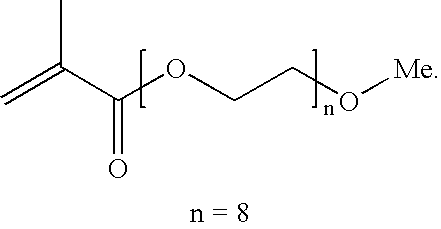
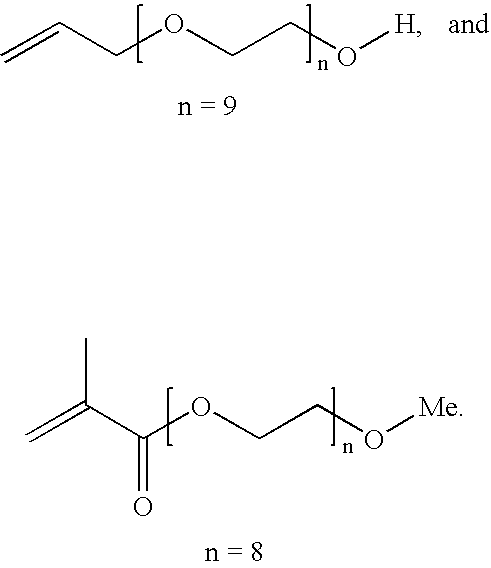
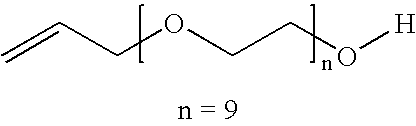Process for production of polymer dispersions containing an acetoacetate moiety
a technology of acetoacetate and polymer dispersions, which is applied in the field of production of polymer dispersions containing acetoacetate moiety, can solve the problems of increasing the difficulty of manufacturing and transportation of polymers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1 (
E1)
MMA / BA / AAEMA Copolymer Dispersion Prepared by Using a Base During Polymerization
[0081] The polymerization recipe and process is similar to that of CE1, except NaOH was added into the Monomer Emulsion I. The compositions of Emulsion I and II are given below. After the emulsion polymerization and the chemical stripping processes, the polymer dispersion has been cooled down to room temperature, 17.32 g of a 28% strength by weight aqueous ammonia and the same amount of the biocide as in CE1 were added. The product was essentially free of coagulum, had a pH of 9.2, solids content of 50.10% by weight and a Brookfield viscosity of 690 cps. The pH values during emulsion polymerizations were recorded. Table 1 summarizes pH values measured, final latex viscosity, and paint scrub resistance. The compositions of the monomer emulsions were as follows:
Monomer Emulsion I242.73 gwater 33.33 gemulsifier 1 15.63 gemulsifier 2 13.16 gemulsifier 3 10.00 gMAA 12.50 gIA 25.00 ga 50% strength by we...
example 2 (
E2)
MMA / BA / AAEMA Copolymer Dispersion Prepared by Using a Base during Polymerization
[0083] The polymerization recipe and process is similar to that of CE1, except NaOH was added into the Monomer Emulsion I. The compositions of Emulsion I and II are given below. After the emulsion polymerization and the chemical stripping processes, the polymer dispersion was cooled down to room temperature, 14.29 g of a 28% strength by weight aqueous ammonia and the same amount of the biocide as in CE1 were added. The product was essentially free of coagulum, had a pH of 9.29, solids content of 49.48% by weight and a Brookfield viscosity of 320 cps. The pH values during emulsion polymerizations were recorded. Table 1 summarizes pH values measured, final latex viscosity, and paint scrub resistance. The compositions of the monomer emulsions were as follows:
Monomer Emulsion I235.08 gwater 33.33 gemulsifier 1 15.63 gemulsifier 2 13.16 gemulsifier 3 10.00 gMAA 12.50 gIA 25.00 g50% strength by weight a...
example 3 (
E3)
MMA / BA / AAEMA Copolymer Dispersion Prepared by Using a Base During Polymerization
[0092] The polymerization recipe and process is similar to that of CE2, except NaOH was added into the Monomer Emulsion I. The compositions of Emulsion I and II are given below. After the emulsion polymerization and the chemical stripping processes, the polymer dispersion was cooled down to room temperature, 17.32 g of a 28% strength by weight aqueous ammonia and the same amount of the biocide as in CE2 were added. The product was essentially free of coagulum, had a pH of 9.33, solids content of 49.56% by weight, and a Brookfield viscosity of 980 cps. Some wet properties of the polymer dispersion and the scrub resistance of the semi-gloss paint based on the polymer dispersion are summarized in Table 2. The compositions of the monomer emulsions were as follows:
Monomer Emulsion I242.73 gwater 33.33 gemulsifier 1 15.63 gemulsifier 2 13.16 gemulsifier 3 10.00 gMAA 12.50 gIA 25.00 g50% strength by weig...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com