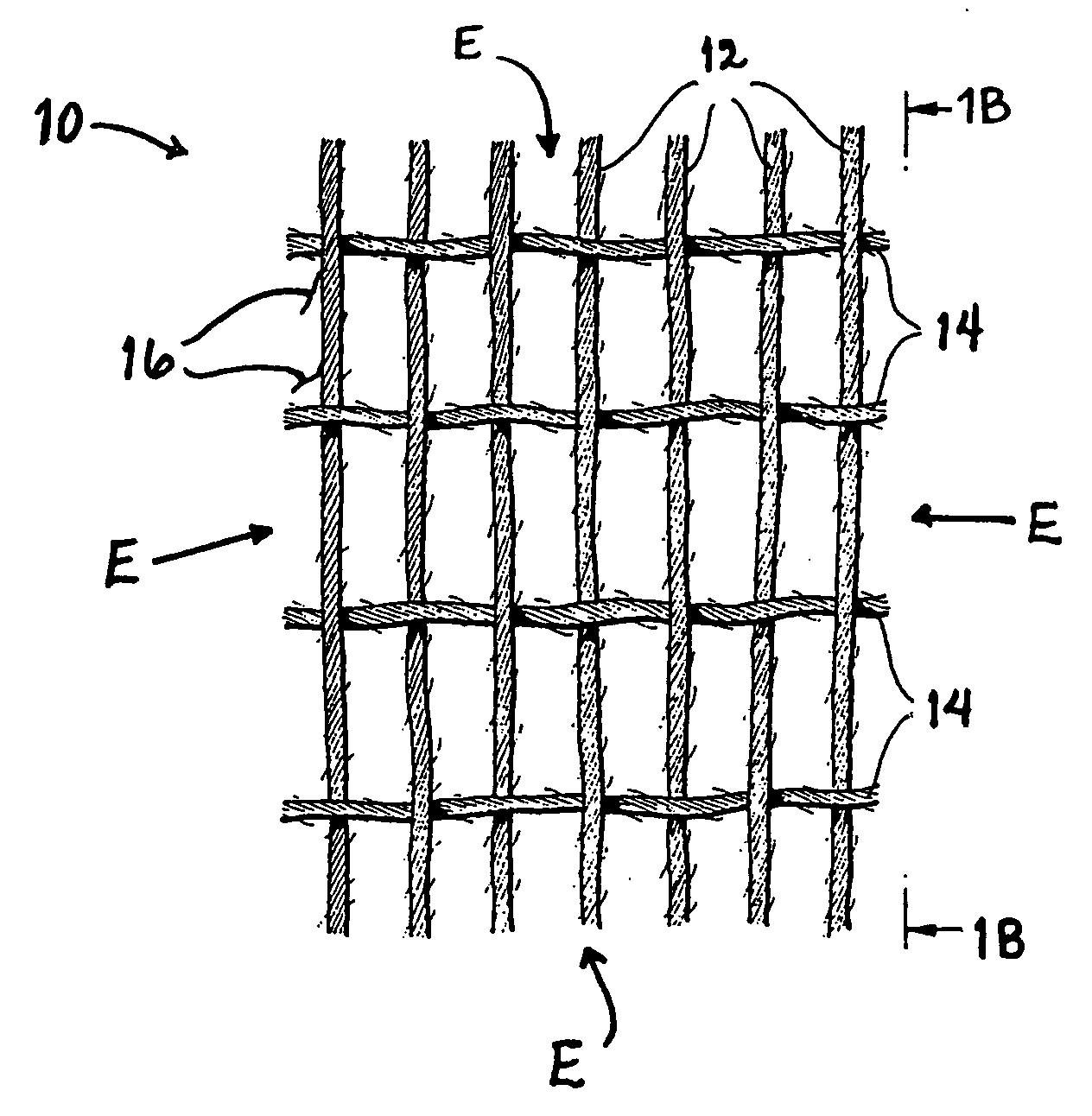
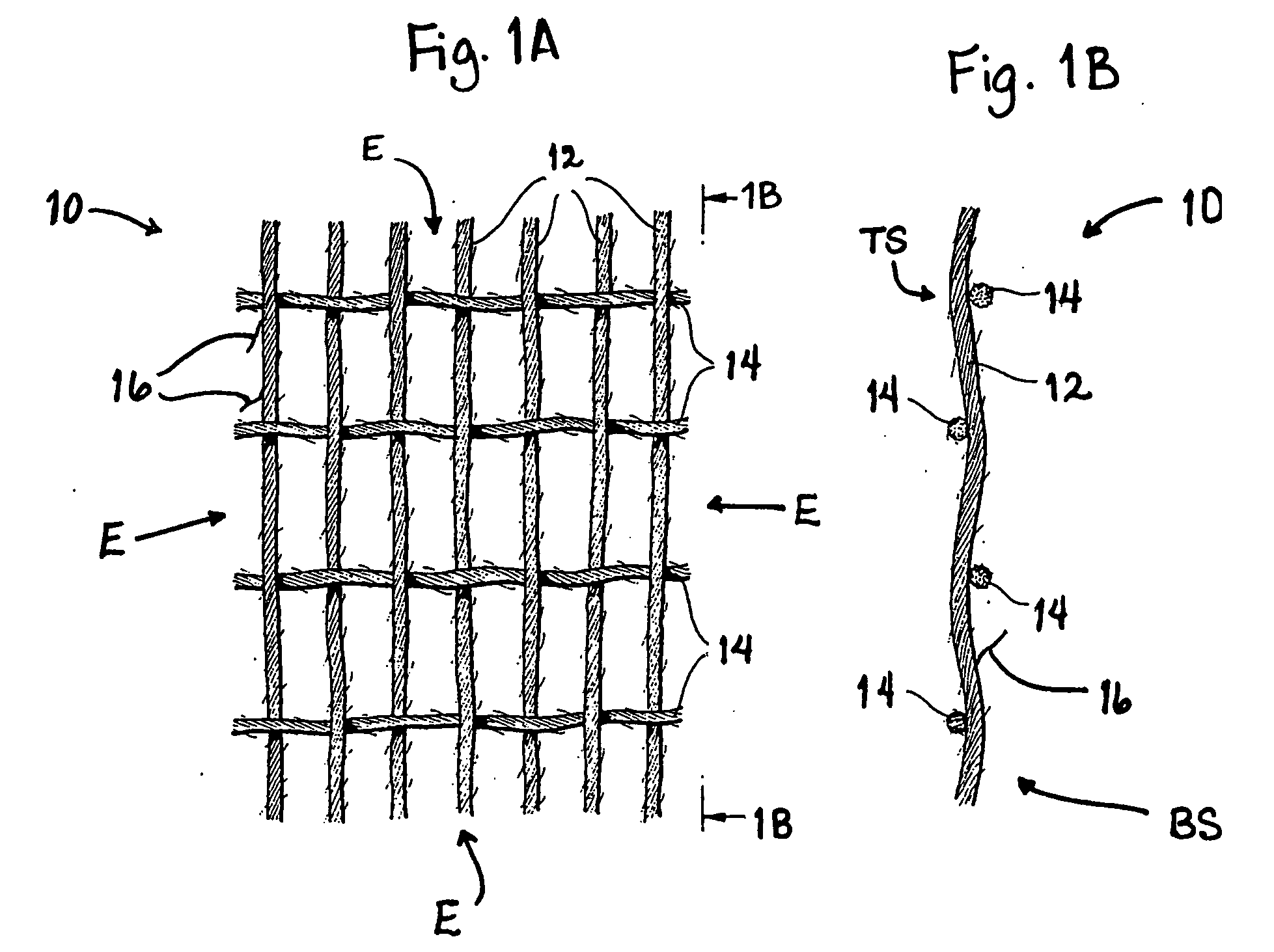
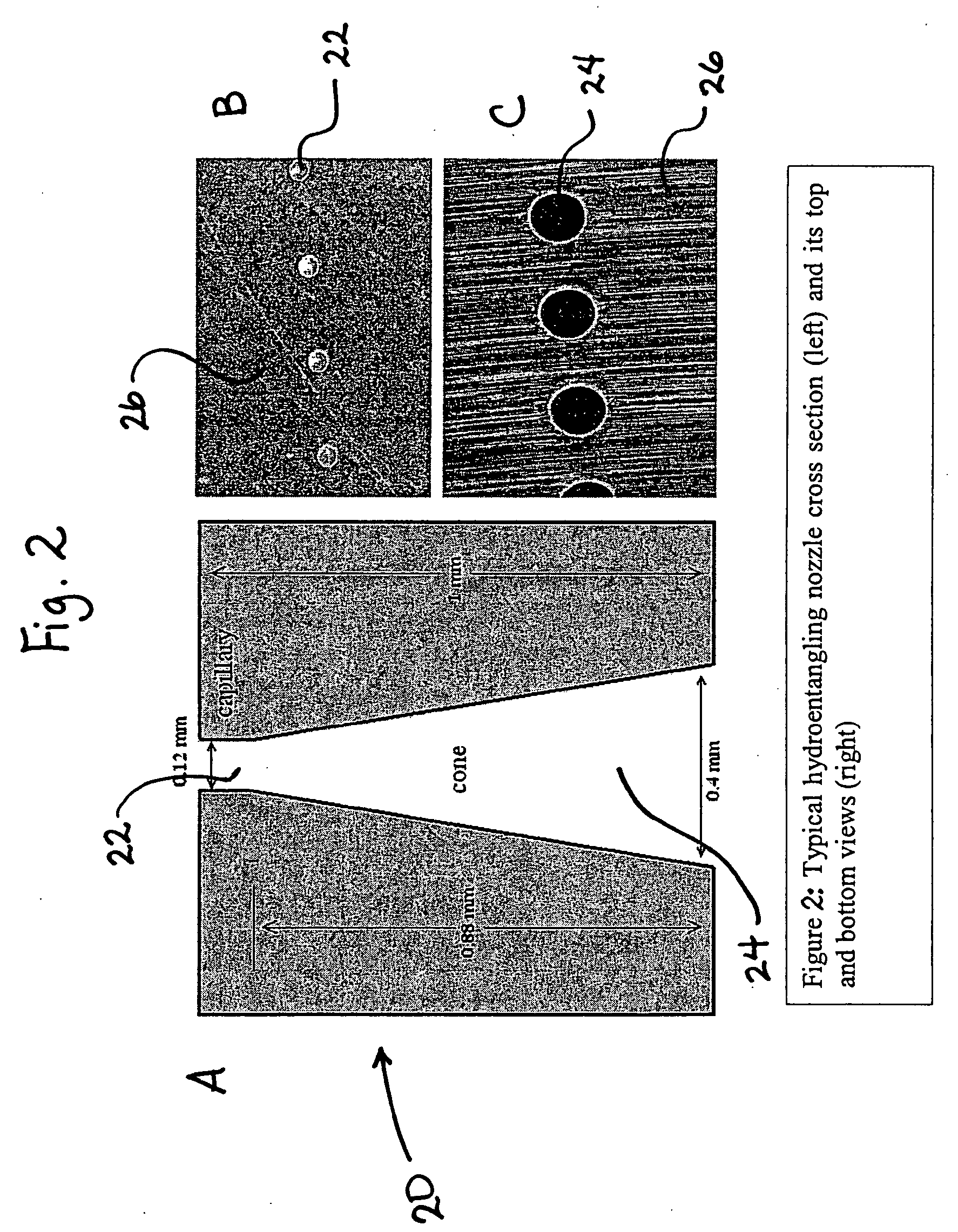
Physical and mechanical properties of fabrics by hydroentangling
a technology of hydroentanglement and physical and mechanical properties, applied in the field of fabrics having antipilling properties, can solve the problems of lowering the commercial value of fabrics, and achieve the effect of reducing the surface pilling tendency and improving the abrasion resistance of pillable fabrics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
Test Methods and Standards Reporting
[0040] Experiments were conducted on sample fabrics using hydroentanglement system 40 (see FIG. 3B) in order to determine the effect on mechanical properties (pilling, abrasion, etc.) and hand improvement of a finished textile utilizing the finishing concept of the present subject matter. Different settings of the hydroentanglement process were tested for physical properties with the results presented below.
[0041] The samples exposed to hydroentangling were subjected to the hydroentangling process as described hereinabove. The hydroentangling process system comprised one bank of three (3) water jet manifolds that enhanced the top surface (face) of the fabric and one bank of two (2) water jet manifolds that enhanced the bottom surface (back) of the fabric. The manifold pressures of the systems were as shown in Table 1.
TABLE 1Water Jet PressuresManifold PositionBeam Pressure (bar)Manifold 1 - Face pre-wet60Manifold 2 - Face entangling150Manifold...
example i
The Effect of the Tightness Factor
[0045] Referring to FIGS. 5-14, experiments were first run on a single type of fiber composition at various fiber tightness factors. Due to its vast usage in the garment industry, the sample textile fabric chosen consisted of a single jersey structure knitted on a circular knitting machine (gauge 18) incorporating yarns of 100% cotton (Ne 18 / 1 cp ringspun; 35 Tex). Three tightness factor fabrics 15 were used and various samples were either washed or not washed and were broken down into groups including no hydroentangling passes, one hydroentangling pass, and two hydroentangling passes. The samples were identified as shown in Table 2.
TABLE 2Descriptions of Sample SetSurface# ofSampleTightnessMassThicknessHydroentanglingIDfactor(g / m2)(mm)PassesWash / DryC16.0016.001830.5970NoNHC16.0016.001830.5971No1PC16.0016.001830.5971Yes1P WC16.6716.671880.6100NoNHC16.6716.671880.6101No1PC16.6716.671880.6101Yes1P WC17.5617.561990.6480NoNHC17.5617.561990.6481No1PC1...
example ii
The Effect of Fiber Composition and Hydroentangling Parameters
[0064] Referring now to FIGS. 15-17, experiments were additionally run on fabrics of various compositions and at varying hydroentangling processing parameters. The textile fabric structure comprised a single jersey construction with a 17.5 tightness factor. The fabric compositions were formed as shown in Table 4 and the samples and hydroentangling parameters (for those samples that were hydroentangled) were identified as shown in Table 5.
TABLE 4Fabric CompositionsFiberTightness factorSurface Mass(g / m2)100% cotton17.522950 / 50 Cotton / polyester17.5216100% Polyester17.5199
[0065]
TABLE 5Descriptions of Sample Set and Hydroentangling ParametersBeltNumberSamplePressurePressurePressurePressurePressureBelt typespeedofID#1(bar)#2(bar)#3(bar)#4(bar)#5(bar)Mesh / inch(m / min)PassesFiber1a60150200150200100101Cotton1b60150200150200100102Cotton1c60150200150200100103Cotton2a60150200150200100101Co / Poly3a60150200150200100101Polyester4a60150...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com