Communication method for wireless LANS
a communication method and wireless lan technology, applied in the field of communication apparatus, can solve the problems of affecting the increase of throughput, unable to improve the effective throughput of communication, and the format of a phy frame ceases to be effective any more, so as to improve the substantial throughput of communication, eliminate overhead, and improve frame format efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
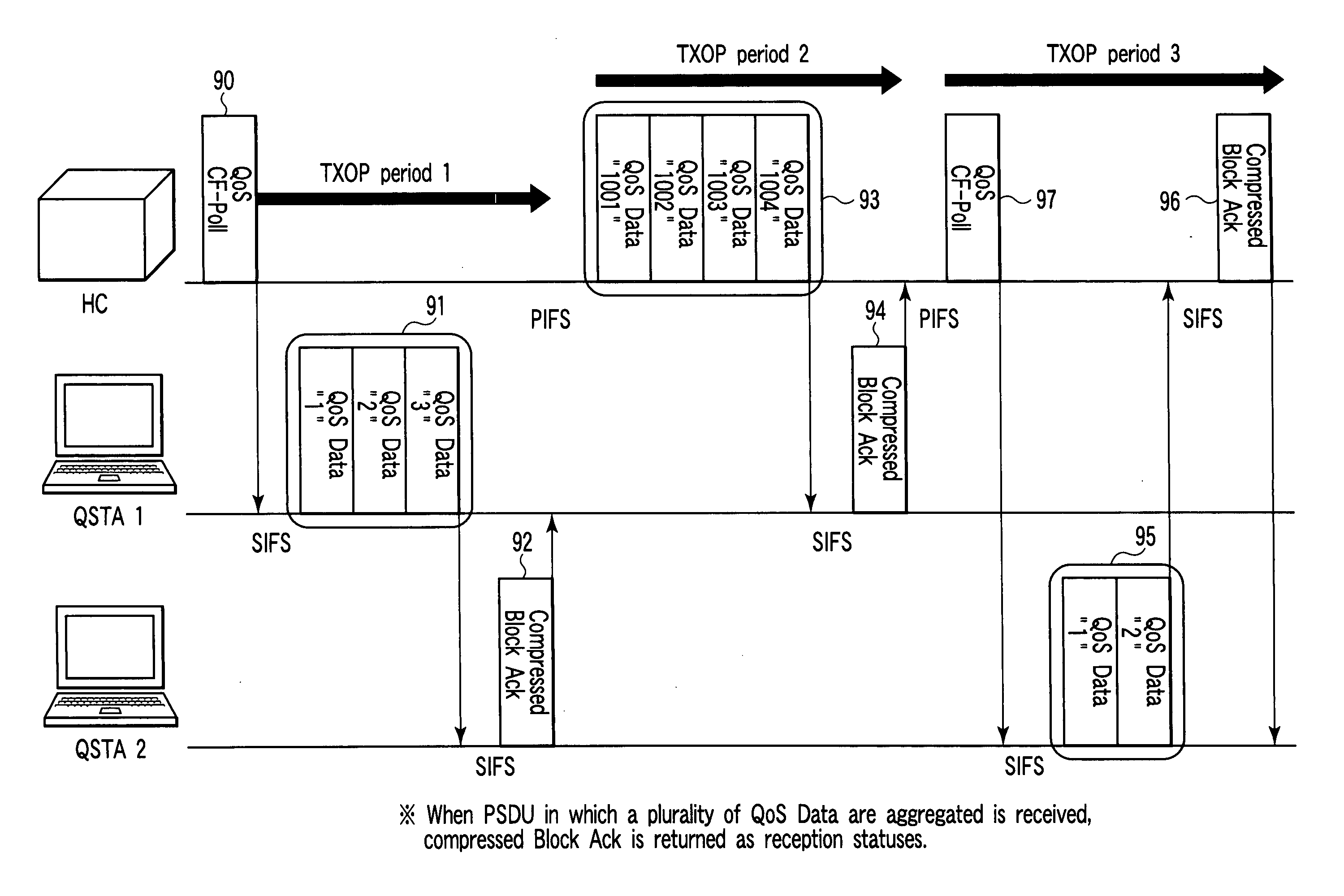
[0069] In the first embodiment of the present invention, the MAC efficiency is improved by aggregating a plurality of MPDUs and then piggybacking the MPDUs in the opposite direction on a partial response from a destination. Application methods for the immediate Block Ack and delayed Block Ack techniques defined in IEEE 802.11e / Draft 10.0 will also be described below.
[0070] More specifically, a communication apparatus according to the first embodiment piggybacks at least one data frame on a Block Ack frame in immediate Block Ack transmission. For this purpose, the initiator side of data transmission transmits a transmission permission frame, which permits a destination terminal to piggyback a plurality of data frames, upon aggregating the control frame (Block Ack Request frame, or Block Ack frame) with a data frame. Such communication apparatus of the first embodiment searches a physical frame returned from a destination, when operating as a transmitting terminal. If Block Ack frame...
second embodiment
[0102] The second embodiment of the present invention is directed to delayed Block Ack transmission, in which a Normal acknowledgement frame for allowing the transmission of a Block Ack to be postponed is replaced with the IAC frame described in the first embodiment. More specifically, a communication apparatus according to the second embodiment of the present invention transmits a plurality of data frames and then uses an IAC frame from a destination terminal to another destination in place of a Normal acknowledgement to a delayed Block Ack. After a lapse of a predetermined period of time, the destination terminal transmits the Block Ack frame and a plurality of data upon aggregating them.
[0103] According to IEEE 802.11e / Draft 10.0, if it is difficult to return a Block Ack frame a SIFS after the reception of a Block Ack Request frame, a delayed Block Ack like the one shown in FIG. 5 can be used. According to the delayed Block Ack technique, first of all, an Ack response (Normal ac...
third embodiment
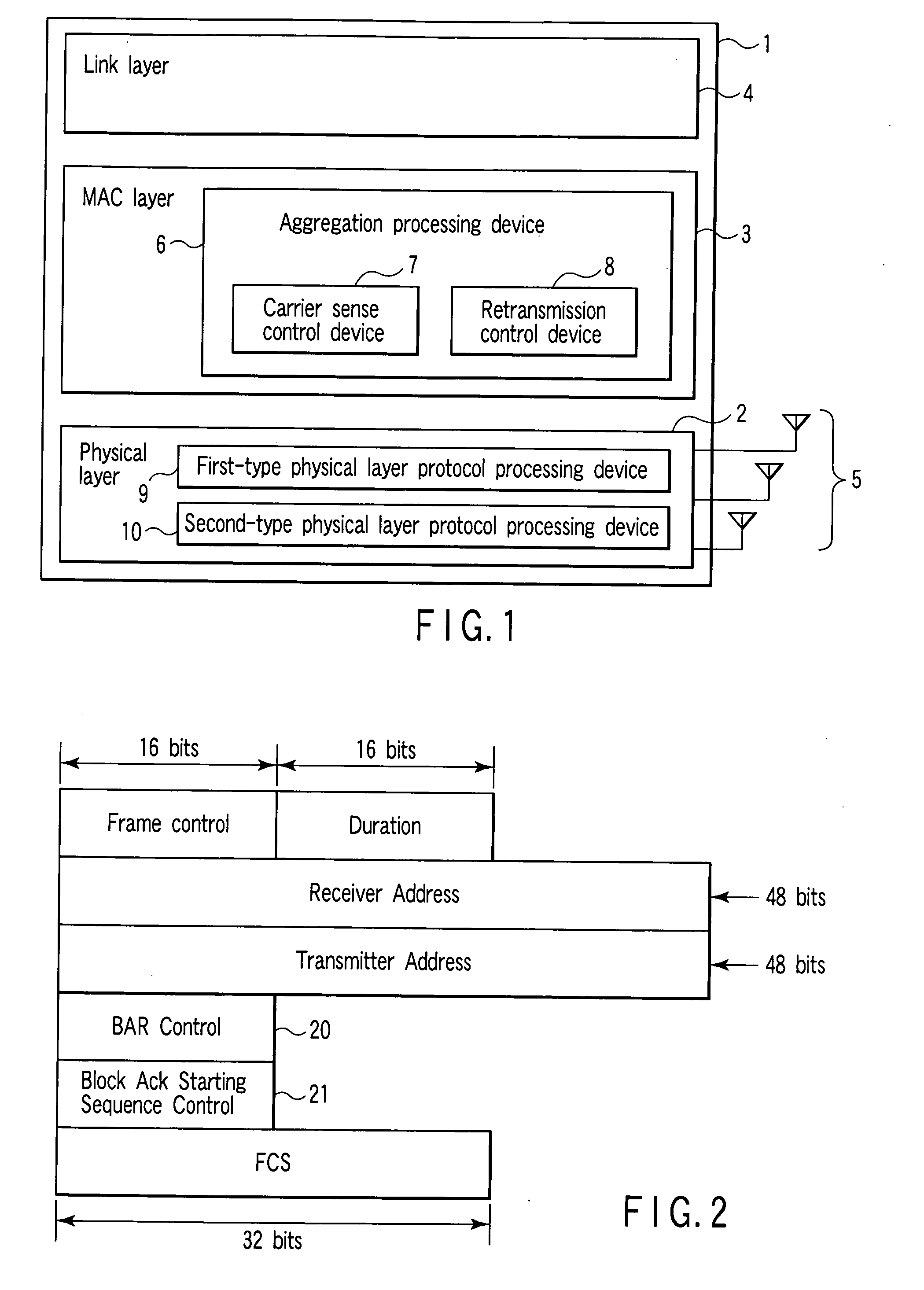
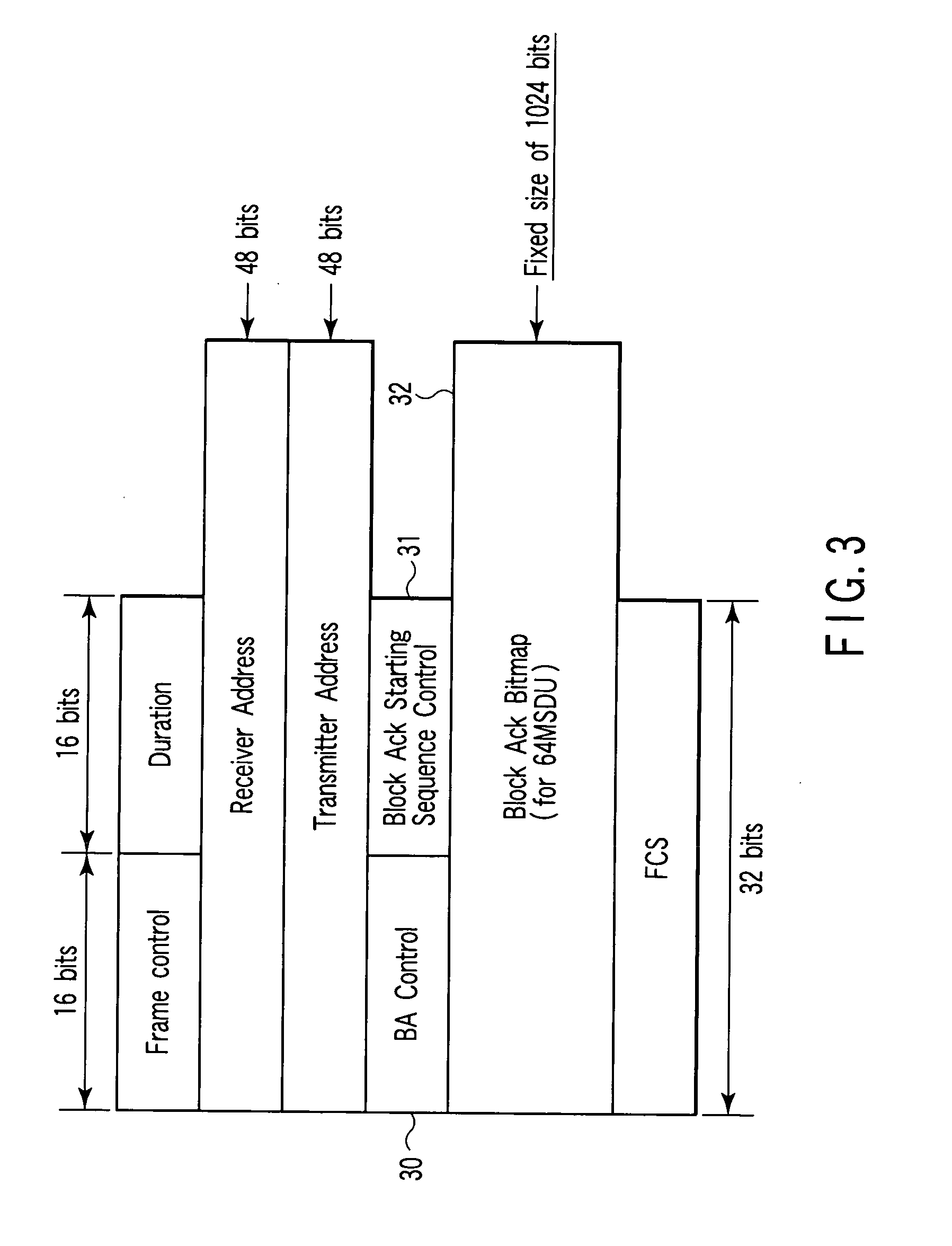
[0116] The third embodiment of the present invention is directed to the application of the immediate Block Ack technique and delayed Block Ack technique in a case wherein a plurality of MPDUs are aggregated and transmitted to a plurality of destinations. When only MAC frames addressed to the same destination are to be aggregated and transmitted, overheads like IFS (Interframe Space) and random backoff occur every time the destination changes. In contrast to this, aggregating MAC frames addressed to a plurality of different destinations into one physical frame makes it possible to reduce these overheads and improve the MAC efficiency.
[0117]FIG. 31 shows an example of a MAC frame containing information associated with a plurality of destinations. Aggregating a MAC frame 310 like this frame in the head of a physical frame allows a physical frame receiving terminal to immediately determine whether or not there is any MPDU addressed to itself exists. The MAC frame 310 like the one shown...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com