Method of amplifying nucleic acids, reagent kit for amplifying nucleic acids, method of detecting single nucleotide polymorphism, and reagent kit for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism
a technology of nucleic acids and reagents, applied in the field of amplifying nucleic acids, can solve the problems of significant amplification of byproducts, and achieve the effect of not amplifying or inhibiting the amplification of the desired nucleic acid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
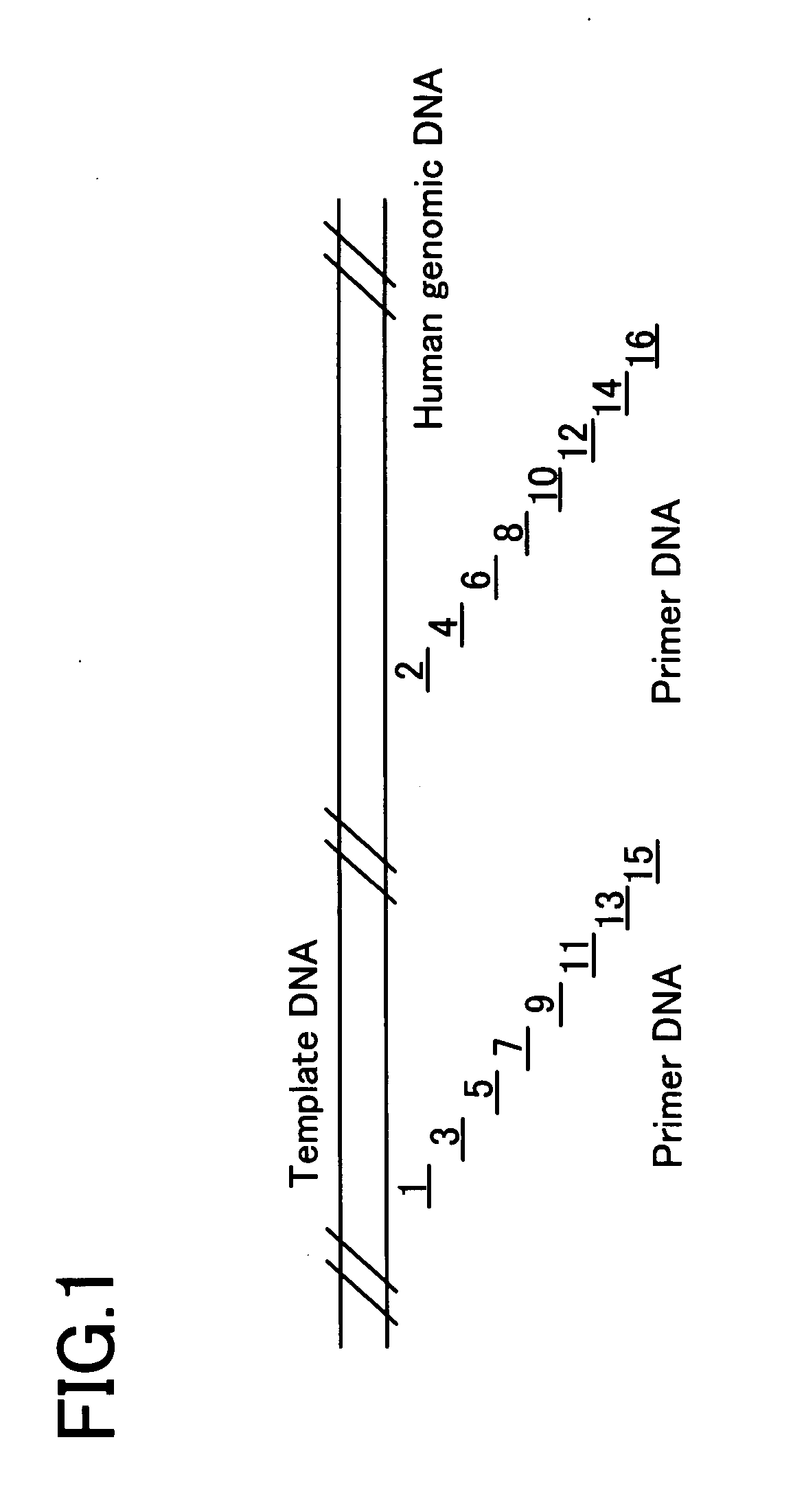
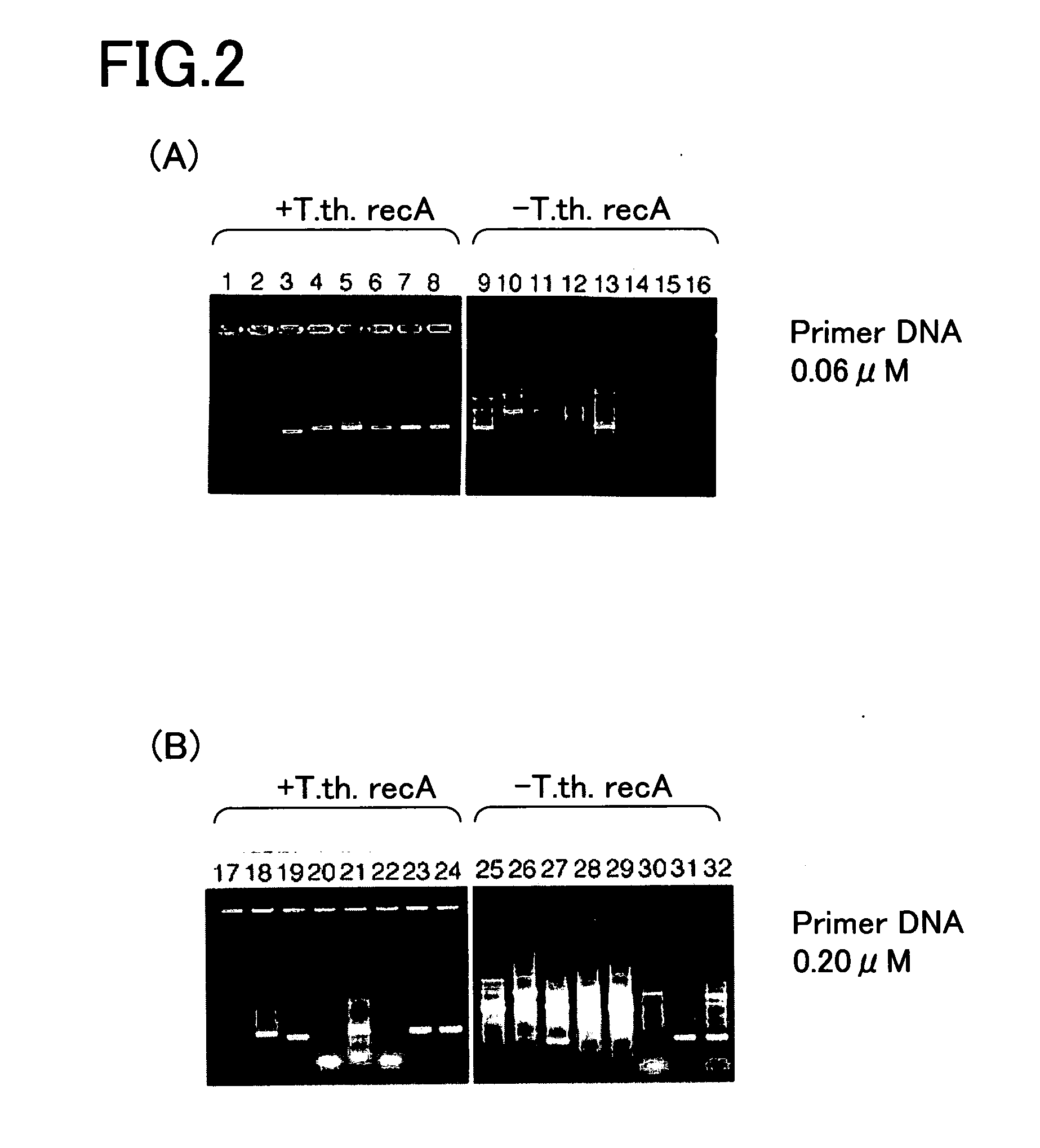
[0133] A human genome DNA (Promega) was prepared as a template DNA as shown in FIG. 1. Further, 16 kinds of oligonucleotides (Oligonucleotides 1 to 16) were prepared as the primer DNAs. Each primer DNA was designed with reference to Homo sapiens PAC clone from RP5-852P6 from 7p11.2-p21, complete sequence (Genbank accession no.; AC006454). The Genbank accession no.; number refers to an access number of Gene Bank (the same in the following). Since each primer DNA has possibility of any primer design, each of the positions was shifted to design the primer DNA. Each primer DNA consists of a 20mer base sequence which is 100% complementary to the template DNA. Each primer DNA may be synthesized by a known method on the basis of the base sequence of the template DNA.
Oligonucleotide 1:5′-ggtgcactcc atcatgctta-3′Oligonucleotide 2:5′-catcagt cagaggggct cac-3′Oligonucleotide 3:5′-cccacatccc tggcaggaat-3′Oligonucleotide 4:5′-tgcaggt gtgggcctag ctg-3′Oligonucleotide 5:5′-tgtcctgggc cccagcagga-...
example 2
[0177] Next, Example 2 will be explained. Explanation of the parts which are similar to those of the Example 1 will be omitted or simplified.
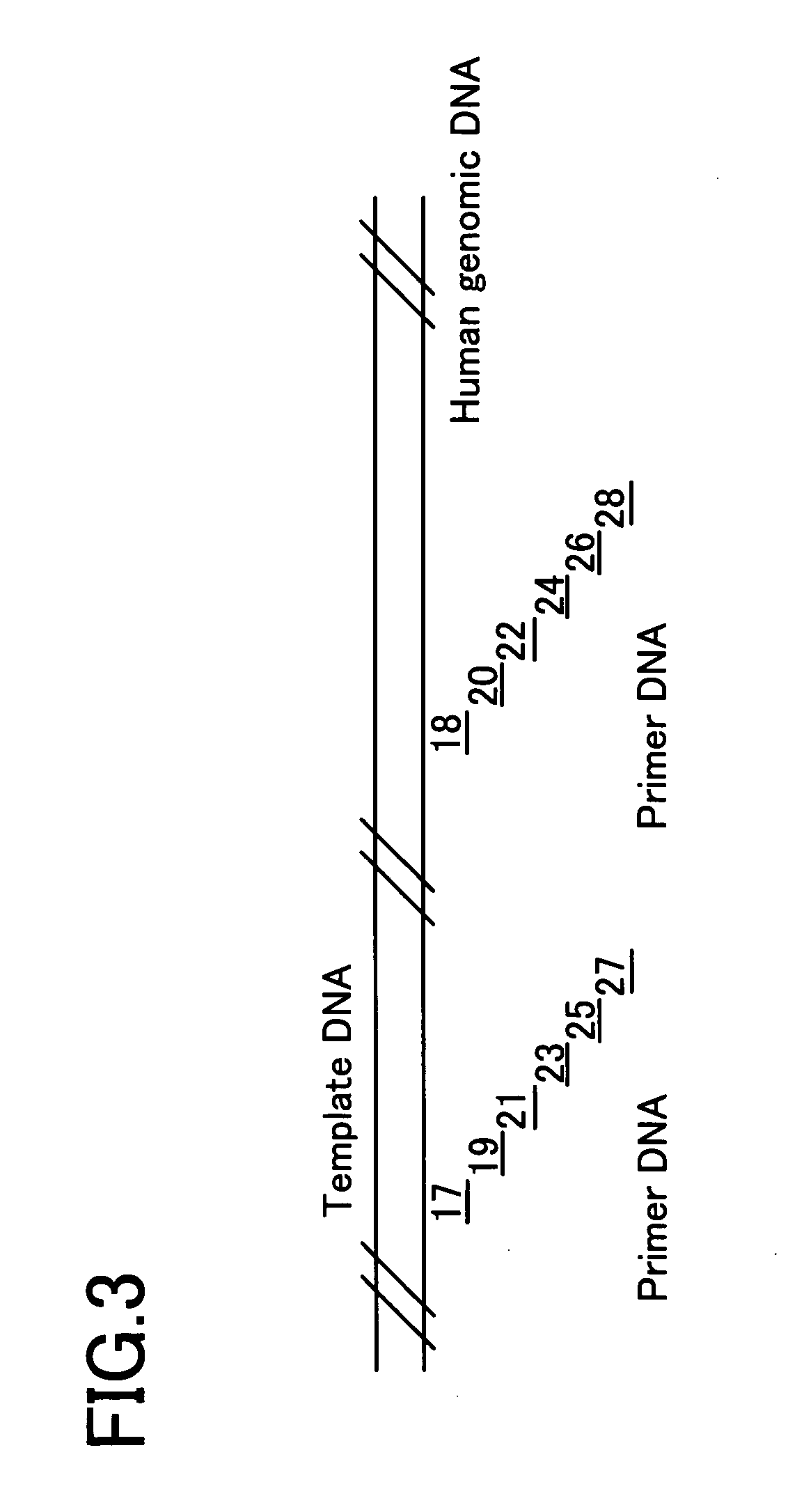
[0178] In this Example, as shown in FIG. 3, a human genome DNA was prepared as a template DNA, and 12 kinds of oligonucleotides (Oligonucleotides 17 to 28) were prepared as the primer DNAs. Each primer DNA was designed with reference to Homo sapiens BAC clone from RP11-16P10 from 7, complete sequence (Genbank accession no.; AC093734, AC011786). Since each primer DNA has possibility of any primer design, each position was shifted to design the primer DNA. Each primer DNA consists of a 20mer base sequence which is 100% complementary to the template DNA.
Oligonucleotide 17:5′-cgggtgc acacaaaggc tgg-3′Oligonucleotide 18:5′-tctctggcca ggtgcctggc-3′Oligonucleotide 19:5′-cgccccg acaaccctga ccc-3′Oligonucleotide 20:5′-cttgggaaga tcctgagact-3′Oligonucleotide 21:5′-tcggtaa acgctggctc ccg-3′Oligonucleotide 22:5′-caaaacgccc cccaccgccc-3′Oligonucleotide 2...
example 3
[0196] Next, Example 3 will be explained. Explanation of the parts which are similar to those of each of the above-mentioned Examples will be omitted or simplified.
[0197] As shown in FIG. 5 and FIG. 6, a human genome DNA was prepared as a template DNA, and 8 kinds of oligonucleotides (Oligonucleotides 29 to 36) were prepared as the primer DNAs. Each primer DNA was designed with reference to the Human DNA sequence from clone RP5-1013A22 on chromosome 20 Contains the HNF4A (hepatic nuclear factor 4, alpha) gene, part of a novel gene encoding a protein similar to cellular retinaldehyde-binding protein, a RPL37A (ribosomal protein L37a) pseudogene, parts of 2 novel genes, ESTs, STSs and GSSs, complete sequence (Genbank accession no.; AL132772). Further, Oligonucleotide 31 and Oligonucleotide 32 were designed with reference to Homo sapiens 3q BAC RP11-529F4 (Roswell Park Cancer Institute Human BAC Library) complete sequence (Genbank accession no.; AC080007). Further, Oligonucleotide 33 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Secondary structure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com