Cranial orthosis for preventing positional plagiocephaly in infants
a positional plagiocephaly and cranial orthosis technology, applied in the field of cranial orthosis for preventing positional plagiocephaly in infants, can solve the problems of limited value of torque helmets, difficult to achieve “turn-over” repositioning treatment, and difficult to achieve consistently. , to achieve the effect of stabilizing the appliance, easy to be peeled off and removed, and good air circulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] The specification which follows describes a cranial orthosis intended for use by newborns and infants less than one year of age that will prevent the development of postural cranial deformities as a result of the child's sleeping on his or her back. Preferred embodiments of the invention will now be described with reference to various examples of how the invention can best be made and used. Like reference numerals are used throughout the description and several views of the drawing figures to indicate like or corresponding parts.
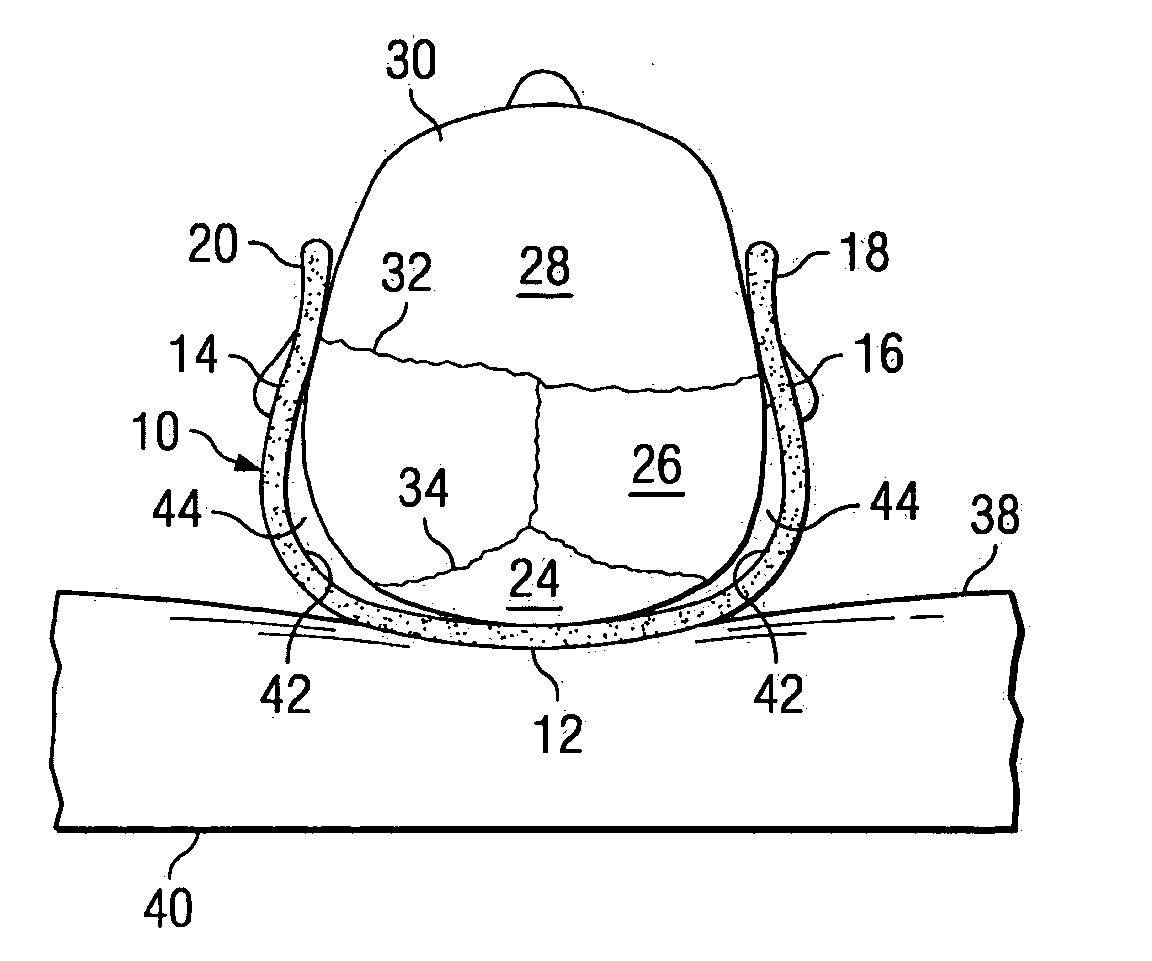
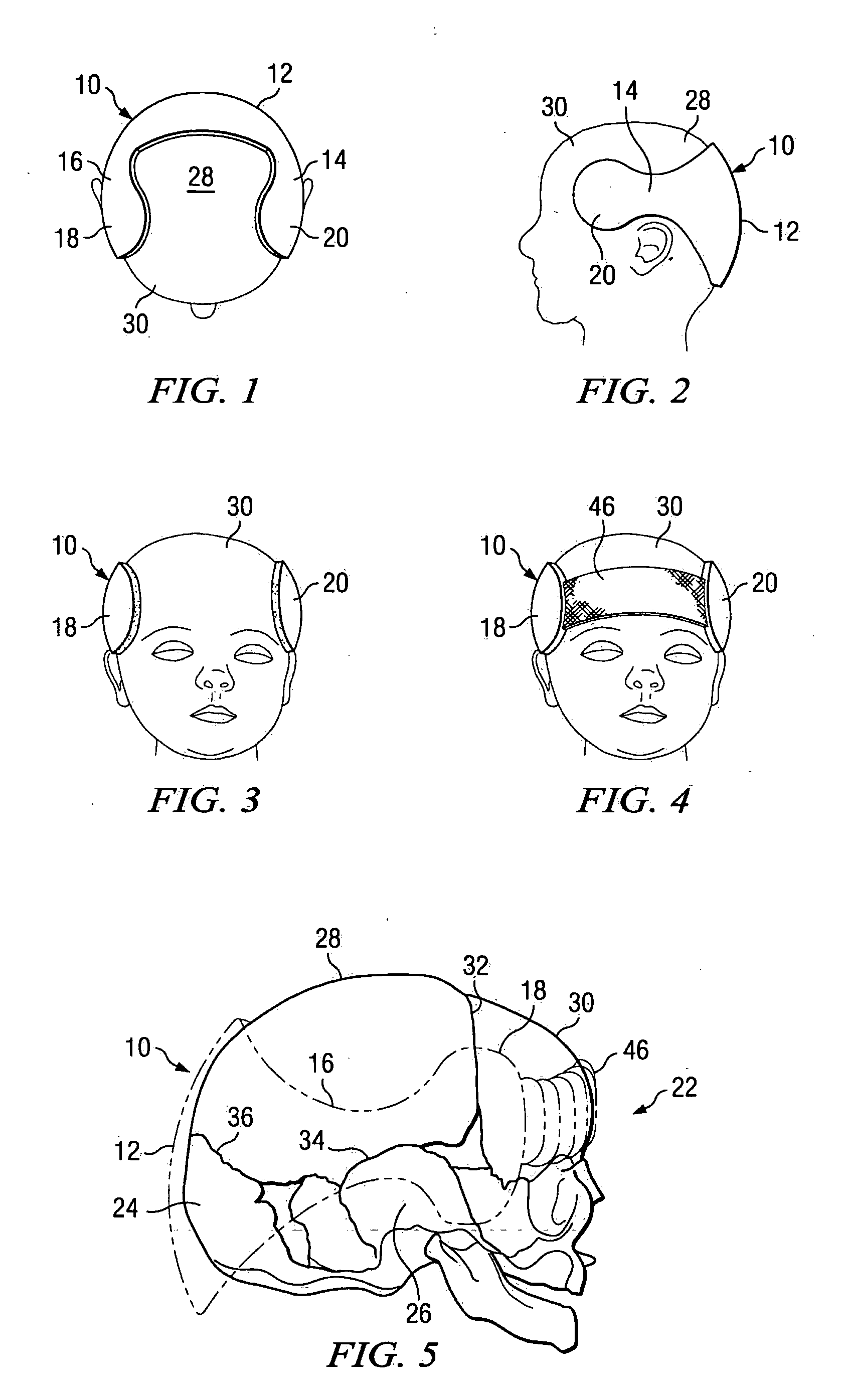
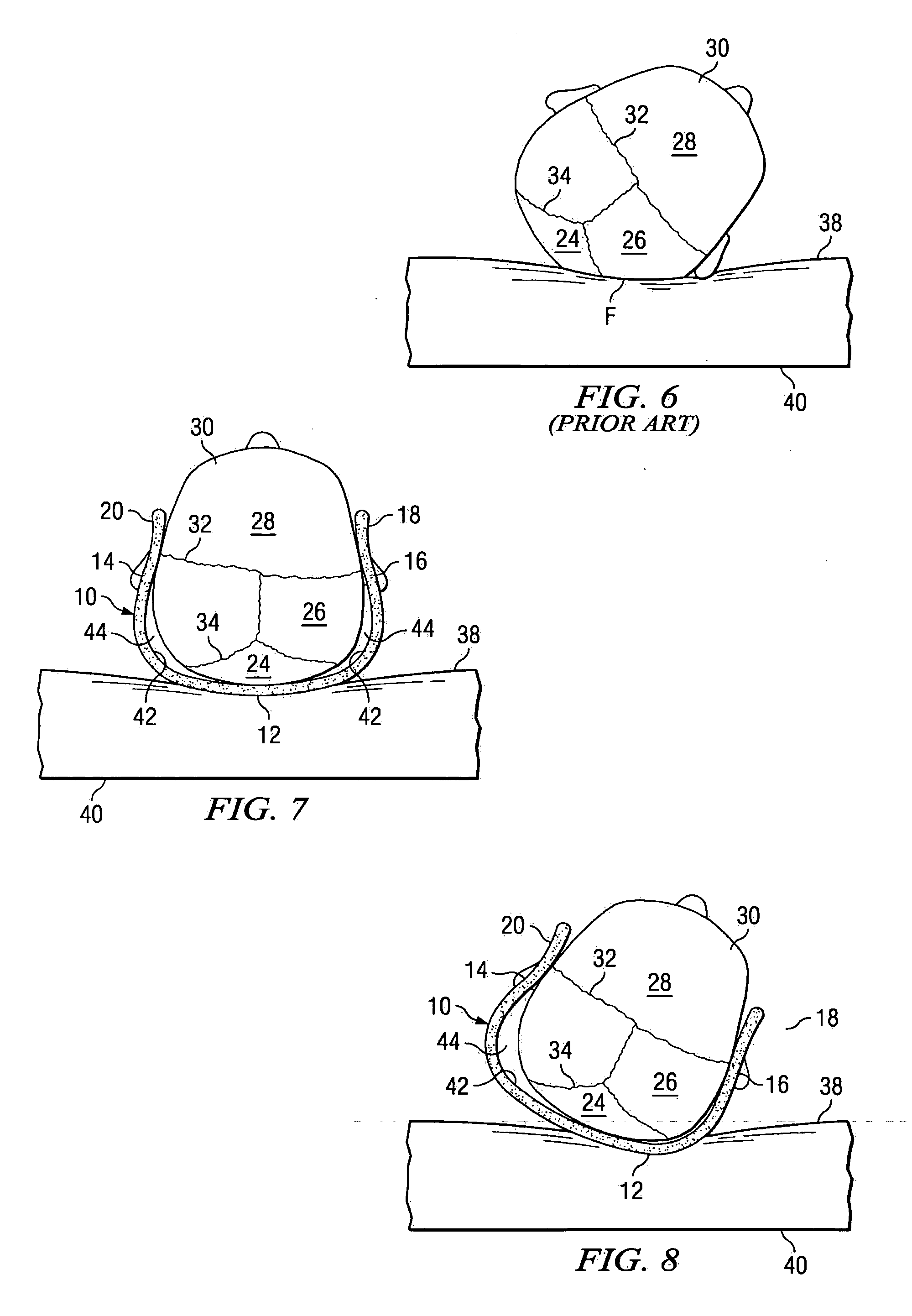
[0035] Referring to FIG. 1, FIG. 2, FIG. 3 and FIG. 10, the cranial orthosis of the present invention is in the form of a molded plastic appliance 10, for example a shell, headband or helmet, made of a unitary plastic molding or shell for protecting the soft, compliant skull base, occiput, left and right parietal bones and left and right temporal bones from deformation as the result of compressive forces caused by head weight while the infant is slee...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com