Wireless communication handoffs within a macrocell
a macrocell and wireless communication technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of pilot pollution, scrambling code assignment, and inability of outside bts equipment to provide adequate radio frequency coverage, and achieve the effect of facilitating handoffs and reducing the number of cell definition codes required
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
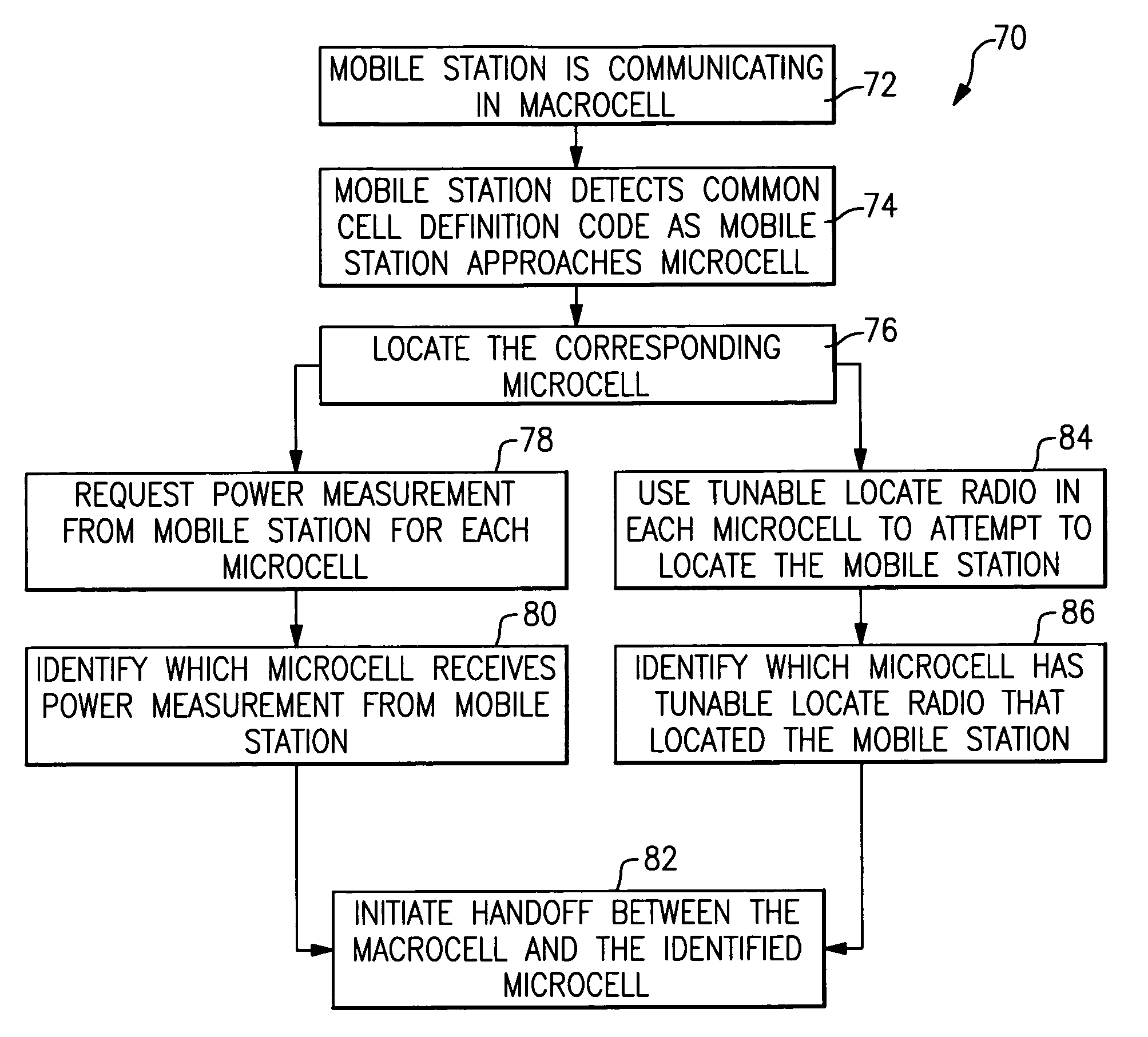
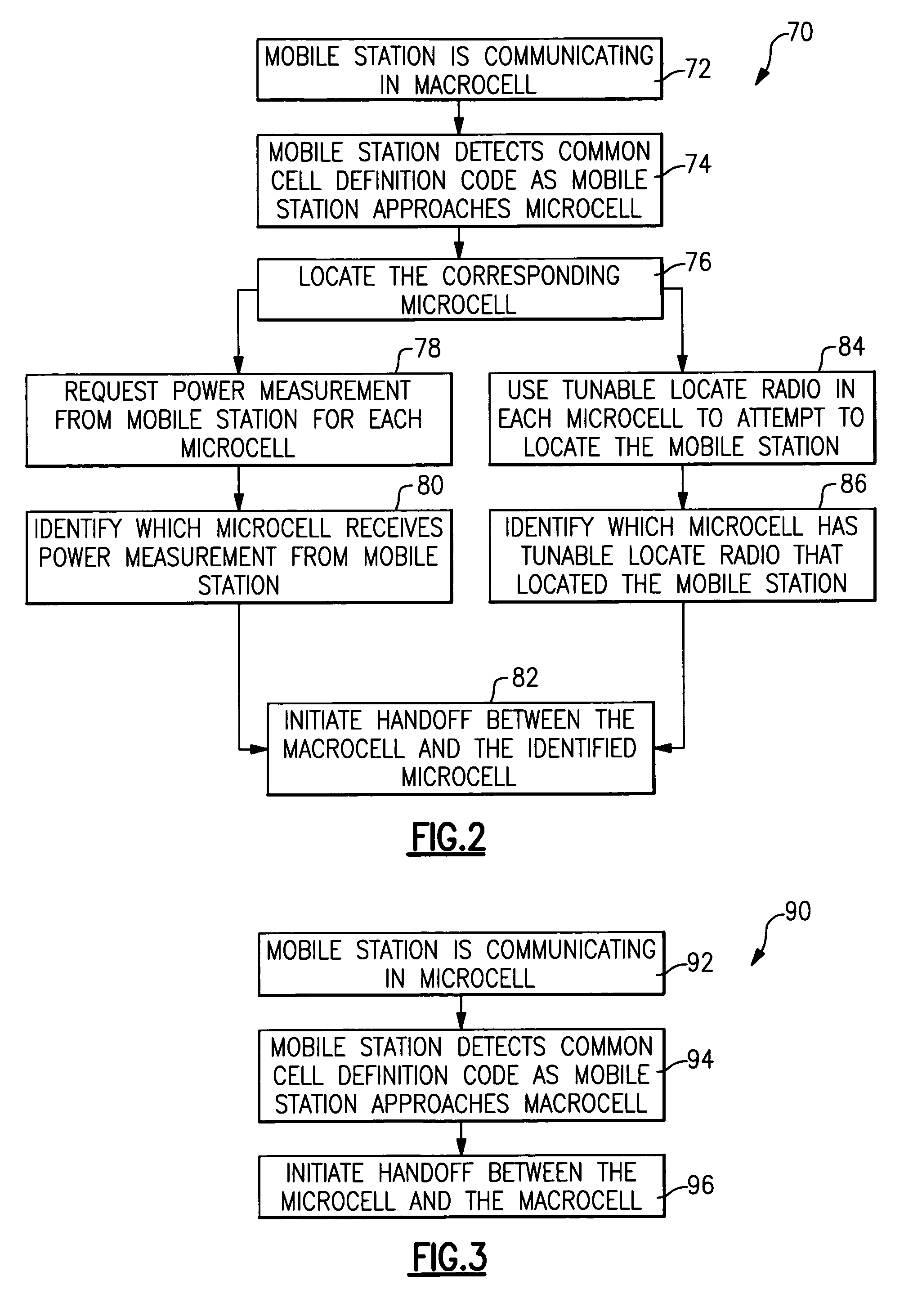
[0027] This invention includes a unique strategy for triggering handoff between a macrocell and any one of a plurality of microcells such as in-building cells within the macrocell coverage area. A disclosed example includes using a common cell definition code for each of a plurality of microcells within a microcell coverage area. One common cell definition code is used for triggering handoffs from the macrocell to a microcell. Another common cell definition code is used for triggering all handoffs from a microcell to the macrocell. Techniques for locating the mobile station provide sufficient identity of the microcell involved in a handoff as a mobile station enters the microcell coverage area.
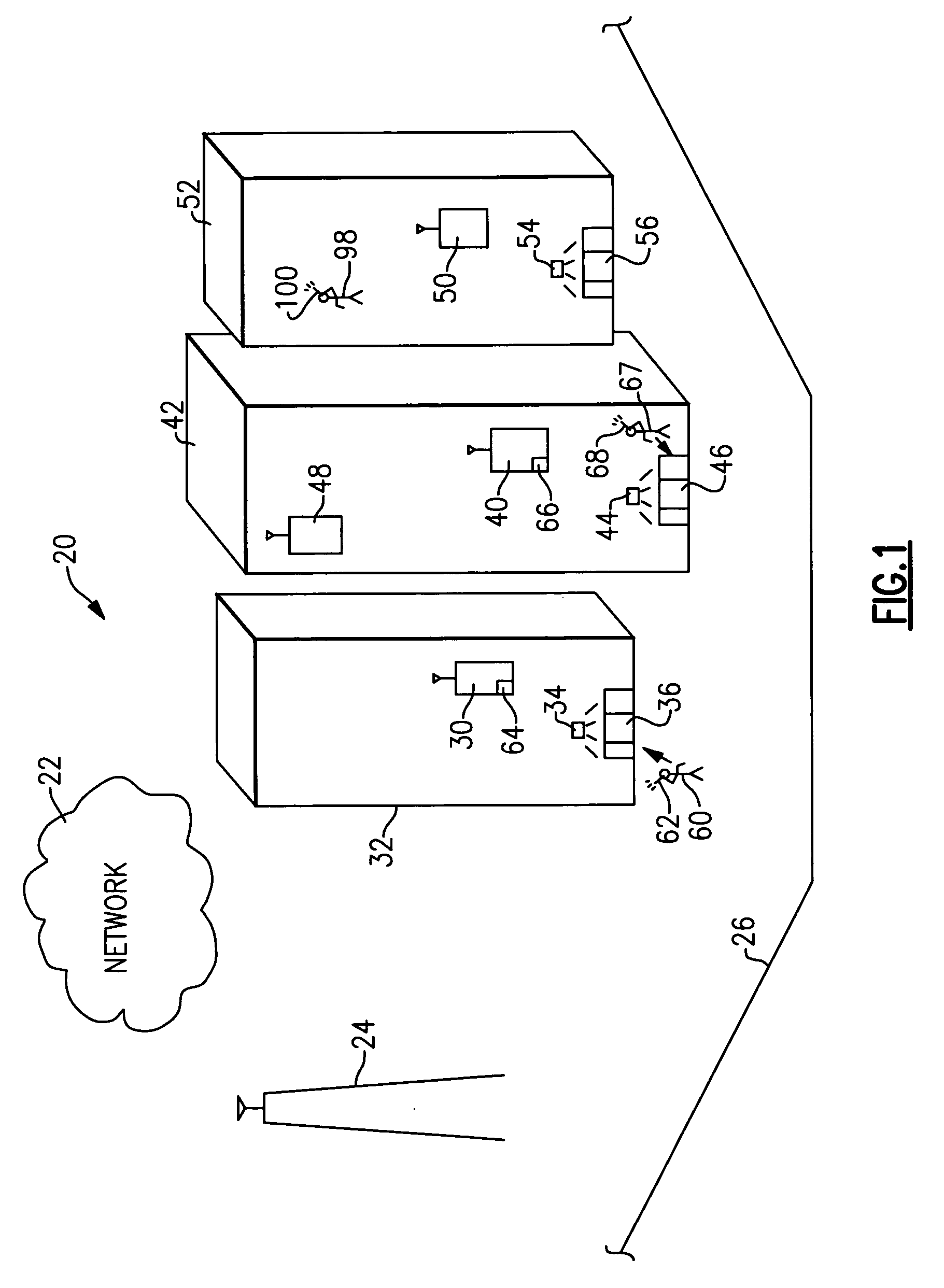
[0028]FIG. 1 schematically shows selected portions of a wireless communication system 20. A wireless network 22 includes known elements and operates in a known fashion to facilitate wireless communications. In the illustration, a base station transceiver (BTS) 24 and an associated radio tower...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com