Semiconductor processing methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018] This disclosure of the invention is submitted in furtherance of the constitutional purposes of the U.S. Patent Laws “to promote the progress of science and useful arts” (Article 1, Section 8).
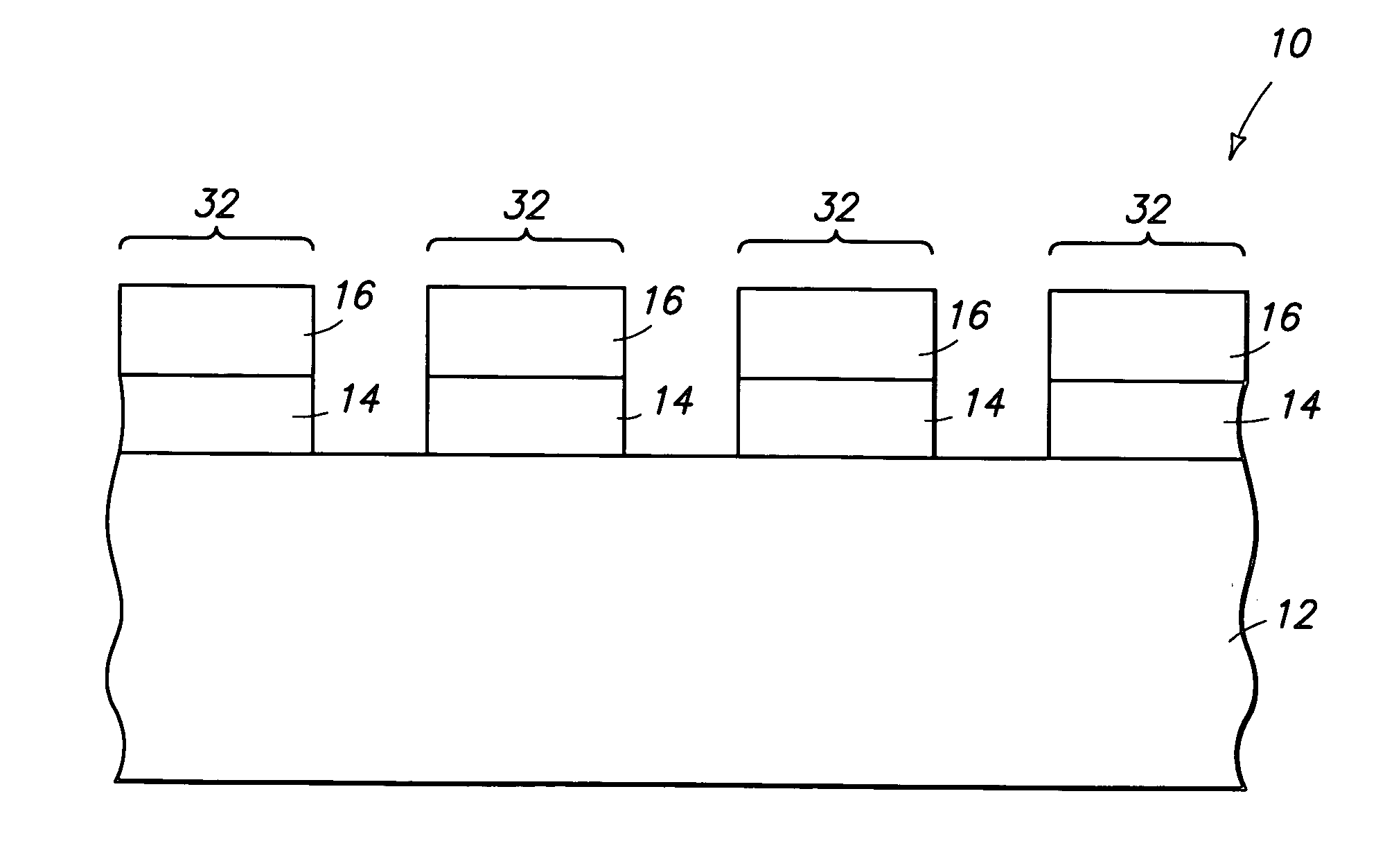
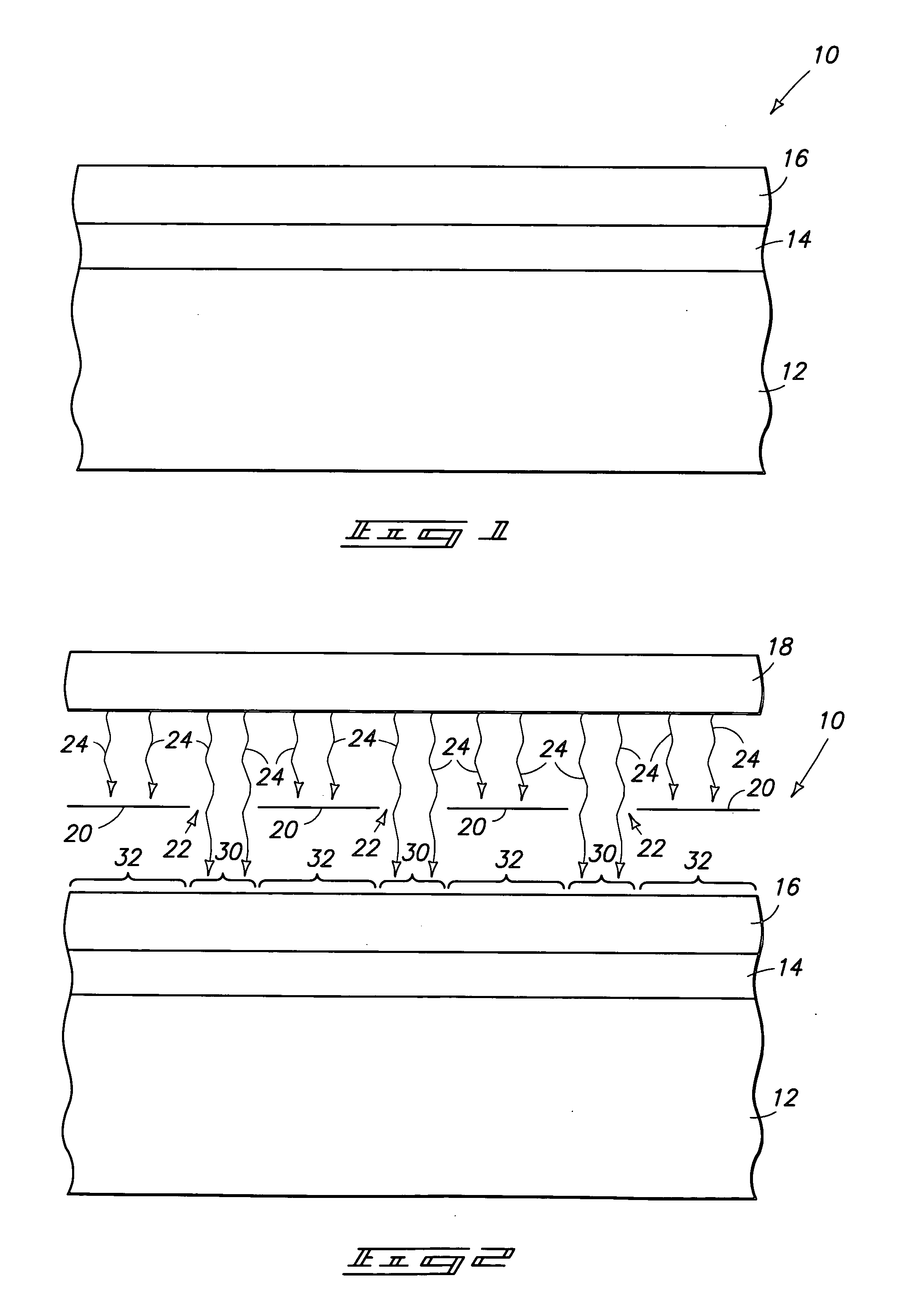
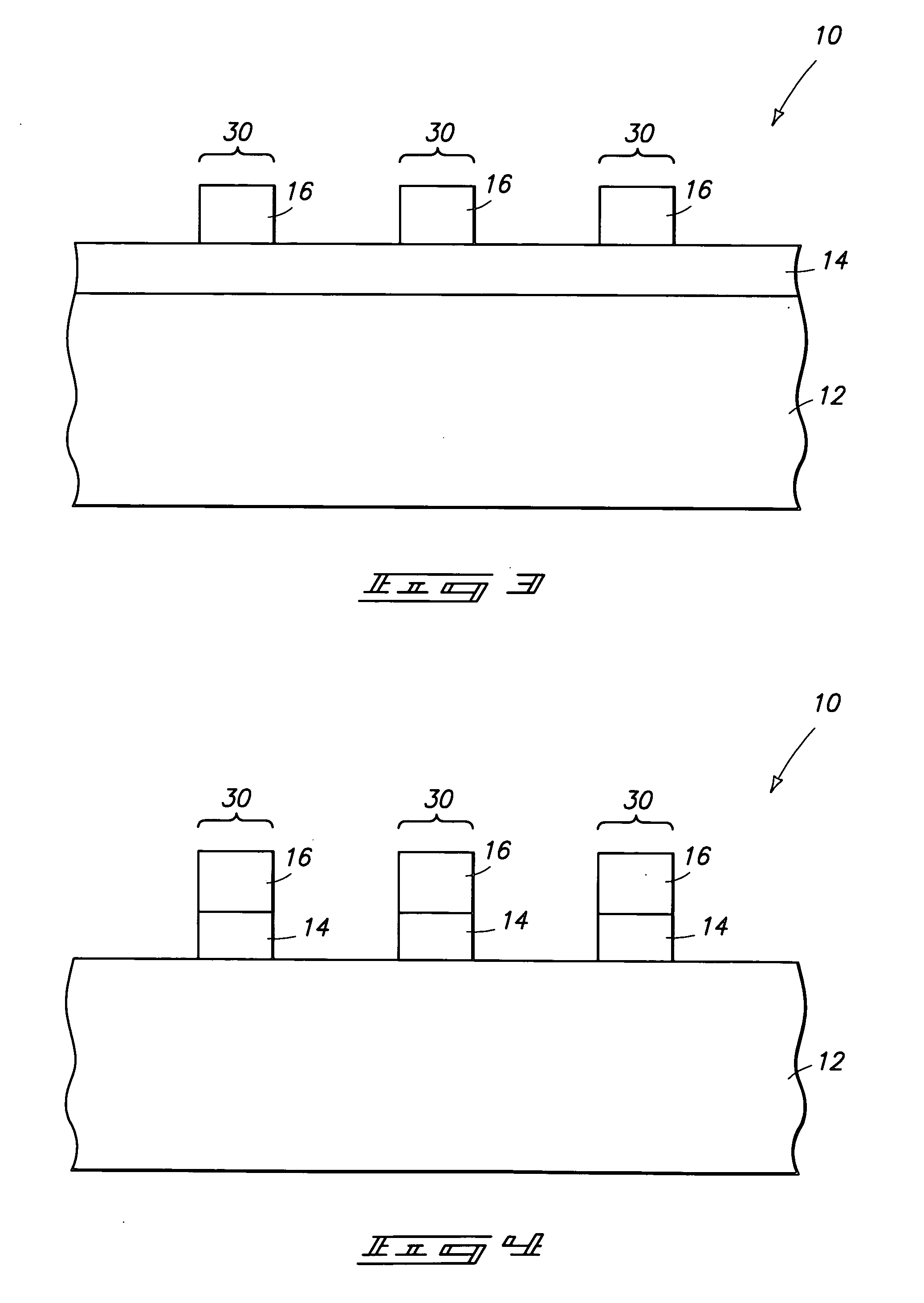
[0019] The invention encompasses methods for utilizing energy to form patterned masking materials on a wafer. In particular aspects of the invention, the patterned masking materials are retained on a wafer after a die-cutting process. In other particular aspects of the invention, the patterned masking materials comprise silicon. The invention is described with reference to a preferred embodiment in FIGS. 1-8.
[0020] Referring to FIG. 1, a semiconductive wafer fragment 10 is illustrated at a preliminary step of a processing sequence encompassed by the present invention. Wafer fragment 10 comprises a semiconductive substrate 12. Substrate 12 can comprise, for example, monocrystalline silicon lightly doped with a p-type conductivity enhancing dopant. To aid in interpretation of the claims ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com