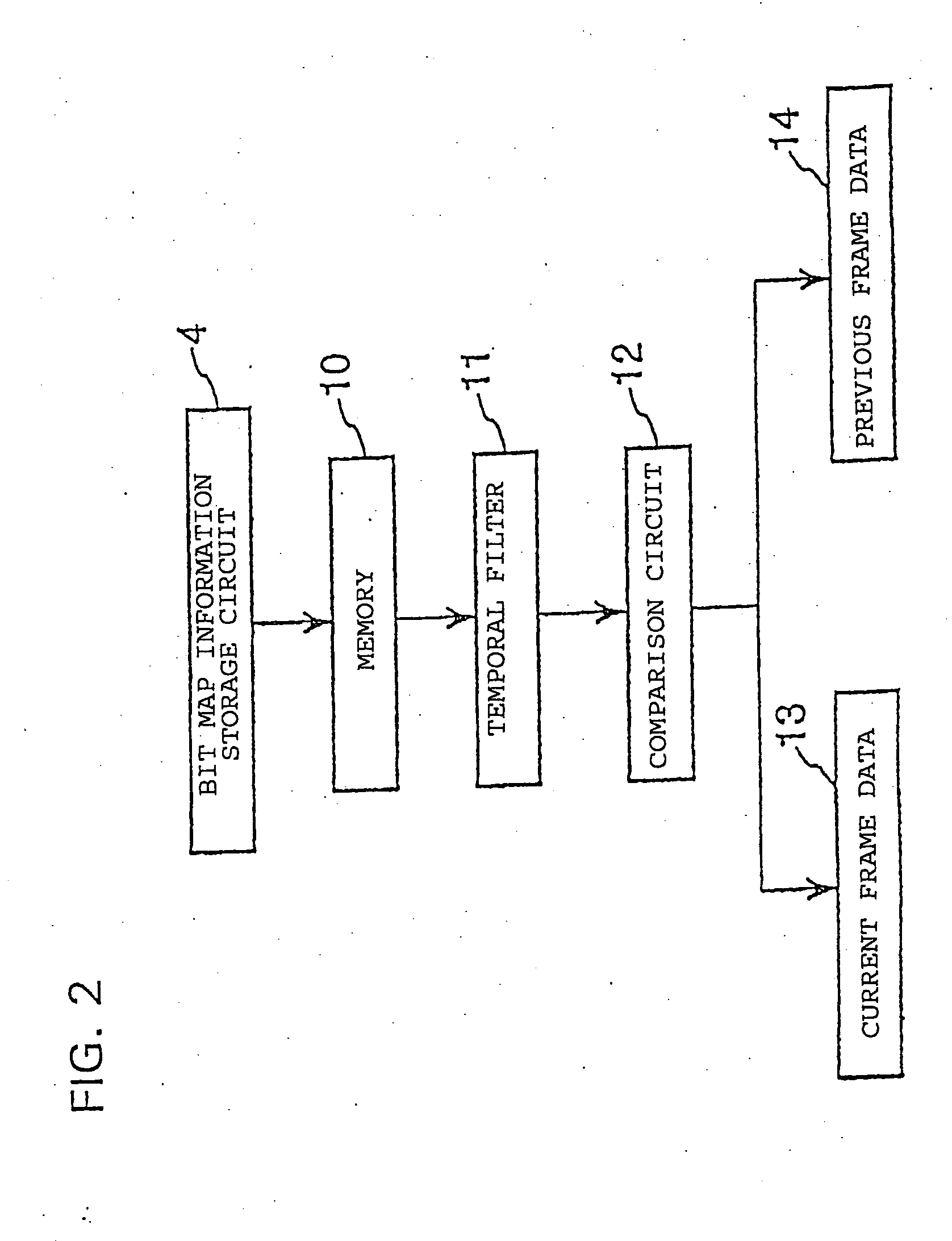
[0042] The present invention is described in further detail below with reference to an embodiment in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. FIG. 1 is a block diagram schematically illustrating a process of compressing motion image information. A composite analog signal output from a device such as a video cameral, a disk player, or a video cassette player, according to the NTSC standard, is input to an analog-to-digital converter 1. The analog-to-digital converter 1 converts the applied analog signal to a digital signal representing one line of a video frame. The resultant digital signal is stored in a buffer 2. Although in the technique shown in FIG. 1 an analog signal output from the device according to the NTSC standard is converted by the analog-to-digital converter 1 into a digital signal and stored in the buffer 2, the signal to be compressed according to the present invention is not limited to such a signal. That is, the technique according to the present invention can b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com