Methods to reprogram splice site selection in pre-messenger rnas
a splice site and pre-messenger technology, applied in the field of splice site selection, can solve the problems of loss of tumor suppressor activity, resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs, and decreased apoptosis in tumors, and achieve the effect of altering the use of splice sites
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Effects of Splice Site Interference Using Oligonucleotide Versus Protein Binding
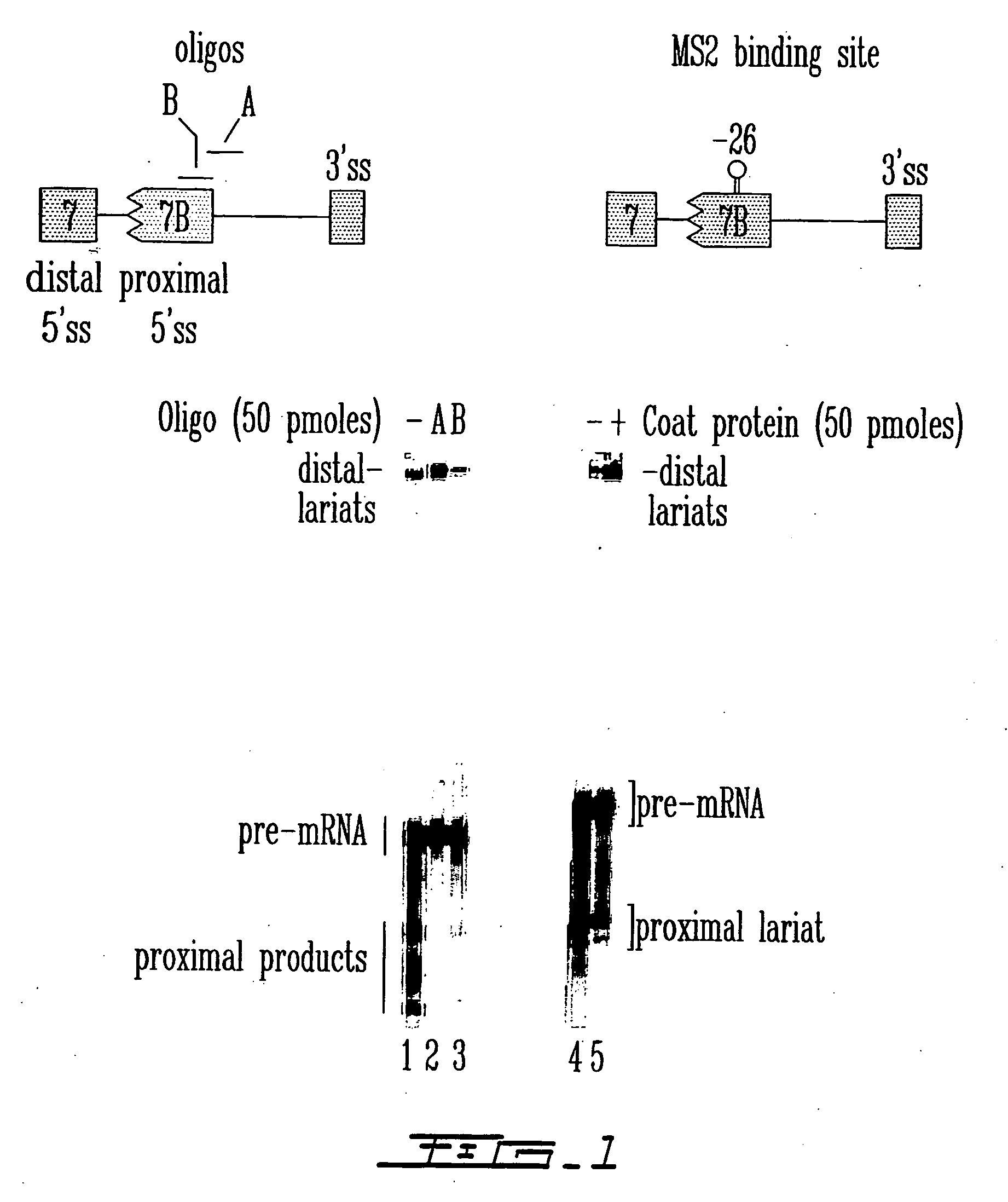
[0144] To determine the relative ability of oligonucleotide binding versus directed protein binding to interfere with splice site selection, an in vitro splicing assay was developed in HeLa cell extracts. This assay utilized a model pre-mRNA substrate (hereafter referred to as “553 or C5′− / − pre-mRNA”) containing competing 5′ splice sites taken from hnRNP A1 exon 7 and exon 7B. The 553 pre-mRNA was radioactively labeled with 32p and incubated in a HeLa nuclear extract for two hours, and then total RNA was isolated and fractionated on acrylamide / urea gels. Oligonucleotides were resuspended in water and added to the splicing mixtures containing extracts and target pre-mRNA at indicated concentrations. Normally, the pre-mRNA was spliced predominantly to the internal (proximal) 5′ splice site of exon 7B. However, if the proximal 5′ splice site was somehow blocked, then the distal site from exon 7 was used. ...
example 2
Effect of Protein Binding at Different Positions
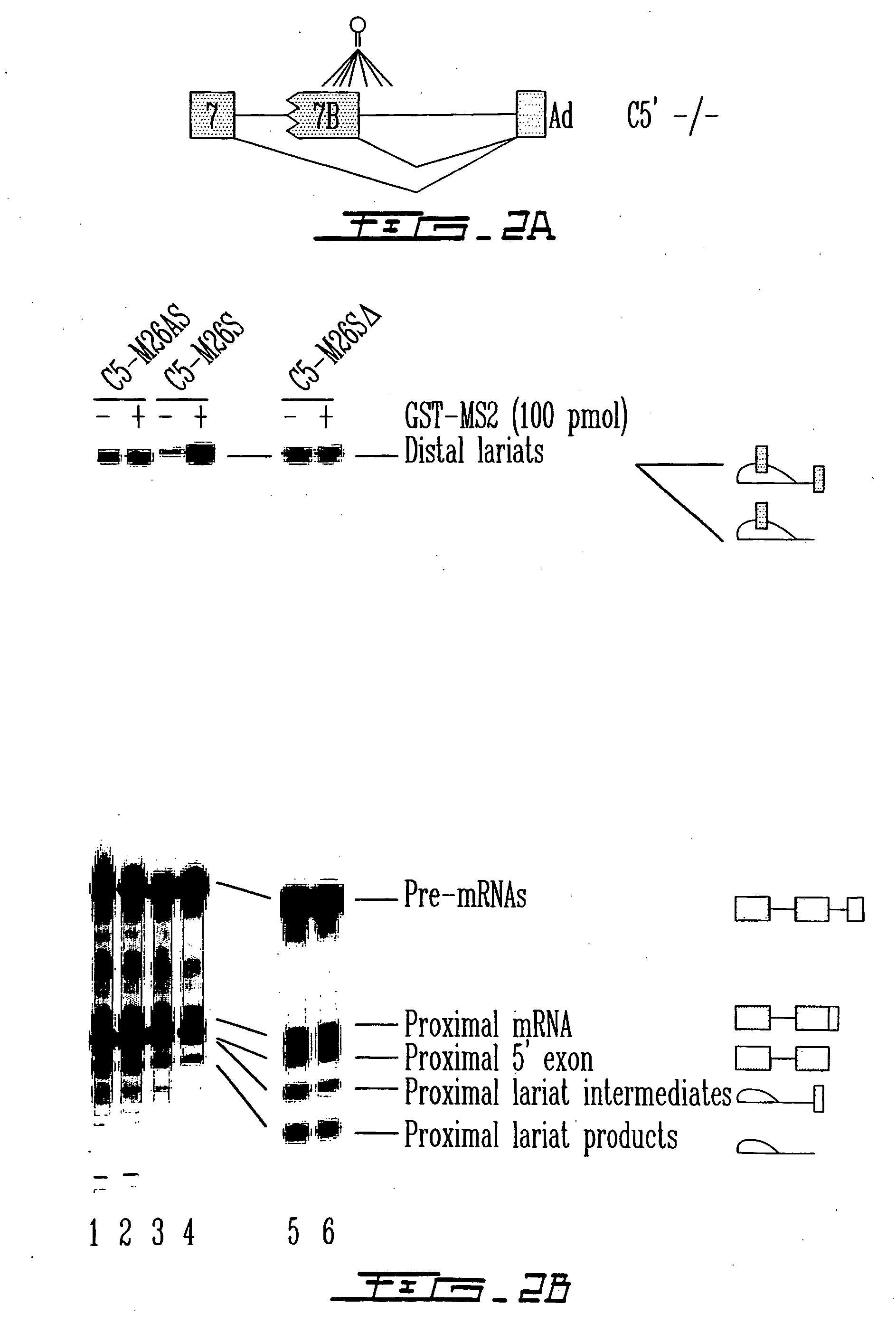
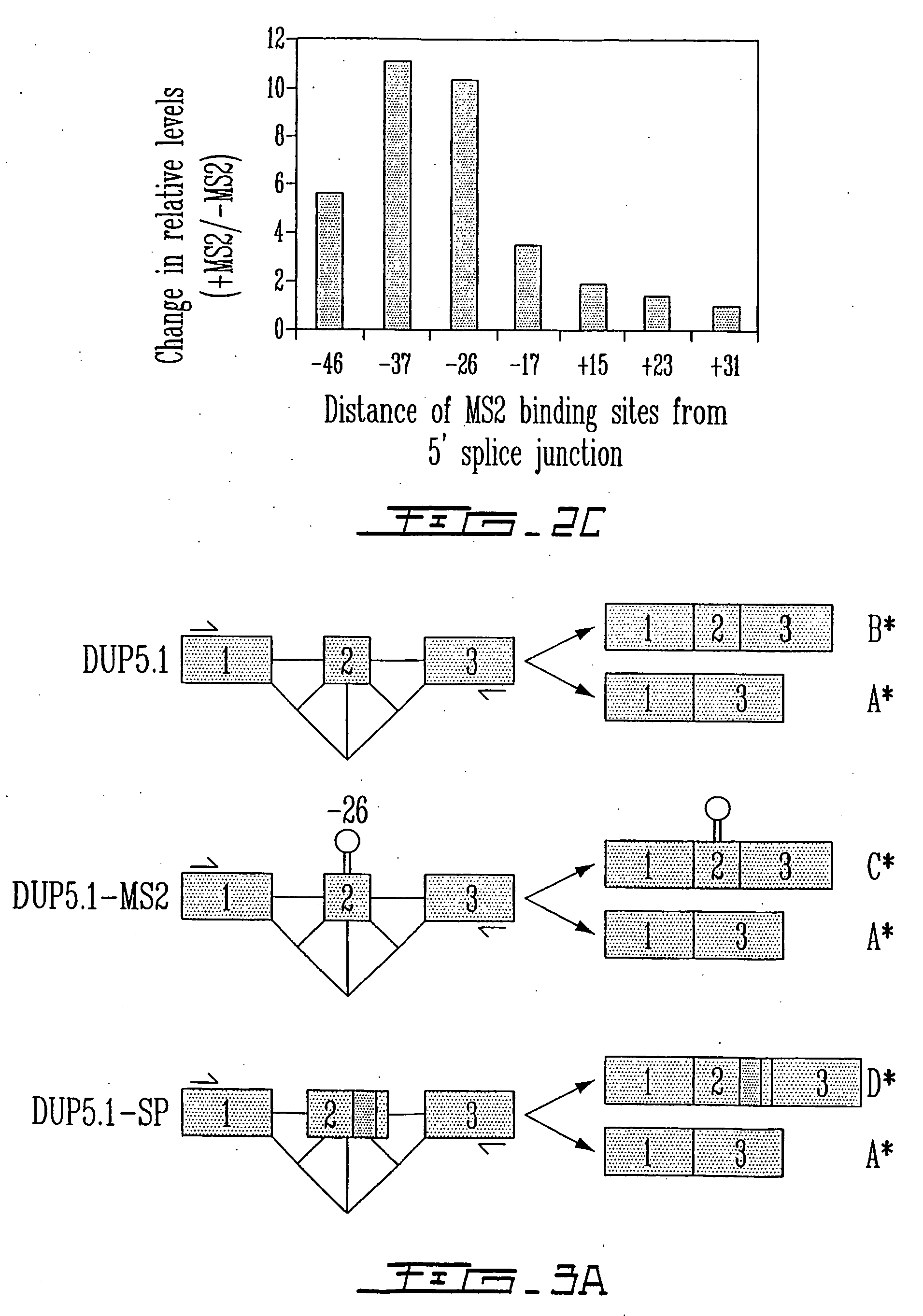
[0147] The effect of targeting the binding of a protein in the vicinity of a 5′ splice site with the goal of interfering with its use through steric hindrance was also tested. Although a few natural cases of this type of splicing control exist, it was intended to ascertain the parameters that are associated with such an effect using a pre-mRNA that contain two competing 5′ splice sites. Using the C5′− / − pre-mRNA derived form the hnRNP A1 gene, the effect of targeting the binding of the bacteriophage MS2 coat protein close to the proximal 5′ splice site was tested. A high-affinity MS2 binding site was inserted at various positions (−46, −37, −26, −17, +15, +23 and +31) upstream or downstream of the proximal 5′ splice junction (FIG. 2A) and the in vitro splicing of the resulting pre-mRNAs was carried out in a HeLa extract supplemented in the presence or the absence of the recombinant GST-MS2 protein. As seen in FIG. 2B, positioning GST-...
example 3
Effects of Targeted Protein Binding in Trans on Splice Site Interference in vitro
[0149] The applicants also determined that targeting protein binding to promote interference did not require that the binding site be present in cis (i.e., on the pre-mRNA itself. Indeed, the binding site was effective when provided in trans using an oligonucleotide that contains the protein binding site and a portion complementary to the target sequence. A series of antisense oligos complementary to a portion of the C5′− / − pre-mRNA −4 to −23 upstream of the proximal 5′ splice site (FIG. 4A) was designed. The C5-M4A1 oligo contains a16 nt-long non-hybridizing 5′ extension made of DNA and carrying one high-affinity binding site for the hnRNP A1 / A2 proteins (TAGGGA). The C5-M4A1W contains the winner RNA sequence for optimal hnRNP A1 binding. A mutated version of this oligo (C5-M4A1M) harboring two GGG to CGC mutation was used as a control. Oligos carrying a non-related 16 nt-long tail (C5-M4CT) or lackin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| structure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| ligand affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com