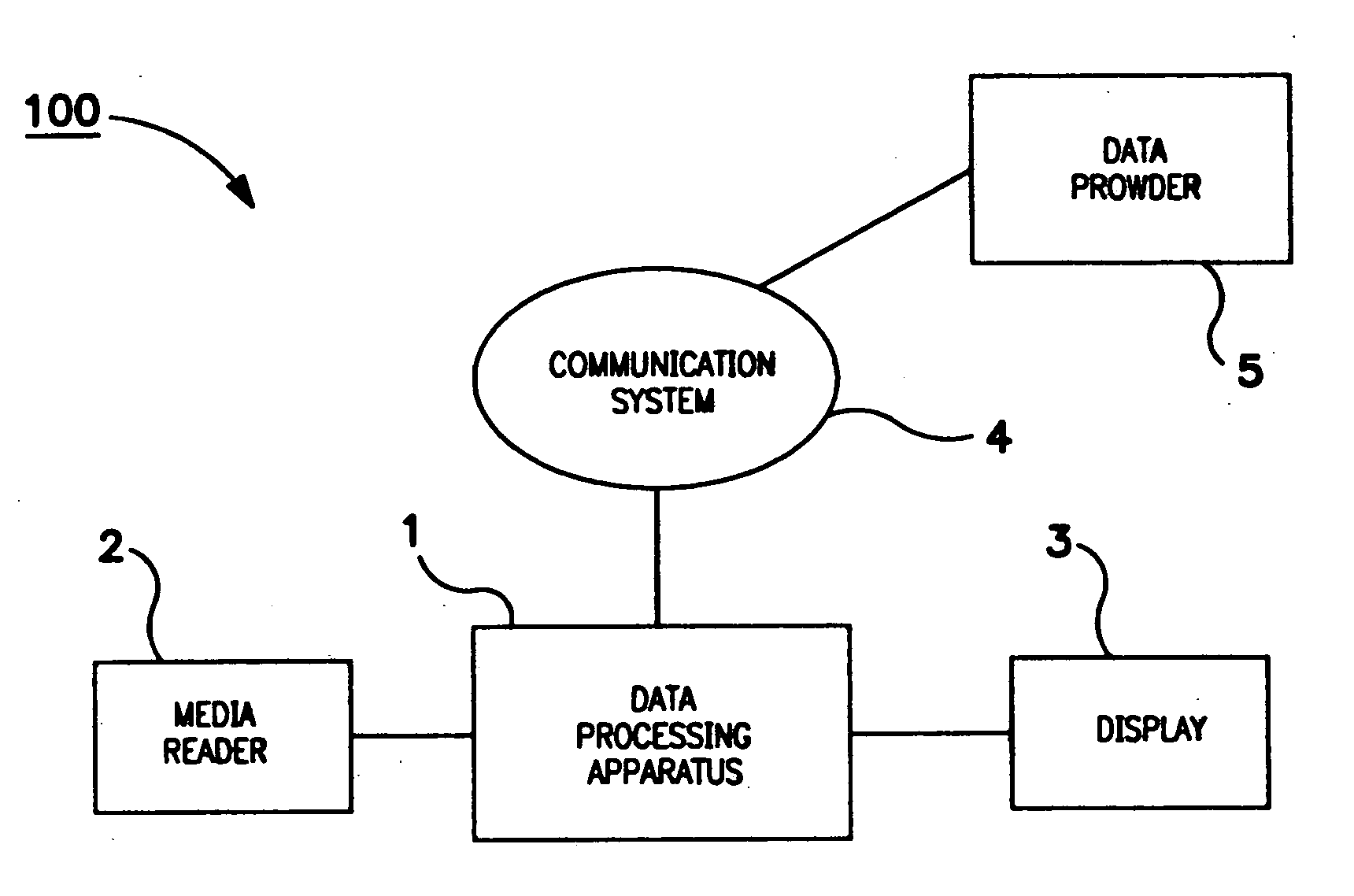
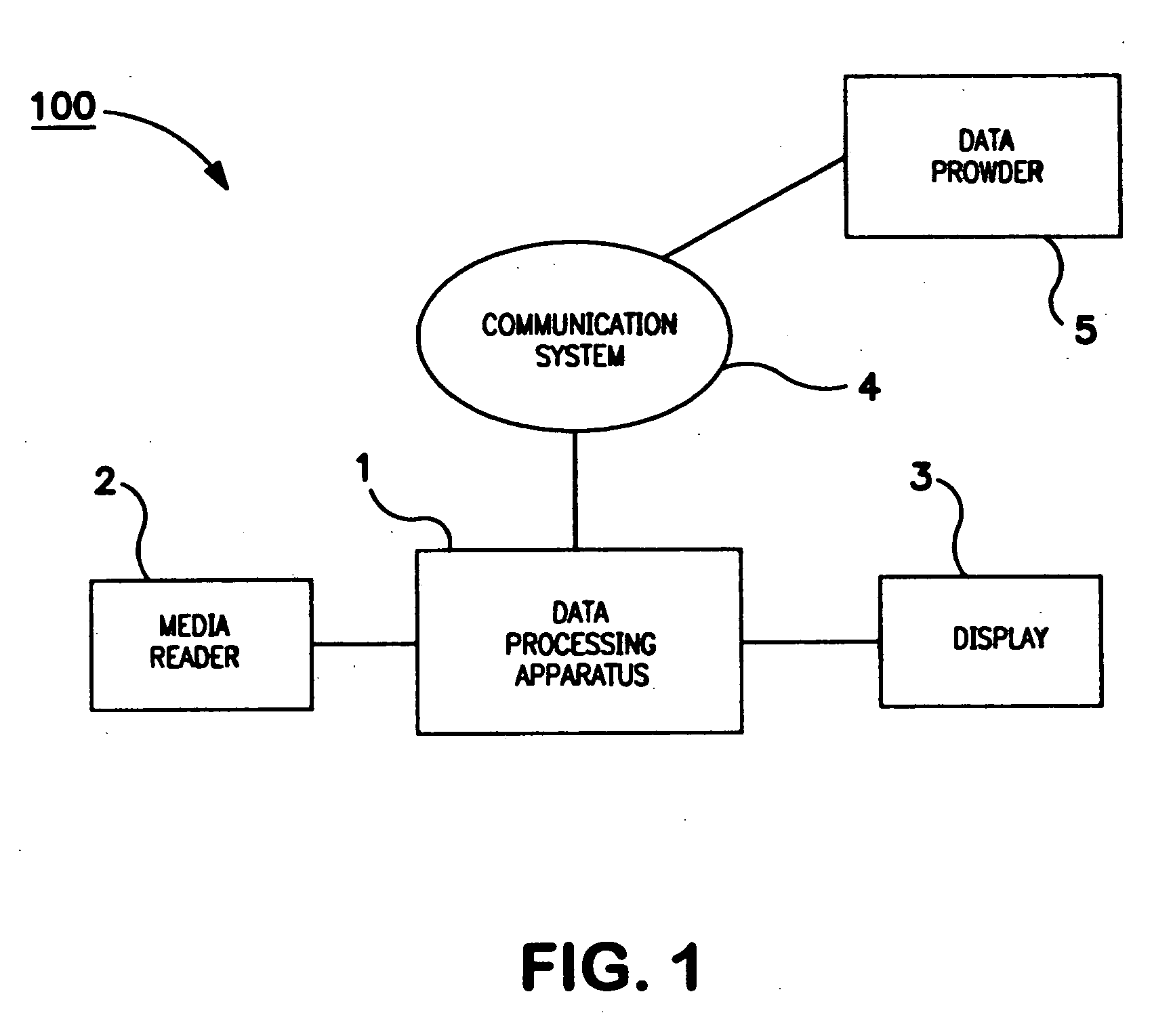
Method and apparatus for controling access to storage media
a technology for controlling access and storage media, applied in the direction of digital signal error detection/correction, instruments, recording signal processing, etc., can solve the problem of material providing a delayed, persistent respons
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
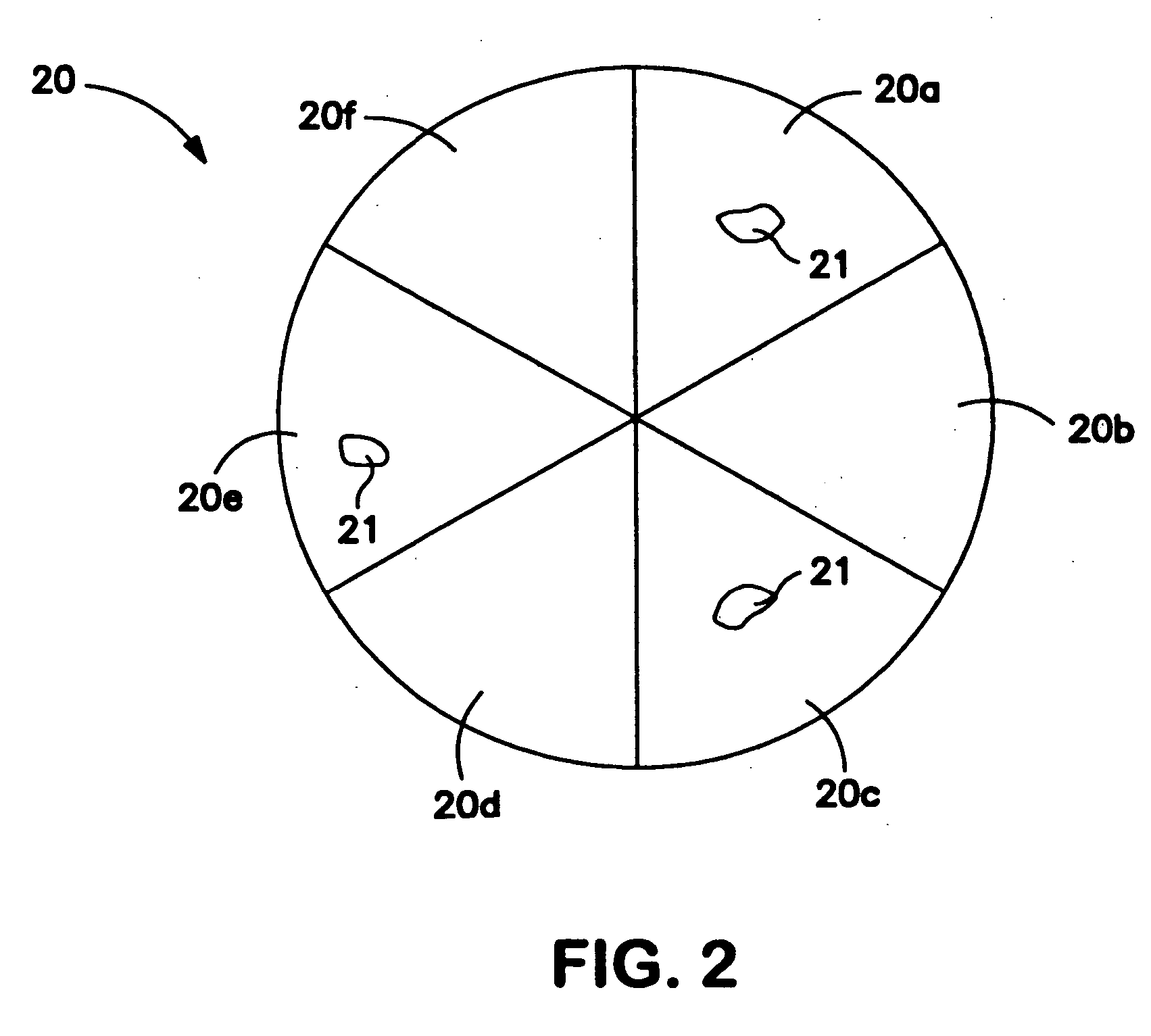
[0057] In one illustrative embodiment, the presence of light sensitive materials 21 on a medium 20 is used to determine that the medium 20 is an authorized medium 20 and / or contains data authorized for a particular use. In this embodiment, the light sensitive material 21 on the medium 20 is used by an installation program to prevent unauthorized installation of software recorded on the medium 20 on a computer, but the same or similar technique may be used to prevent unauthorized use of the medium 20, unauthorized use, such as reading or writing, of data on the medium 20, and so on. In this example, the installation program along with data representing the software code are recorded on the medium 20, but the installation program may be provided in other ways, such as stored in a memory of a media reader 2, on another medium 20, etc.
[0058] When an attempt is made to install the software on the medium 20 shown in FIG. 2, the installation program is read from the medium 20, e.g., by th...
example 2
[0063] Those of skill in the art will appreciate that Example 1 described above may be altered in many ways to provide different and / or varying levels of protection. As a second example, authentic media 20 may be provided with-an alphanumeric security code that is unique to each disk and is printed on a card accompanying the media 20. At the time of installation, the installation program may request the user to enter the security code. The installation program may then use the code to verify the authenticity of the medium 20 having the software to be installed. For example, the installation program may use the security code to determine a sector 20a-20f read sequence and / or timing, as an encryption key or password, to determine where on the medium 20 light sensitive material 21 is positioned, to determine an expected output from the media reader 2 when using a predefined sector read sequence, and so on. Based on this information, the medium 20 may be read, and the output from the re...
example 3
[0065] In the examples described above, no distinction was made regarding reading specific portions of a medium 20 that is associated with a single spot of light sensitive material 21. In this illustrative embodiment of the invention, different portions of a medium 20 that are associated with a single spot of light sensitive material 21 are read. FIG. 3 shows a portion of the medium 20 and a spot or area of light sensitive material 21. Although the medium 20 may have a plurality of regions each associated with a corresponding spot of light sensitive material 21, only the reading of a single portion of the medium 20 is discussed below for simplicity. In light source, the light sensitive material 21 may be caused to alter state. That is, illumination of any of the tracks a-d for reading may illuminate the light sensitive material 21 and cause it to change from one state to another. For example, if the reader 2 is directed to sample a section of track a, and light sensitive material 21...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com