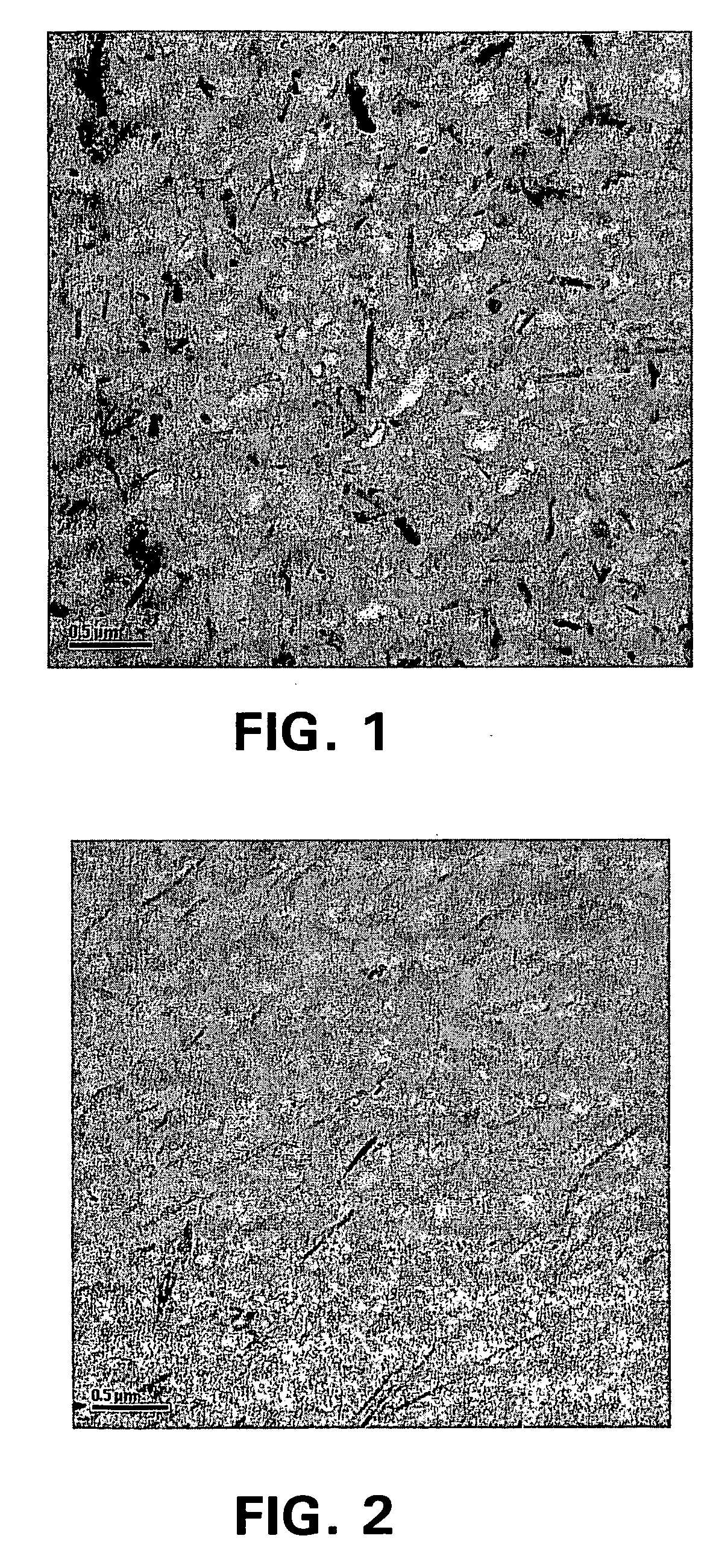
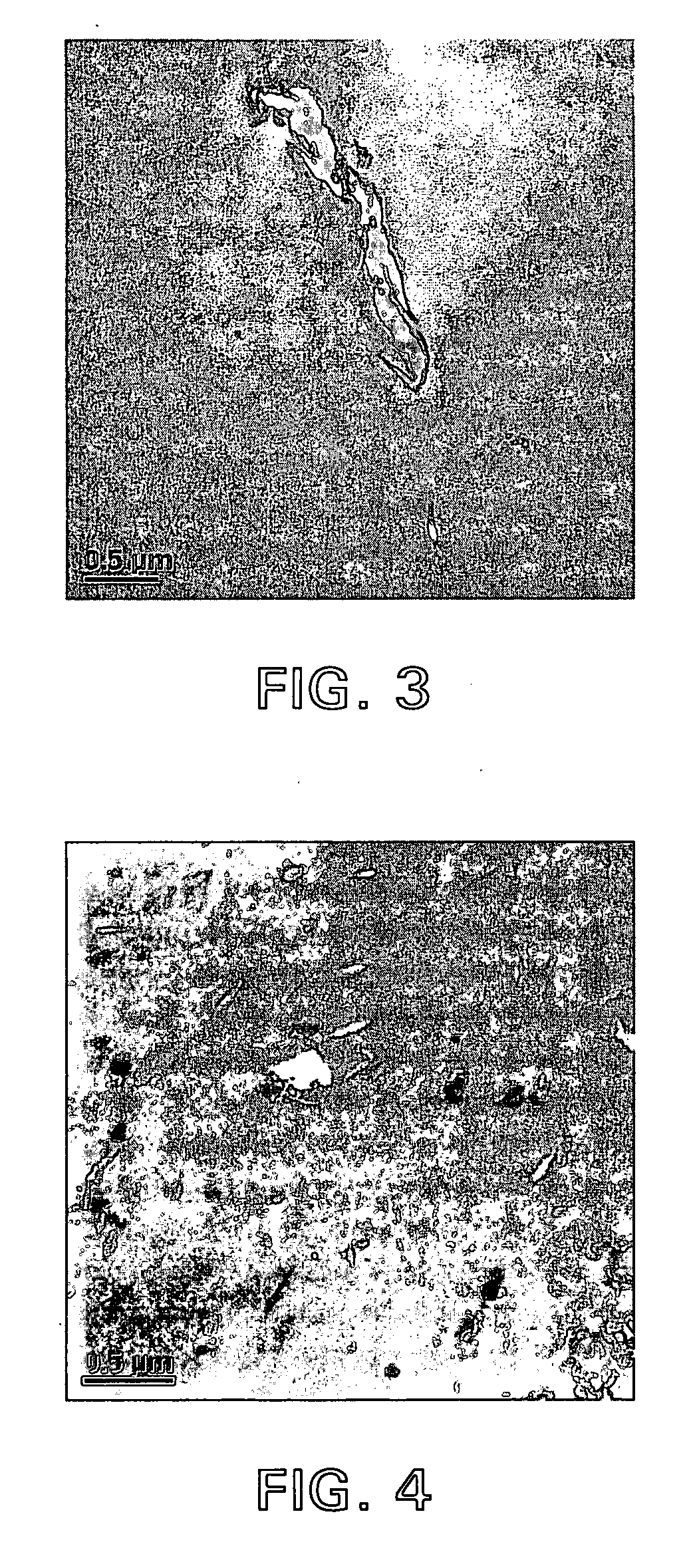
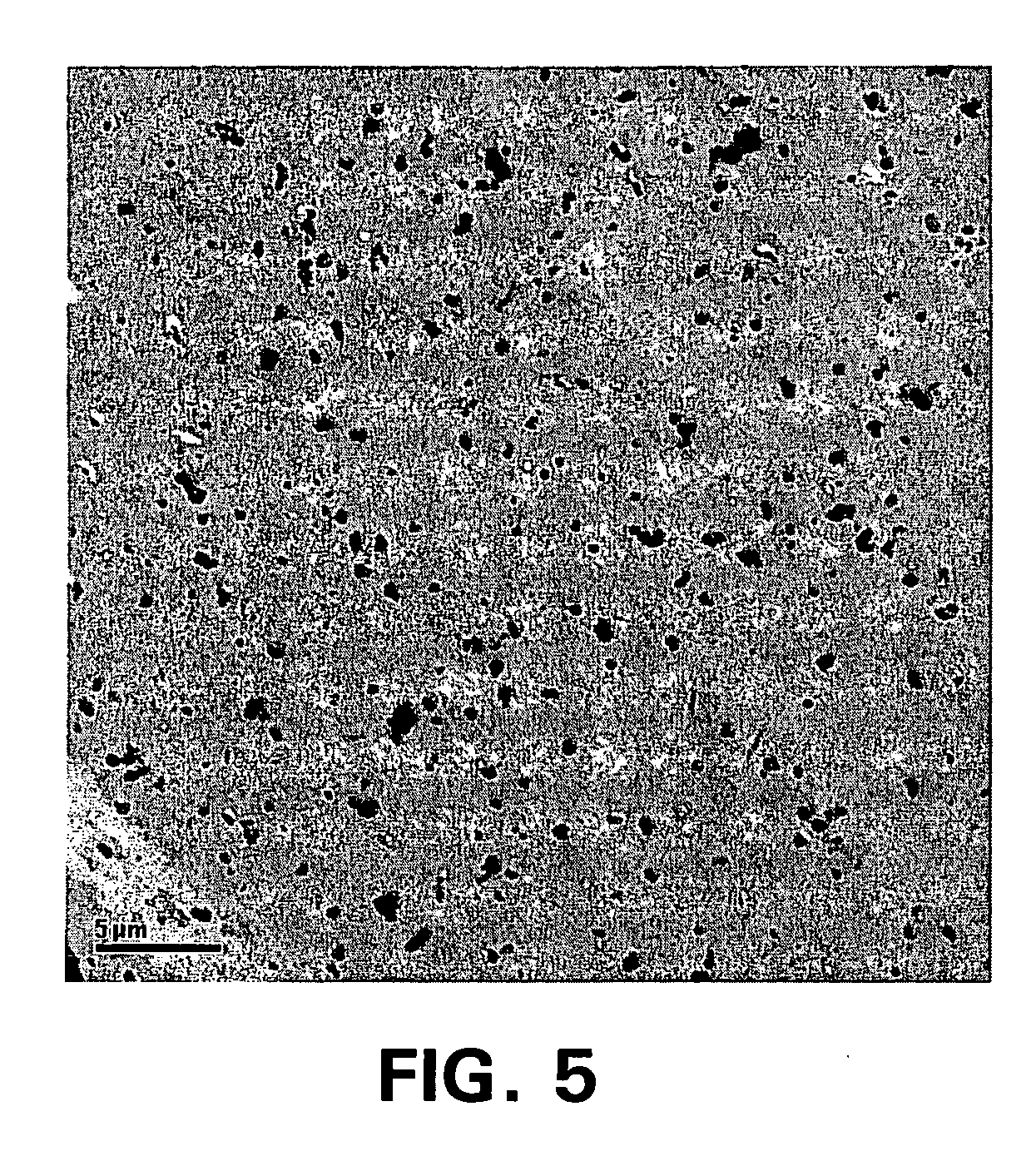
Compositions of polyesters and sepiolite-type clays
a technology of sepiolite clay and polyester, which is applied in the field of polymer polyester and sepiolite clay compositions, can solve the problems of introducing the same thermal stability problems, sacrificing the performance and material toughness of low temperature impact, and only marginally successful attempts to generate nanocomposites or compositions containing nanosized particles dispersed in thermoplastic polyester matrix
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0143] BHET (300 g, 1.17 mol), sepiolite (Pangel® S9, 9 g), antimony oxide (96.5 mg, 321 ppm), and manganese acetate (102 mg, 340 ppm) were charged to a 500 mL three necked round-bottomed flask. An overhead stirrer was attached and a distillation condenser was attached. The reaction was heated to 180° C. under a light nitrogen flush. The reaction was held at 180° C. for 90 min. The reaction temperature was increased to 225° C. The reaction temperature was held at 225° C. for 30 min. The reaction temperature was increased to 295° C. at a rate of 1° C. / min. When the temperature reached 295° C., the reaction temperature was held constant for 30 min. The nitrogen flush was closed off and vacuum was slowly introduced. After 15 min, the vacuum was increased to a full vacuum eventually reaching a vacuum of 5 Pa. The reaction was maintained under vacuum for approximately 120 min. Mn=26000, PDI=1.81, % DEG=13 wt %, IV=0.9, Tg=65° C., Tm=228° C. The material so produced was characterized usin...
example 2
[0144] BHET (300 g, 1.17 mol), sepiolite (Pangel® B20, 9 g), antimony oxide (96.5 mg, 321 ppm), and manganese acetate (102 mg, 340 ppm) were charged to a 500 mL three necked round-bottomed flask. An overhead stirrer was attached and a distillation condenser was attached. The reaction was heated to 180° C. under a light nitrogen flush. The reaction was held at 180° C. for 90 min. The reaction temperature was increased to 225° C. The reaction temperature was held at 225° C. for 30 min. The reaction temperature was increased to 295° C. at a rate of 1° C. / min. When the temperature reached 295° C., the reaction temperature was held constant for 30 min. The nitrogen flush was closed off and vacuum was slowly introduced. After 15 min, the vacuum was increased to a full vacuum eventually reaching a vacuum of 5 Pa. The reaction was maintained under vacuum for approximately 120 min. Mn=26400, PDI=1.88, % DEG=6 wt %, IV=0.8, Tg=78° C., Tm=248° C. The material so produced was characterized usin...
example 3
[0149] BHET (300 g, 1.17 mol), sepiolite clay (Pangel® S9, 6g), antimony oxide (80 mg, 343 ppm), and sodium acetate (80 mg, 343 ppm) were charged to a 500 mL three necked round-bottomed flask. An overhead stirrer was attached and a distillation condenser was attached. The reaction was heated to 180° C. under a light nitrogen flush. The reaction was held at 180° C. for 90 min. The reaction temperature was increased to 225° C. The reaction temperature was held at 225° C. for 30 min. The reaction temperature was increased to 295° C. at a rate of 1° C. / min. When the temperature reached 295° C., the reaction temperature was held constant for 30 min. The nitrogen flush was closed off and vacuum was slowly introduced. After 15 min, the vacuum was increased to a full vacuum eventually reaching a vacuum of 5 Pa. The reaction was maintained under vacuum for approximately 120 min. The reaction was cooled under a nitrogen purge.
[0150] Tm and Tg were determined as described above, and t1 / 2 was ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight percent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com