Patents
Literature
2181results about "Accidental erasing/double-recording prevention" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
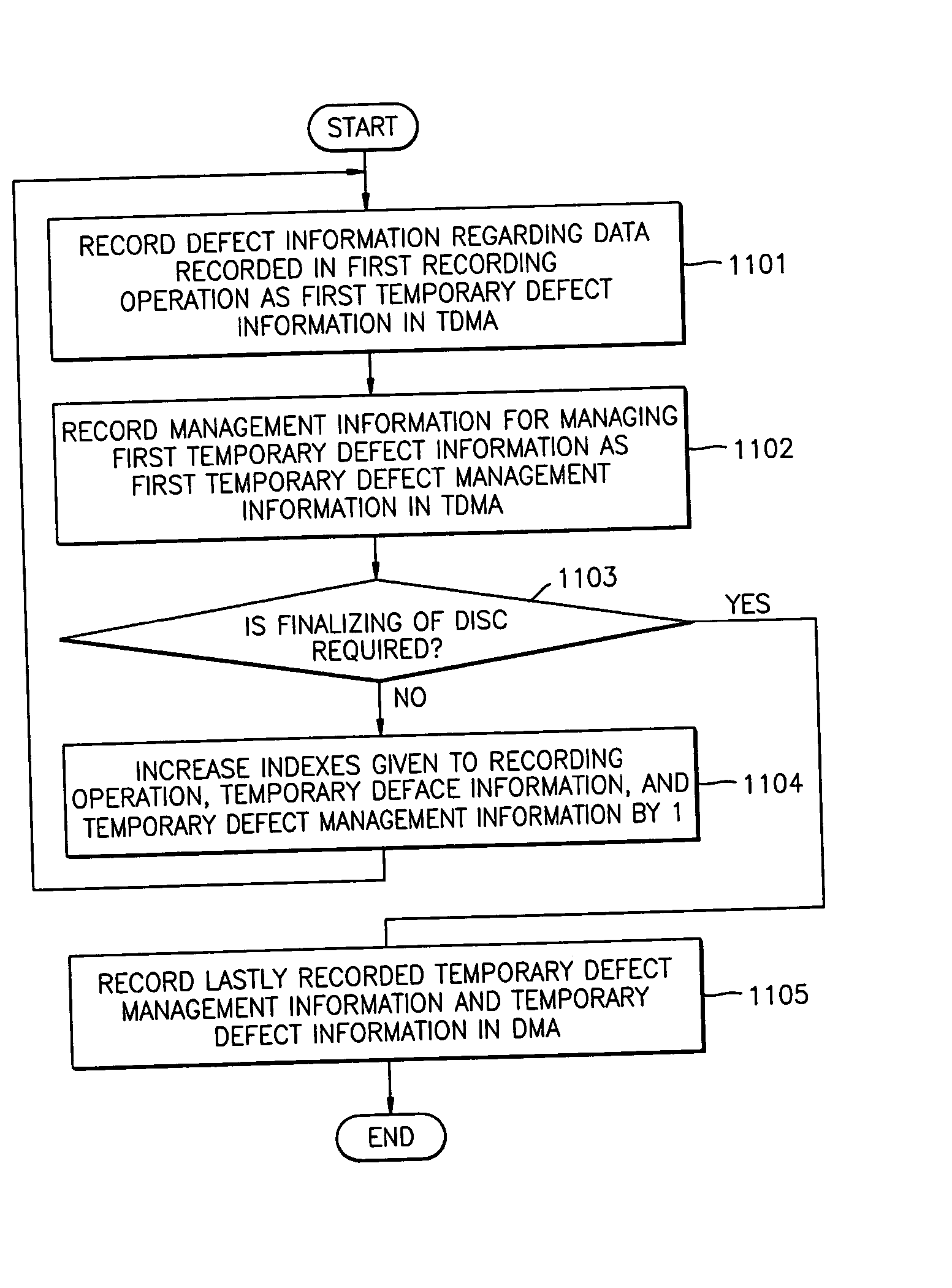
Method of and apparatus for managing disc defects using temporary defect management information (TDFL) and temporary defect management information (TDDS), and disc having the TDFL and TDDS
ActiveUS20040076096A1Combination recordingRecord information storageComputer hardwareManagement area
A disc having an updatable defect management area used by an apparatus for managing defects on the disc, the disc including a user data area which includes user data, a spare area that is a substitute area for a defect existing in the user data area, and an area in which are recorded an address of data that is last recorded in the user data area and an address of a replacement data recorded in the spare area. Accordingly, the disc defect management method and apparatus are applicable to a recordable disc such as a write-once disc while effectively using a defect management area of the disc.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
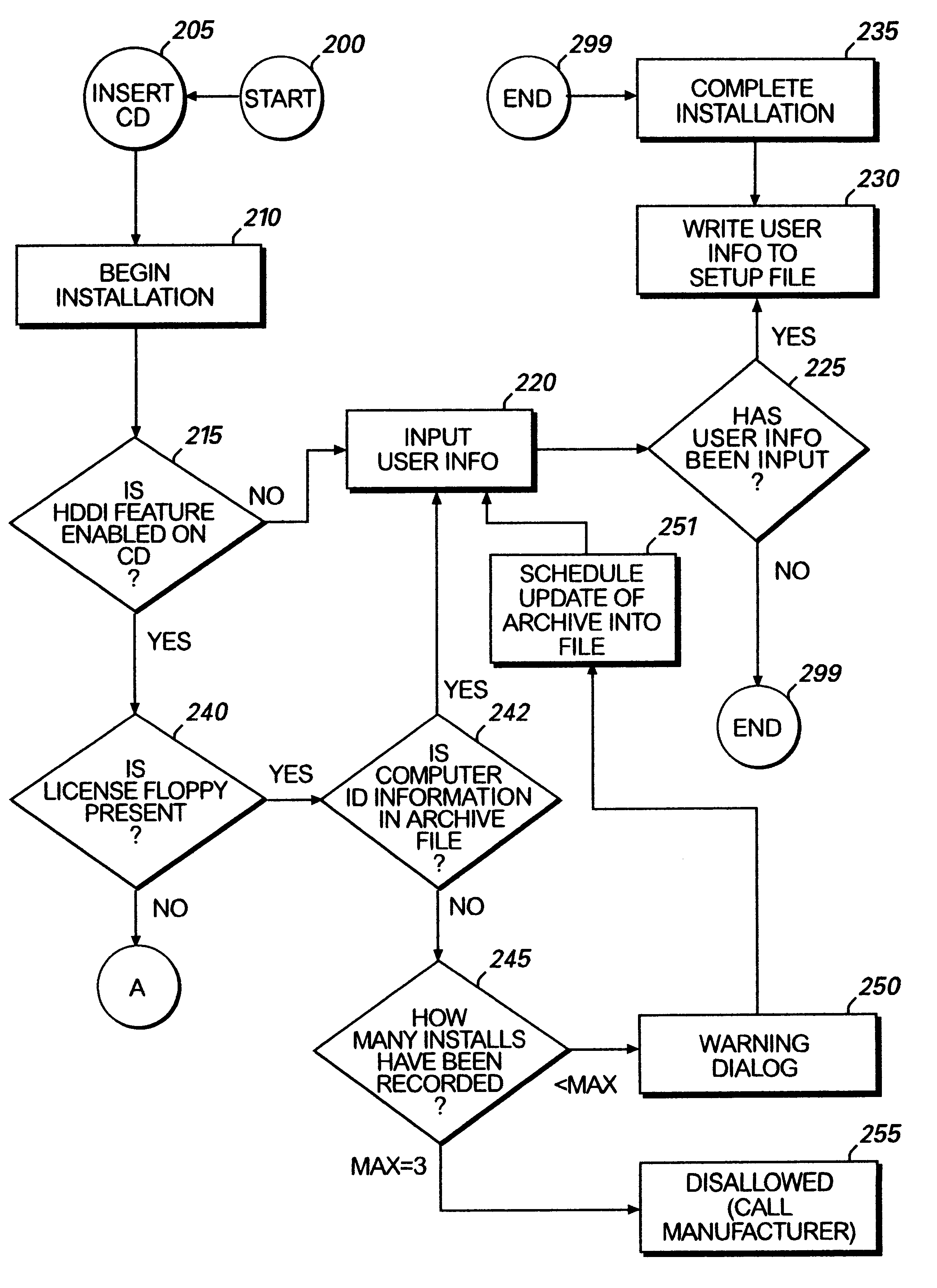
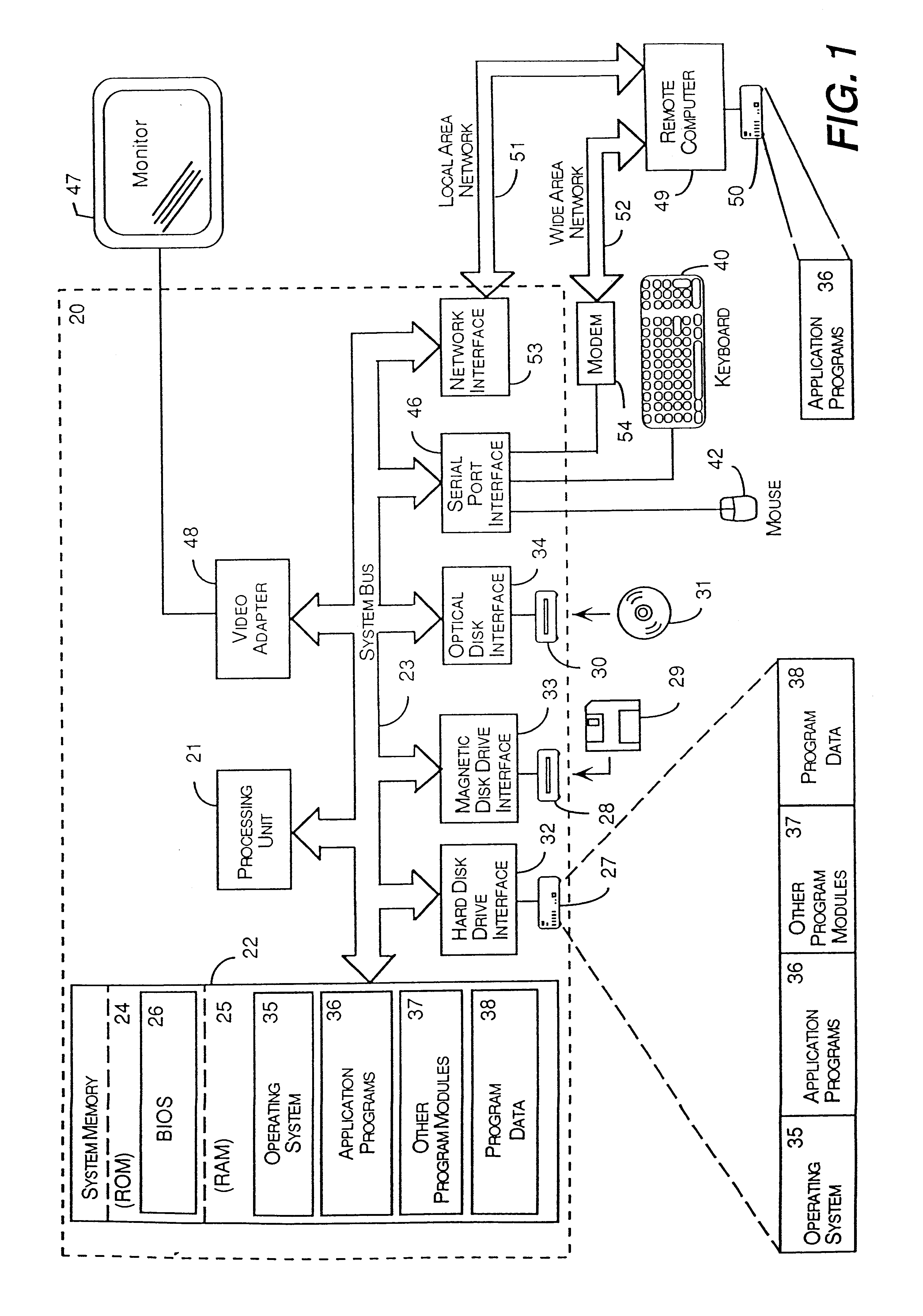
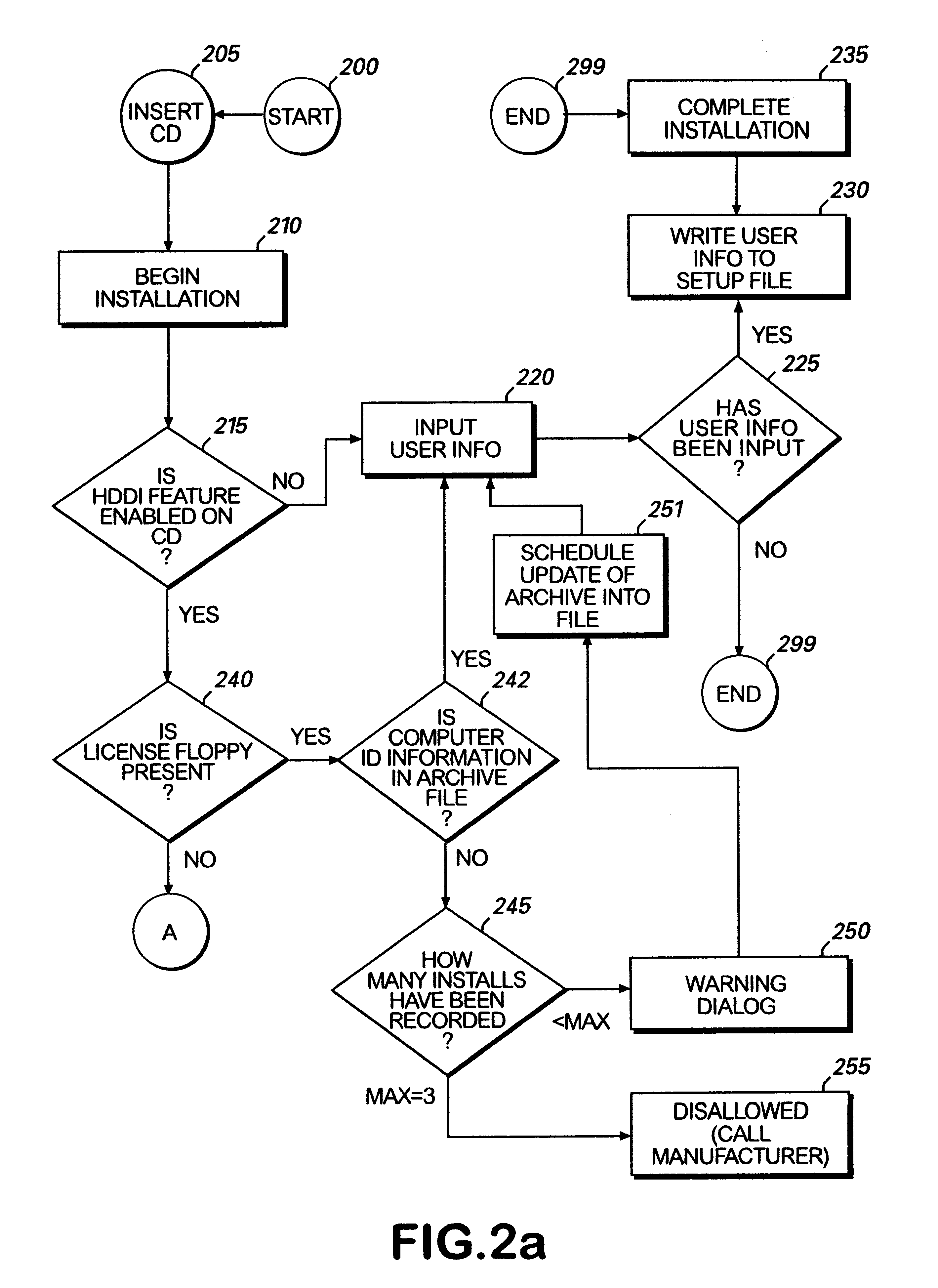
Method for preventing software piracy during installation from a read only storage medium
InactiveUS6226747B1Easy to installDigital data processing detailsRecord information storageSoftware licenseComputer software
The method and system for limiting the number of installations of a computer software program located on a read only disk from the read only disk to a computer. The read only disk is linked to a removable read / write memory by data on the removable read / write memory corresponding to data on the read only disk. Prior to installation of the computer software program from the read only disk to the computer, software residing on the removable read / write memory determines whether the installation is authorized. Such determination is made by comparing identification information corresponding to computers on to which the computer software program has previously been installed to installation limitations dictated by a software license agreement.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
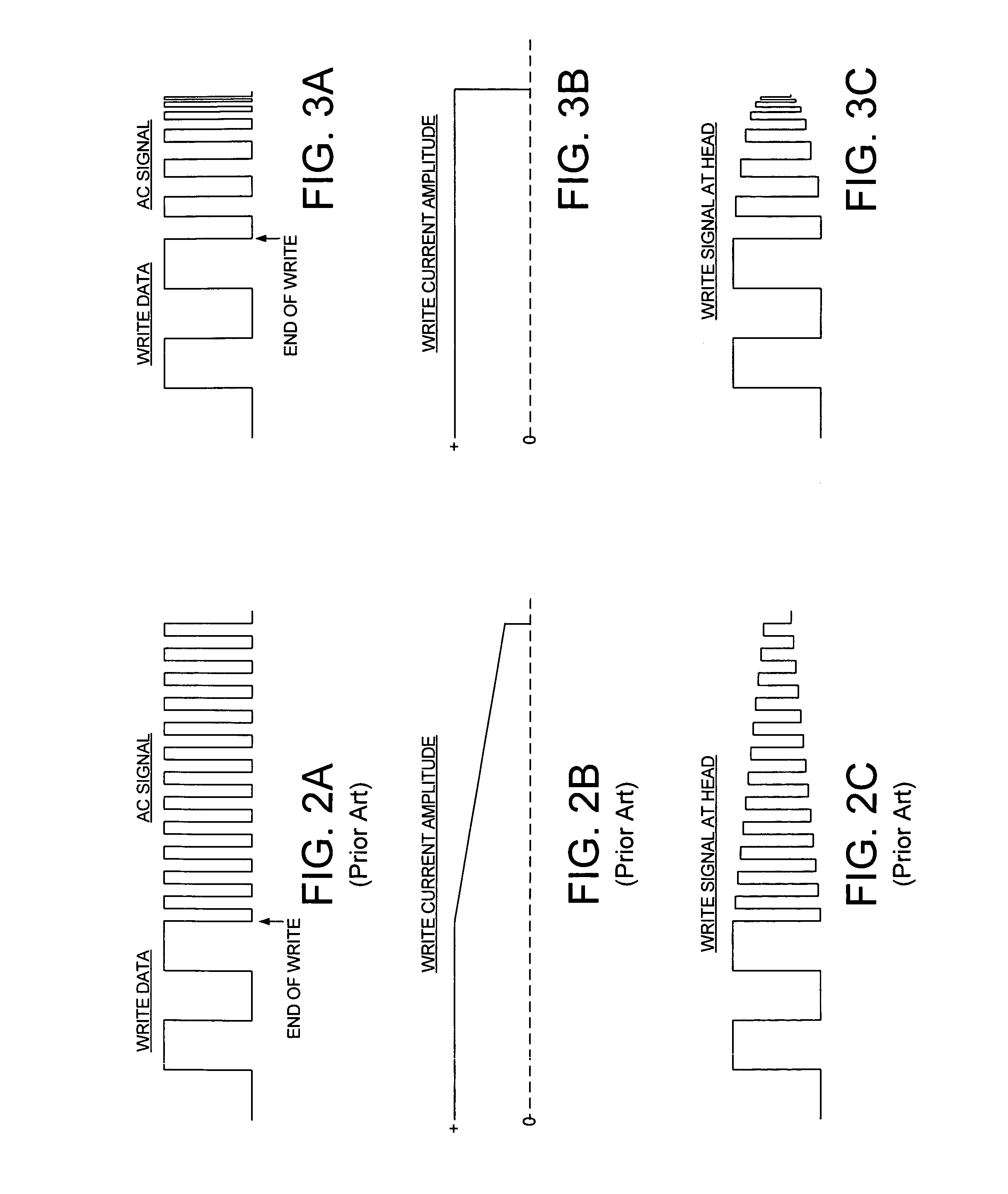
Demagnetizing a head in a disk drive by increasing the frequency of an AC write signal while maintaining the write current amplitude
ActiveUS7092186B1Reduce the amplitudeDemagnetisation of recording headsRecord information storageHemt circuitsControl circuit
A disk drive is disclosed which demagnetizes the head after a write operation. Write circuitry applies a write signal to the head in order to write data to a selected data sector during a write operation, wherein the write signal comprises a predetermined write current amplitude. Control circuitry demagnetizes the head at the end of the write operation by maintaining the write current amplitude while increasing a frequency of an AC write signal applied to the head over a predetermined demagnetization interval, wherein increasing the frequency of the AC write signal decreases an amplitude of the AC write signal when observed at the head.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
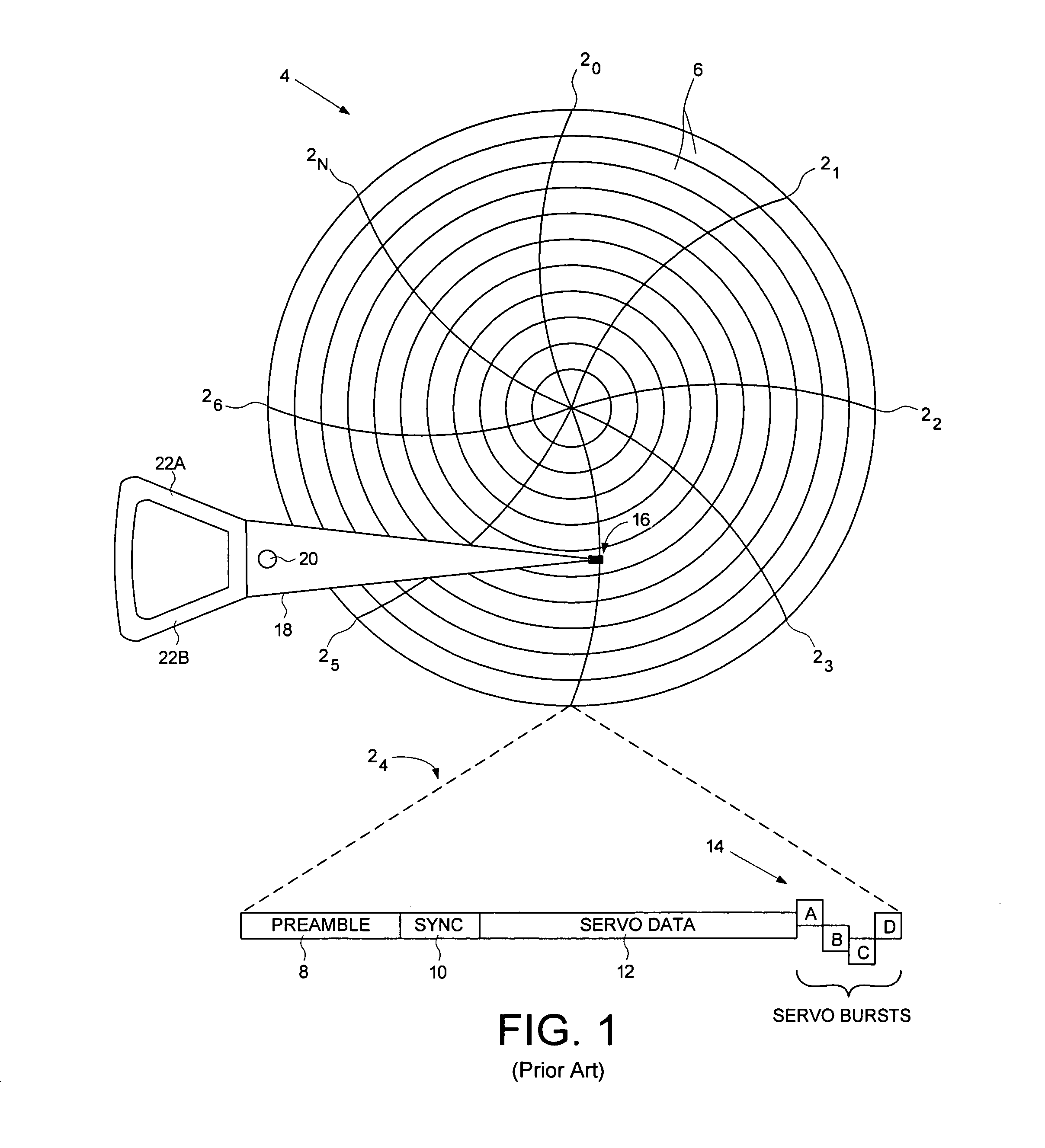
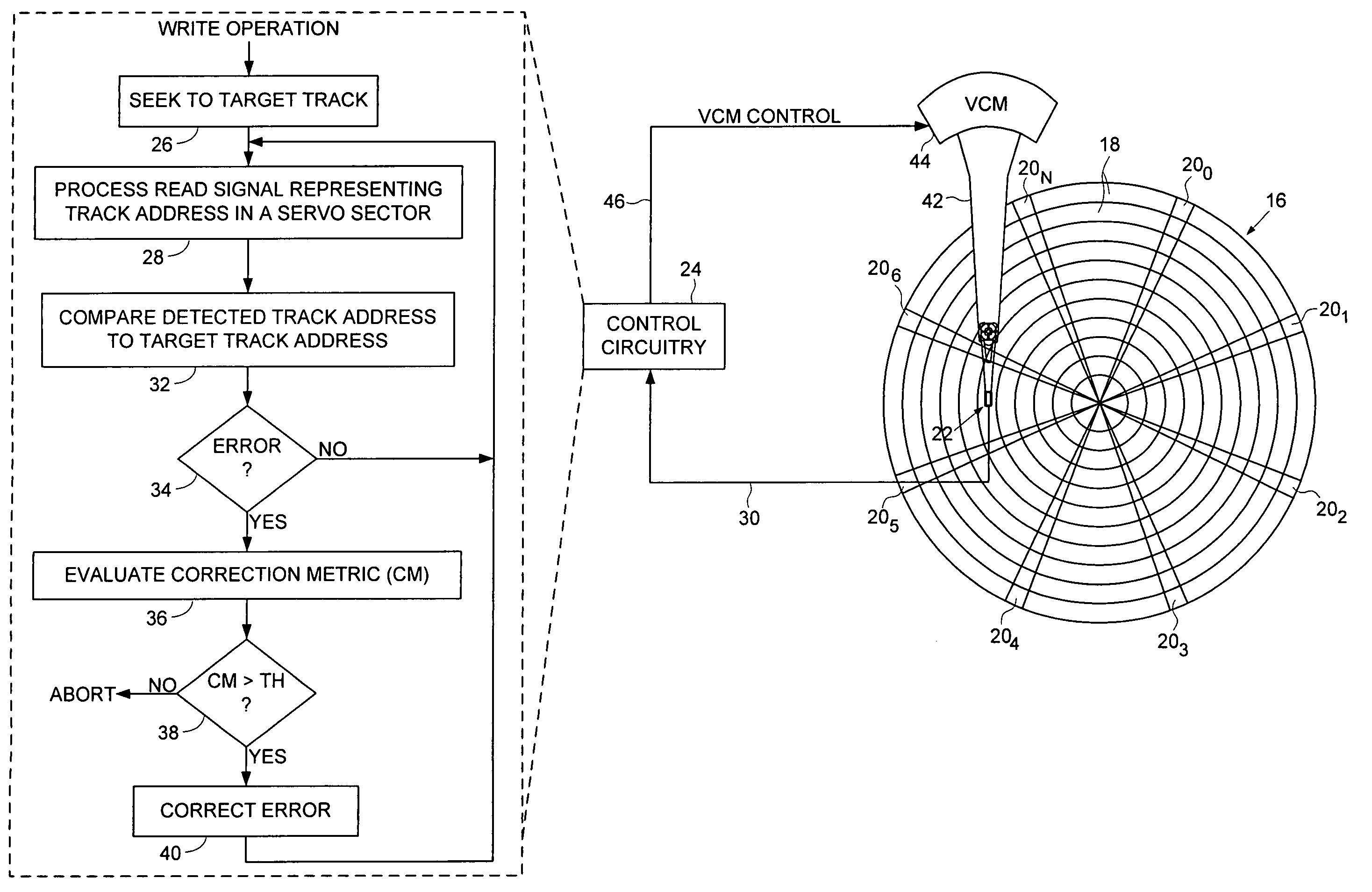
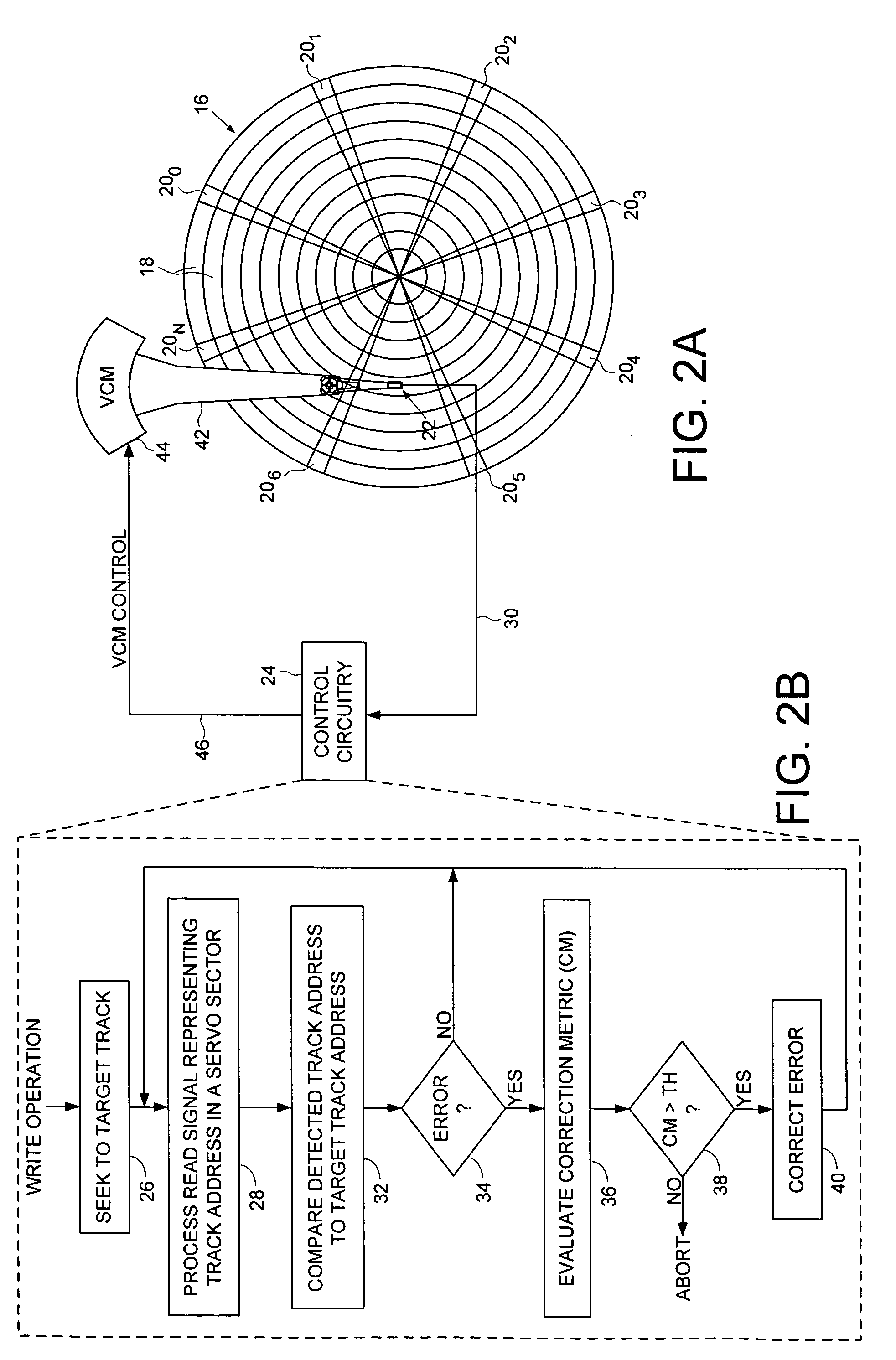
Disk drive correcting track address during a write operation
InactiveUS7369343B1Recording carrier detailsRecord information storageControl theoryComputer hardware
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a head actuated over a disk having a plurality of servo tracks, wherein each servo track comprises a plurality of servo sectors and each servo sector comprises a track address. A read signal from the head representing a first track address in one of the servo sectors is processed in order to generate a detected track address which is compared to a first target track address to obtain a first track address error. A correction metric is generated representing a likelihood that the first track address error was caused by a detection error, and if the correction metric exceeds a threshold, the detected track address is corrected in response to the first track address error, and the write operation is continued. If the correction metric does not exceed the threshold, the write operation is aborted.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
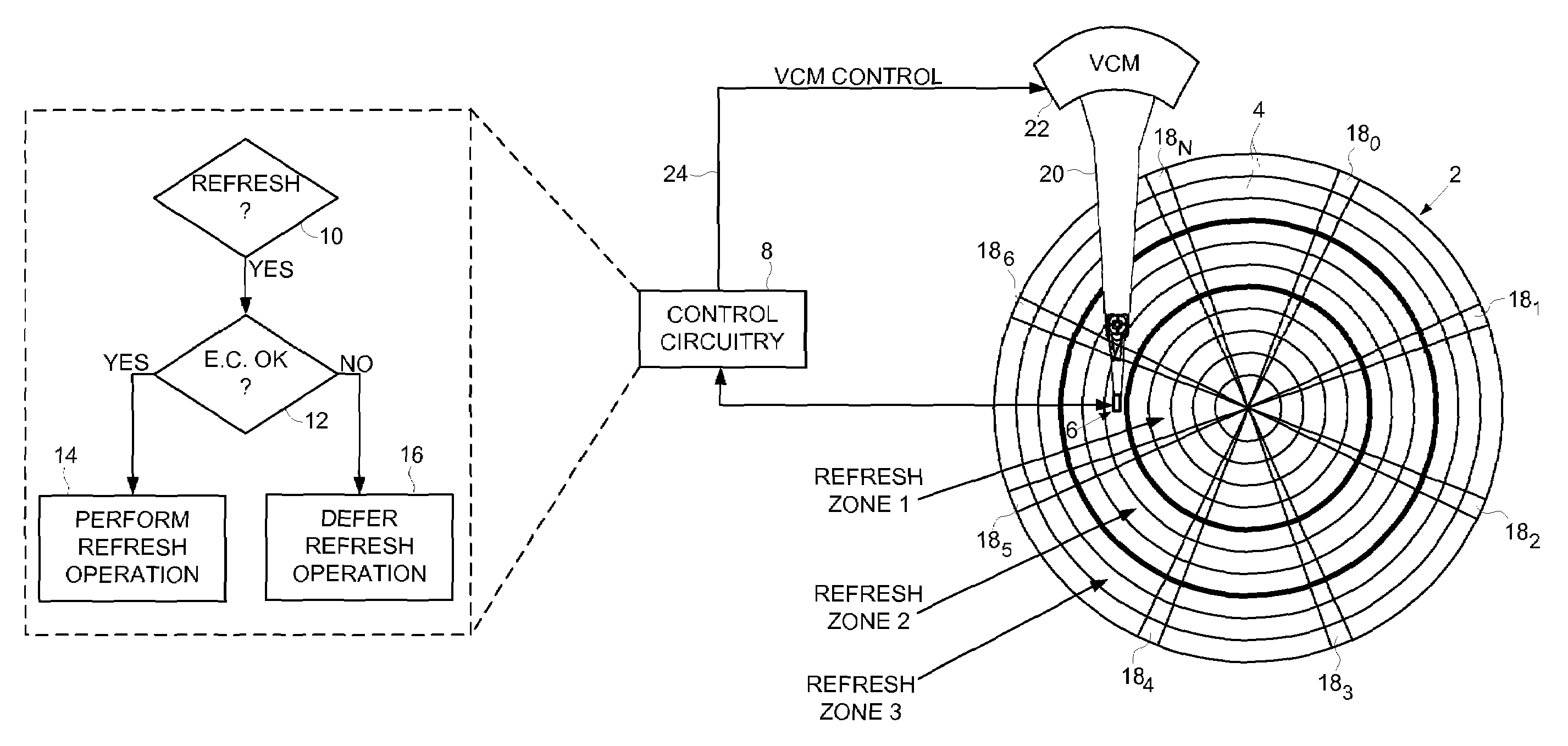
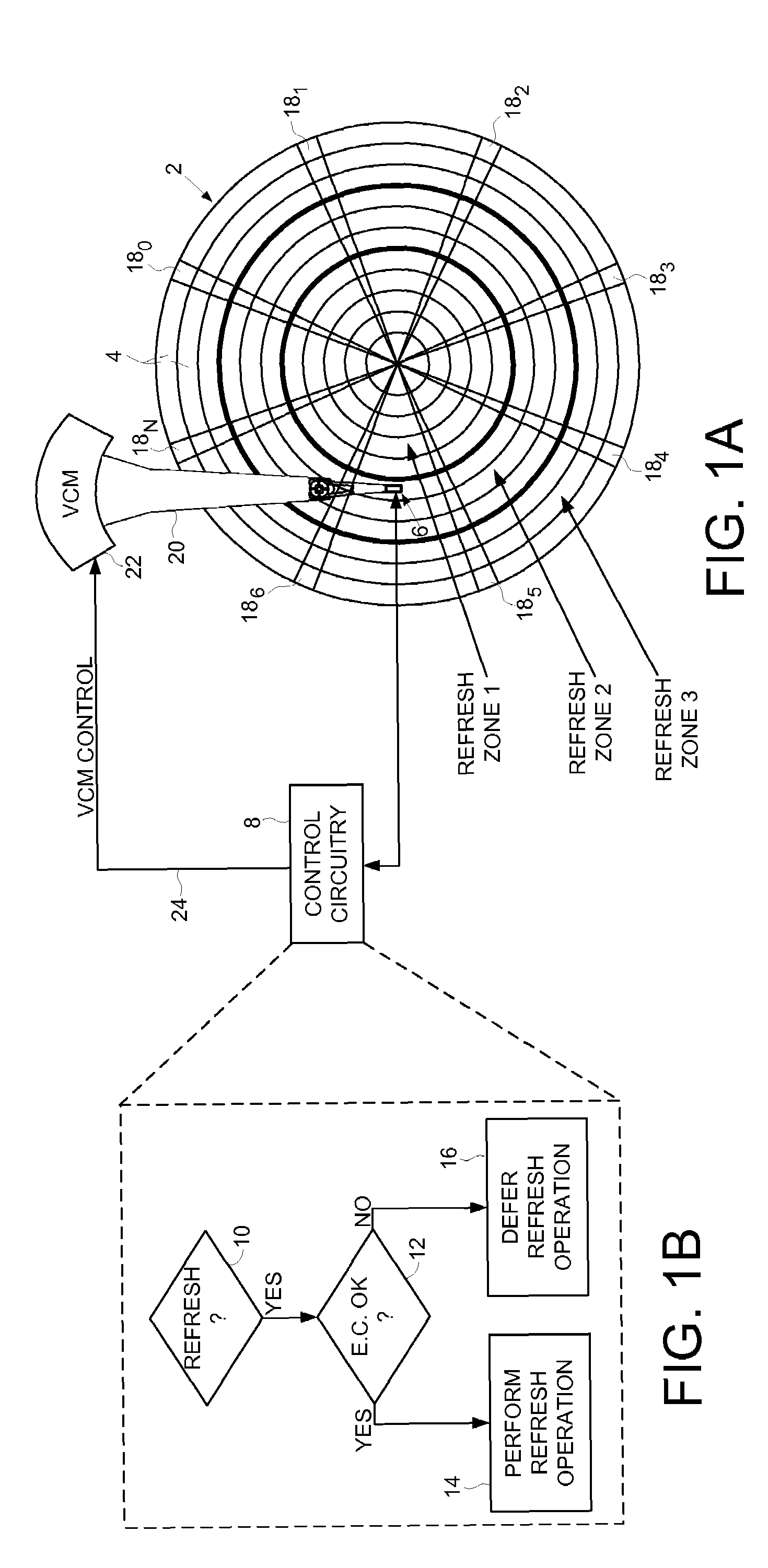
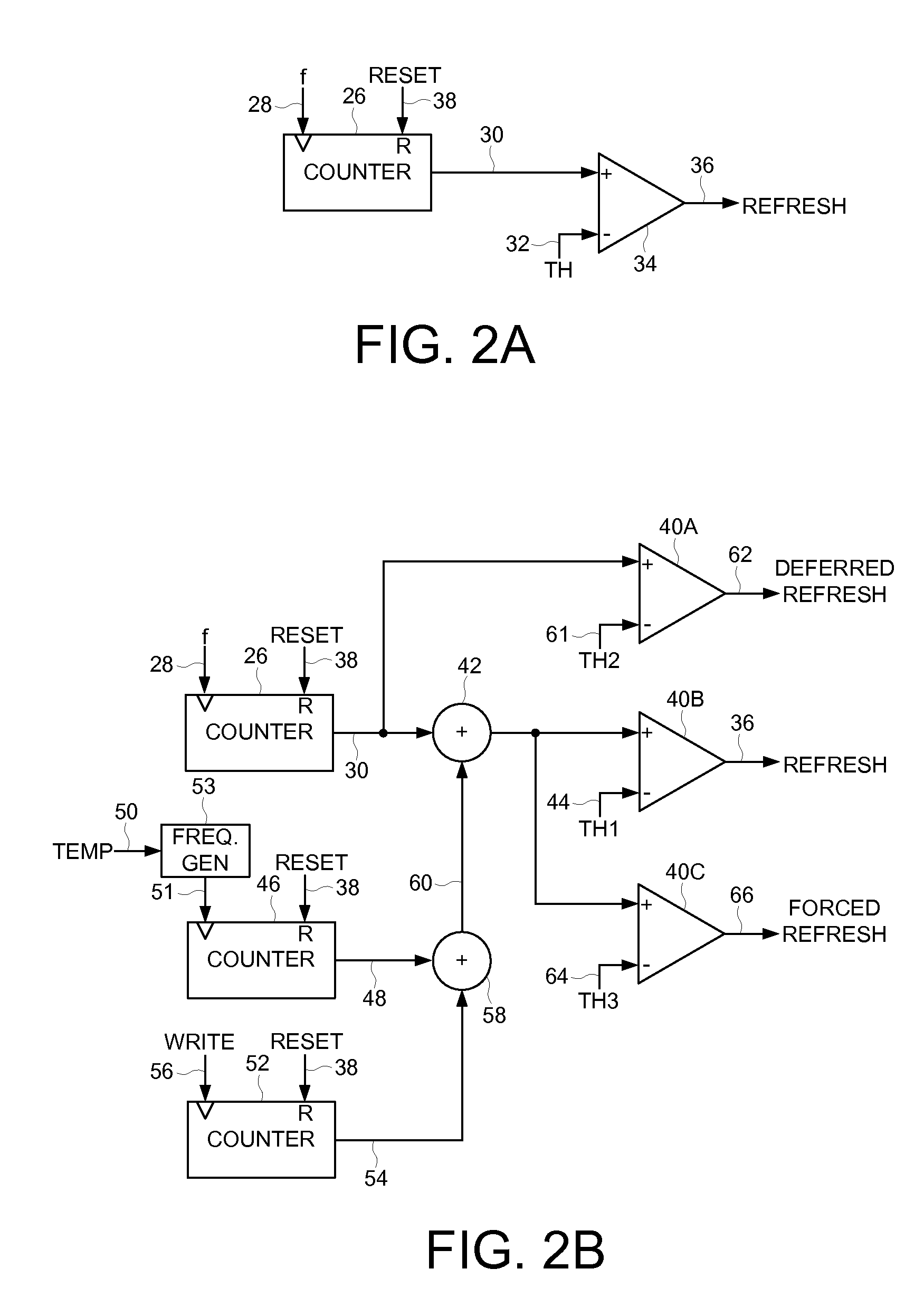
Disk drive deferring refresh based on environmental conditions
InactiveUS7649704B1Undesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionRecord information storageData storingComputer science
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Disk drive including a delay circuit to provide a delayed reset signal
InactiveUS7907364B2Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageDisk controllerCircuit delay
A disk drive including a delay circuit to provide a delayed reset signal is disclosed. The disk drive includes a head to perform write and read operations to and from a disk and a disk controller that is coupled to the head to control the write and read operations performed by the head. The disk drive further includes: a power loss detection circuit to detect a power loss and to generate a reset signal in response to the power loss; a reset power line coupled to the disk controller and the power loss detection circuit to provide a non-delayed reset signal to the disk controller; and a delay circuit coupled to the reset power line wherein the delay circuit delays the reset signal to provide a delayed reset signal.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method and system for controlling video media
ActiveUS20050078944A1Prevent illegal useMechanism usedTelevision system detailsColor television signals processingDatapathData path
A method and system for controlling video input media is described. The method includes receiving video media via a video media input device. The video media input device is communicatively coupled with and operable in conjunction with the electronic device. The method further includes monitoring a data path within the electronic device associated with the video media. The monitoring is performed by a compliance mechanism communicatively coupled with and operable in conjunction with the electronic device. The method further includes preventing the video media from reaching a usage mechanism via the data path, the usage mechanism communicatively coupled with the electronic device. The usage mechanism is able to create an environment in which the video media can be used in an unauthorized manner. The preventing performed by the compliance mechanism is done when usage of the video media with the usage mechanism violates a usage restriction applicable to the video media.
Owner:MEDIA RIGHTS TECH
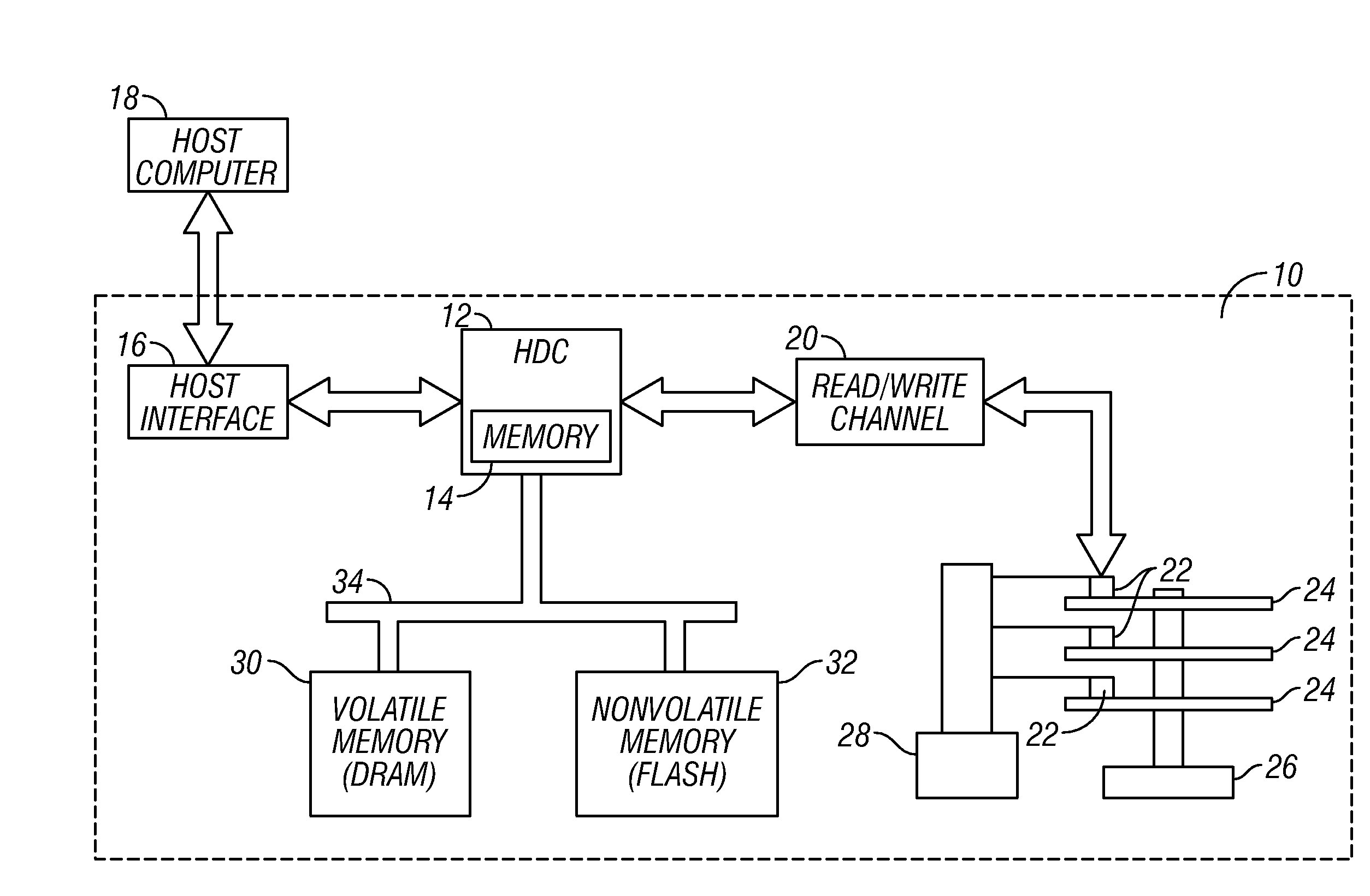
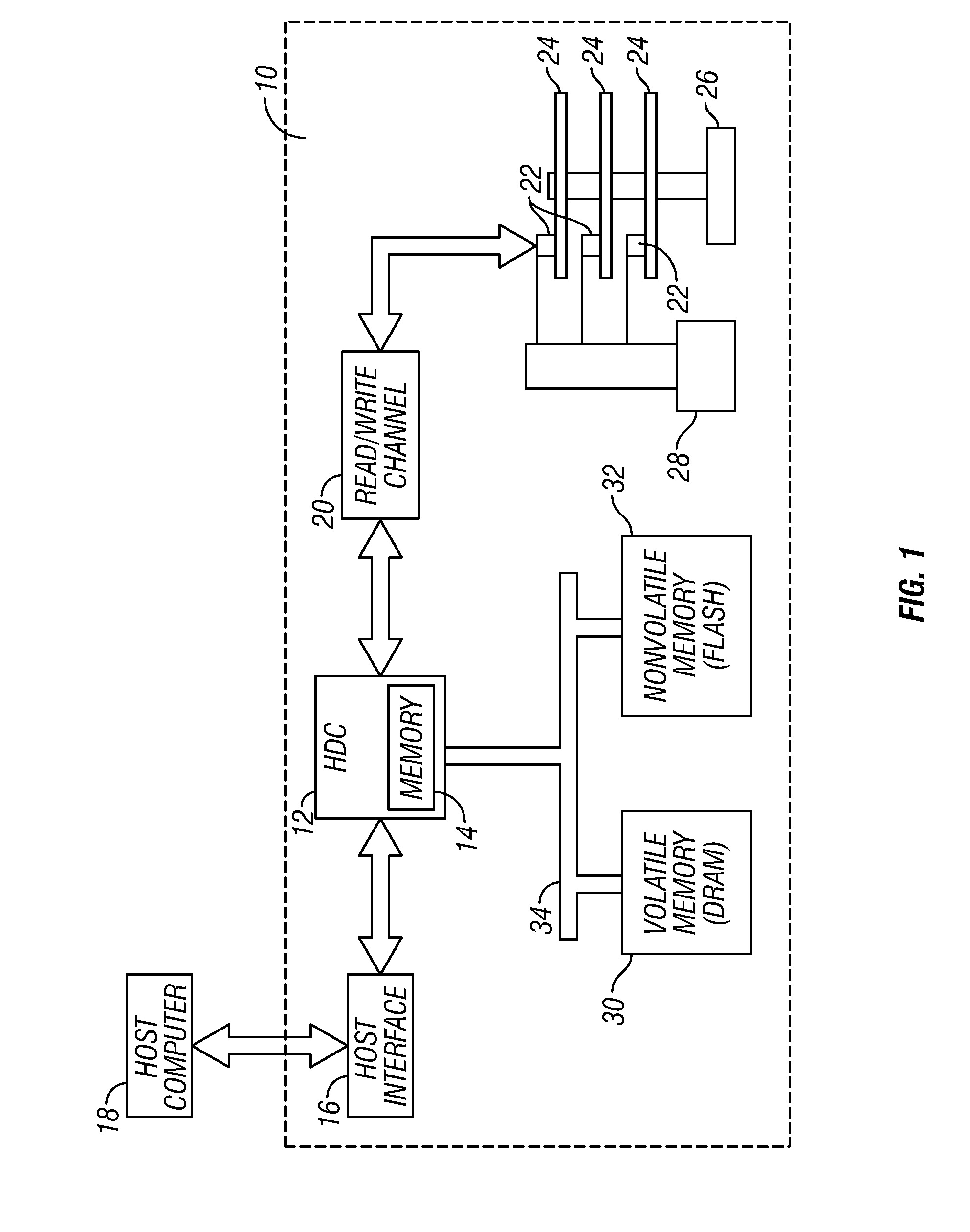
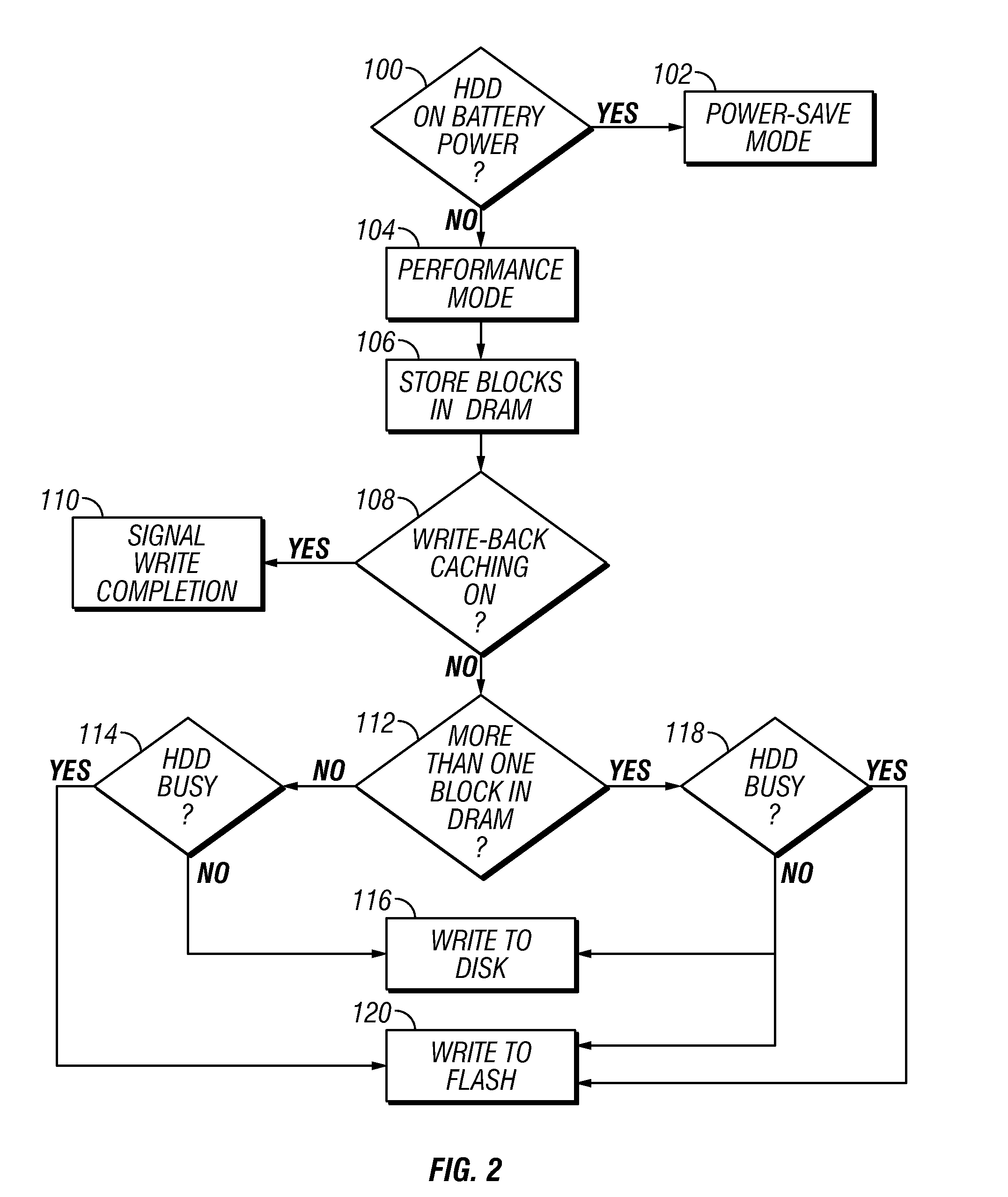
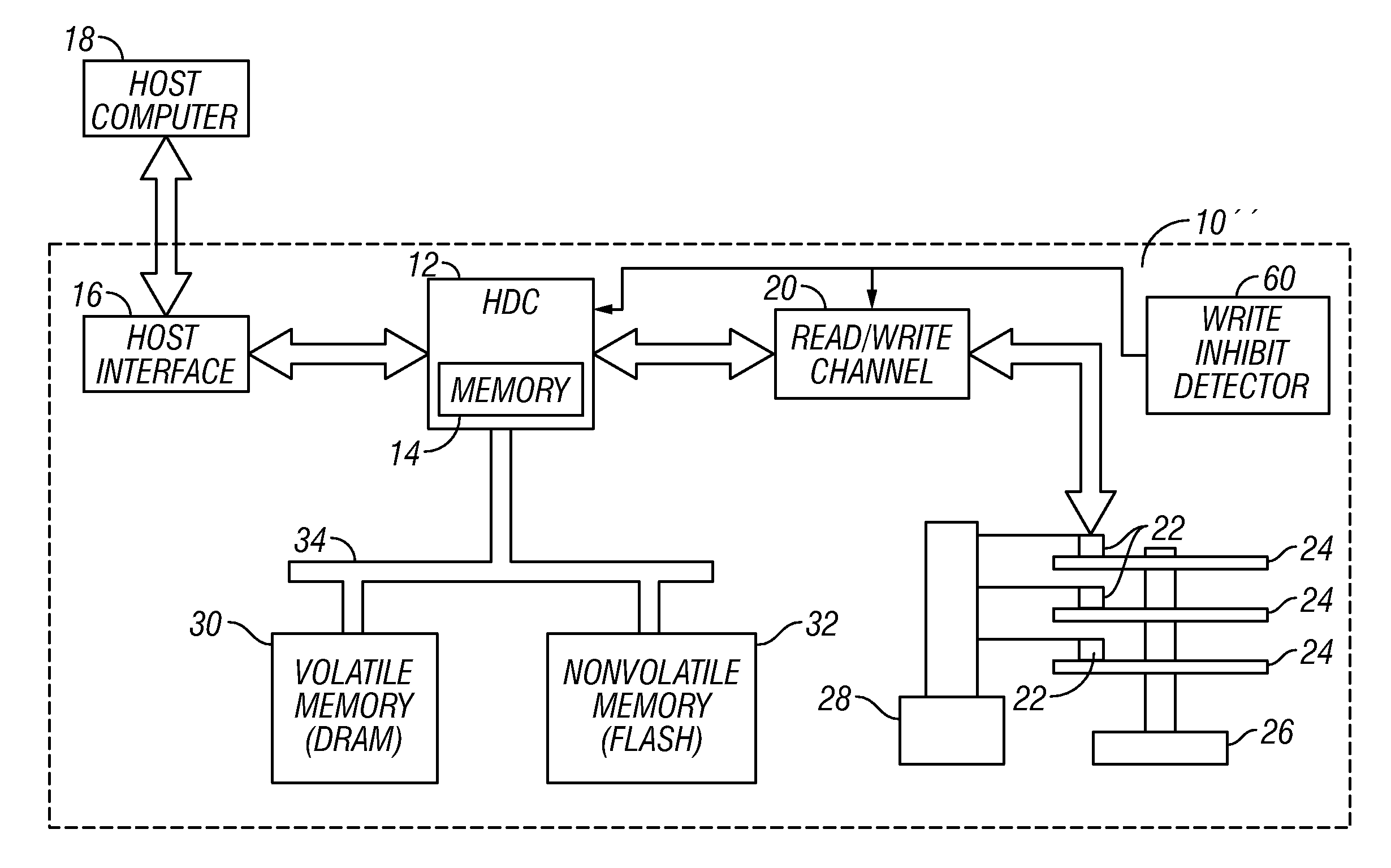
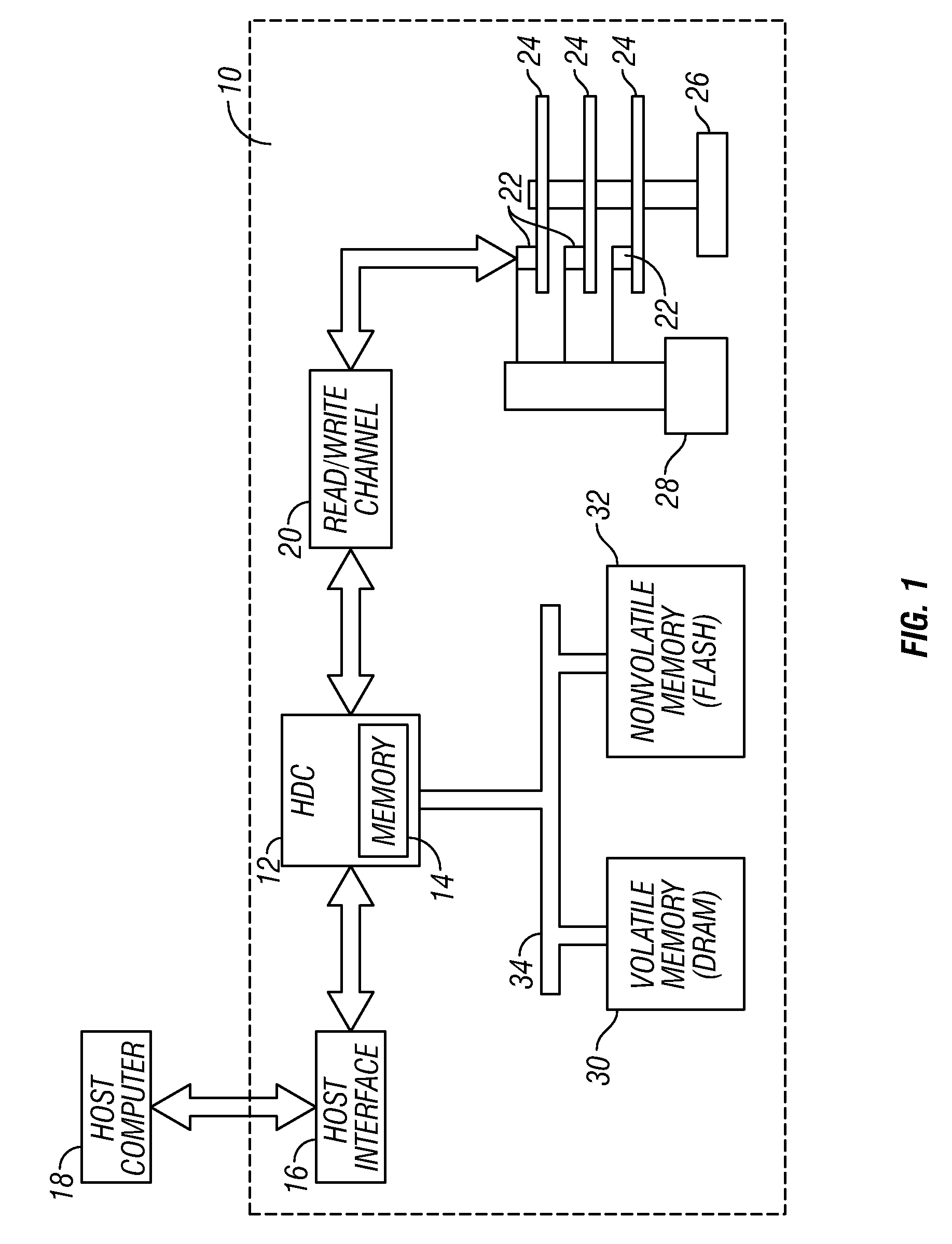
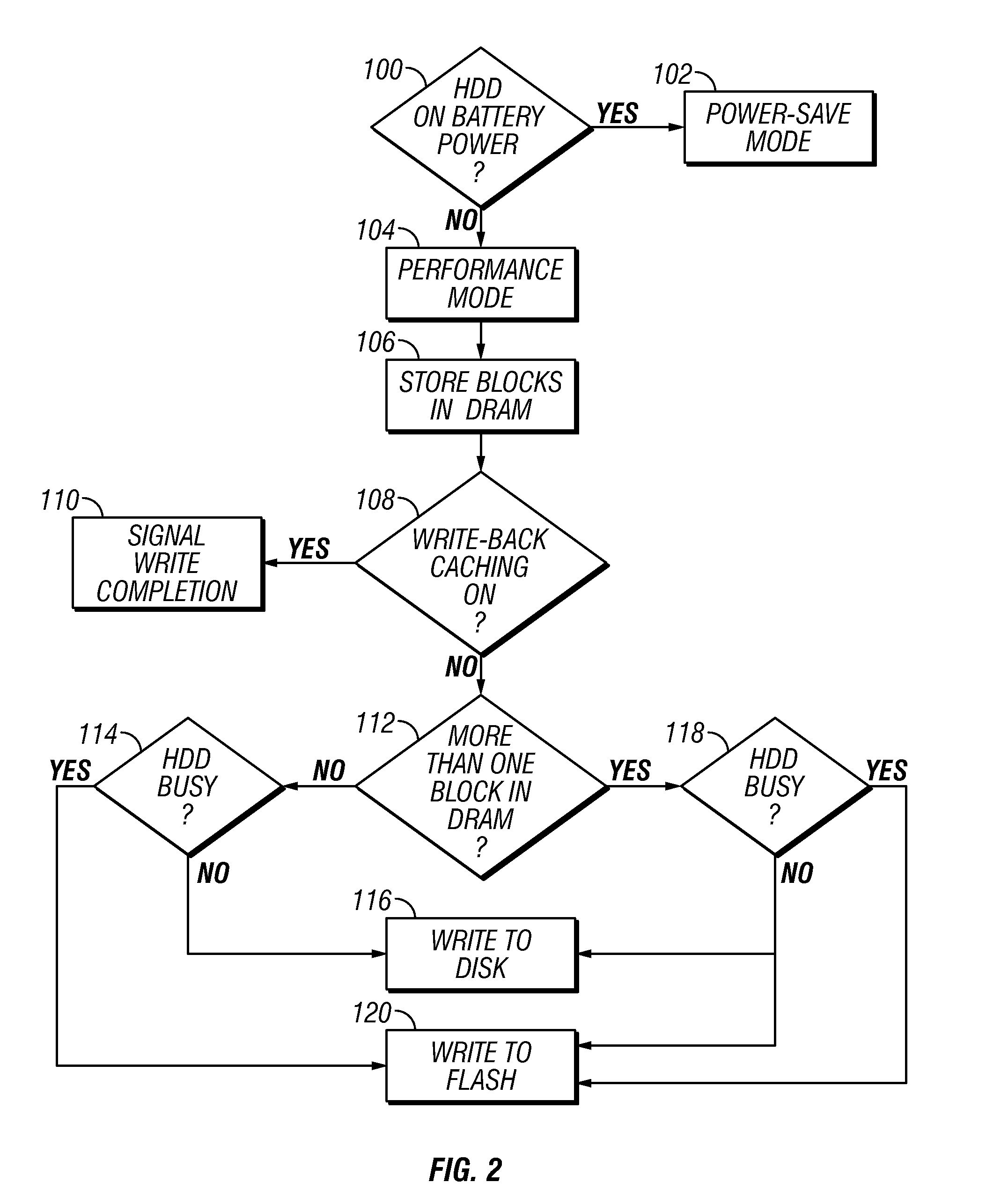
Disk drive with nonvolatile memory having multiple modes of operation
InactiveUS20080024899A1Improve throughputPenalty is avoidedMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTOperation modeMultiple modes
A hybrid disk drive, i.e., a disk drive with two types of permanent storage media (conventional disk media and nonvolatile memory, such as flash memory), uses its nonvolatile memory in operational modes other than the power-save or “standby” mode wherein the disks are spun down. In a first additional mode, called a “performance” mode, one or more blocks of write data are destaged from volatile memory (the disk drive's write cache) and written to the disk and simultaneously one or more data blocks of write data are destaged from the volatile memory and written to the nonvolatile memory. In a second additional mode, called a “harsh-environment” mode, the disk drive includes one or more environmental sensors, such as temperature and humidity sensors, and the nonvolatile memory temporarily replaces the disks as the permanent storage media. In a third additional mode, called a “write-inhibit” mode, the disk drive includes one or more write-inhibit detectors, such as a shock sensor for detecting disturbances and vibrations to the disk drive. In write-inhibit mode, if the write-inhibit signal is on then the write data is written from the volatile memory to the nonvolatile memory instead of to the disks.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Information editing apparatus, information editing method, and information recording medium on which program for controlling edit is recorded so as to be read by computer
InactiveUS6845069B2Efficient executionTelevision system detailsRecord information storageComputer hardwareRecording media
Owner:PIONEER CORP
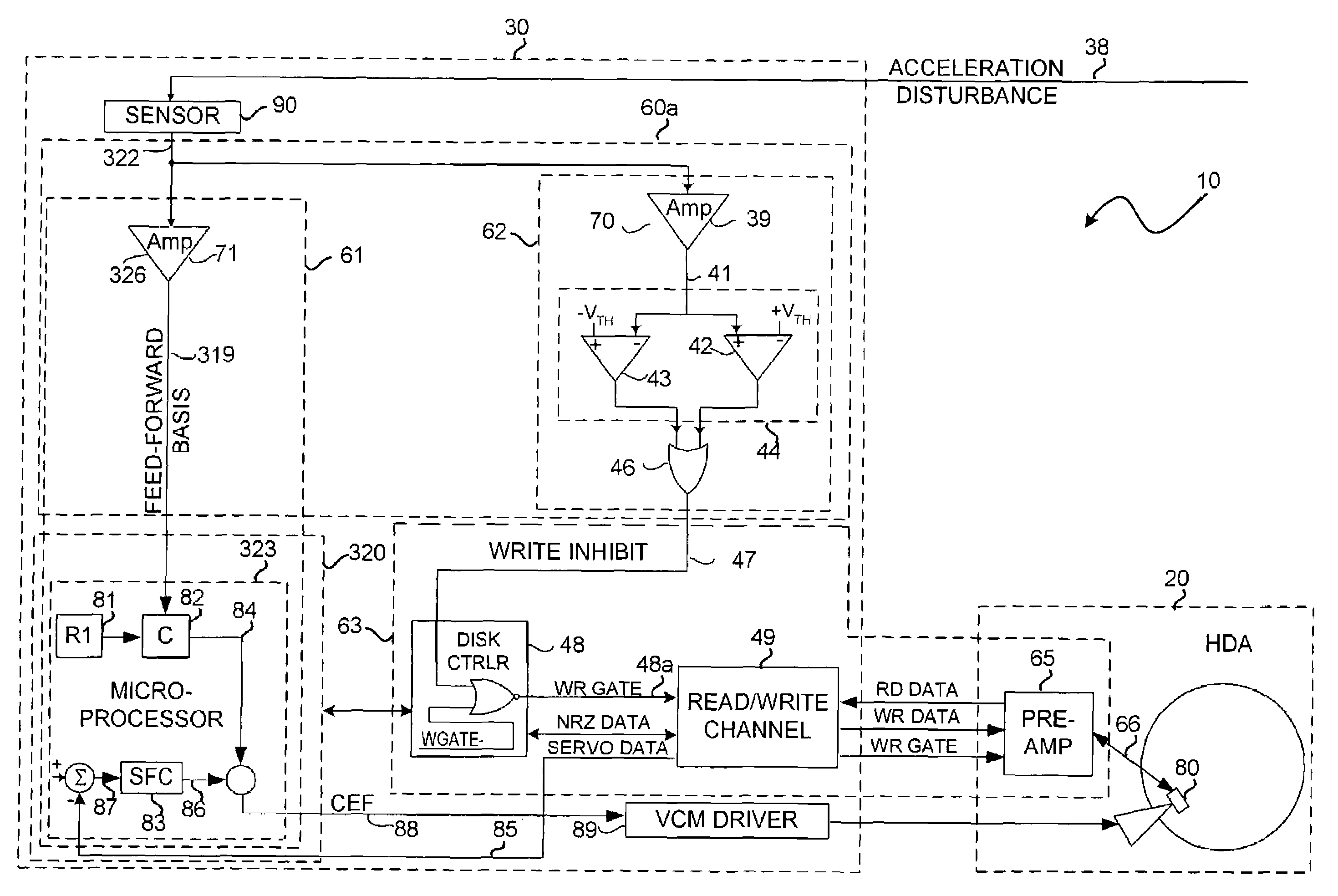
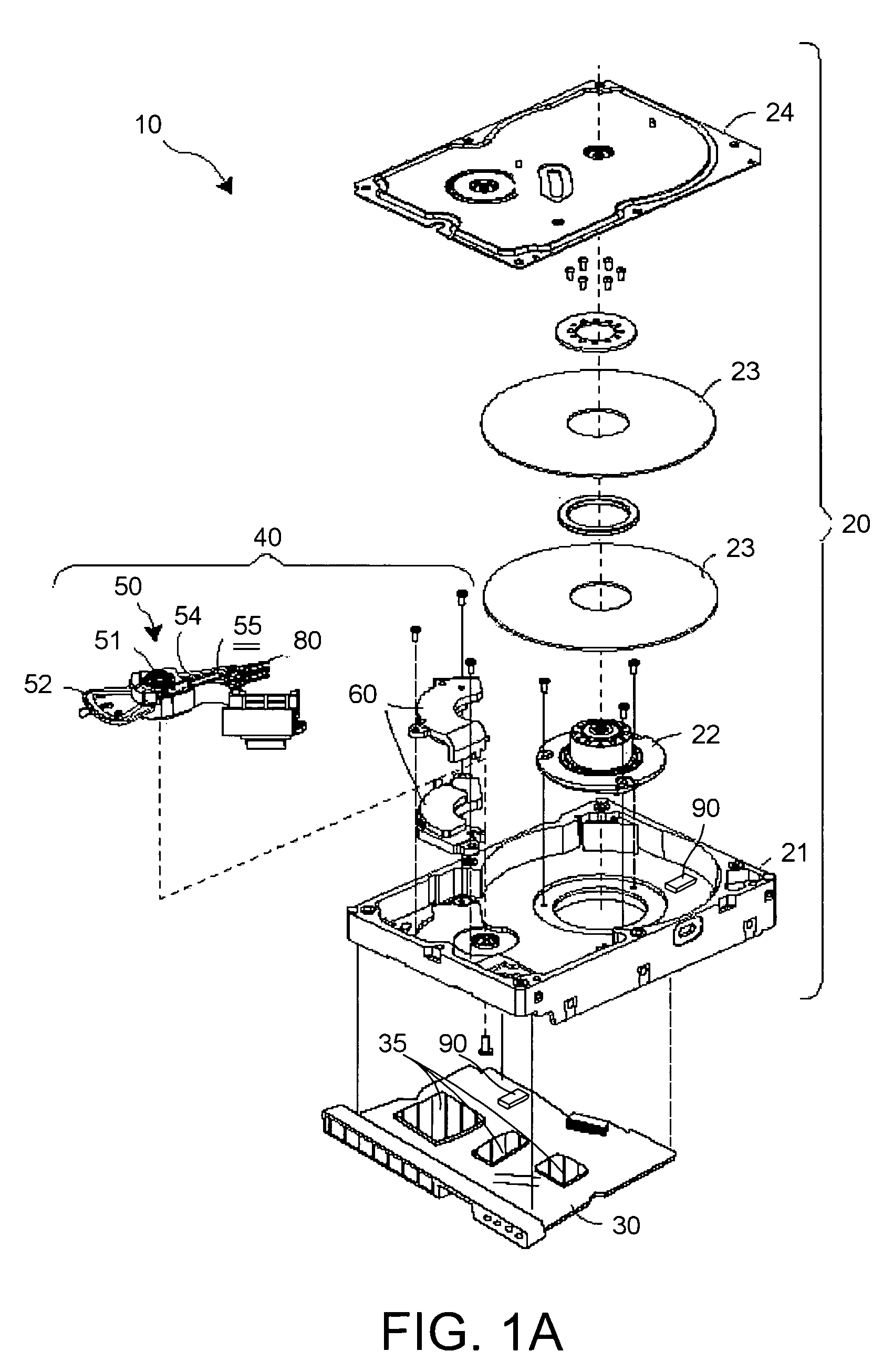
Acceleration disturbance detection subsystem for use with disk drives
ActiveUS7023640B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageDual functionAcceleration Unit
A disk drive comprising a first sensor mounted on a nominally stationary portion of the disk drive and adapted to detect acceleration disturbances of the disk drive. The disk drive further comprising: a dual-function subsystem having a first circuit adapted to provide a write-inhibit signal and a second circuit adapted to provide a feed-forward basis signal, the dual-function subsystem adapted to receive a first sensor signal from the first sensor and to provide (a) the write-inhibit signal based on the received first sensor signal and a first threshold value, and (b) the feed-forward basis signal based on the received first sensor signal.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
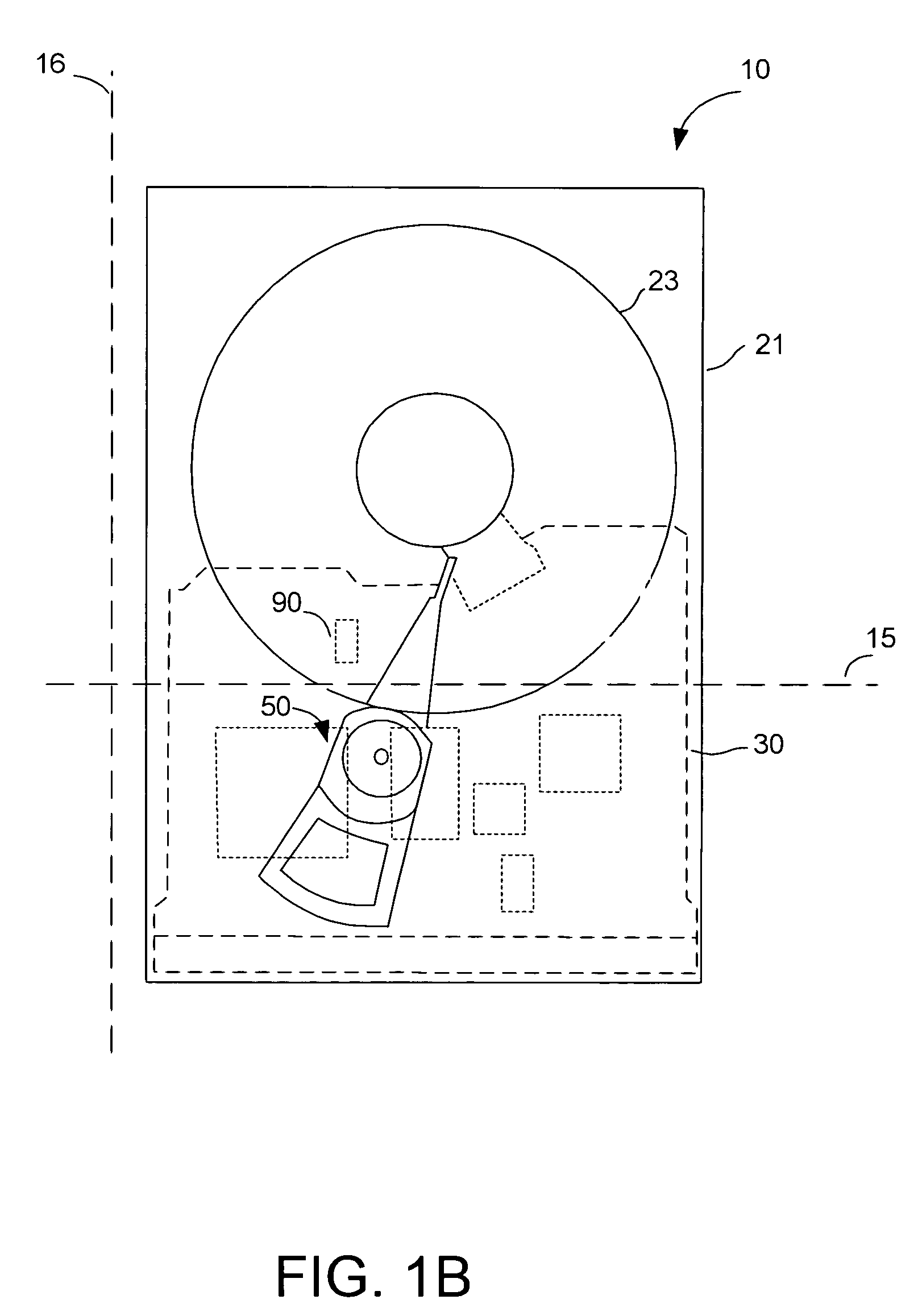
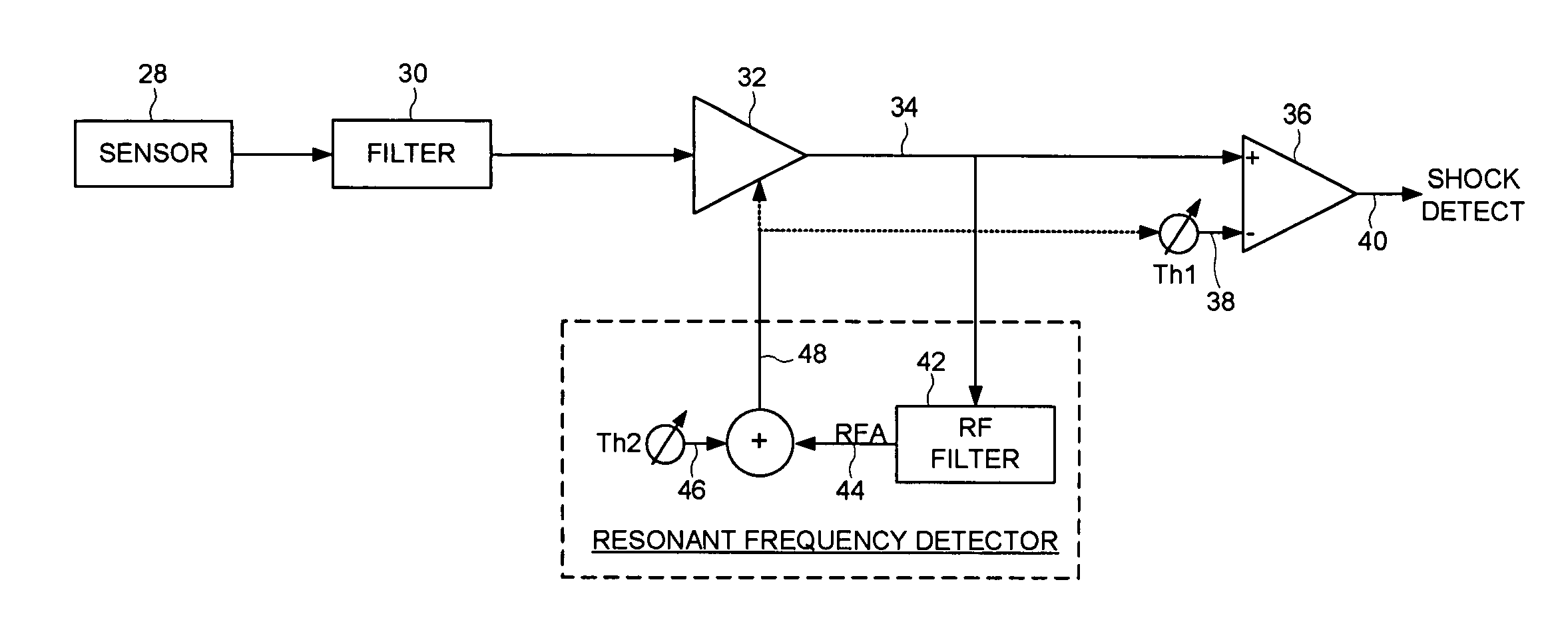
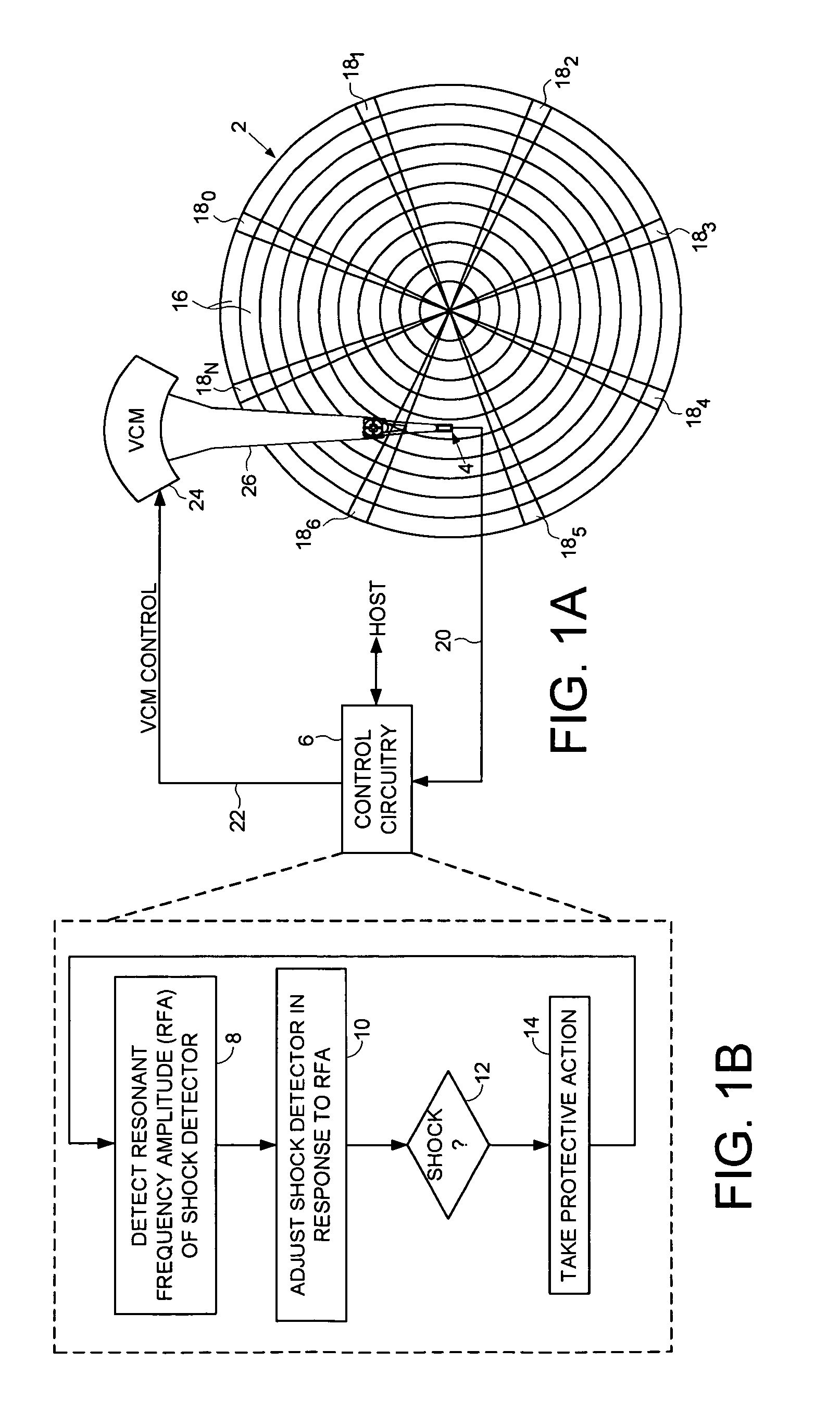
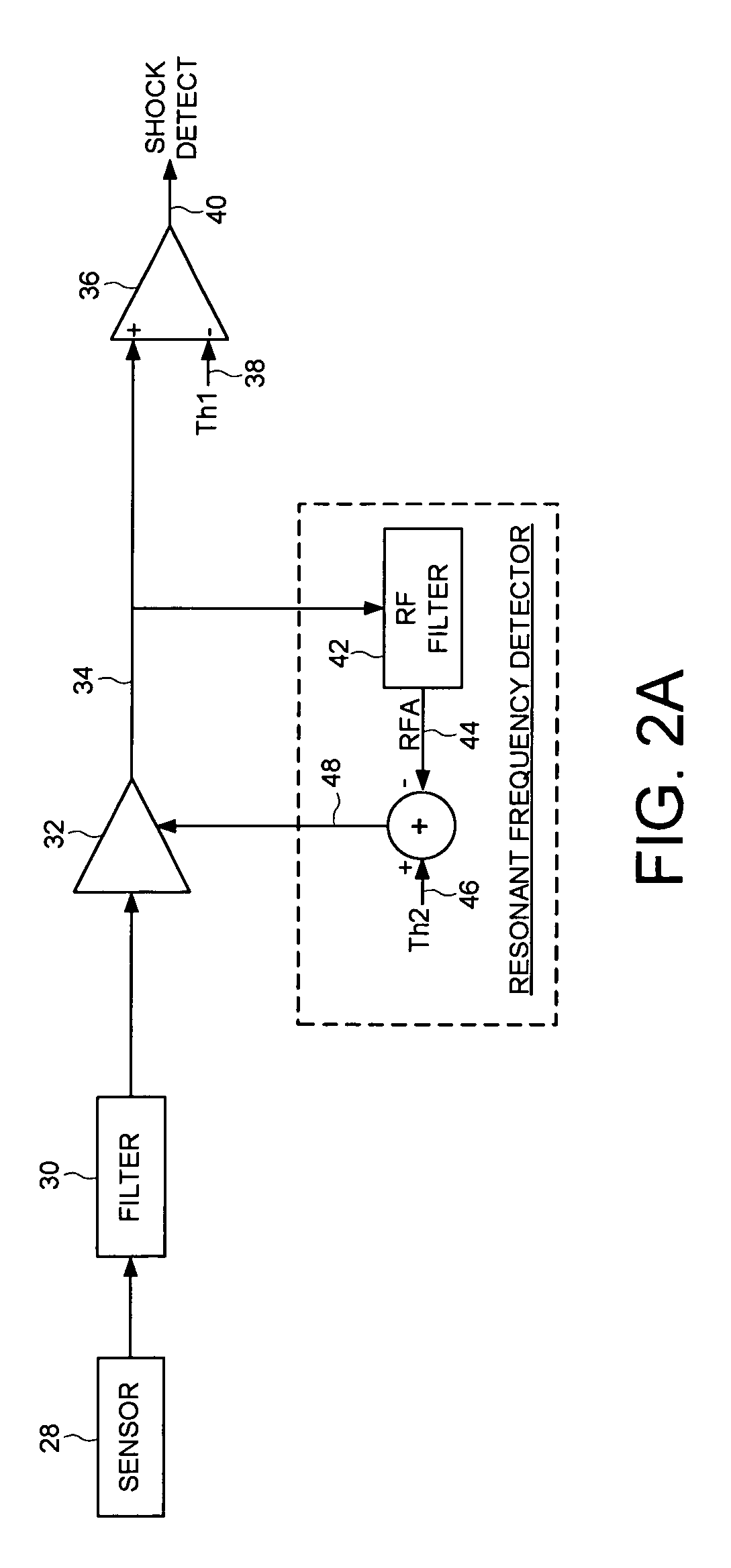
Disk drive adjusting gain of shock detector relative to resonant frequency amplitude
InactiveUS7852588B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageShock detectorControl theory
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a disk, a head actuated radially over the disk, and control circuitry including a shock detector. The control circuitry is operable to detect a resonant frequency amplitude (RFA) of the shock detector, adjust the shock detector in response to the RFA, and take protective action in response to the shock detector.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
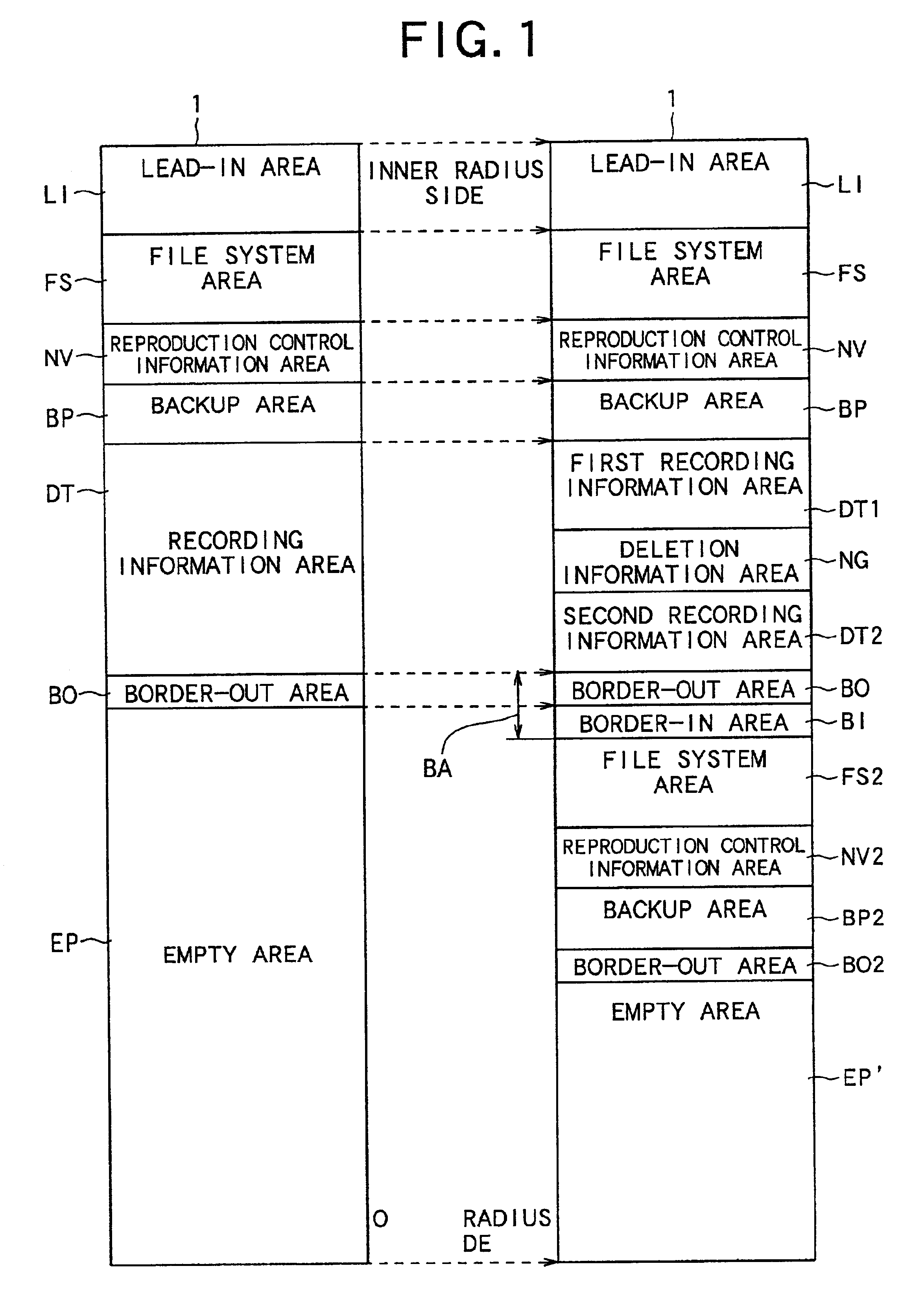
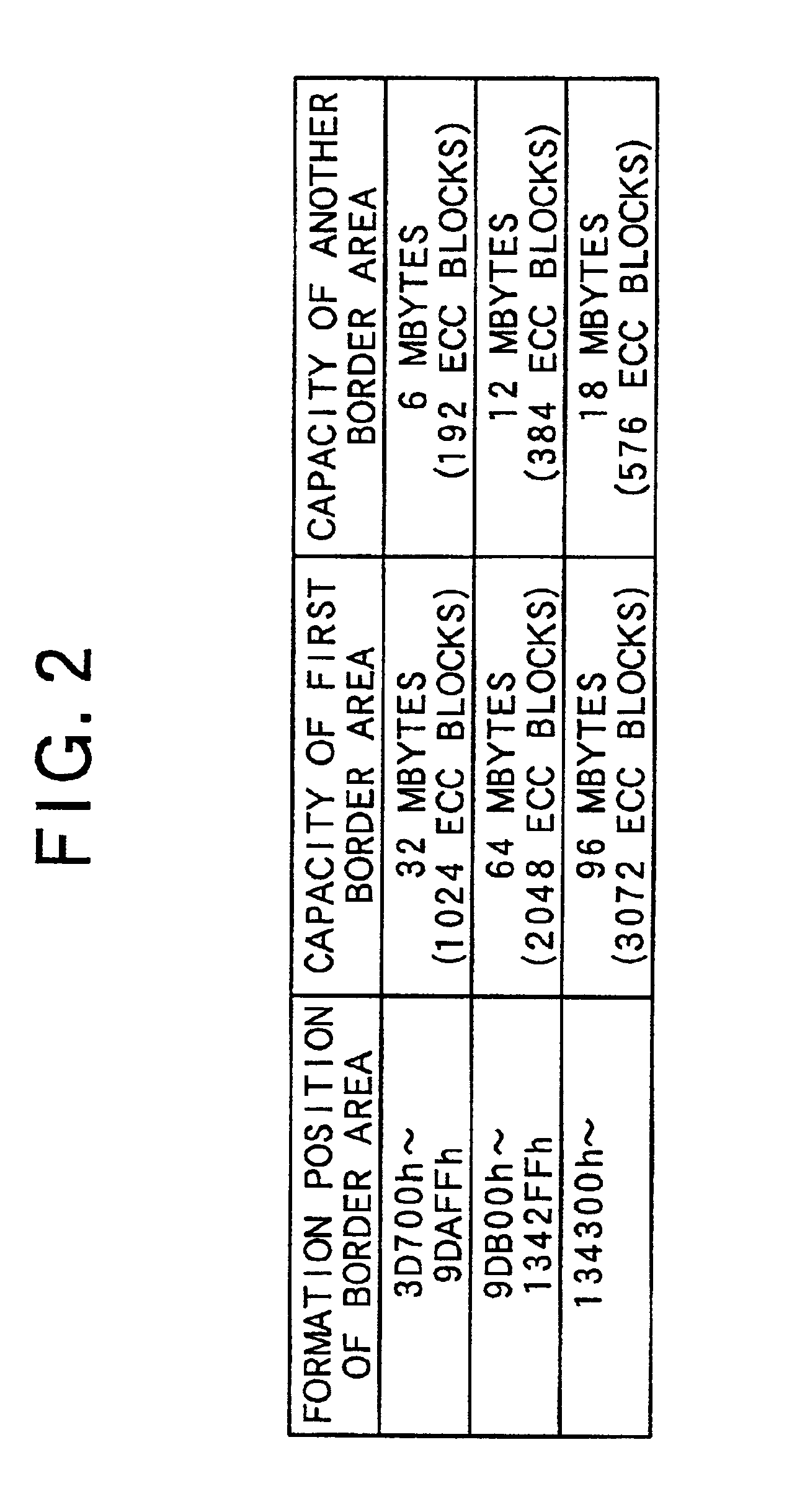
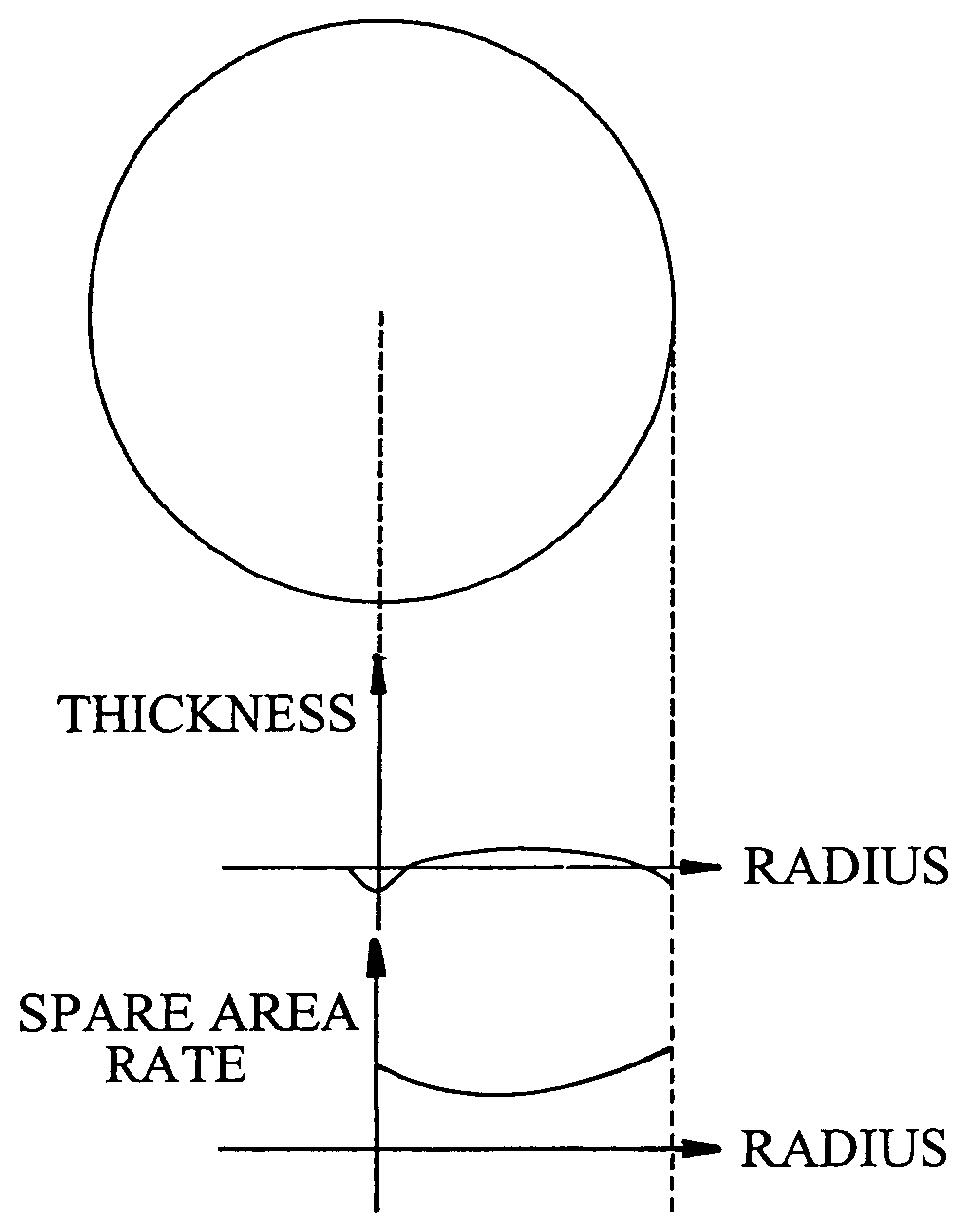
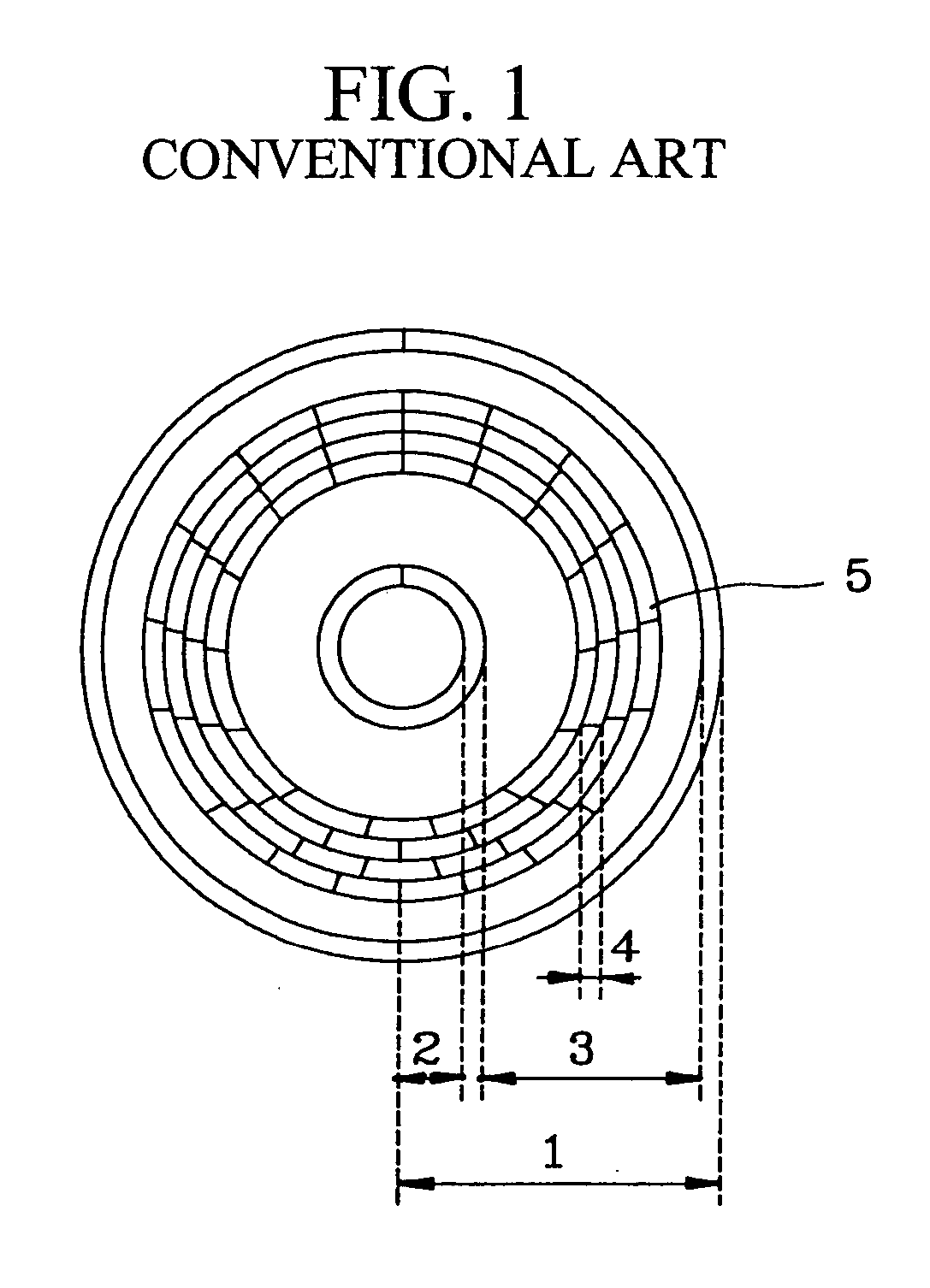
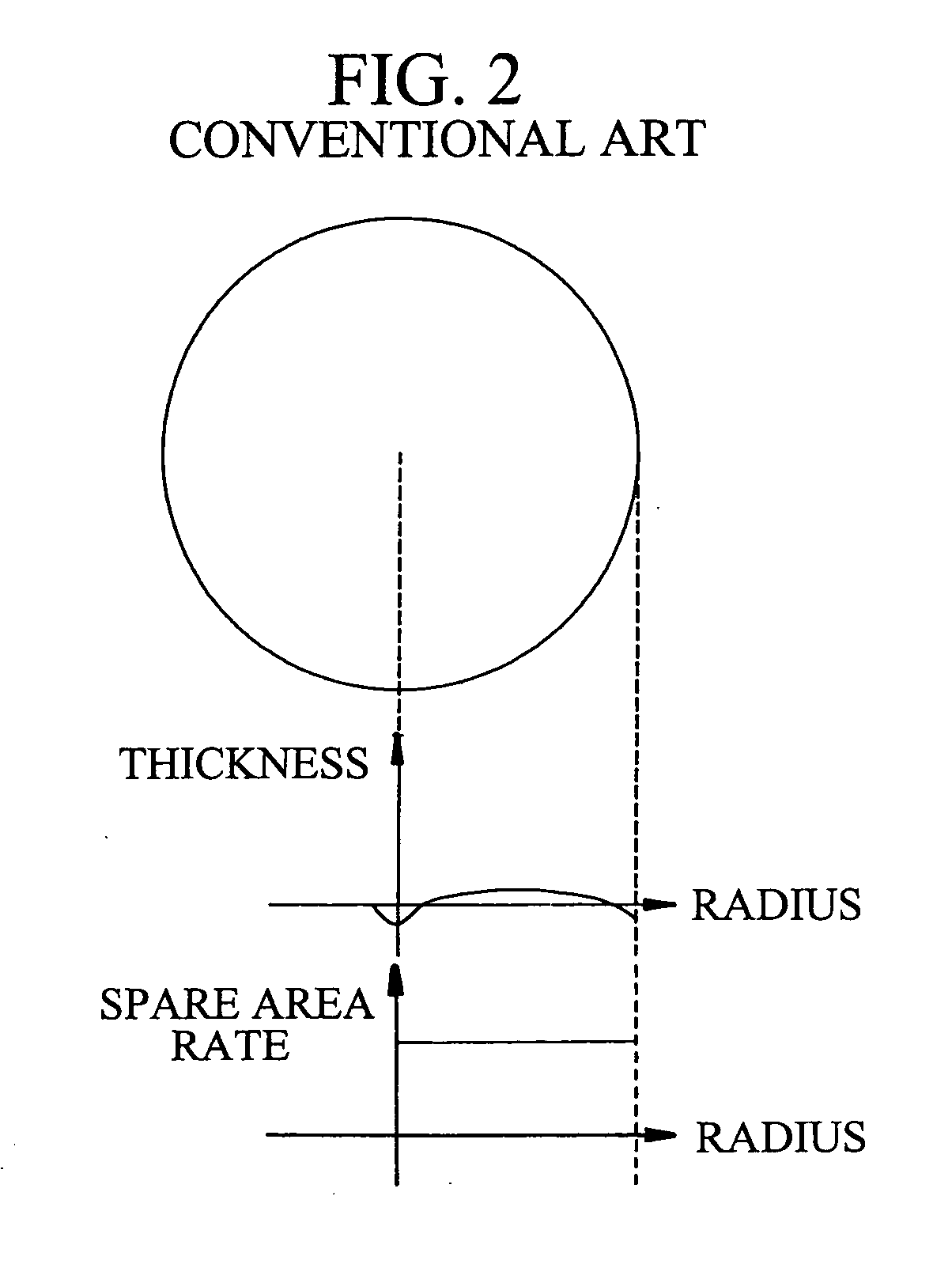
Optical disc having variable spare area rates and method for variably setting the rate of spare areas in the optical disc
InactiveUS20050068877A1Improve reliabilityTelevision system detailsDisc-shaped record carriersEngineeringOptical disc
In a method for setting variable areas of an opical disc which variably sets spare area rates of a prescribed quantity provided for preparing a liably-occurring recording error due to a defect of the optical disc having the variable spare areas, the total quantity of the spare areas installed to the optical disc may be the same as the prescribed quantity. Also, the size rates of the spare areas are variably set in the radius direction by centering about a center portion of the optical disc. Particularly, the more spare area rates are given to the inner circumferential portion and outer circumferential portion, and the less spare area rates are given to the center portion which is relatively stable portion, thereby minimizing the defect occurring rate to decrease the number of defective discs.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
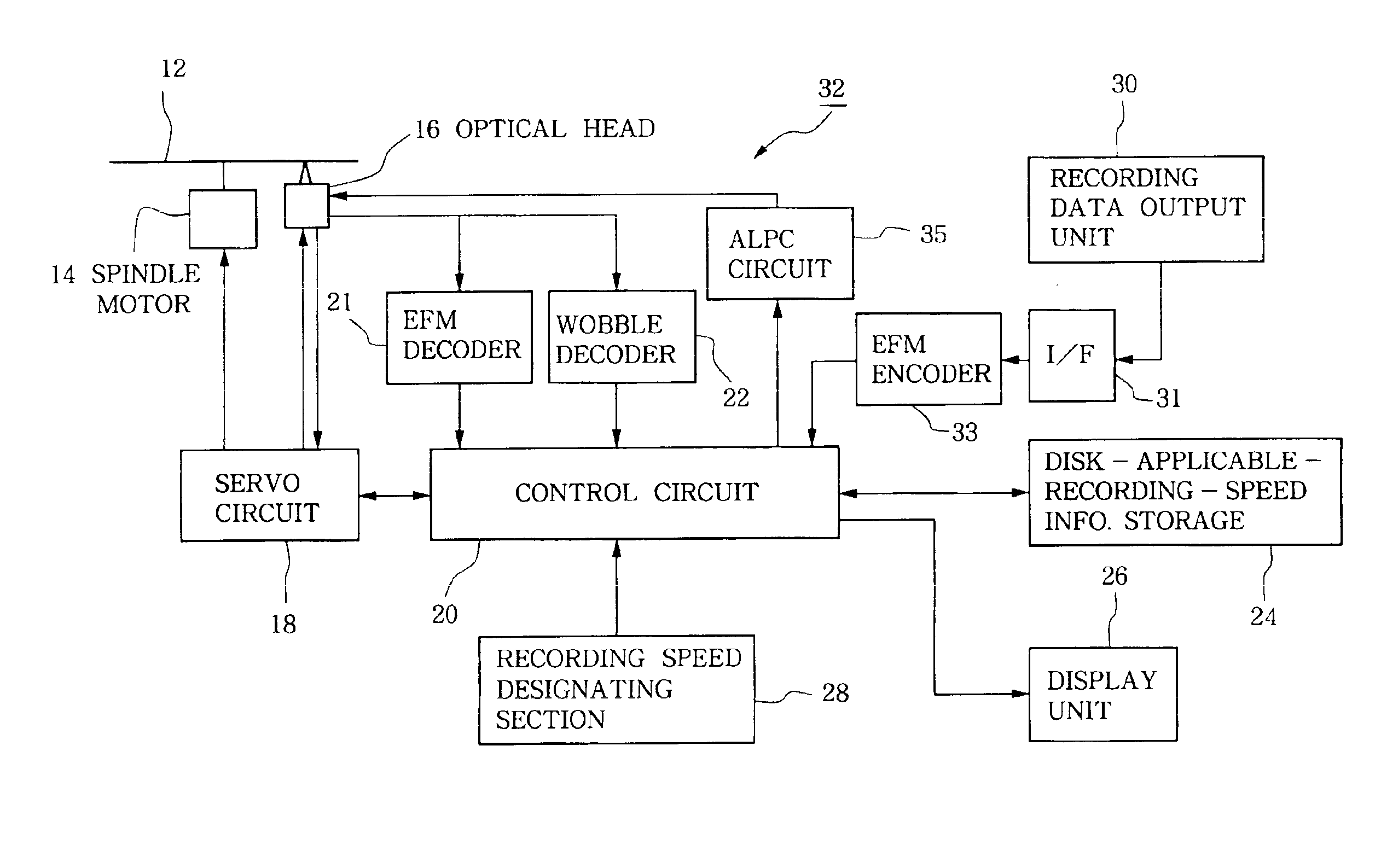
Recordable optical disk and optical disk recording device utilizing pre-recorded recording speed information
InactiveUS6894961B1Error minimizationRecord information storageDigital recordingTime informationStart time
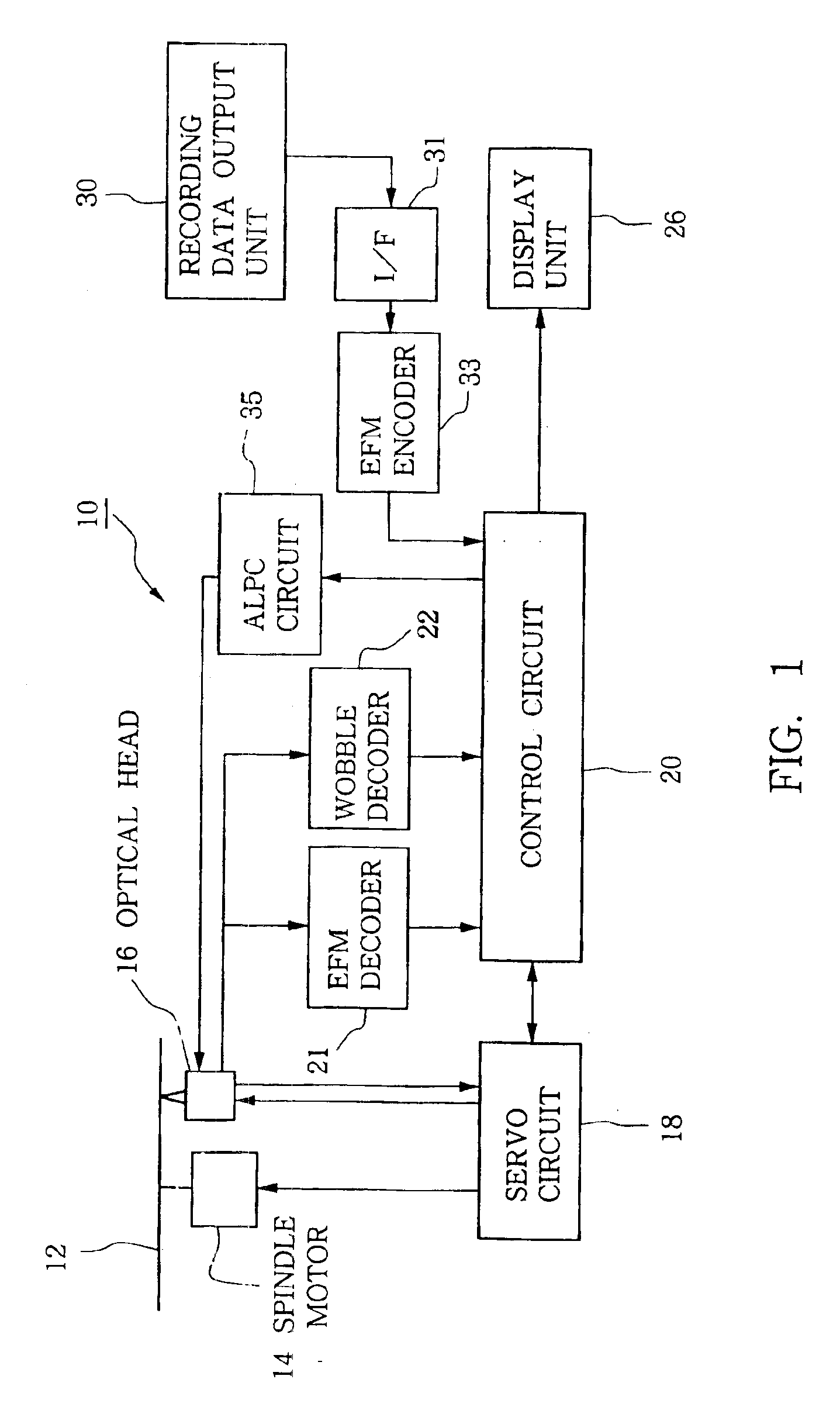
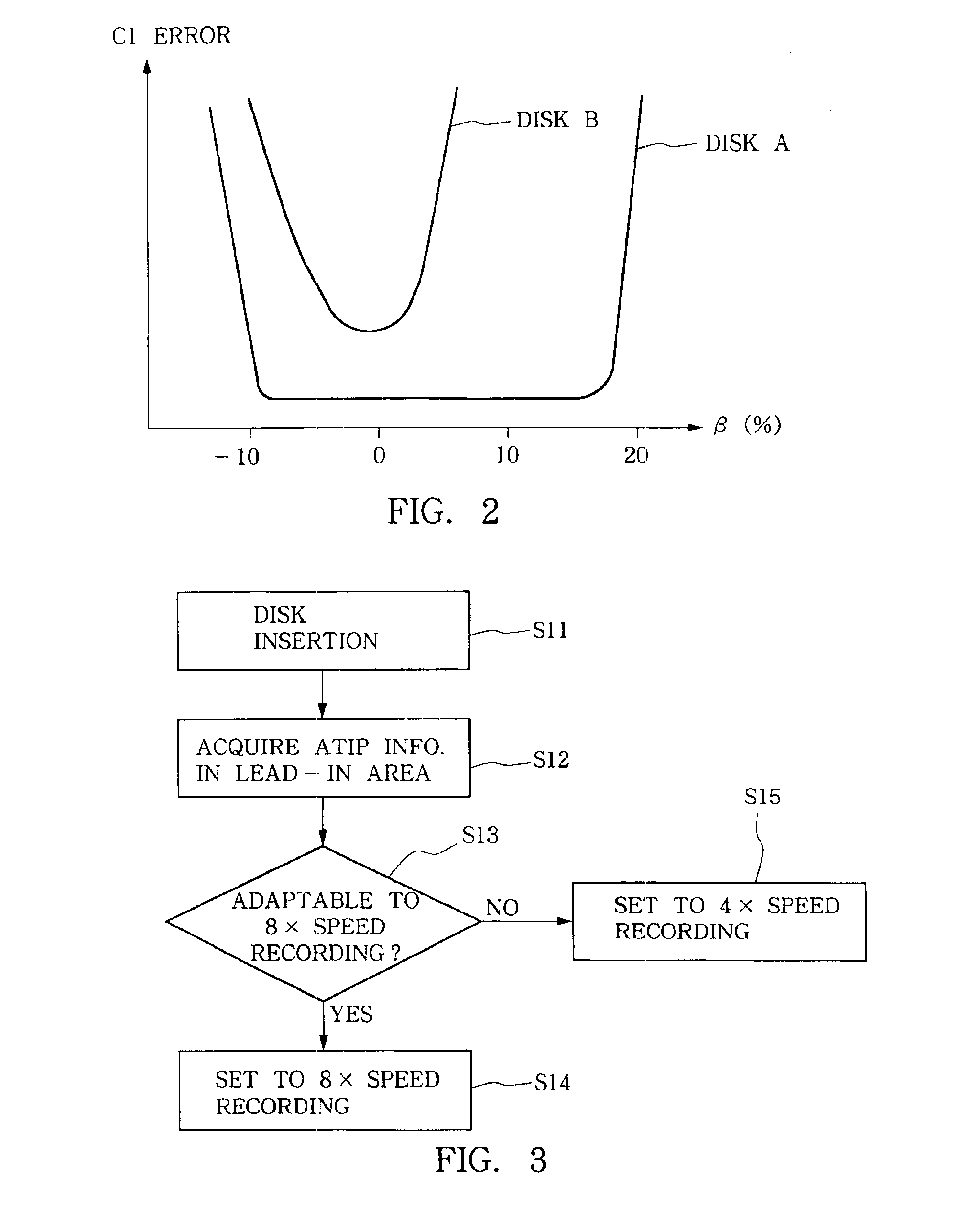
Information indicative of disk-applicable recording speeds is incorporated in lead-out start time information within ATIP information that is recorded in pre-grooves located in a lead-in area of an optical disk. Once the optical disk is inserted in an optical disk recording device, the lead-out start time information is read out, so that recording is performed on the optical disk after a recording speed is automatically set to a highest settable speed value within a range specified by the read-out lead-out start time information. This arrangement can reliably prevent recording at speeds beyond predetermined limit values unique to the optical disk.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Disk unit and information processing apparatus
InactiveUS6867939B2Improve the operating environmentNot easily affectedApparatus for flat record carriersRecord information storageInformation processingEngineering
A disk unit, such as a magnetic disk unit, has a temperature sensor, a humidity sensor, a heater, a Peltier element, etc. The disk unit heats and cools in accordance with temperature and humidity. The disk unit has a double-structure of outline comprising a first outline and a second outline surrounding said first outline, so that an internal environment is isolated from an external environment.
Owner:TOSHIBA STORAGE DEVICE CORP
Test carriers for storage devices
InactiveUS7646596B2Weather/light/corrosion resistanceDigital data processing detailsElectrical and Electronics engineeringEngineering
Owner:INNOVATIVE POLYMERS PTE
Optical disc, information playback apparatus, information playback method, and information recording method
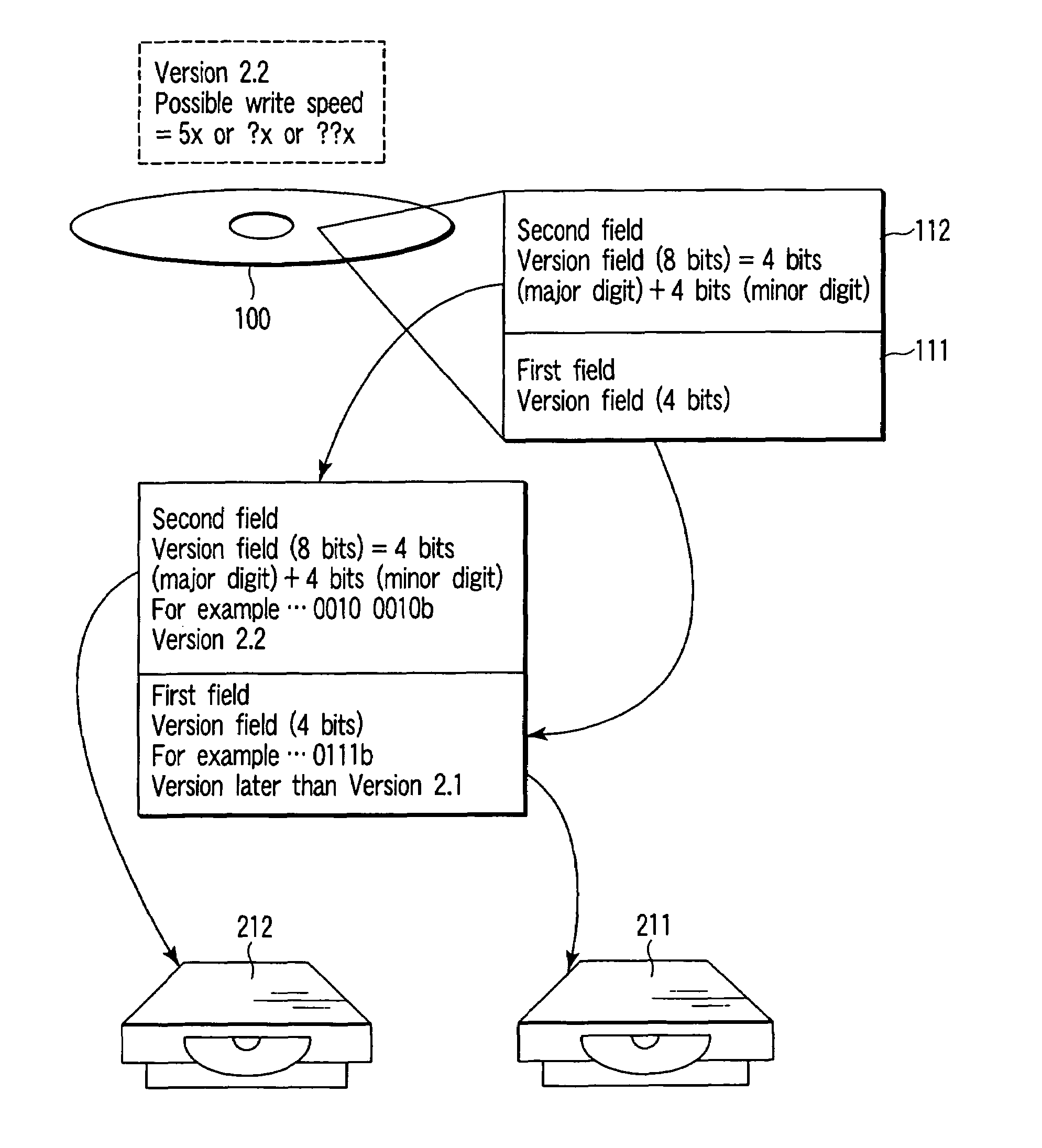
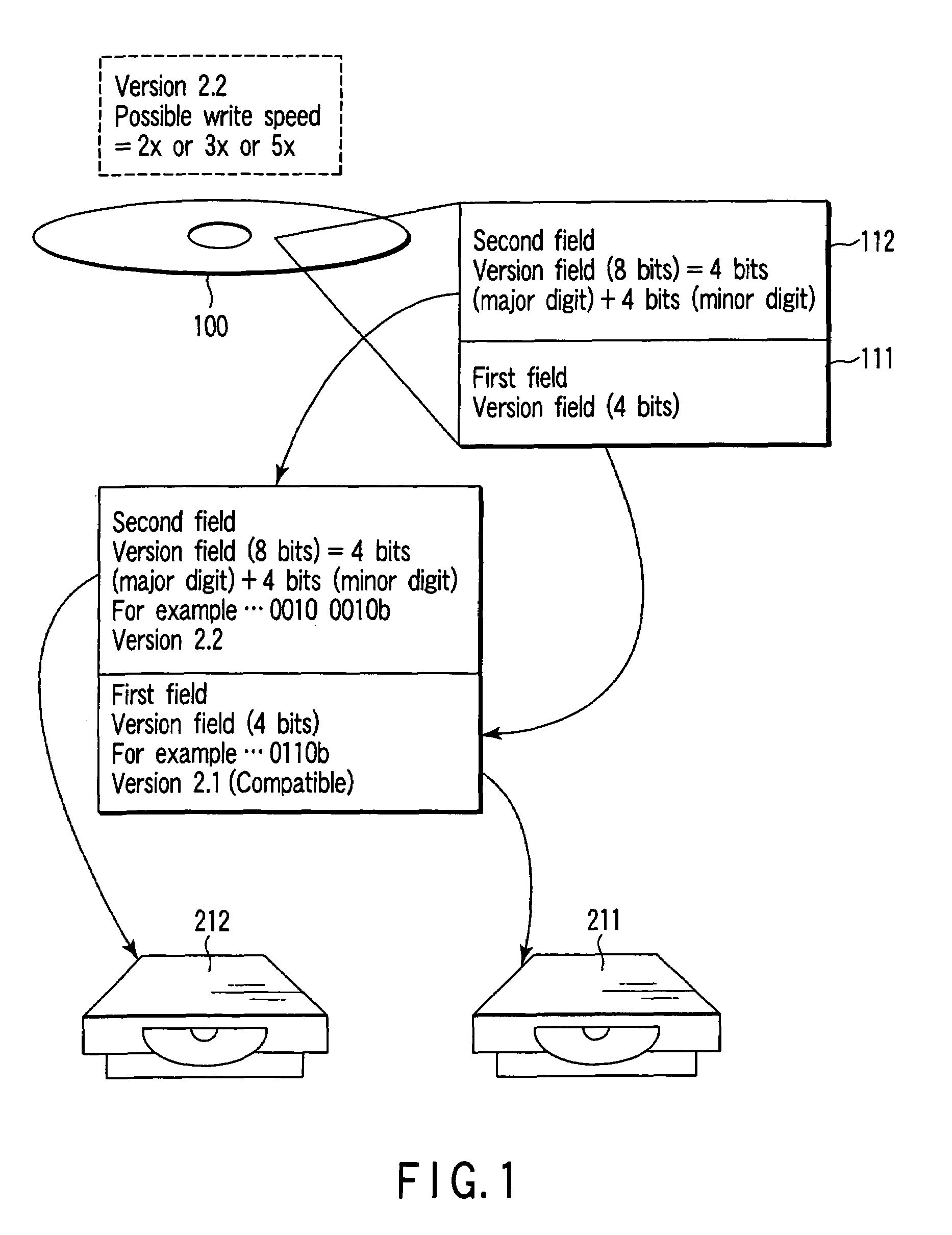
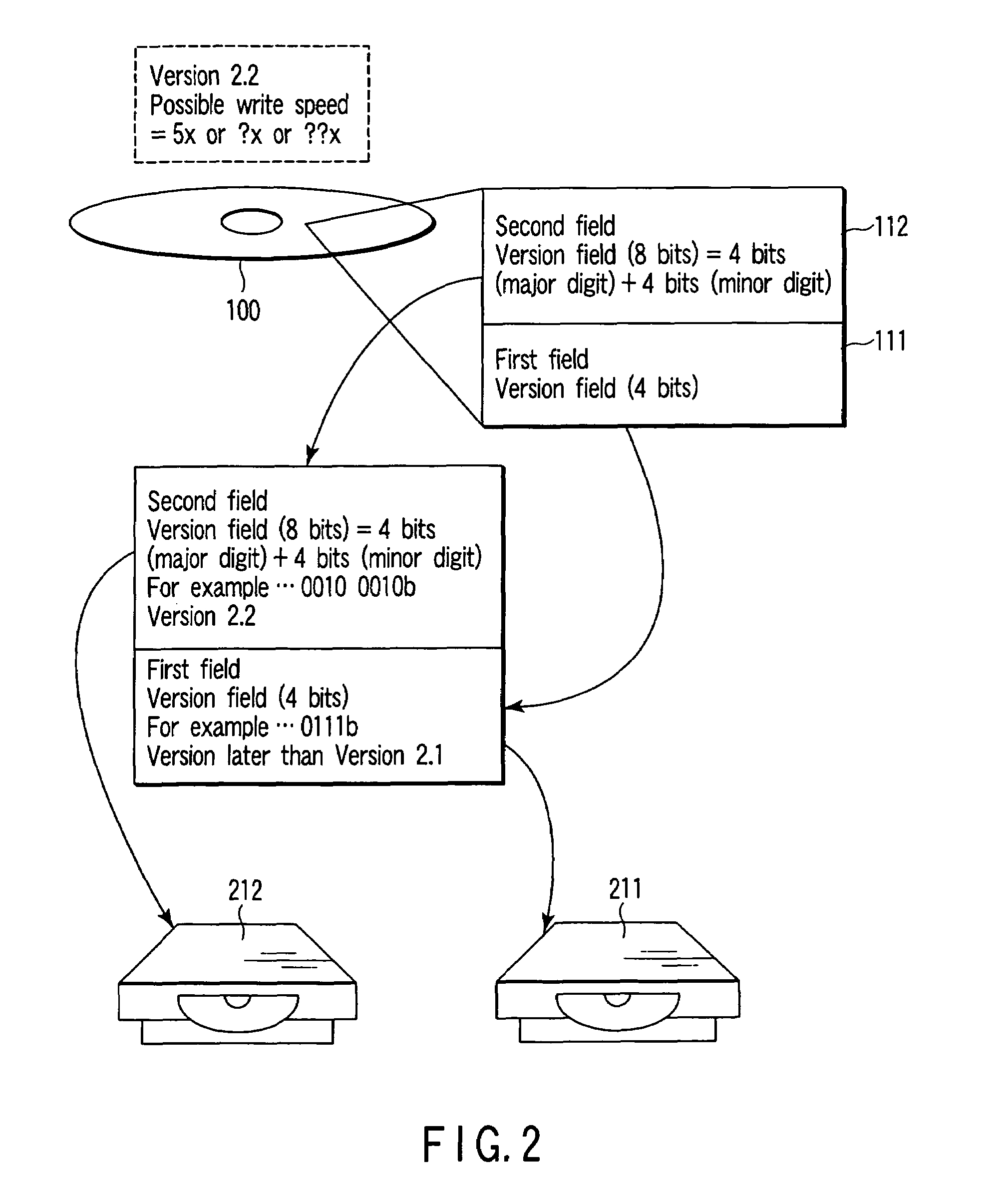
An optical disc according to one aspect of this invention has a first field to record first version information, and a second field to record second version information obtained by updating the first version information.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
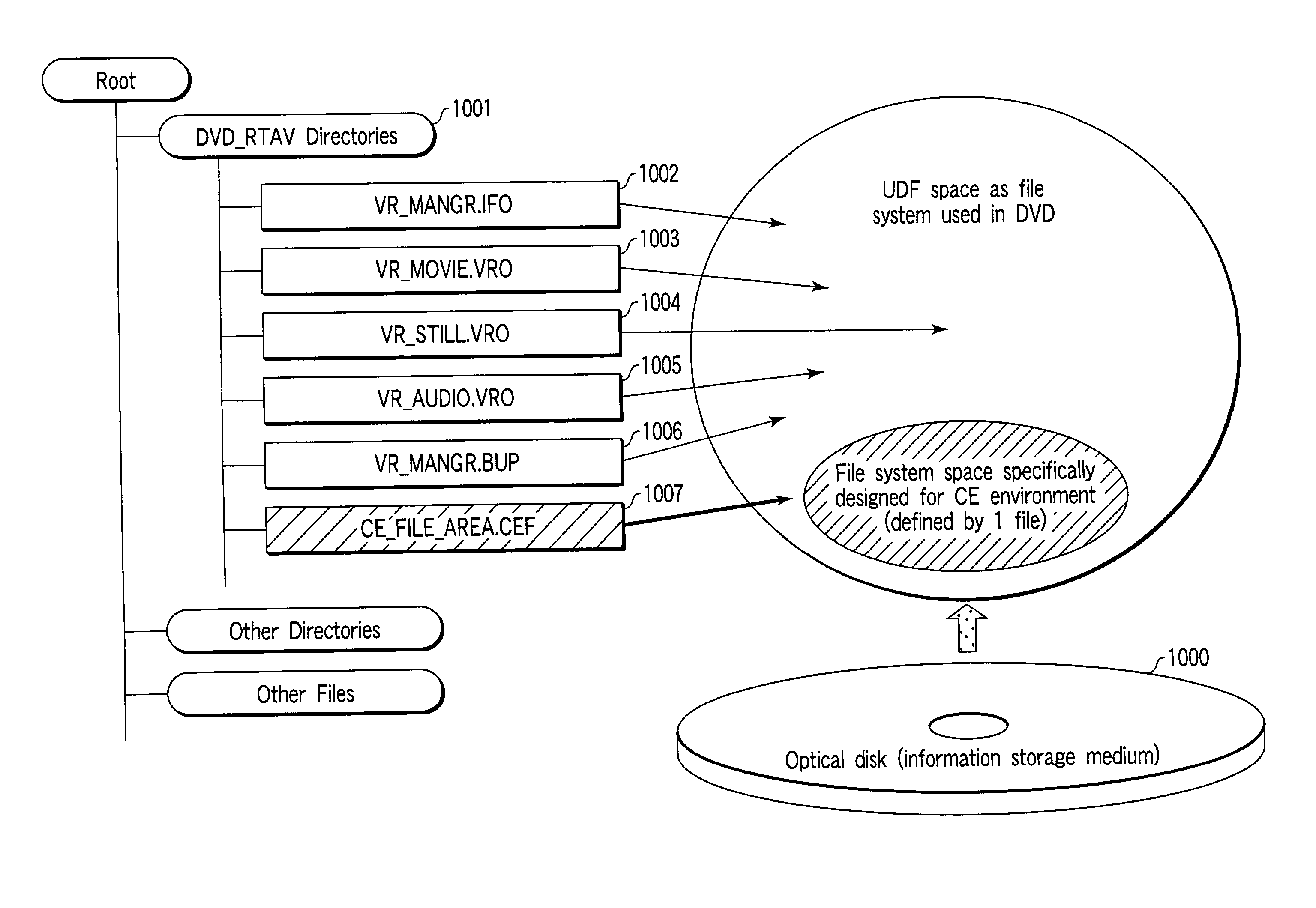
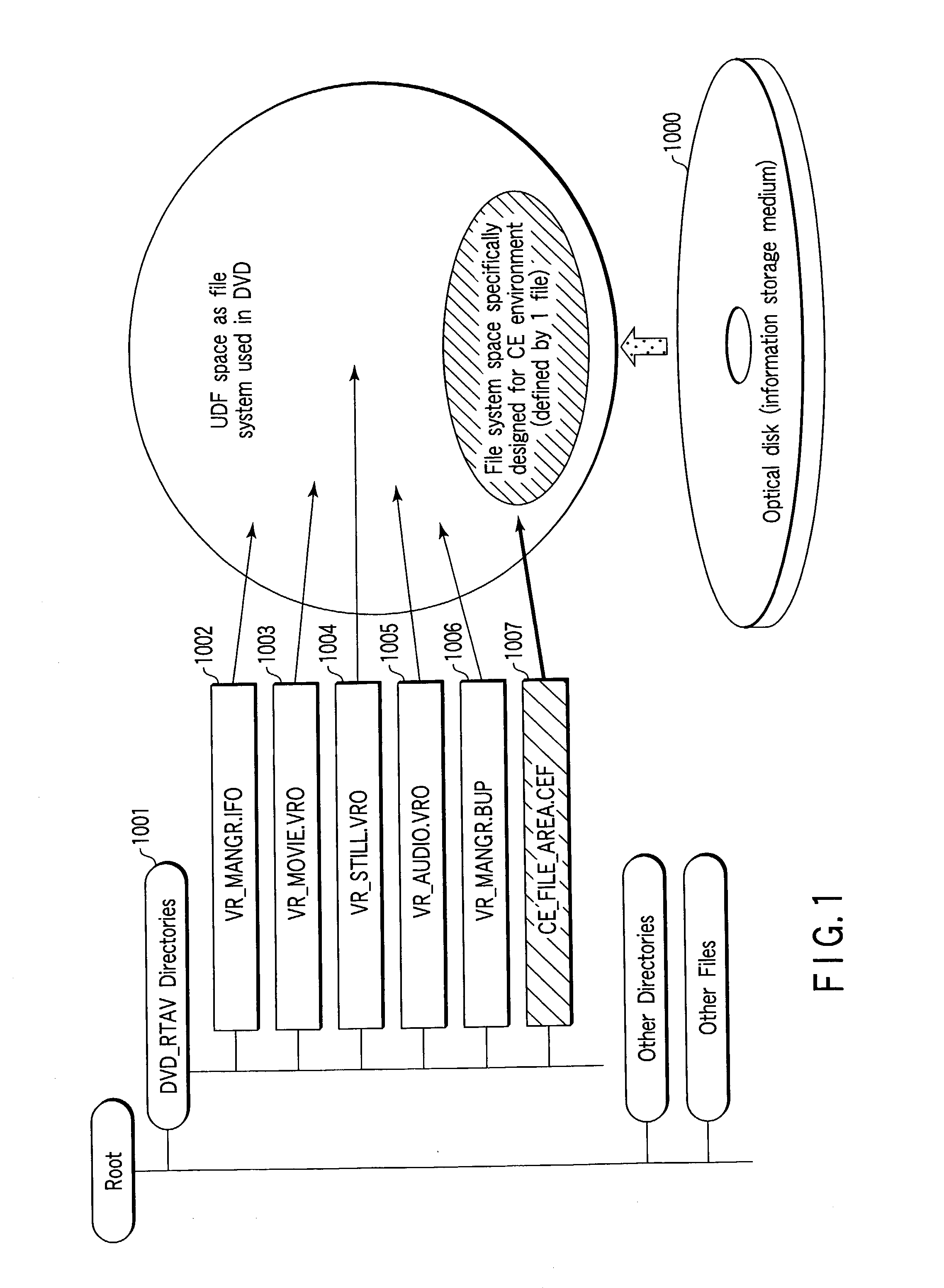
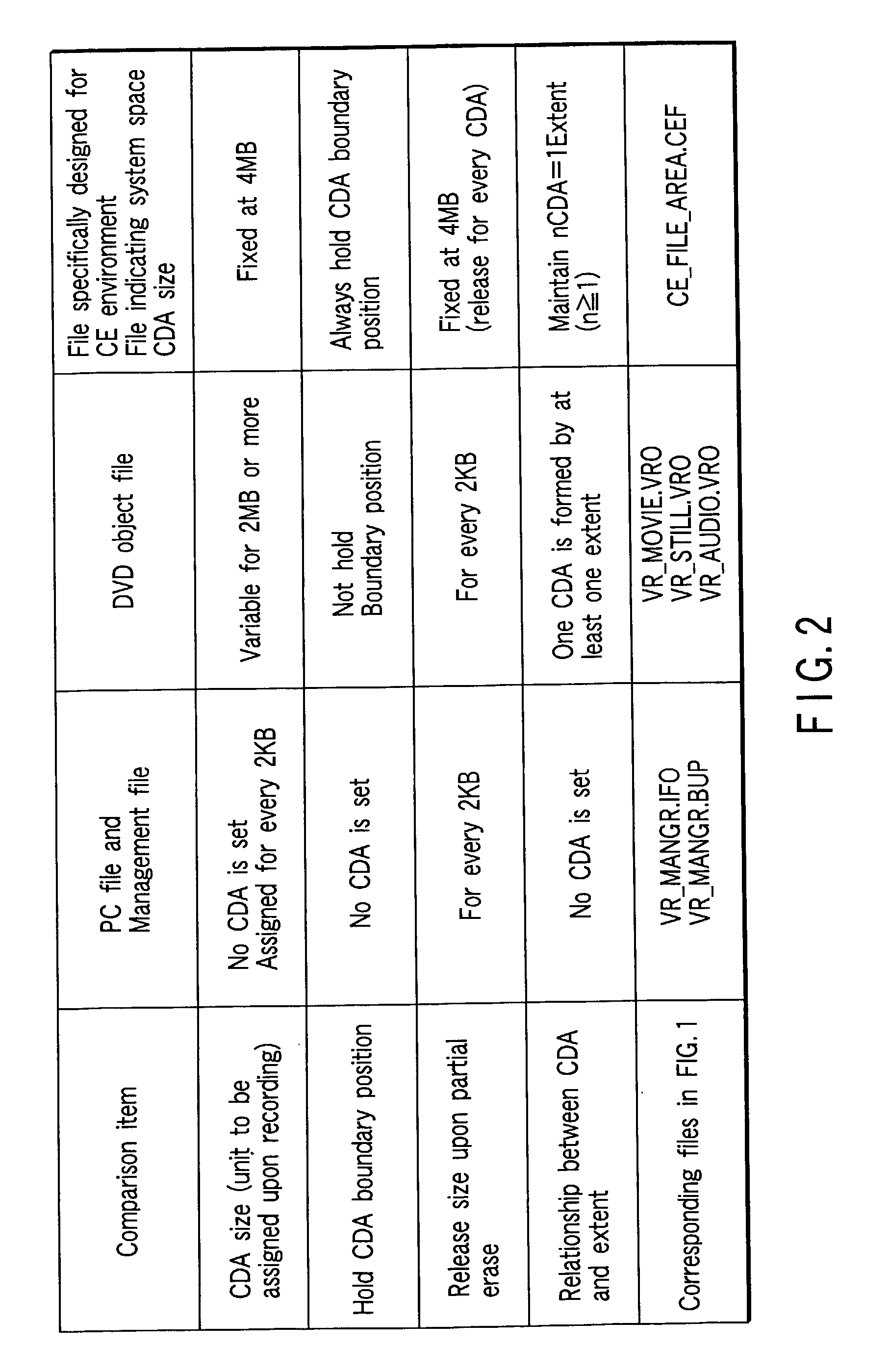
Information storage medium and information recording method
An information storage medium has a logical space managed by a first file system, and the logical space has a space for storing a file used to designate a space area of a second file system, which is different from the first file system.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Limited use DVD-video disc
InactiveUS20030081521A1Efficient interfaceCombination recordingAccessories for indicating/preventing prior/unwanted useOptical propertyTime segment
A limited-use Digital Versatile Disc (DVD) includes a storage layer for storing content data and control key data. At least one mark of photosensitive dye is disposed on the disc exterior to the storage layer and over at least a portion of the control key data. In one embodiment, the mark is initially transparent to allow a DVD player to read the control key data. The mark changes from clear to become opaque when it is exposed to DVD reader laser light for a cumulative period of time. This change in the optical property of the mark and the configuration of the control key data prevents further reading of the content data after predetermined reading and playback usage of at least some of the content data is permitted. In another embodiment, the mark is initially opaque to initially prevent the successful reading of the control key data, and permanently changes to transparent when exposed to DVD reader laser light for a cumulative period of time.
Owner:NOW SHOWING ENTERTAINMENT
Method of recording or reproducing data on or from high density multi-layer recording medium using variable light intensity
InactiveUS7009927B2Diminishing of dataDiminishing of surfaceOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageHigh densityData recording
A high-density optical recording medium and method of recording data on the optical recording medium. The optical recording medium includes a plurality of data recording / reproducing surfaces having reflectances for light passing through a pit area, a land / groove area, and a land / groove area on which data are recorded, of a data recording / reproducing surface included between a light source for emitting light and a recording / reproducing surface selected from the plurality of data recording / reproducing surfaces, the reflectances satisfy the expressions r1≧r2≧r3 and {(r1−r3) / r3}≦0.2, where r1, r2 and r3 are the reflectances of the pit area, the land / groove area and the land groove area on which data are recorded, respectively.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Device and method for providing data exchange and storage
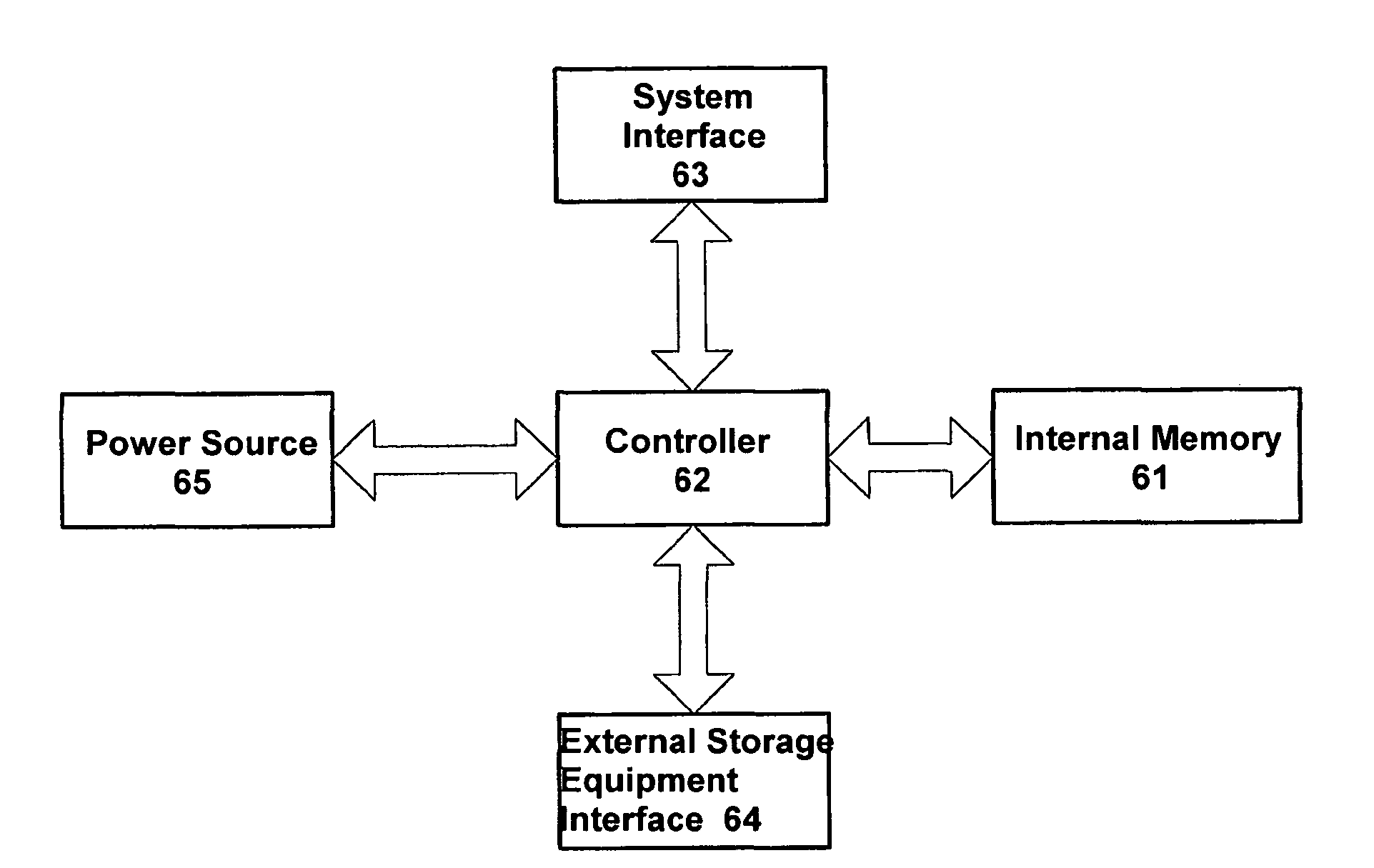
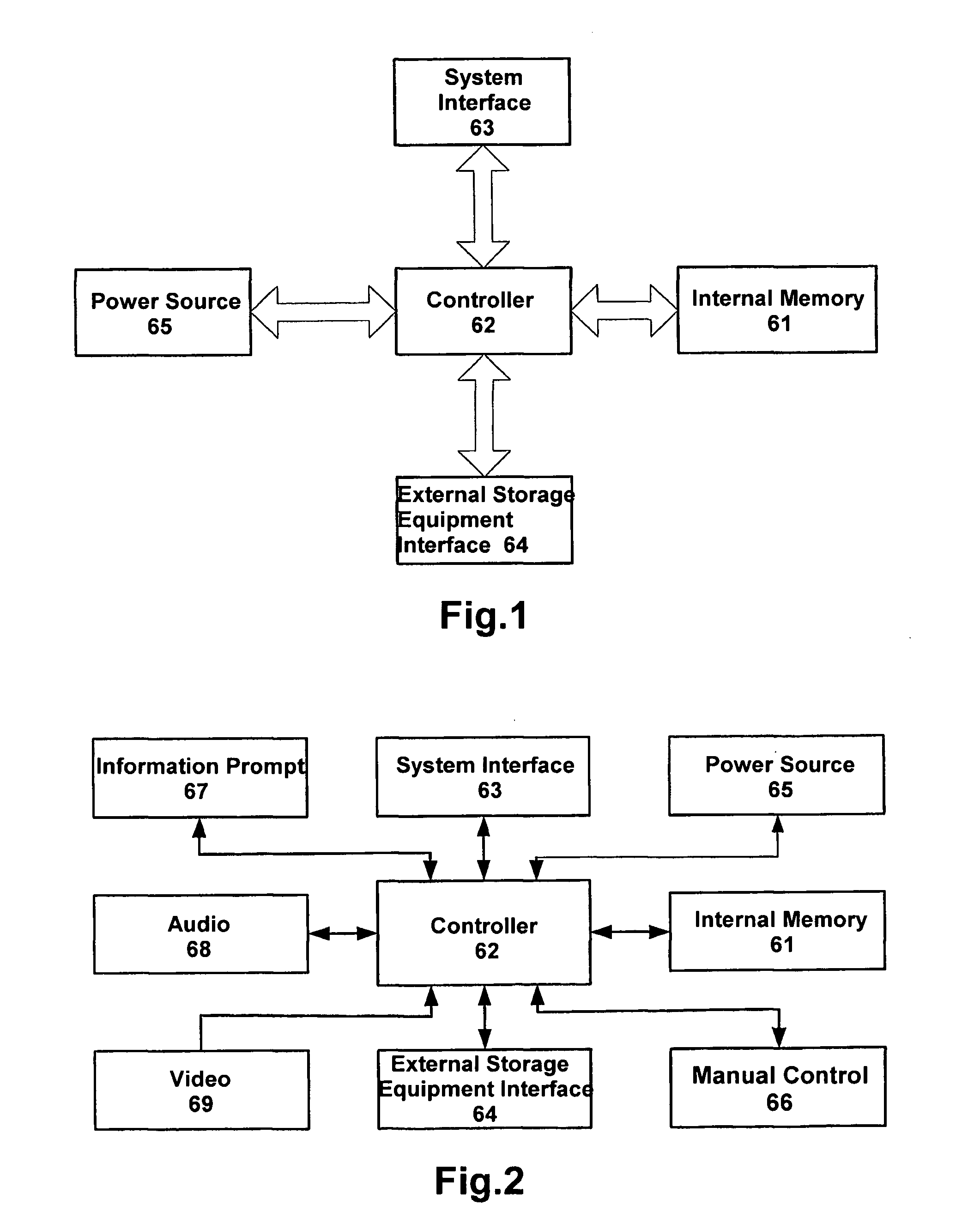
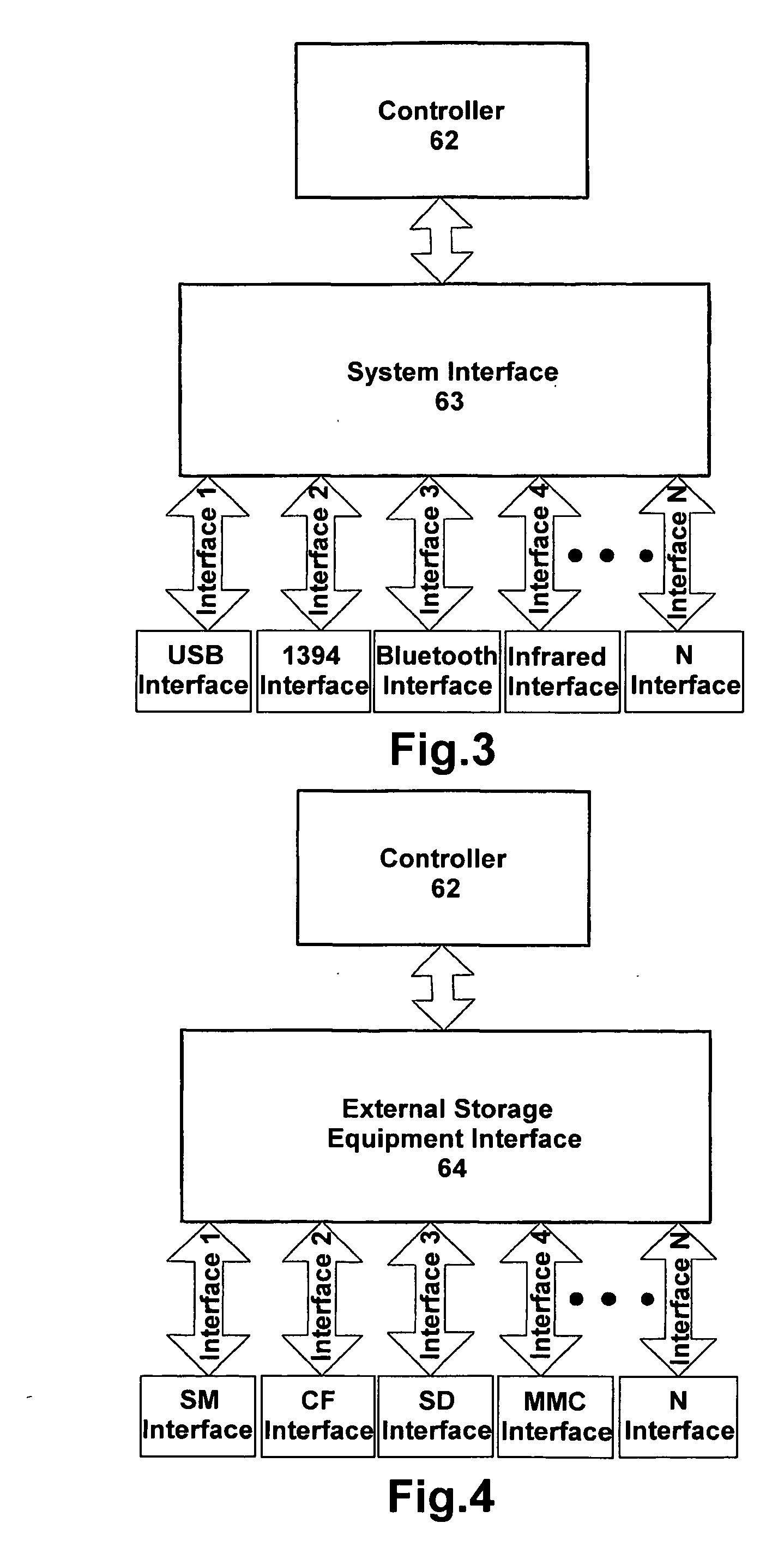
ActiveUS20050216624A1Input/output to record carriersAccidental erasing/double-recording preventionInternal memoryData processing system
The invention relates to a device and method for providing data exchange and storage. The device comprises a controller module (62) which includes a firmware for controlling operation of each modules in the data exchange and storage device (60) and performing data processing and information exchange; and an internal memory module (61) for storing data under the control of the controller module (62); a system interface (63) module for connecting with the system interface and performing data exchange with the data processing system (10) under control of the controller module (62); and an external storage interface module (64) for connecting with external storage equipment and performing data exchange with the external storage equipment under control of the controller module (62). The device can accomplish connection with the data processing system of various types of interfaces and external storage equipment of various types of interfaces. The device can also implement functions that the data processing system access to the interior storage module and the external storage equipment. Thus, the device of this invention is called user's personal moveable storage center.
Owner:NETAK TECH KO LTD
Disk drive with nonvolatile memory having multiple modes of operation
InactiveUS7411757B2Improve throughputPenalty is avoidedMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTOperation modeMultiple modes
A hybrid disk drive, i.e., a disk drive with two types of permanent storage media (conventional disk media and nonvolatile memory, such as flash memory), uses its nonvolatile memory in operational modes other than the power-save or “standby” mode wherein the disks are spun down. In a first additional mode, called a “performance” mode, one or more blocks of write data are destaged from volatile memory (the disk drive's write cache) and written to the disk and simultaneously one or more data blocks of write data are destaged from the volatile memory and written to the nonvolatile memory. In a second additional mode, called a “harsh-environment” mode, the disk drive includes one or more environmental sensors, such as temperature and humidity sensors, and the nonvolatile memory temporarily replaces the disks as the permanent storage media. In a third additional mode, called a “write-inhibit” mode, the disk drive includes one or more write-inhibit detectors, such as a shock sensor for detecting disturbances and vibrations to the disk drive. In write-inhibit mode, if the write-inhibit signal is on then the write data is written from the volatile memory to the nonvolatile memory instead of to the disks.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
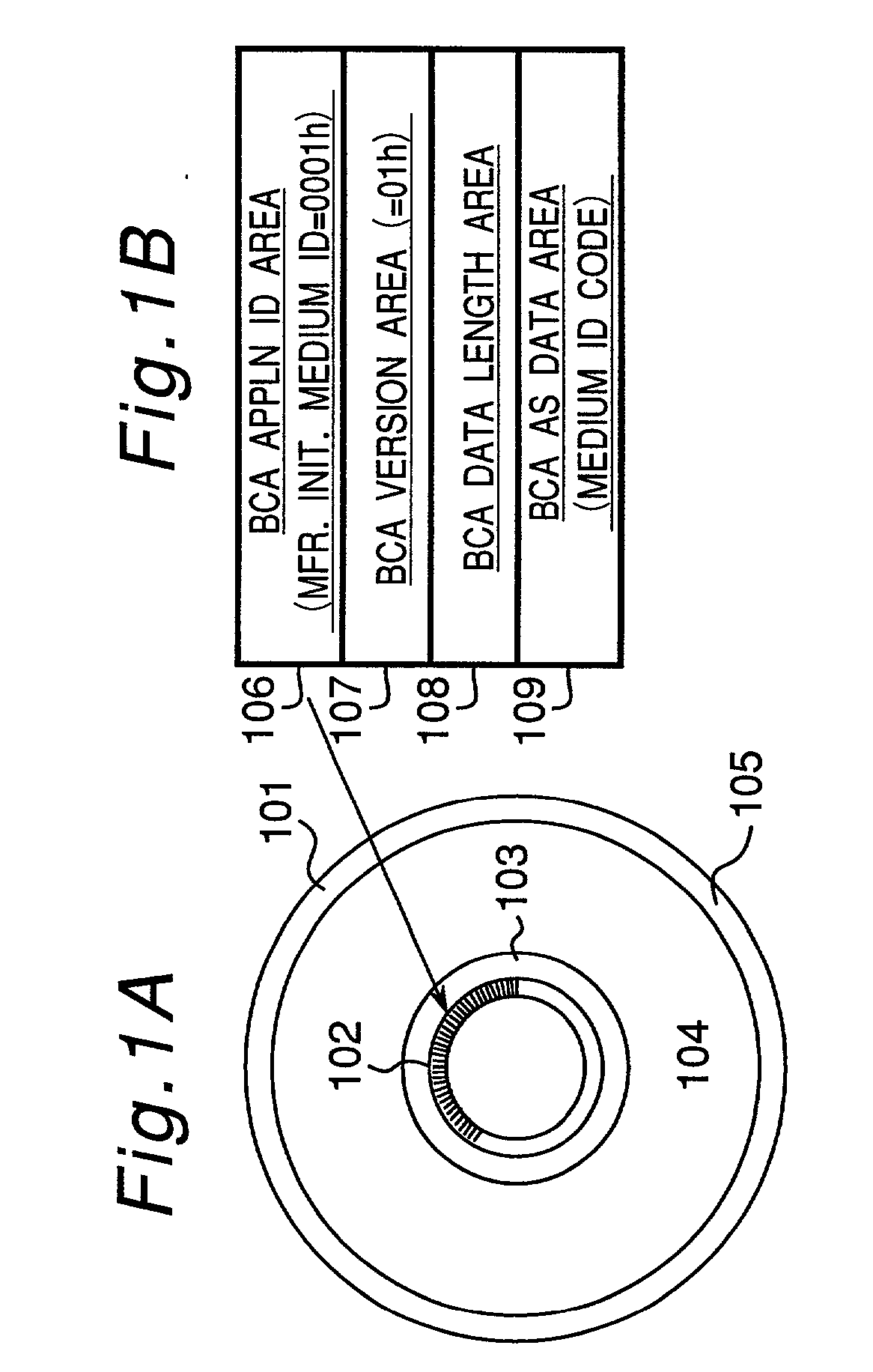
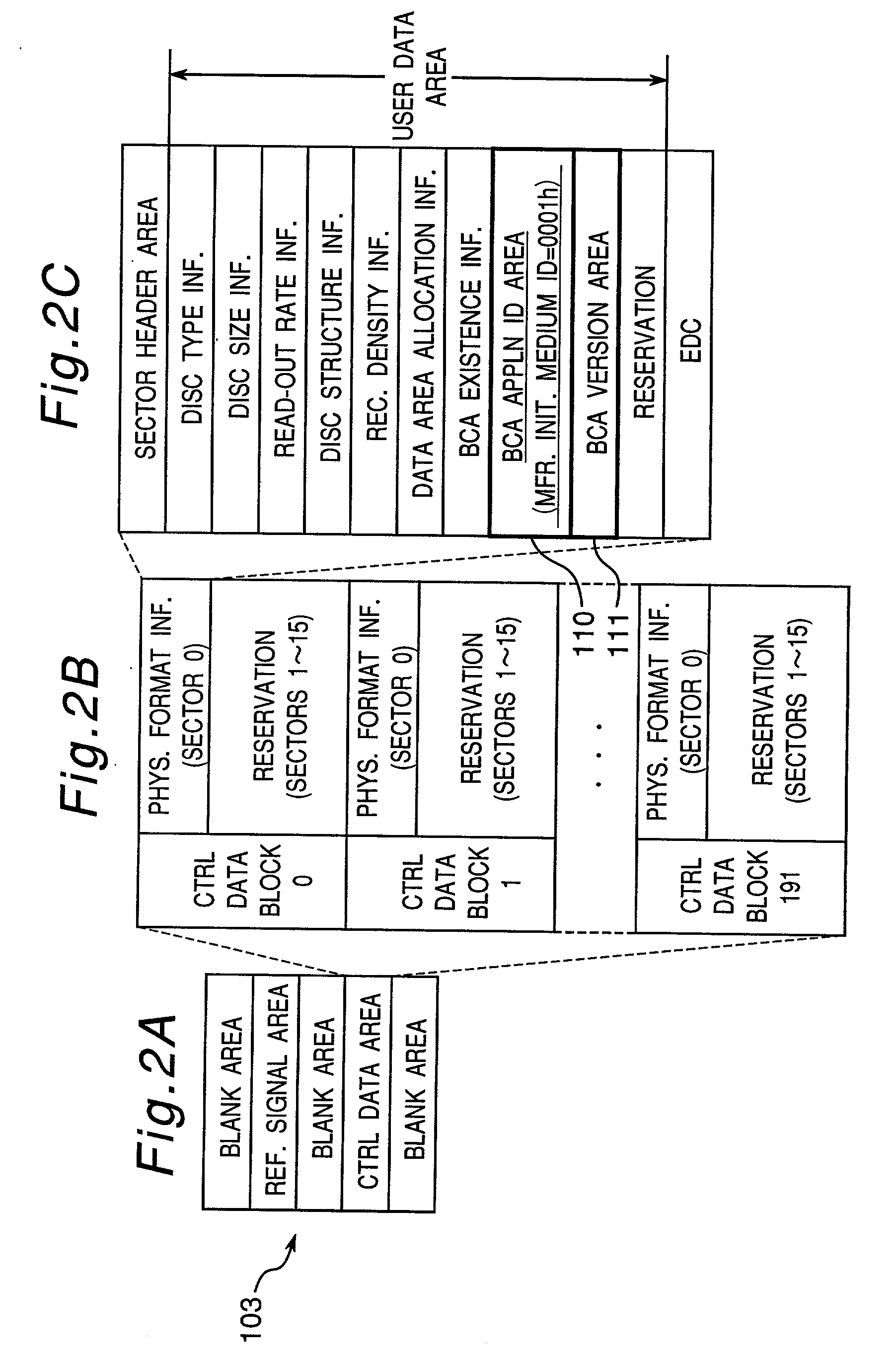
Information recording disc and information reproducing system
InactiveUS20010007545A1Method securityAccessories for indicating/preventing prior/unwanted useRecord information storageControl dataApplication specific
An information recording disc having a burst cutting area (BCA) for recording control information for a reproducing apparatus by removing a reflective layer of the disc in a striped shape and a data recording area for recording user data, wherein the burst cutting area includes at least one BCA control information area and the BCA control information area comprises: an application identifier area for identifying applications of control data; a data length area for indicating data length of the control data; and an application specific data area for recording the control data, and an information reproducing drive for reproducing data from the information recording disc.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
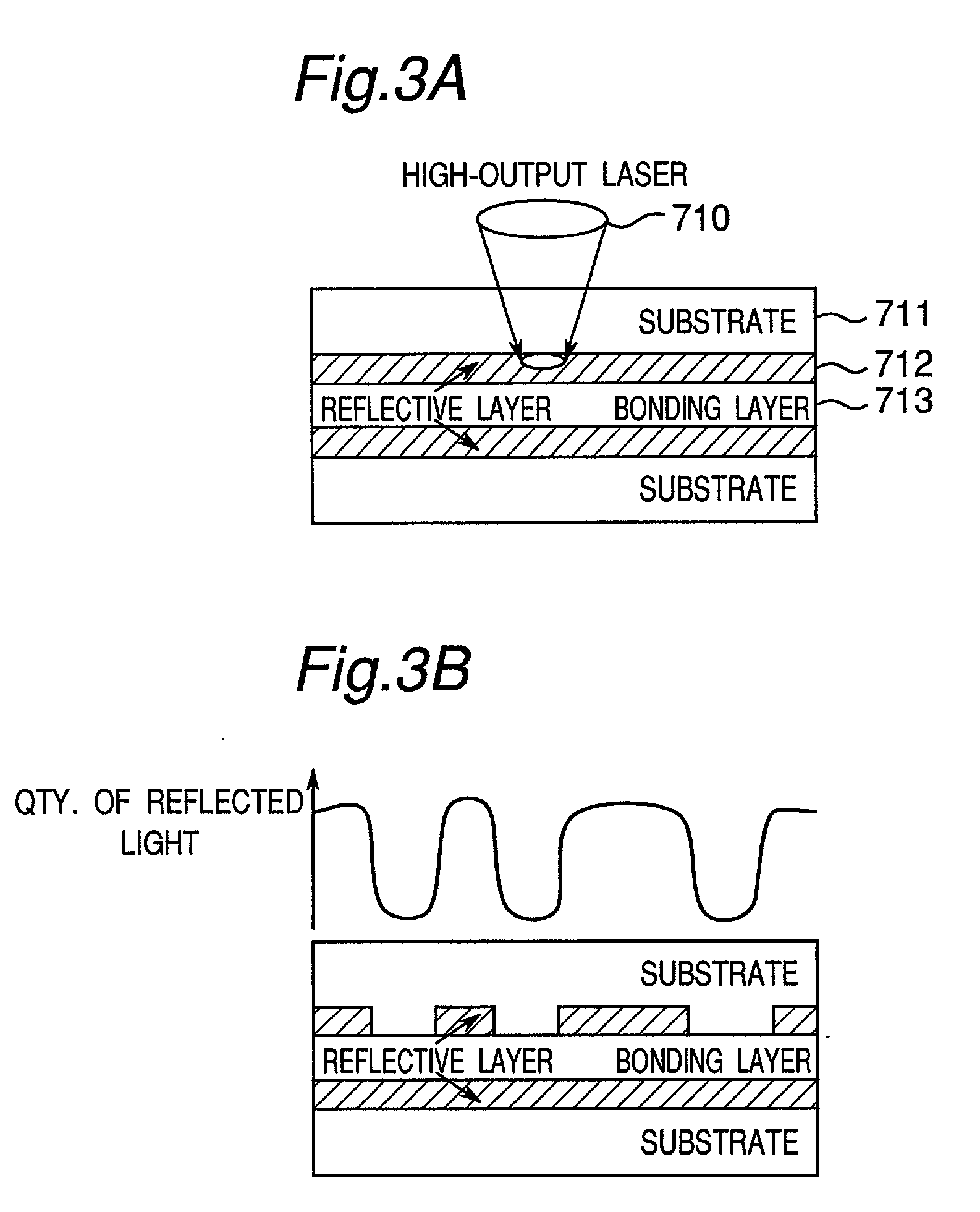
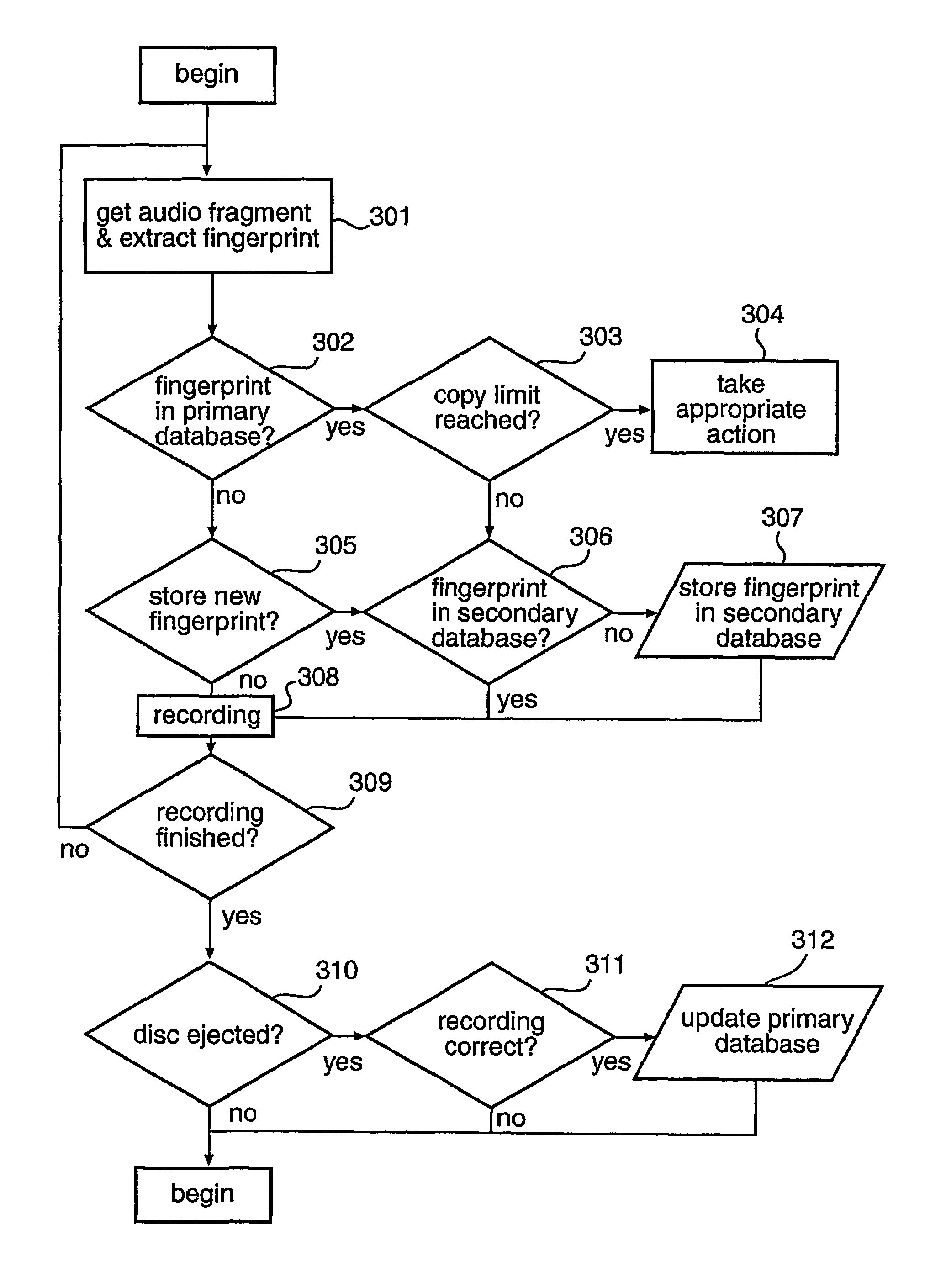
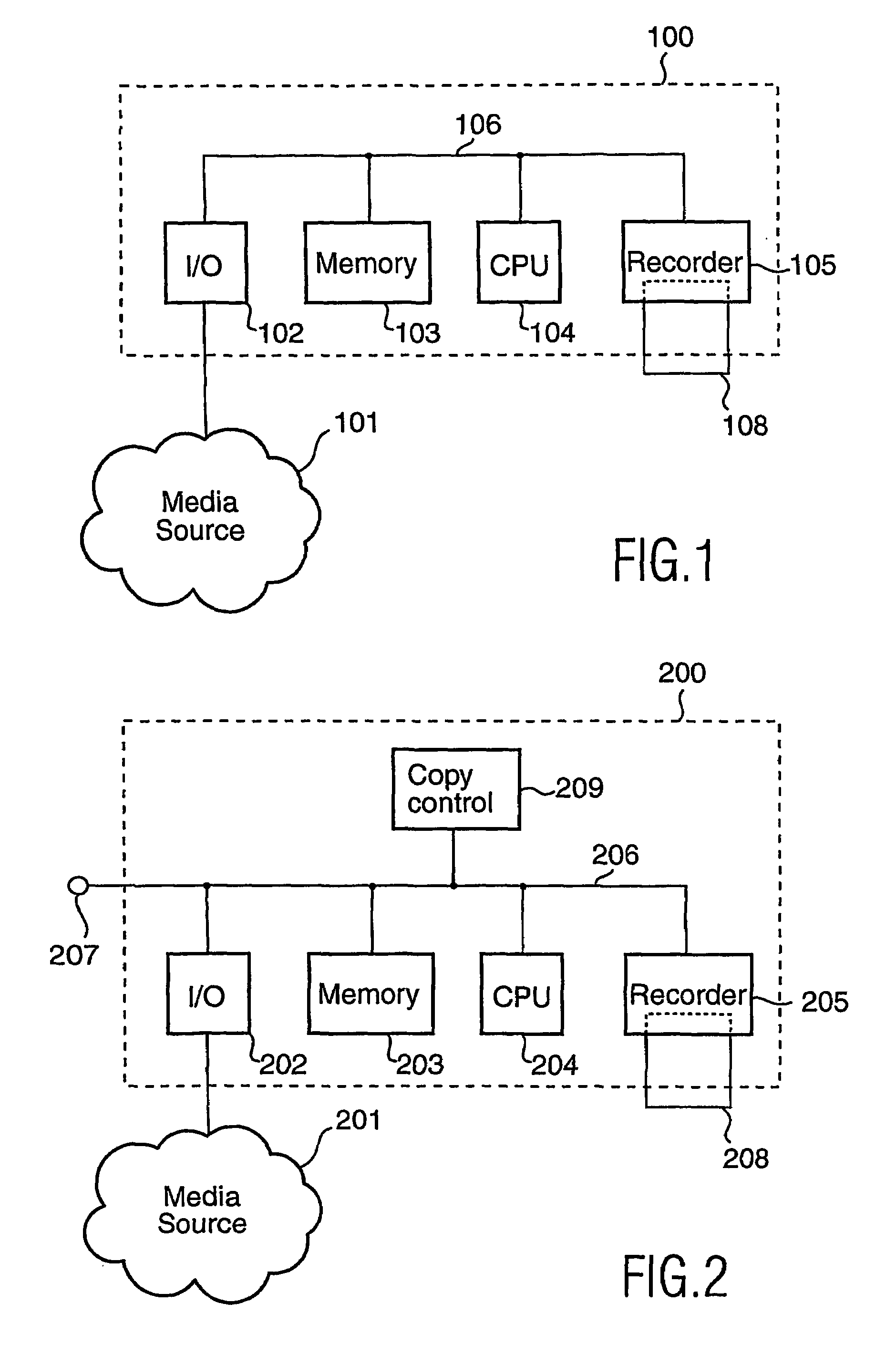
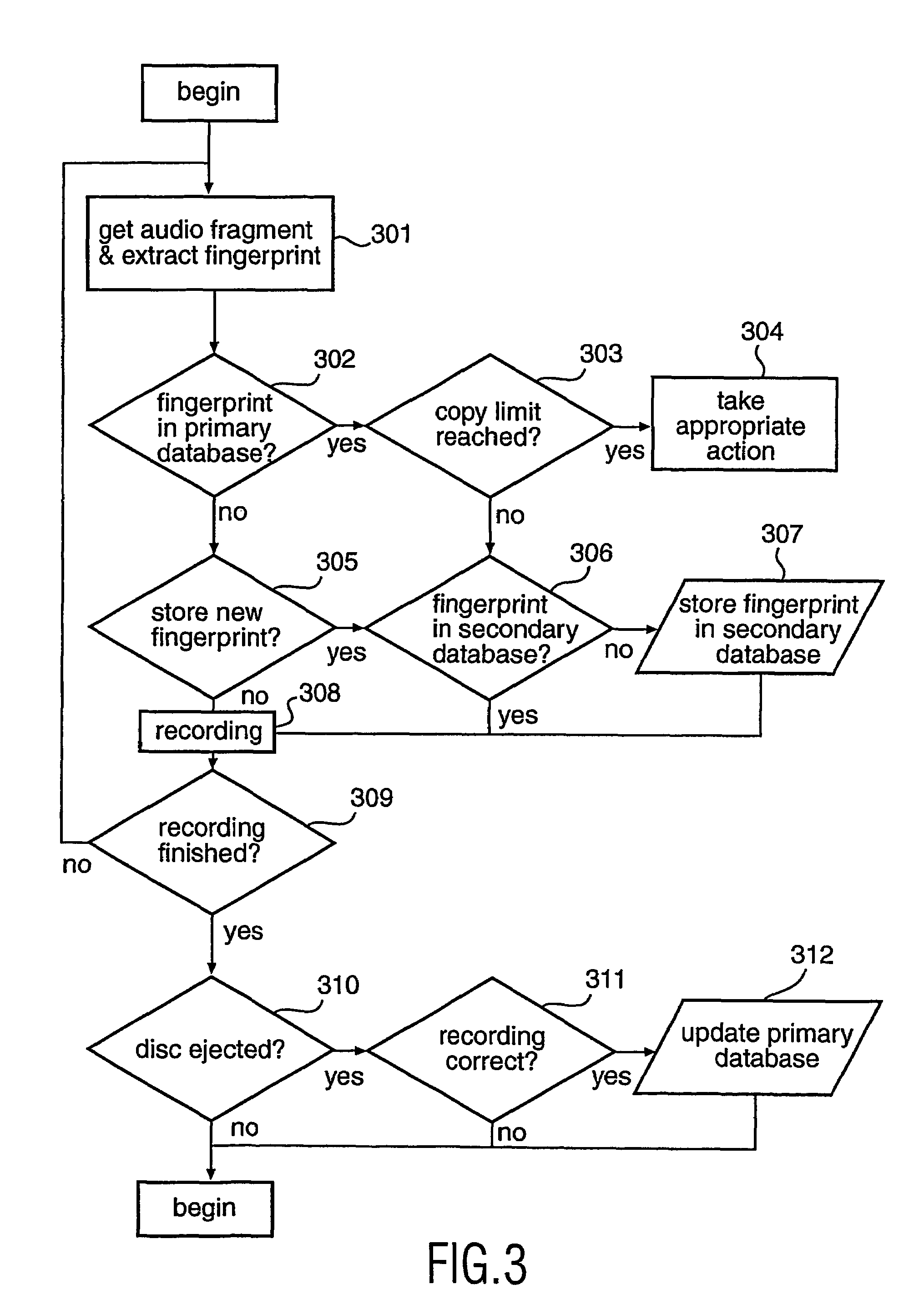
Copy control using digital speed bumps
A digital media recorder and a method of controlling such are provided. During attempts to copy media content, sub-sequences are extracted from an input media sequence. A digital fingerprint of the sub-sequence is calculated and compared with at least one first reference fingerprint from a database. The outcome of the comparison determines the action to take in the further processing. Recording of the input media sequence on a media carrier is either allowed or obstructed, e.g. disallowed. In the case recording of the sequence is allowed, the database is updated with information that the digital media sequence has been recorded.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Optical disc for coordinating the use of special reproduction functions and a reproduction device for the optical disc
InactiveUS6553179B1Preventing executionDamage the interactive nature of a titleTelevision system detailsRecord information storageComputer hardwareReproduction function
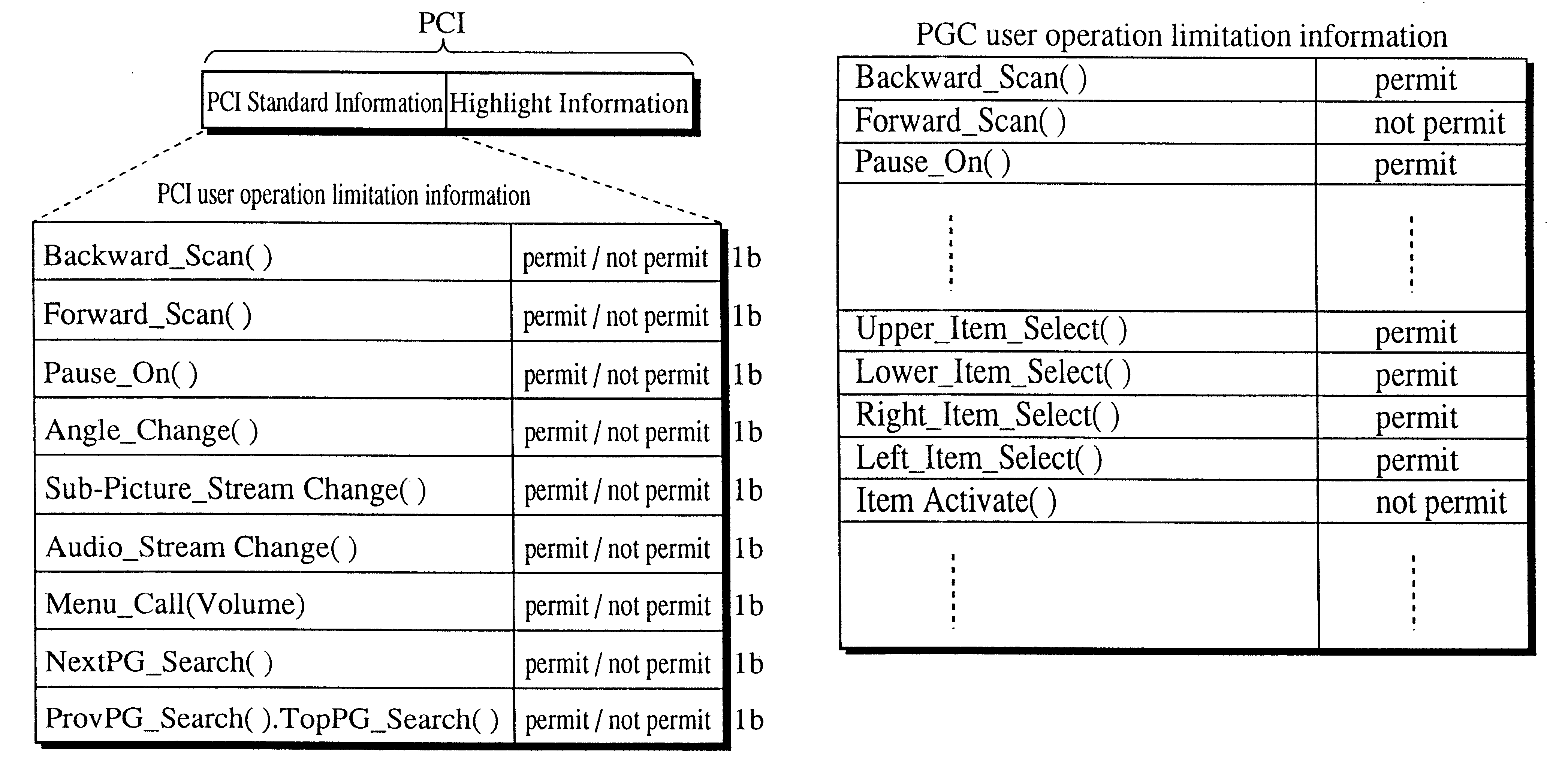
A multimedia optical disc includes a lot of blocks each of which stores moving picture data, audio data, sub-picture data, and control information. Each piece of moving picture data, audio data, sub-picture data, and control information in the same block has the same reproduction time limit. Each piece of control information includes a mask flag indicating whether to mask a key interrupt requesting a special reproduction such as fast forward, the key interrupt being generated by the user by pressing a key on a remote controller and the like. The mask flag is effective for the key interrupt generated during the reproduction time limit stored in the control information.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical information recording medium with sector address information
InactiveUS6894962B1Reduce errorsData stabilityOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageInformation layerLight beam
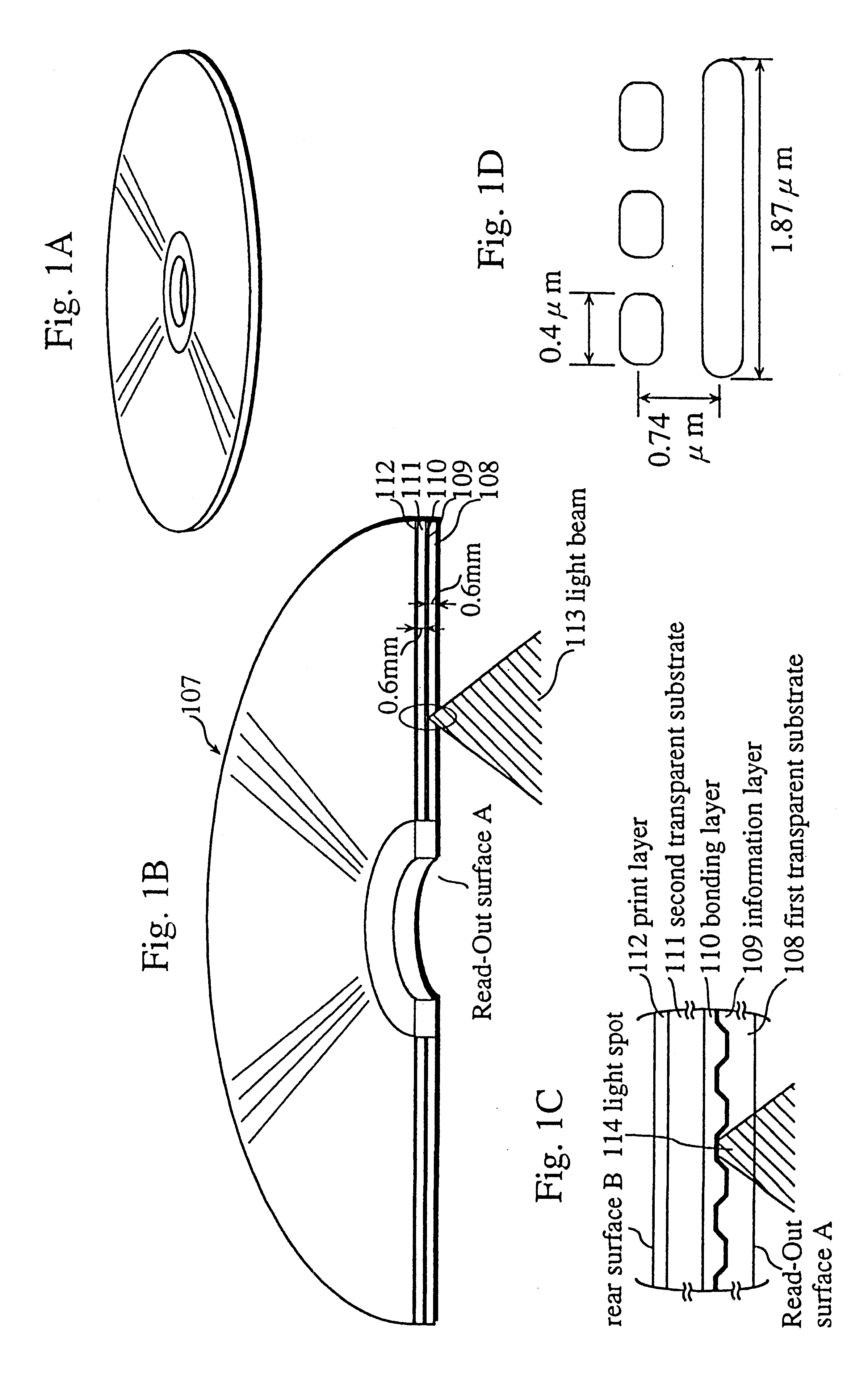
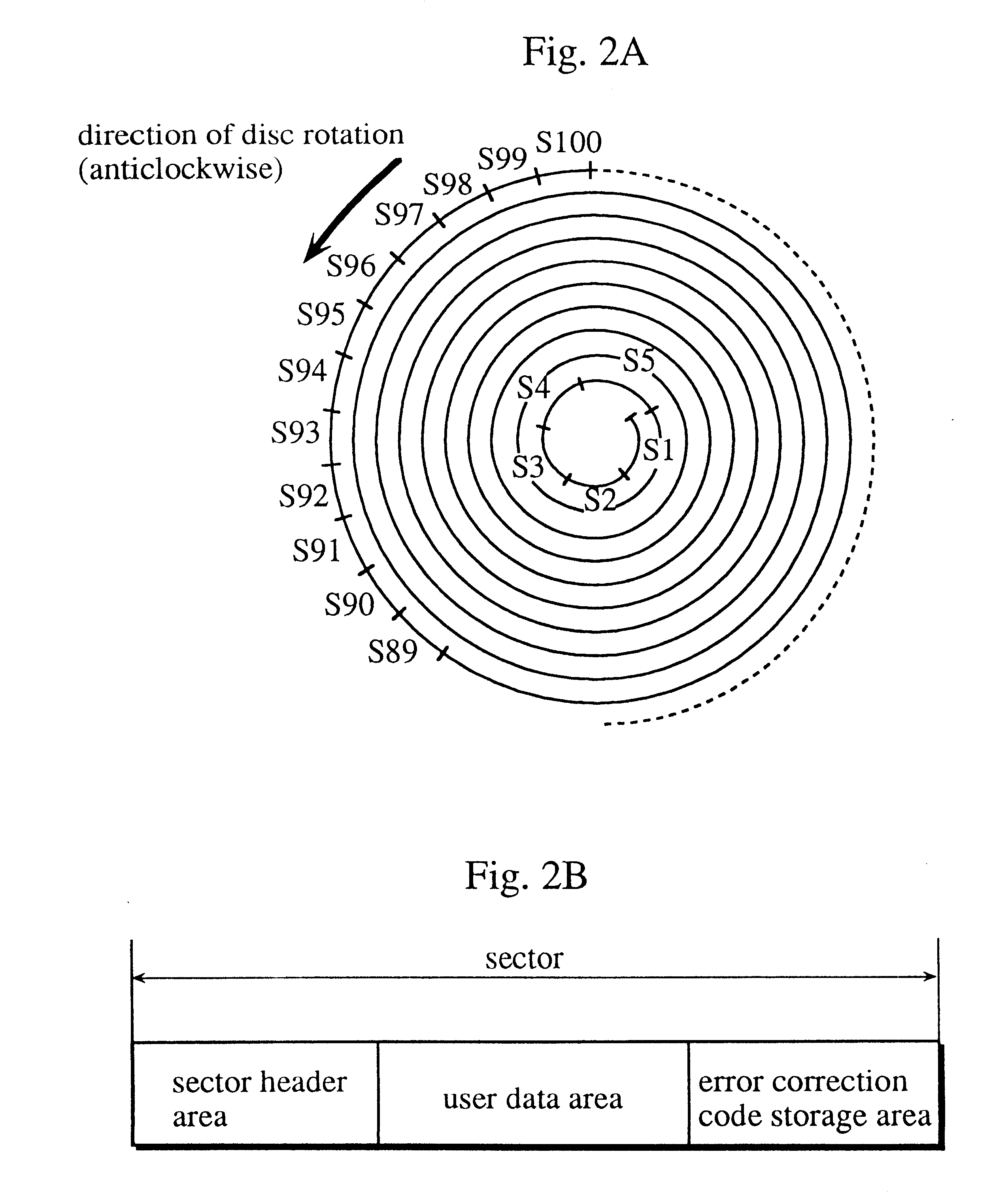
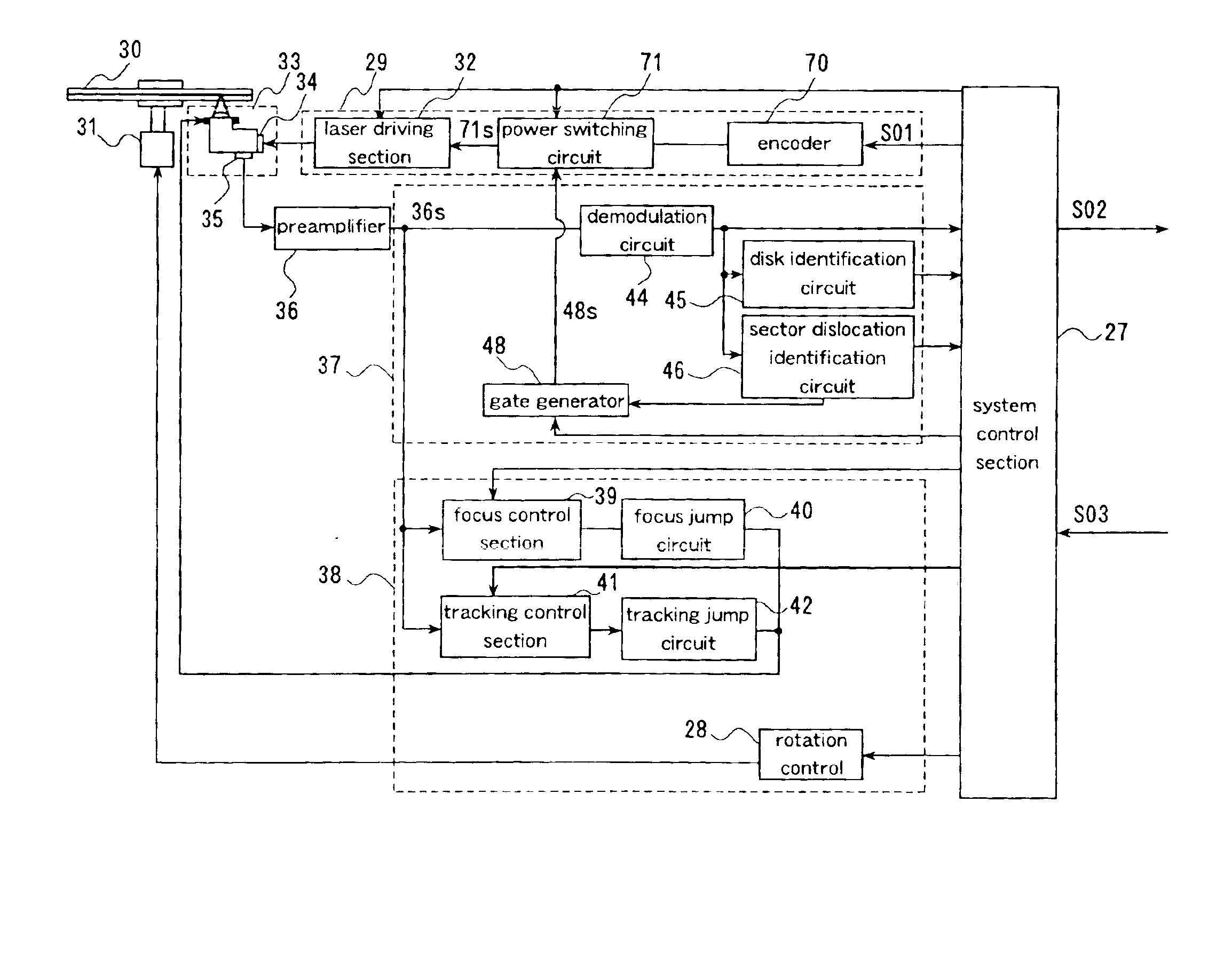
An optical information recording medium includes a substrate 1 and two information layers (2, 4) formed on the substrate. The information layer is formed of a thin film showing a change that can be detected optically by irradiation of a light beam 7. A separating layer 3 that is transparent to a wavelength of the light beam 7 is formed between the information layers 2 and 4. Each information layer (2, 4) includes a sector area having sector address portions (9, 13) and data areas (8, 12) for recording information signals, the sector address portion and the data area being divided in the circumferential direction, and a management area (10, 14) for recording identification information about the amount of dislocation between the sector address portions 9 and 14 in the circumferential direction. Thus, the identification information about the amount of dislocation can be recorded, so that demodulation errors during reproduction can be reduced by switching amplification gain or slice level during reproduction according to the identification information. Also, stable data recording can be achieved by switching recording power according to a gate signal.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
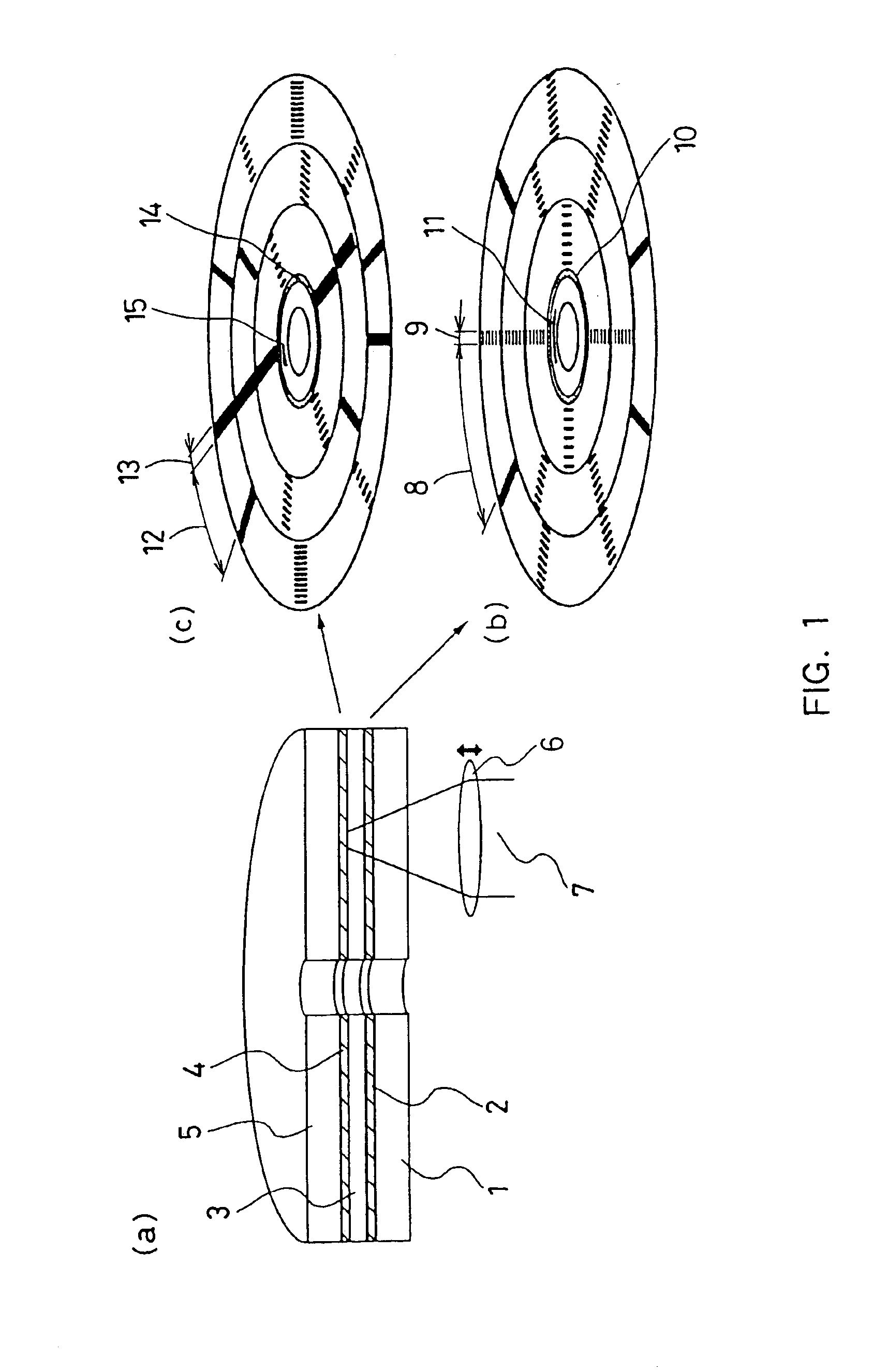
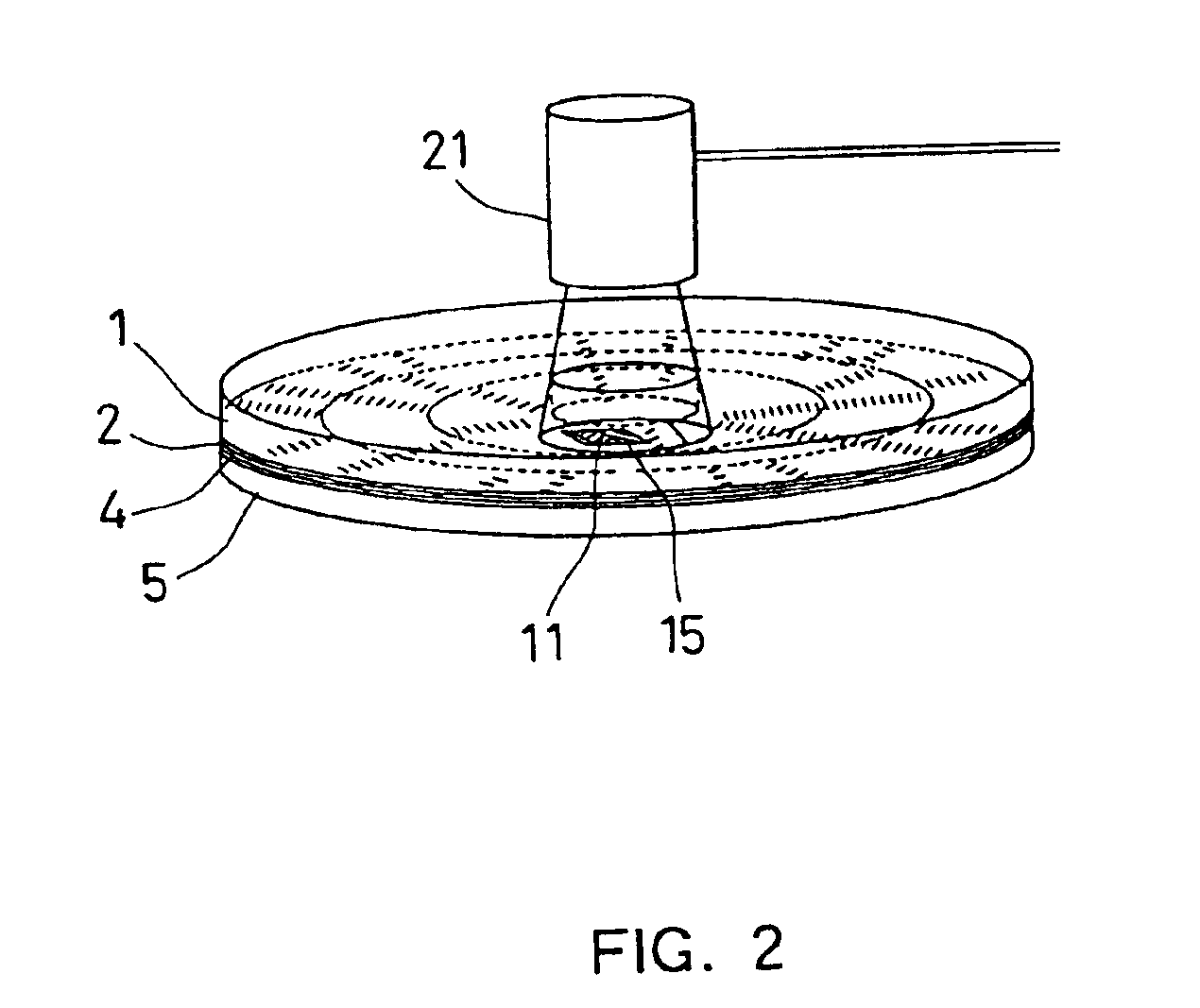
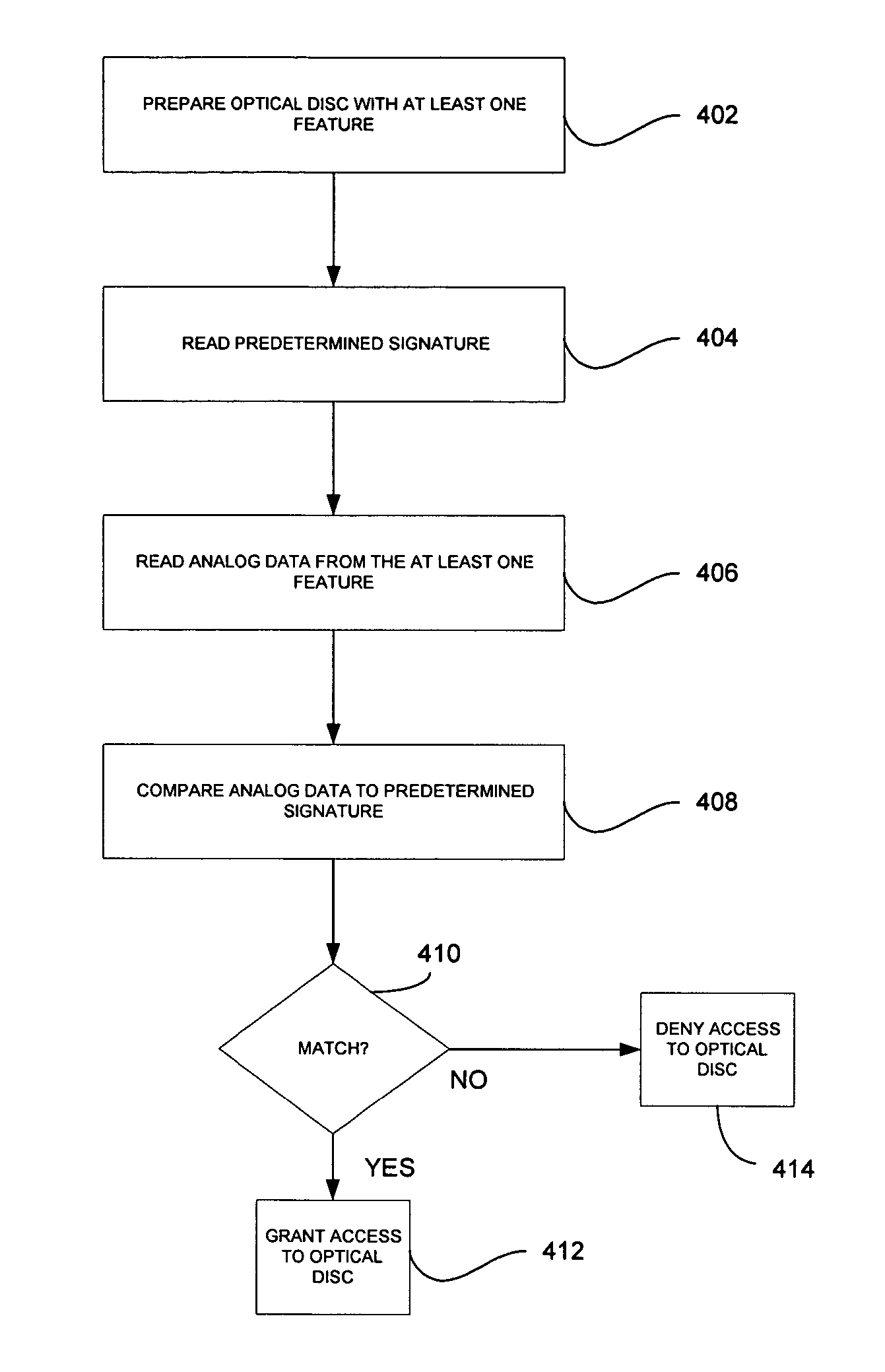
Authenticable optical disc, system for authenticating an optical disc and method thereof
InactiveUS7218589B2Combination recordingDigital data processing detailsReflective layerComputer science
An authenticable optical disc and a system and method for authenticating the optical disc are provided. The optical disc comprising a reflective layer; an optically transparent substrate disposed between the reflective layer and a light incident surface of the optical disc; a data layer disposed between the substrate and the reflective layer, the data layer including a predetermined signature; and at least one measurable feature, wherein the at least one feature is compared to the predetermined signature for authenticating the optical disc. The method comprises the steps of preparing an optical disc with at least one optical feature; measuring intensity of transmitted light from the at least one optical feature; and comparing the measured intensity to a predetermined signature, wherein if the measured intensity and predetermined signature matches, access to the optical disc is granted.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
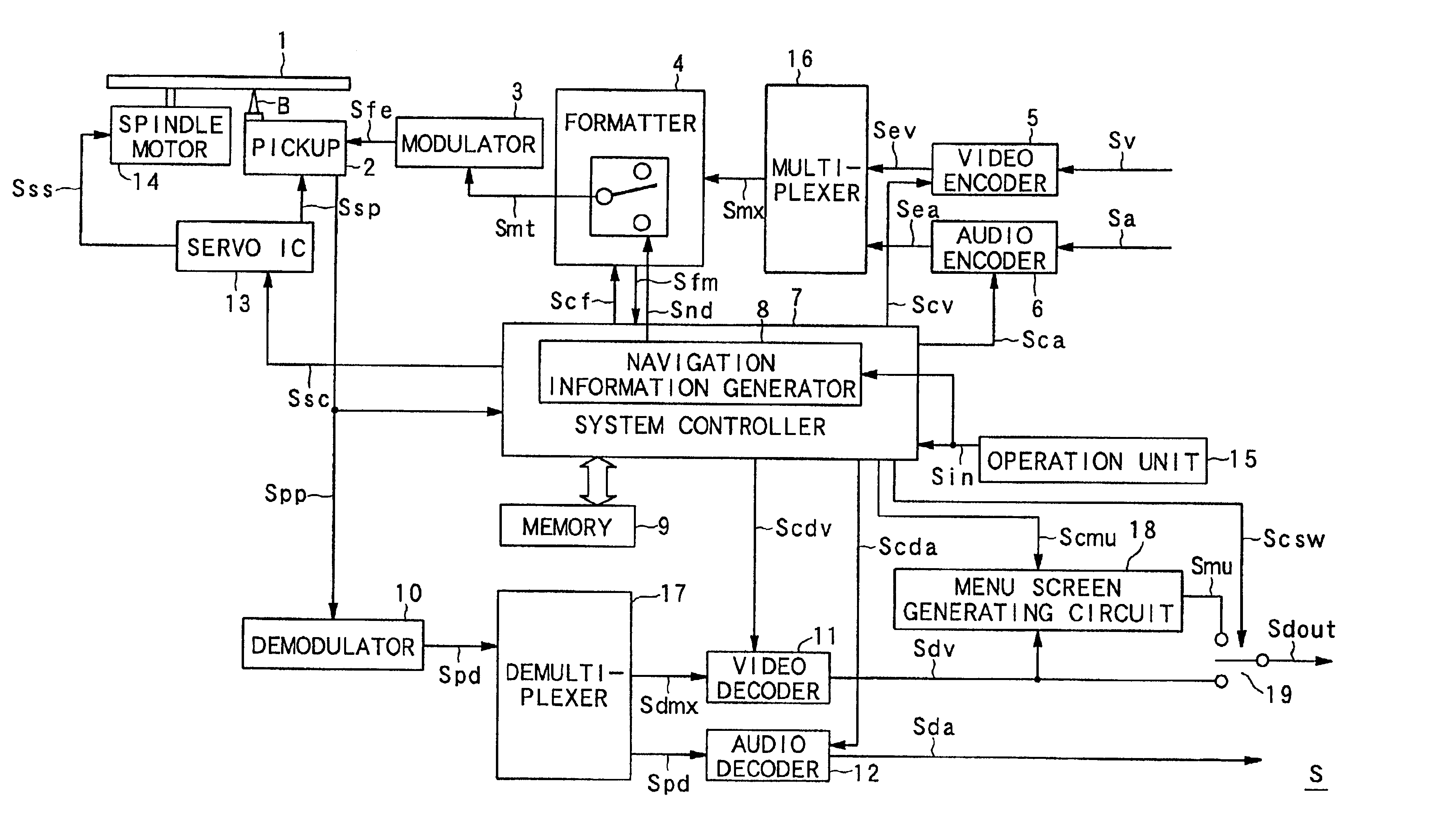
Process for recording a scrambled MPEG stream
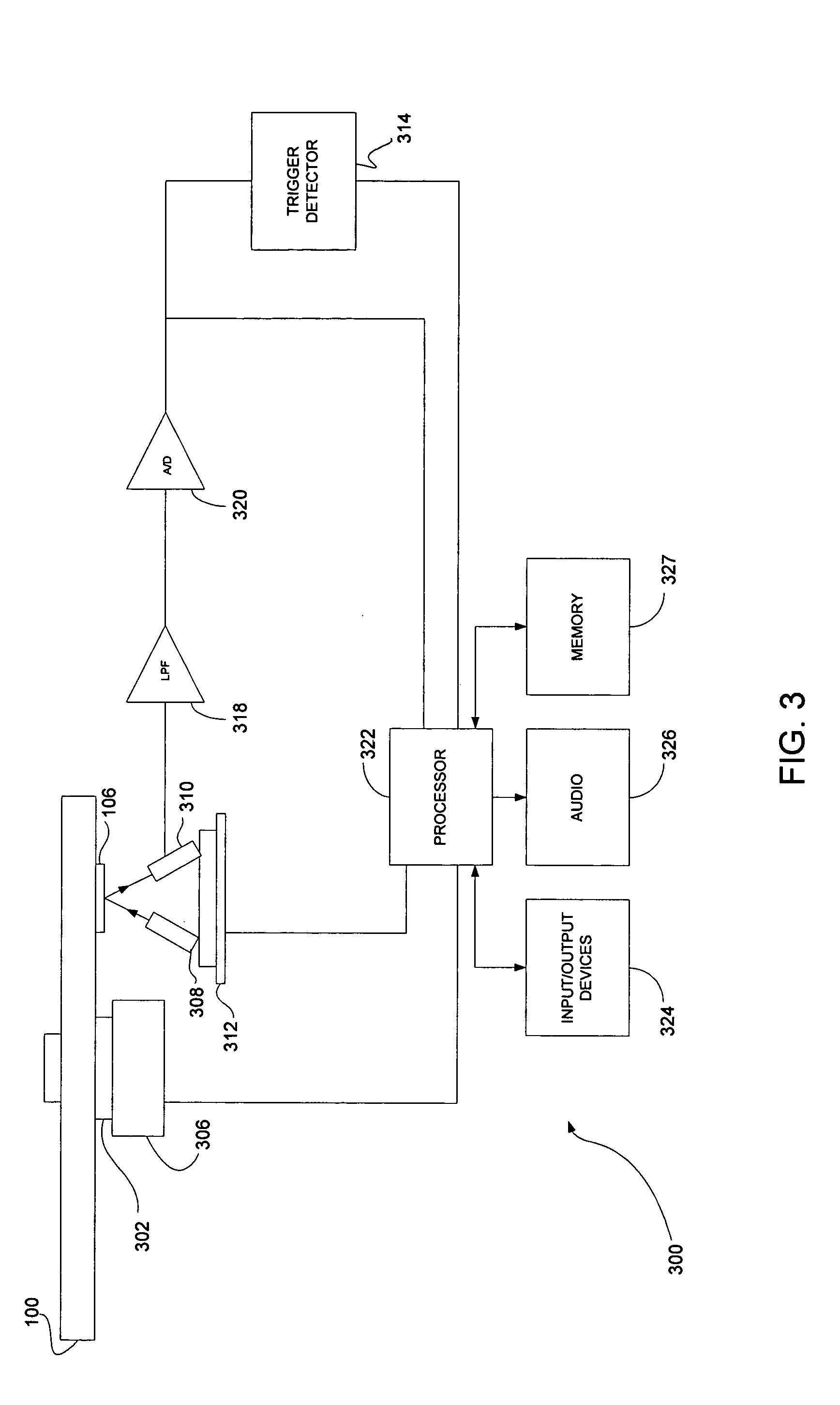
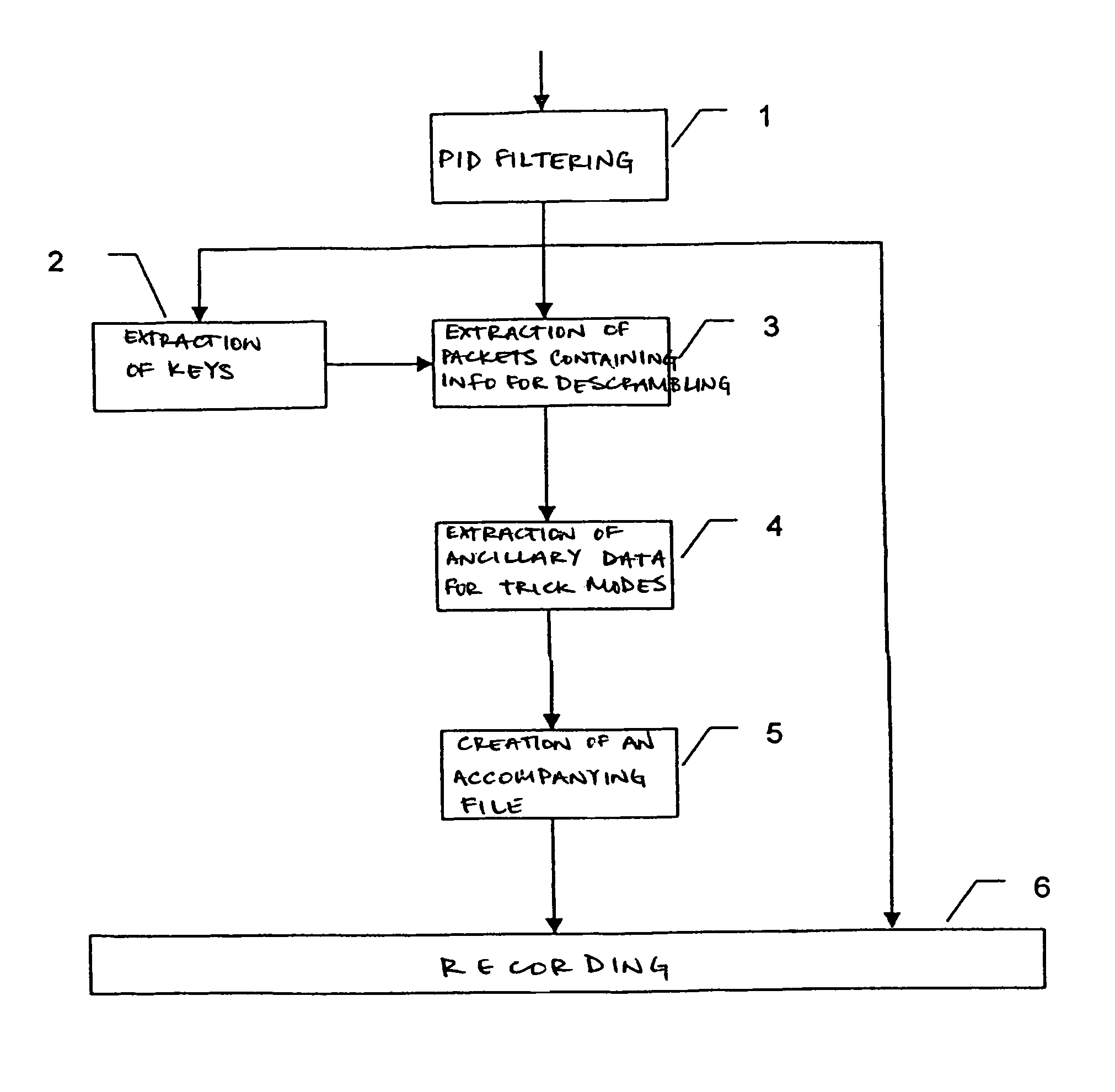
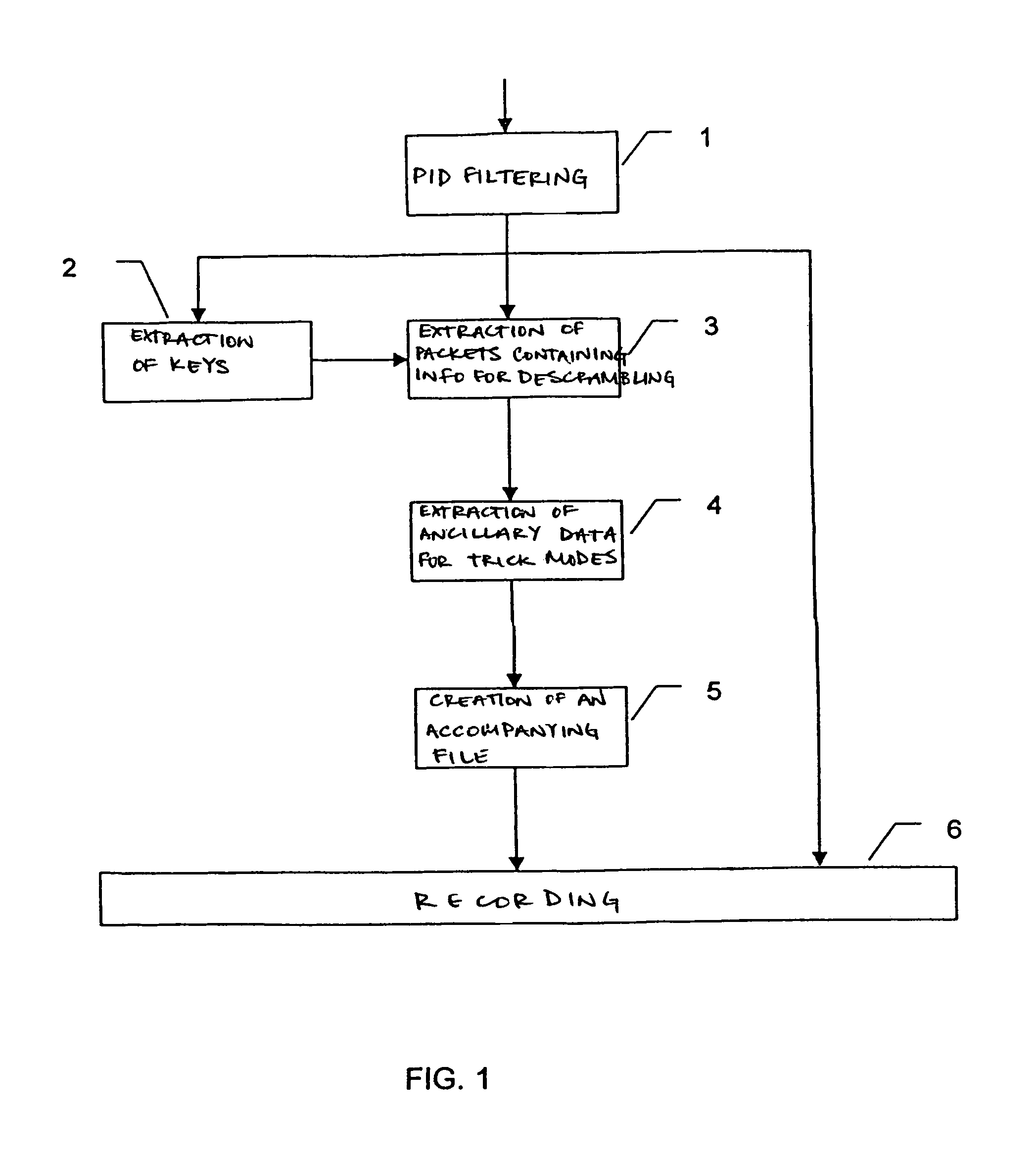
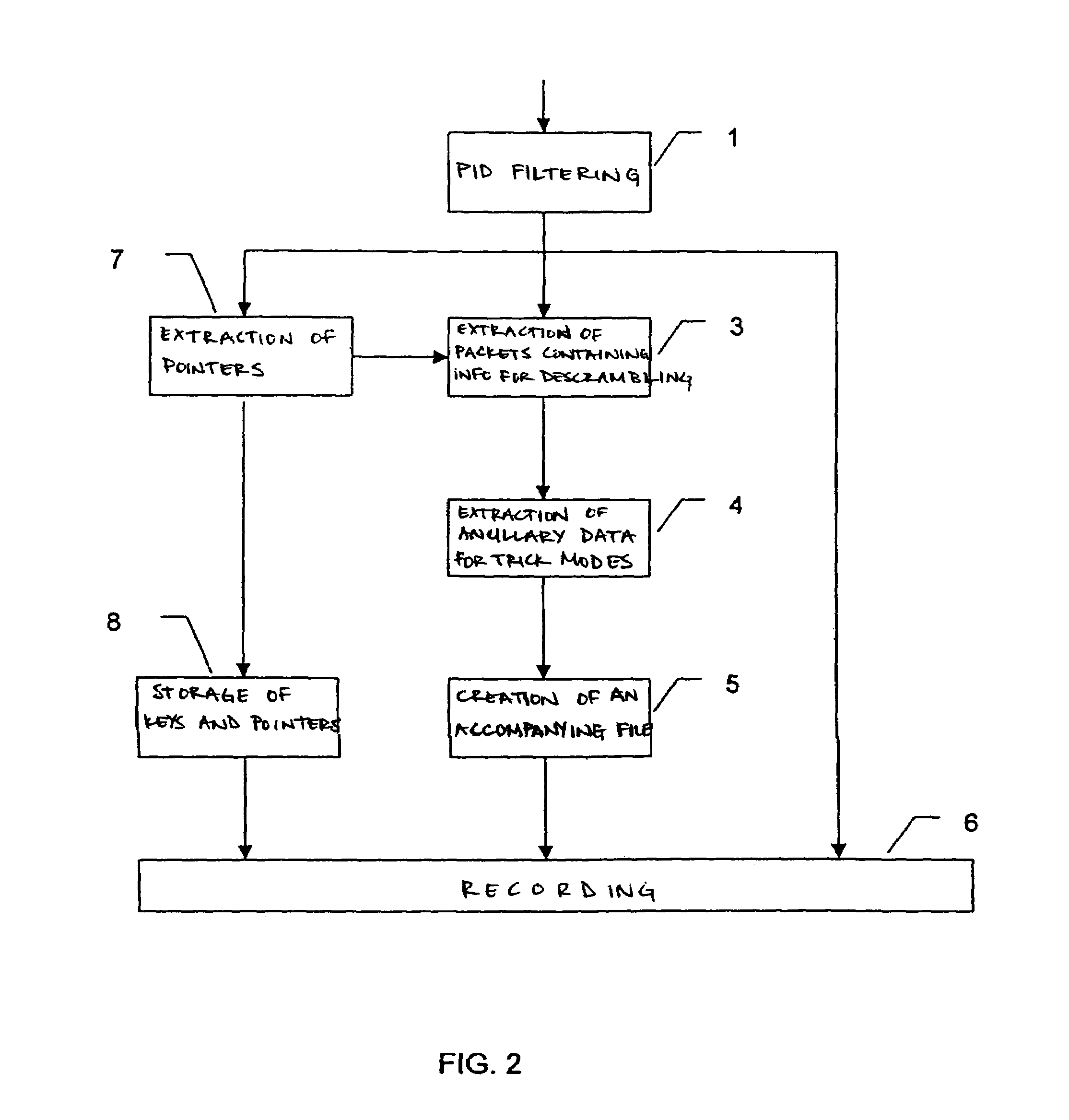
ActiveUS7079752B1Television system detailsColor television signals processingComputer hardwareSlow motion
A process whereby scrambled data of the stream are, in parallel with their recording (6), descrambled (2, 3) so as to extract (4) therefrom additional data corresponding to information required by at least one function of the special mode or “trick mode” (fast forward, fast rewind, accelerated motion, slow motion, etc.). These additional data are also recorded (6) on the recording medium. Applications relate most particularly to recordings on hard disk or DVD.
Owner:DIATEK LICENSING LLC
Method, apparatus and program storage device for magnetic disk drive protection
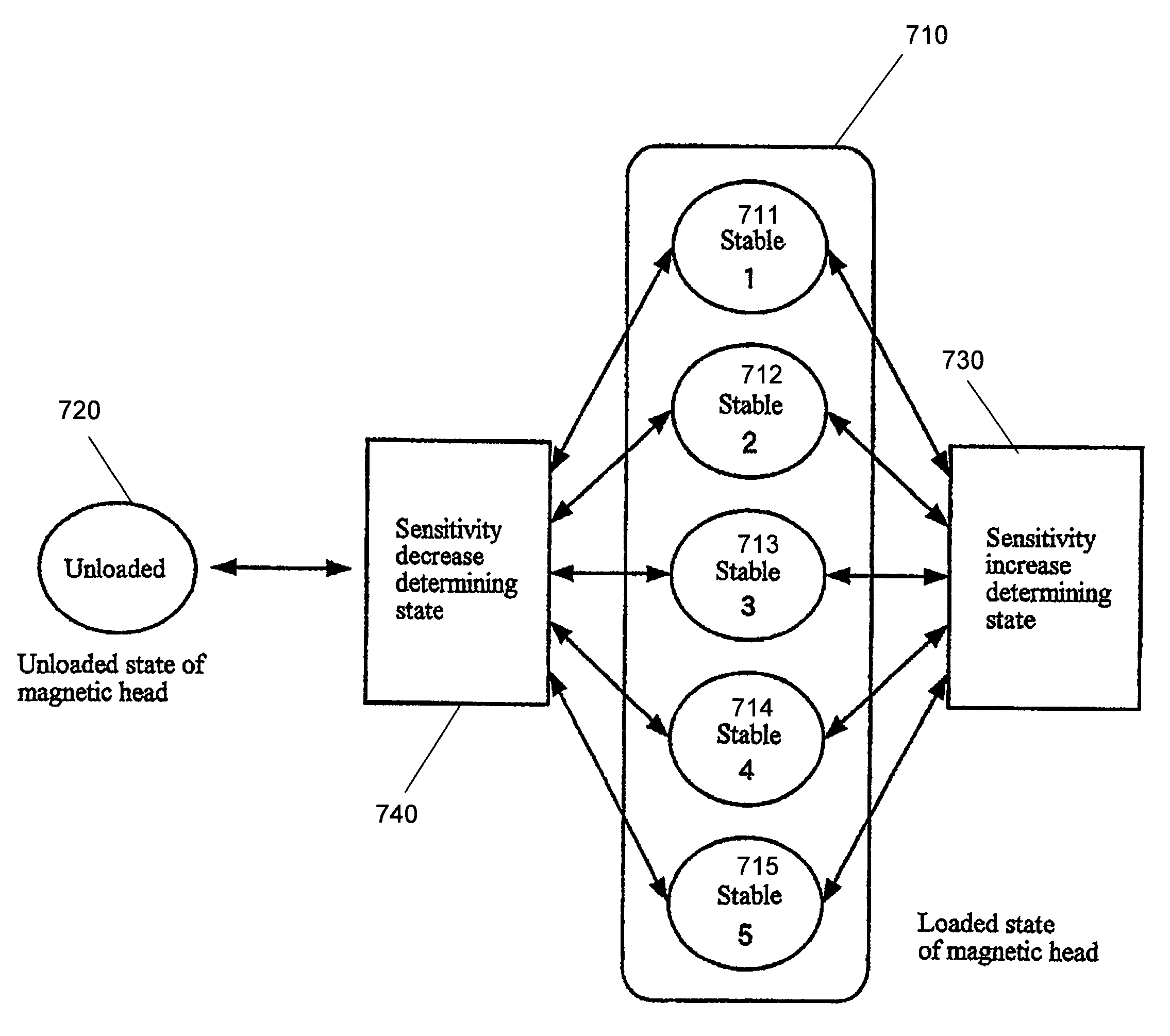
ActiveUS7142385B2Record information storageAccidental erasing/double-recording preventionStable stateEngineering
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
Methods and apparatus for persistent control and protection of content
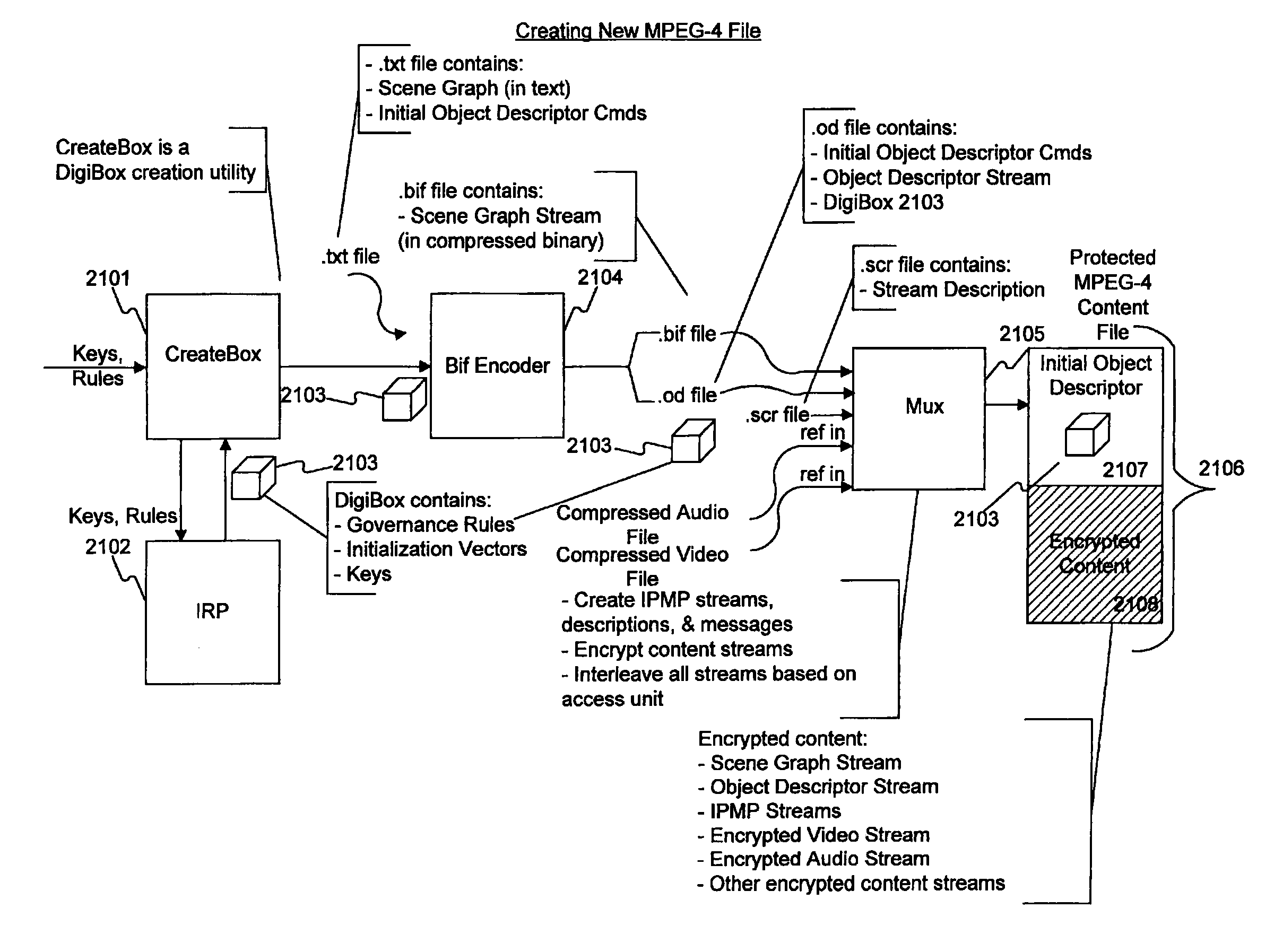
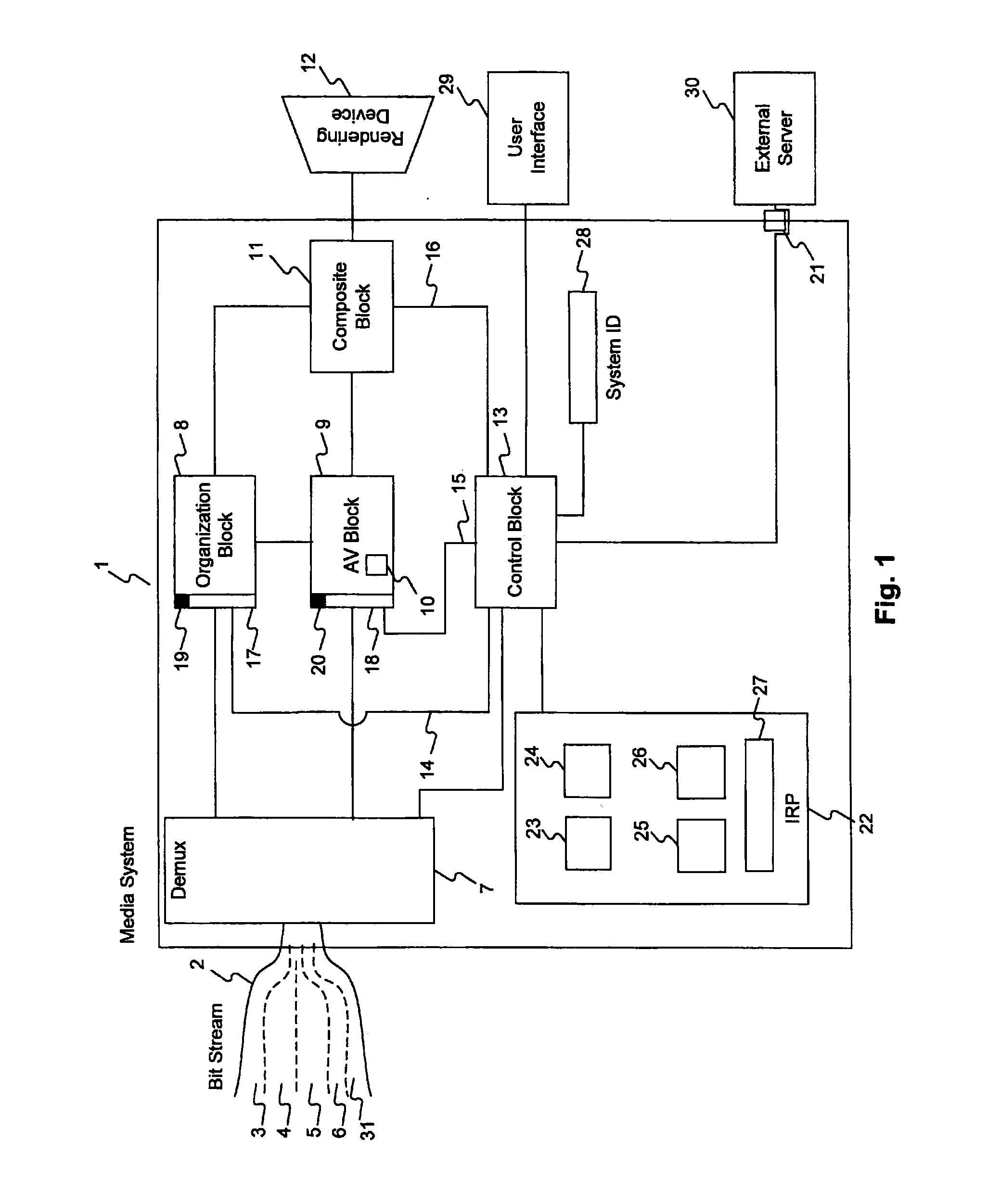
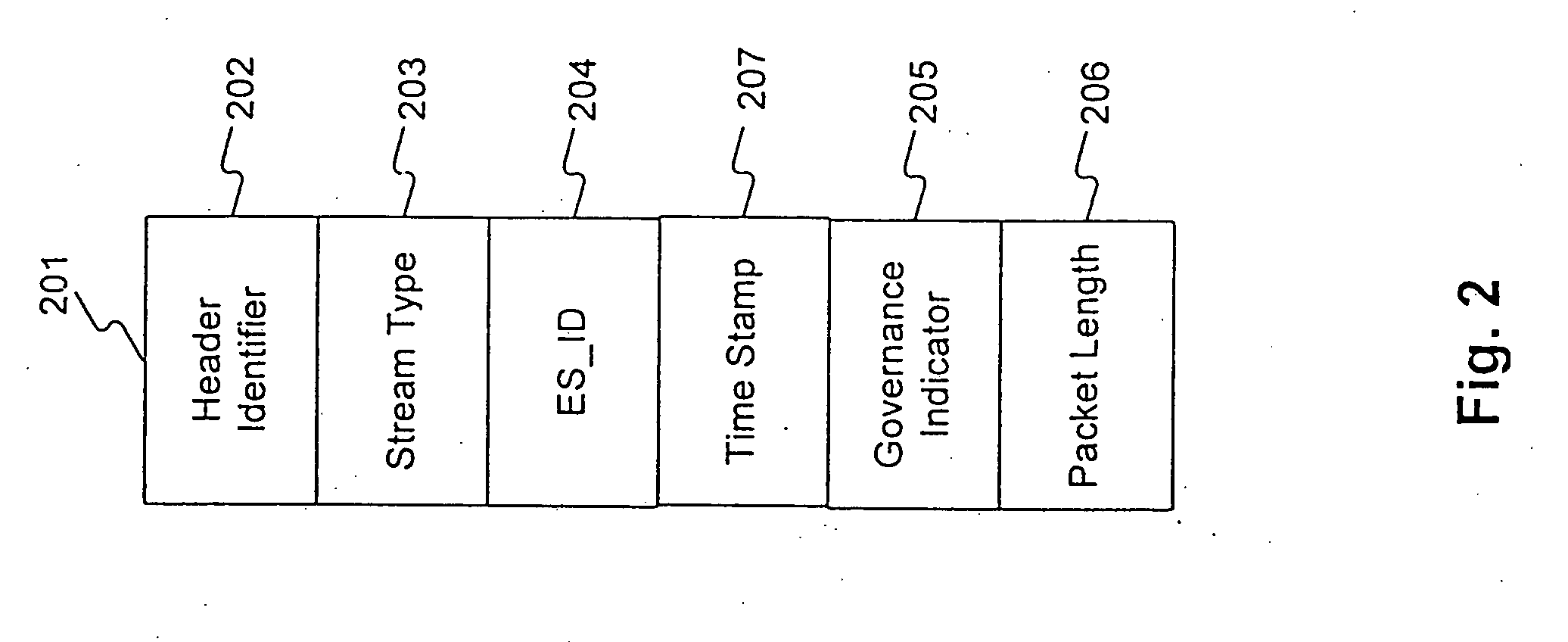
A novel method and apparatus for protection of streamed media content is disclosed. In one aspect, the apparatus includes control means for governance of content streams or content objects, decryption means for decrypting content streams or content objects under control of the control means, and feedback means for tracking actual use of content streams or content objects. The control means may operate in accordance with rules received as part of the streamed content, or through a side-band channel. The rules may specify allowed uses of the content, including whether or not the content can be copied or transferred, and whether and under what circumstances received content may be “checked-out” of one device and used in a second device. The rules may also include or specify budgets, and a requirement that audit information be collected and / or transmitted to an external server. In a different aspect, the apparatus may include a media player designed to call plugins to assist in rendering content. A “trust plugin” is disclosed, along with a method of using the trust plugin so that a media player designed for use with unprotected content may render protected content without the necessity of requiring any changes to the media player. In one aspect, the streamed content may be in a number of different formats, including MPEG-4, MP3, and the RMFF format.
Owner:INTERTRUST TECH CORP
Information recording apparatus
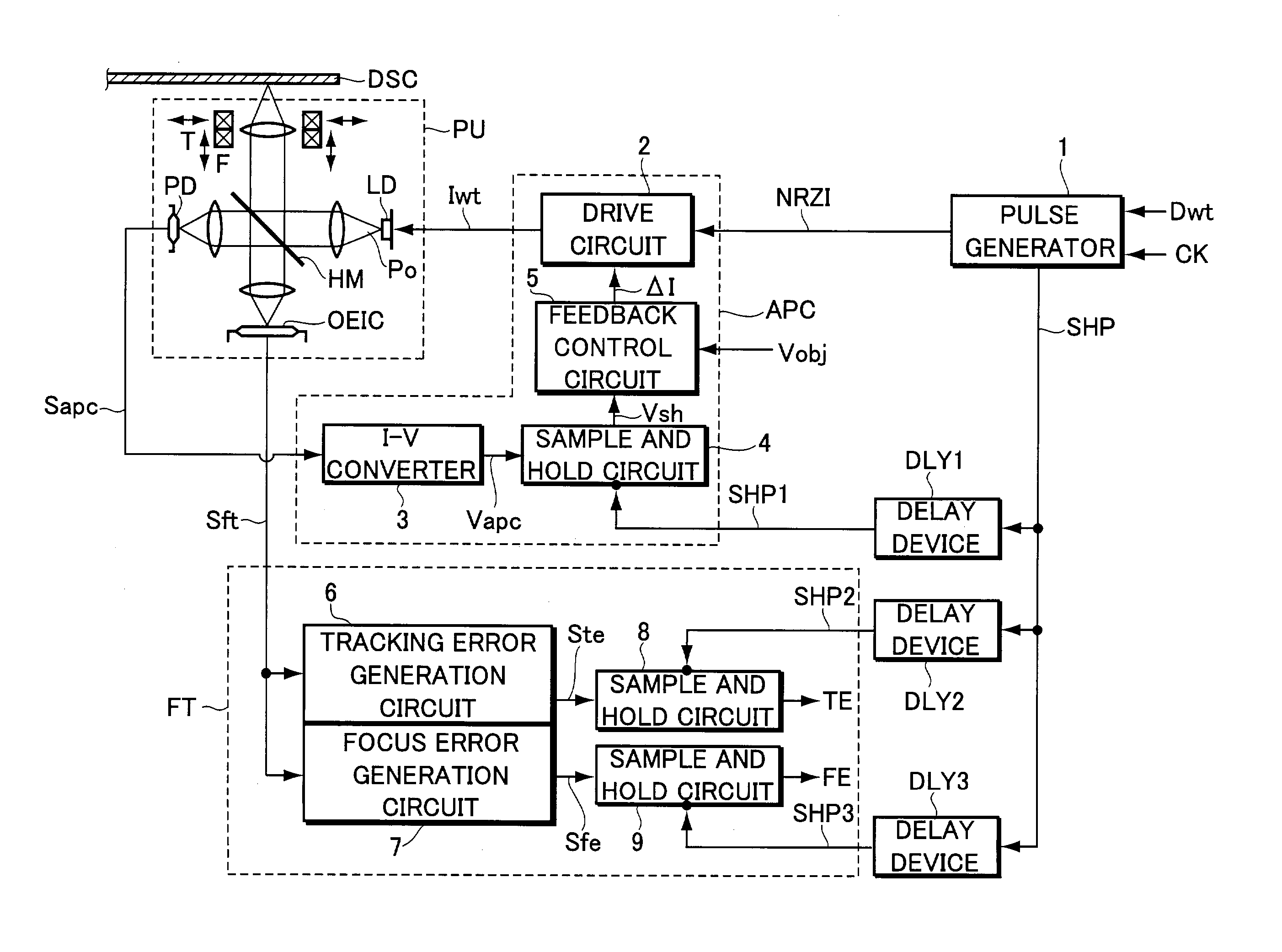
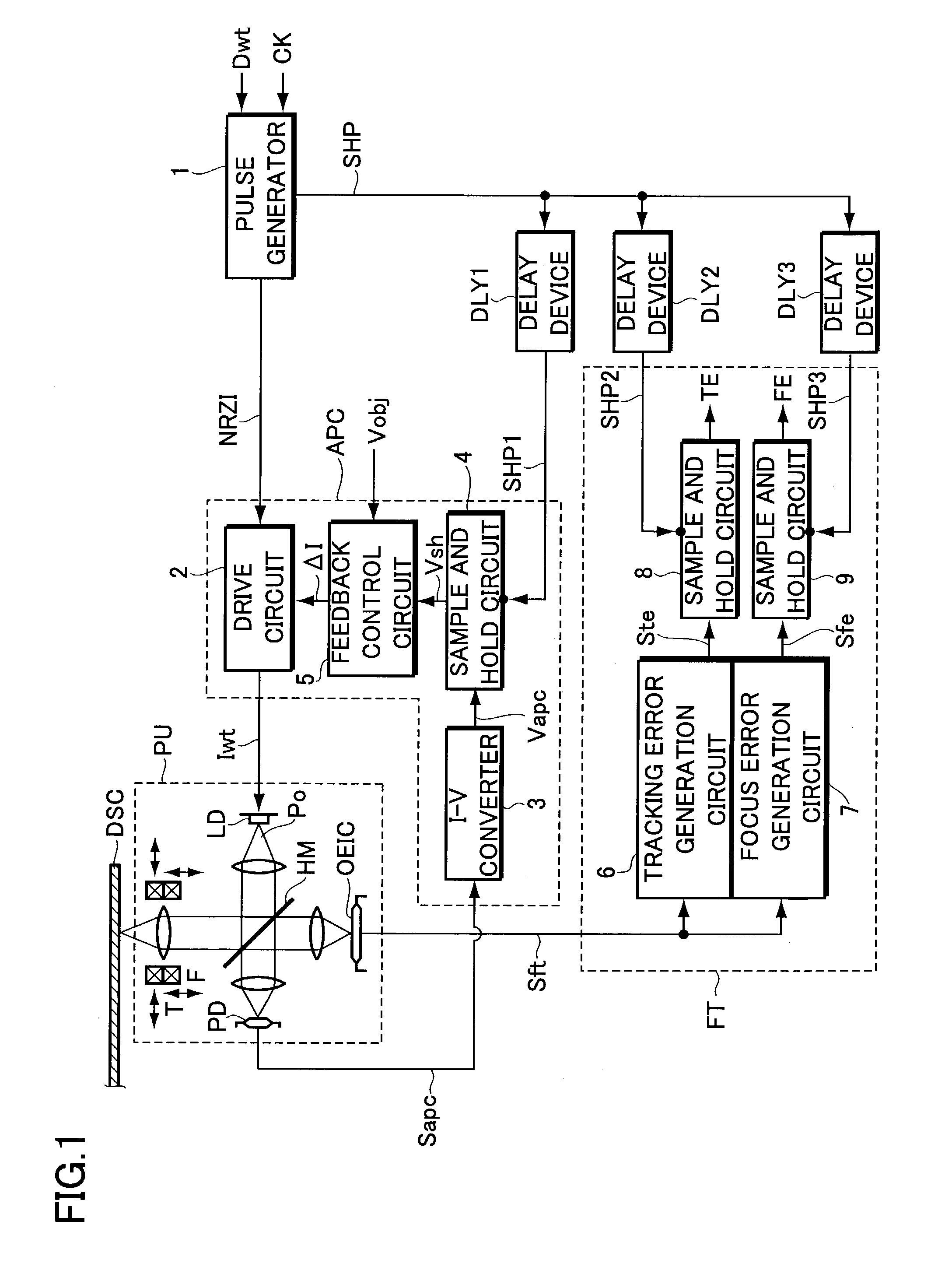
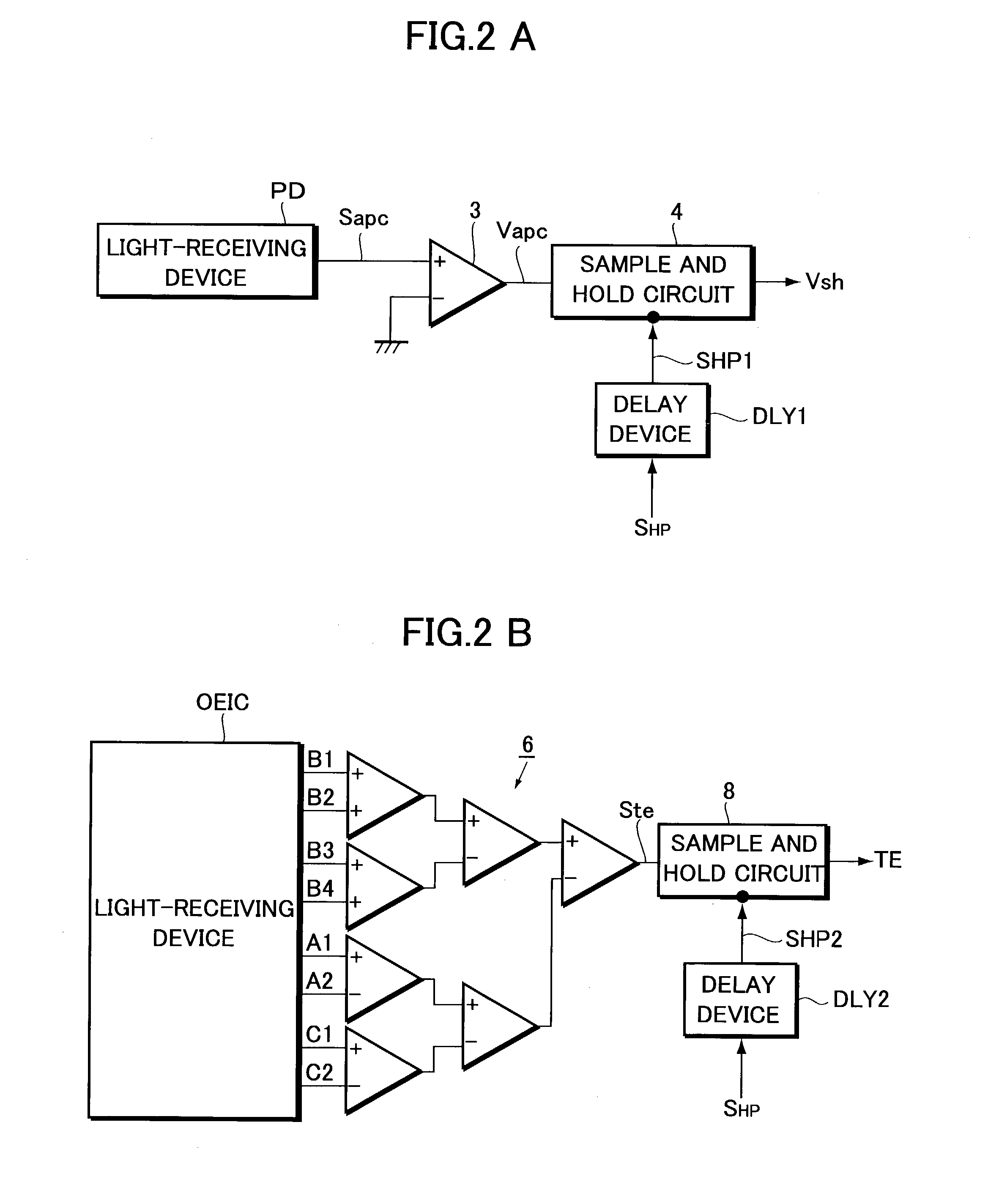
InactiveUS7164631B2Improve accuracyAccurate power adjustmentCombination recordingOptical beam sourcesTime delaysDelayed time
An information recording apparatus is provided, which can control over the power of light beams emitted from a light source and various types of servo control with higher accuracy. A laser beam is emitted from a semiconductor laser to write information onto an optical disc. A detection signal indicative of the power of the laser beam output from a light-receiving device is sampled and held with a sample and hold circuit via an I-V converter at a timing delayed by the time corresponding to the delay time of the I-V converter. A tracking error generation circuit and a focus error generation circuit generate a tracking error signal and a focus error signal, respectively, on the basis of a detection signal having information about tracking error and focus error and output from a light-receiving device. Sample and hold circuits sample and hold the tracking error signal and the focus error signal at a timing delayed by the time corresponding to the delay time of each of the generation circuits, respectively. Power control, tracking servo, and focus servo are performed using each of the signals held by the sample and hold circuits, respectively.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com