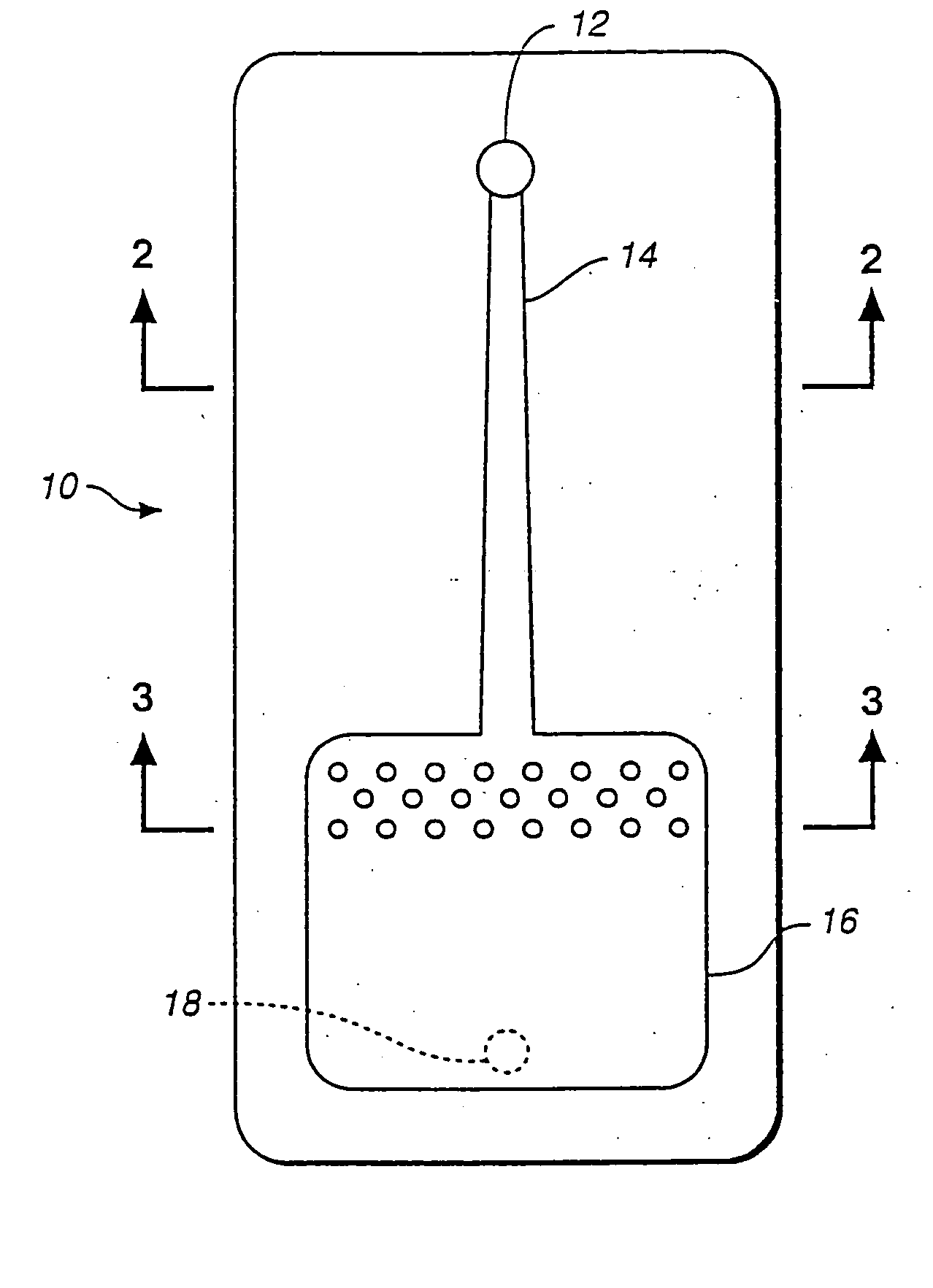
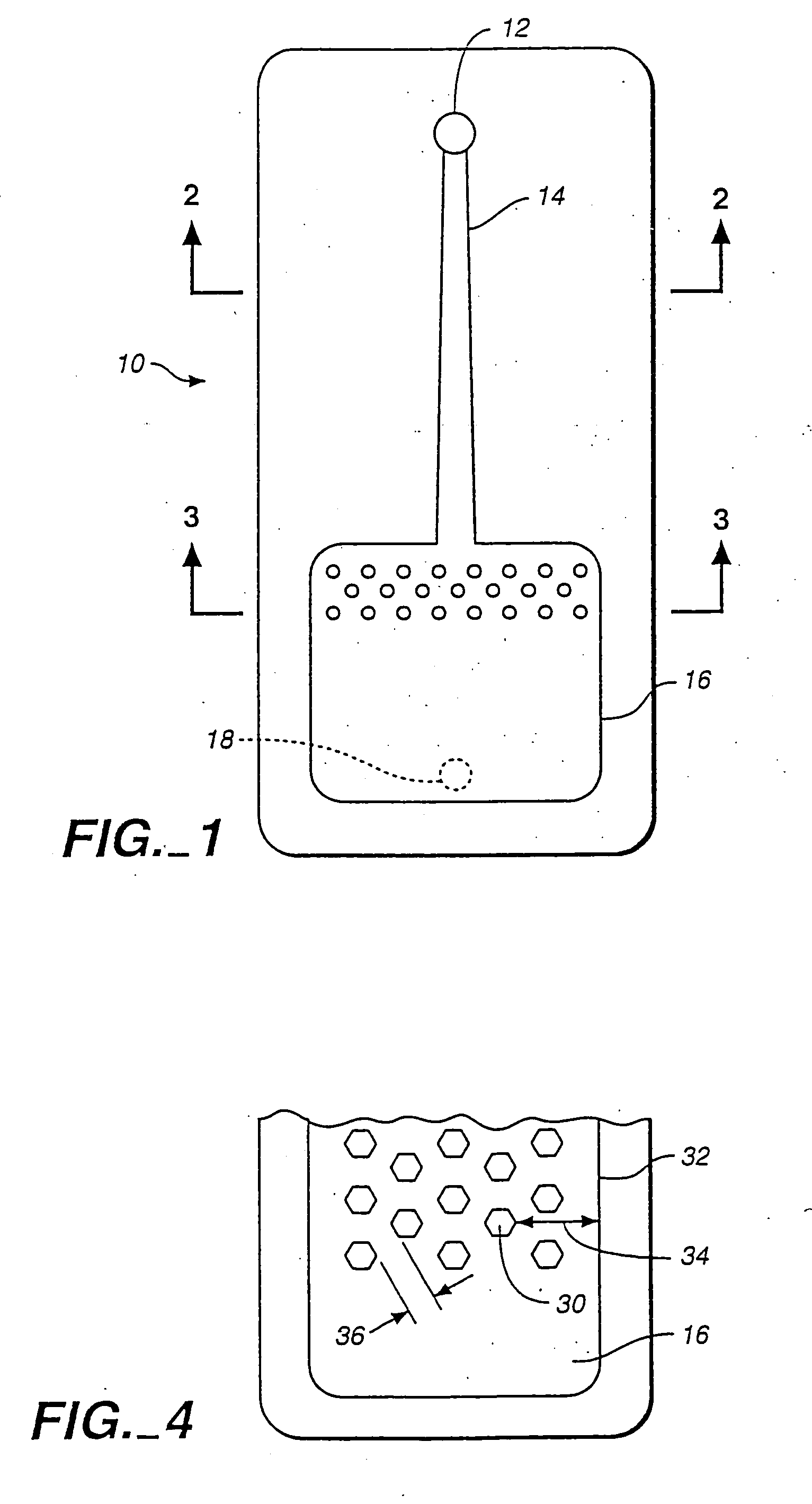
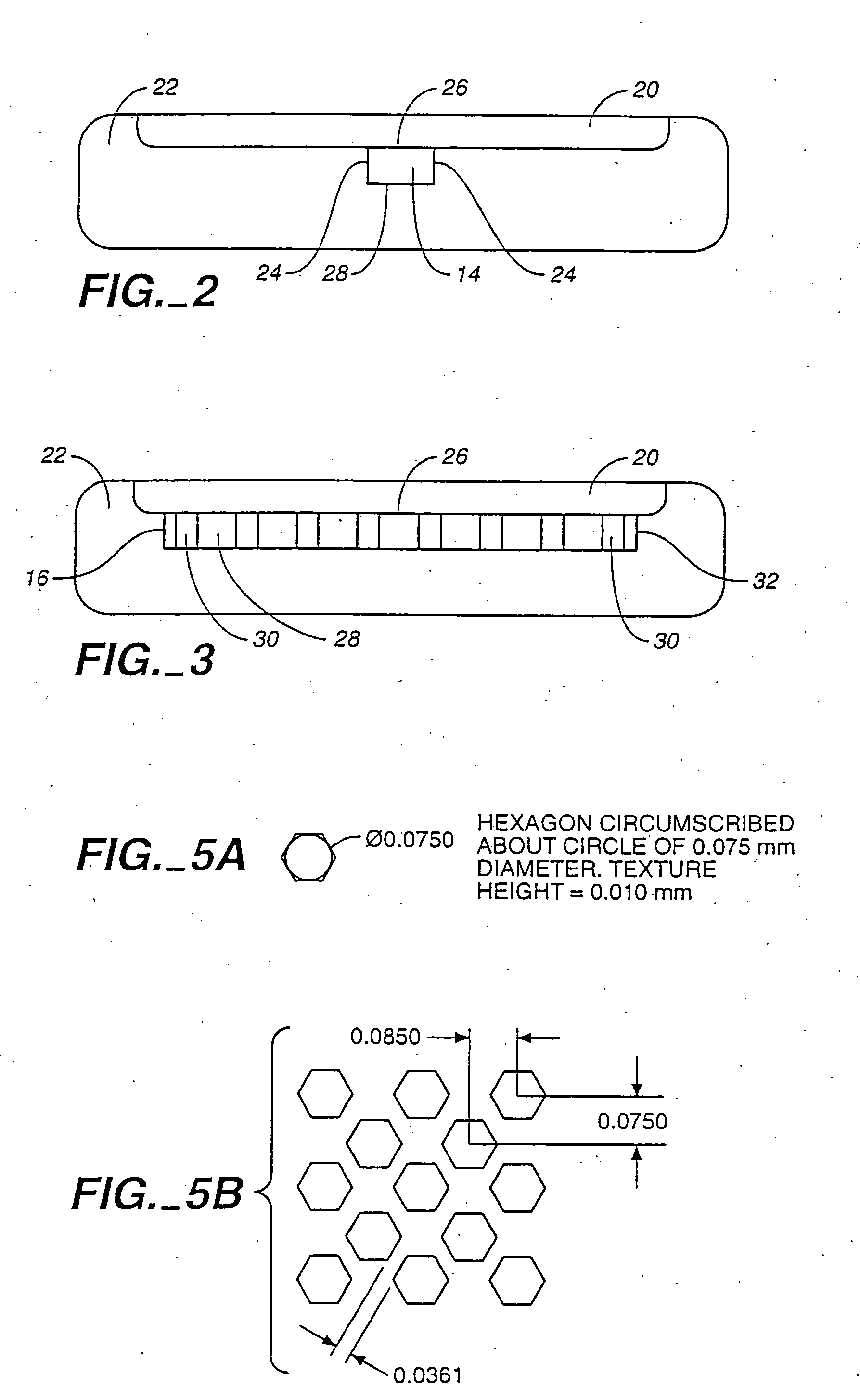
Devices comprising multiple capillary inducing surfaces
a capillary inducing surface and device technology, applied in the field of capillary, can solve the problems of inability to achieve the same level of access to assay equipment or reagents in non-laboratory settings, and inability to meet the requirements of laboratory or field settings. , to achieve the effect of enhancing reaction kinetics, easy manipulation, and increasing assay volum
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0069] In this embodiment, fluid was found to flow between a proximal region comprising an array of structures as depicted in FIG. 7B, and a distal region comprising an array of capillarity-inducing structures such as depicted in FIG. 8B. The effective capillarity of the proximal region was believed to be induced by the 12 micron distance from the inner surface of the lid to the upper surface of the base, i.e., capillary force induced in a “vertical” direction. The effective capillarity of the distal region was believed to be induced by the 10.2 micron distance between parallel walls of adjacent capillarity-inducing structures, i.e., capillary force induced in a “horizontal” direction.
[0070] The proximal region comprised a height of 12 microns from the inner surface of the lid to the upper surface of the base; the height of the distal region was 22 microns from the inner surface of the lid to the upper surface of the base. Accordingly, the distal region had a greater capacity than ...
example 2
[0071] In this embodiment, fluid was found to flow between a proximal region comprising an array of structures such as found in FIG. 6B, and a distal region comprising an array of capillarity-inducing structures such as depicted in FIG. 9B.
[0072] The effective capillarity of the proximal region was believed to be induced by the 12 micron distance from the inner surface of the lid to the upper surface of the base, i.e., capillary force induced in a “vertical” direction. The effective capillarity of the distal region was believed to be induced by the 12 micron distance between parallel walls of adjacent capillarity-inducing structures, i.e., capillary force induced in a “horizontal” direction.
[0073] The proximal region comprised a height of 12 microns from the inner surface of the lid to the upper surface of the base; the height of the distal region was 22 microns from the inner surface of the lid to the upper surface of the base. Accordingly, the distal region had a greater capacit...
example 3
[0074] In this embodiment, fluid was found to flow between a proximal region comprising an array of structures such as depicted in FIG. 5B, and a distal region comprising an array of capillarity-inducing structures such as depicted in FIG. 8B.
[0075] The effective capillarity of the proximal region was believed to be induced by the 12 micron distance from the inner surface of the lid to the upper surface of the base, i.e., capillary force induced in a “vertical” direction. The effective capillarity of the distal region was believed to be induced by the 10.2 micron distance between parallel walls of adjacent capillarity-inducing structures, i.e., capillary force induced in a “horizontal” direction.
[0076] In this embodiment, the height of the first distal region was 12 microns from the inner surface of the lid to the upper surface of the base; the height in the distal region was 22 microns from the inner surface of the lid to the upper surface of the base. Accordingly, the distal reg...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com