Method for controlling an in-flight entertainment system
a technology for entertainment systems and in-flight entertainment, applied in the field of computer networks, can solve the problems of large hardware resources, labor-intensive and error-prone integration and testing, and severe restrictions on the selection of hardware and software components by the system provider, and achieve the effect of increasing hardware resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
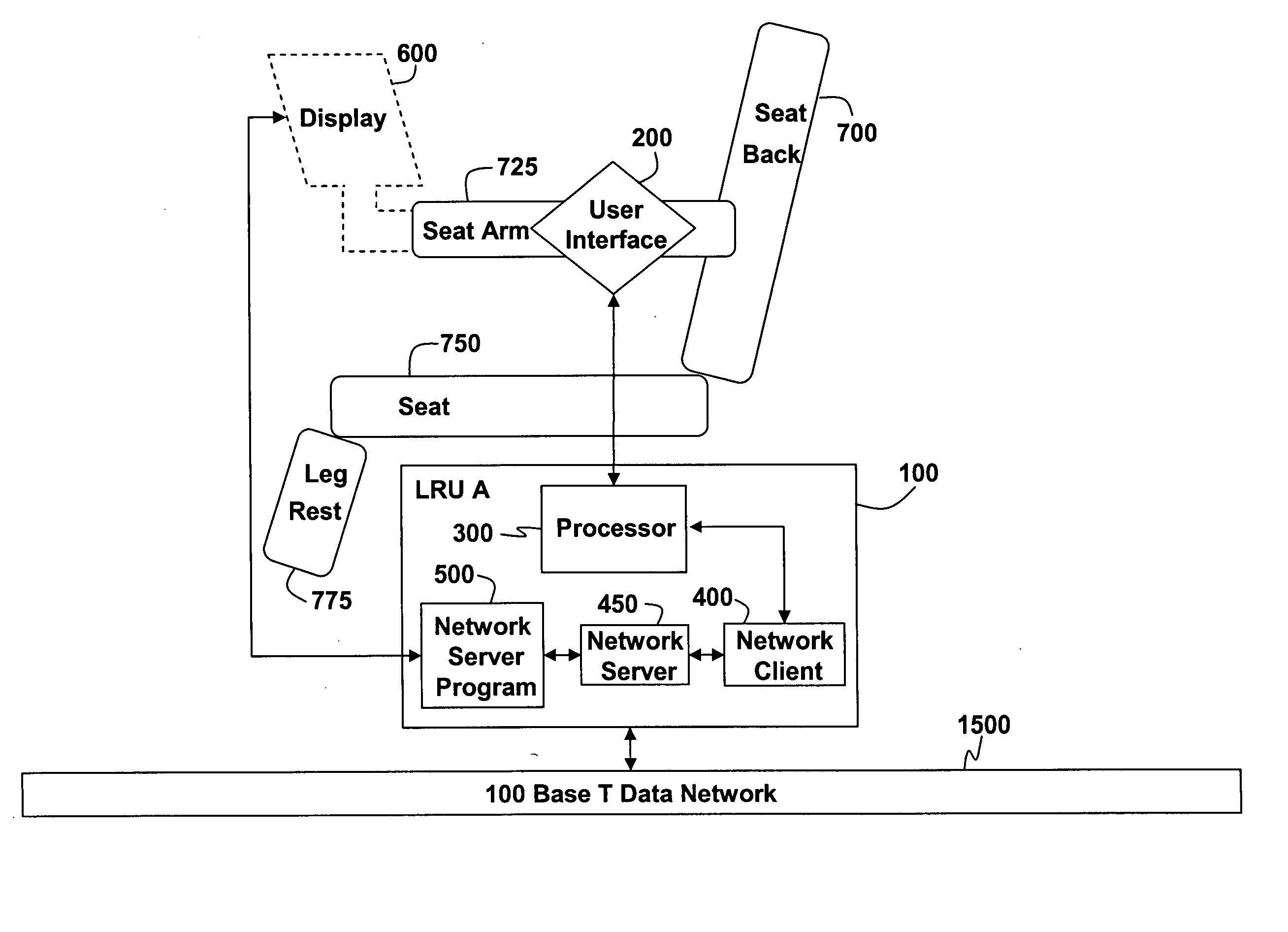
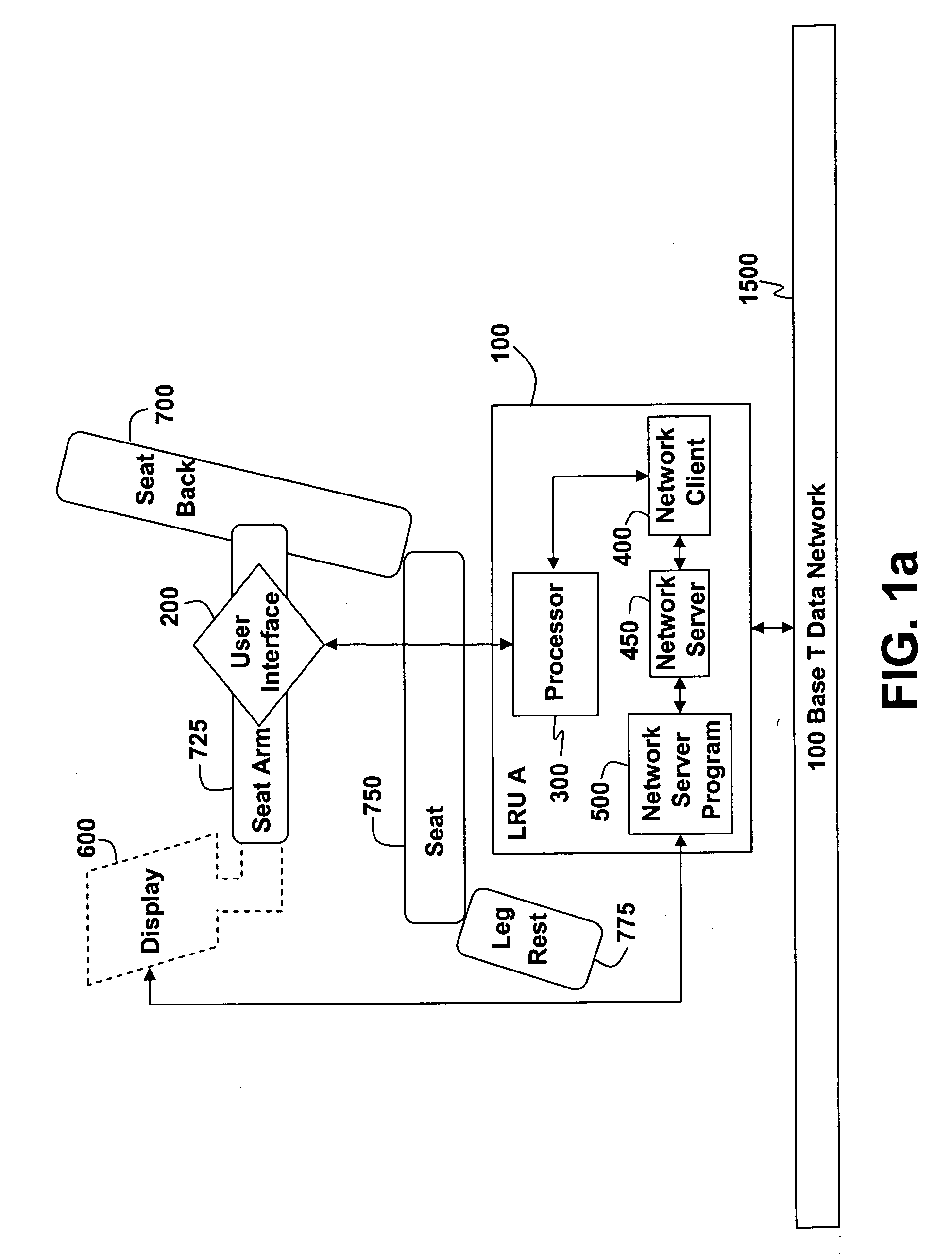
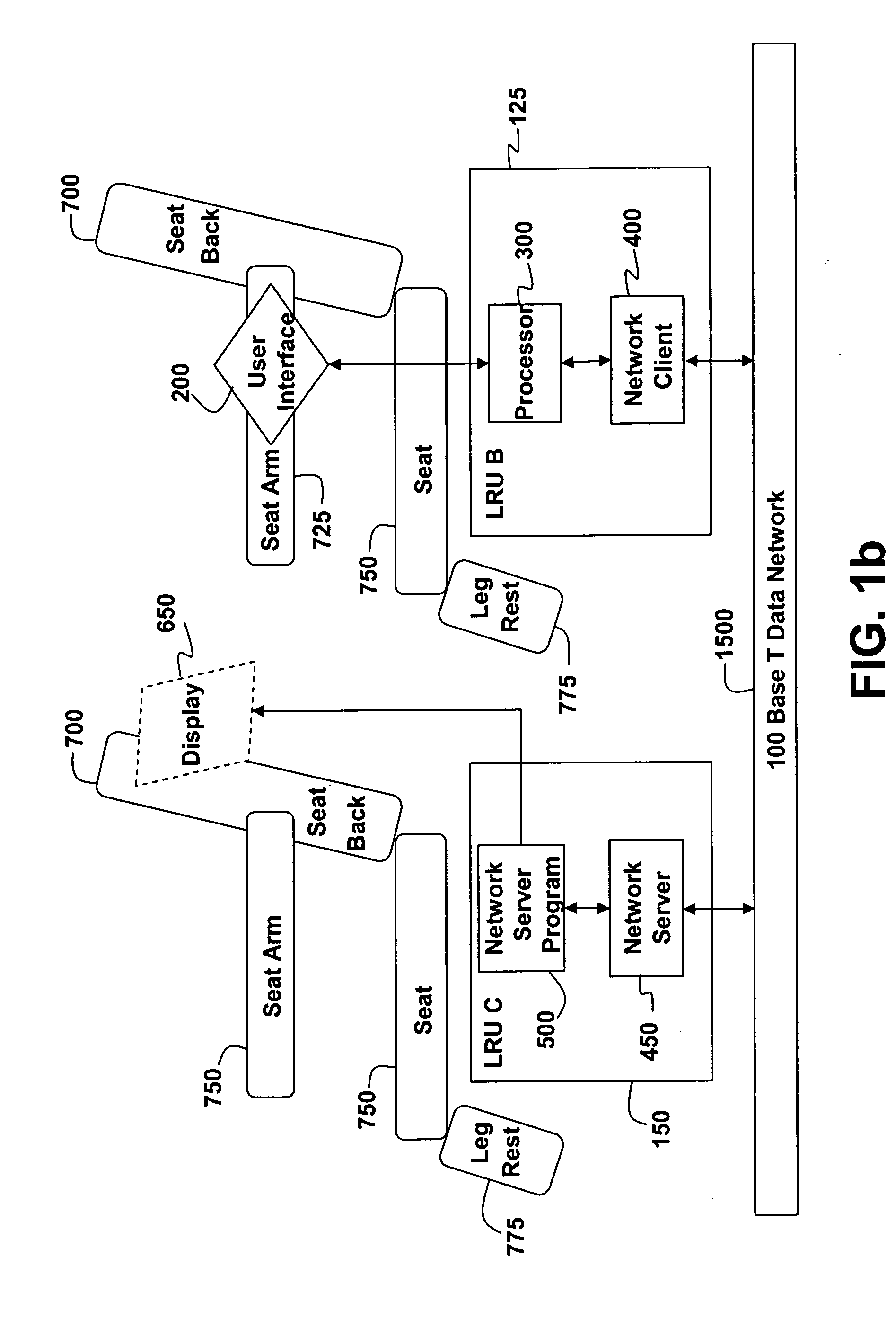
[0044] While the present invention is susceptible to various modifications and alternative forms, certain preferred embodiments are shown by way of example in the drawings and will be described in detail herein. It should be understood, however, that the description is not intended to limit the invention to the particular forms described; to the contrary, the description is intended to cover all modifications, alternatives, and equivalents falling within the spirit and scope of the invention defined by the appended claims.
[0045] The system and method of the present invention allow for a more flexible and modular IFE system by using network protocols for communication between LRUs within the system. Using network protocols improves efficiency of development efforts by reducing the probability of unintended conflicts between software loaded onto the plurality of LRUs within the system, and allows for easier upgrades and maintenance of software currently loaded within an IFE system. N...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com