Simulated training environments based upon fixated objects in specified regions
a training environment and fixation point technology, applied in the field of system and method for calculating eye events (or foveatedobject events), can solve the problems of difficulty in mapping the sequence of fixation points produced by an eyetracker to objects, the failure of wide-spread application of the technology, and the high cost of eyetracker devices, etc., to achieve high cognitive fidelity and workload. high
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
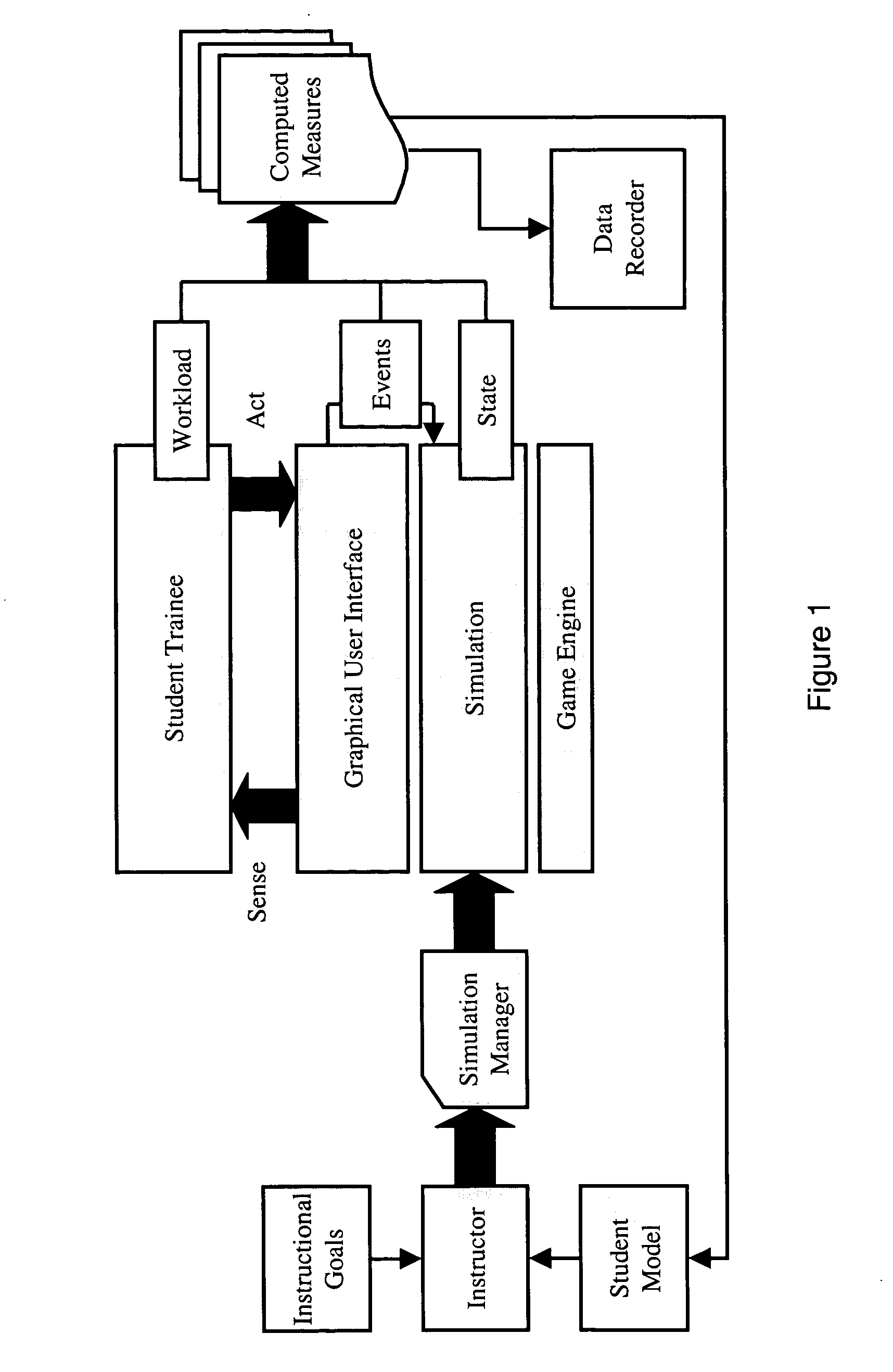
[0026]FIG. 1 is a block diagram of an eye-event-based student training system according to the invention. The trainee interacts through a graphical user interface with a computer simulation that may be built using a game engine. As with all of the embodiments described herein, the operator workload is optional and the degree of complexity associated with the system state is variable.
[0027] A simulation manager responds to feedback that results from student trainee interaction with the interface by dynamically directing the activities and presentation of the simulation. As the simulation is running, workload, events, and simulation state data are collected and combined to form computed measures that may be recorded using a data recorder for later analysis and / or playback. The computed measures are fed back into a student model that represents current student understanding. An instructor dynamically synthesizes the current student understanding in the student model with the overall i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com