Ultrahigh density ferroelectric storage and lithography by high order ferroic switching
a high-density, ferroelectric technology, applied in the direction of ferroelectric carrier recording, record information storage, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of limiting the minimal domain size that can be achieved
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
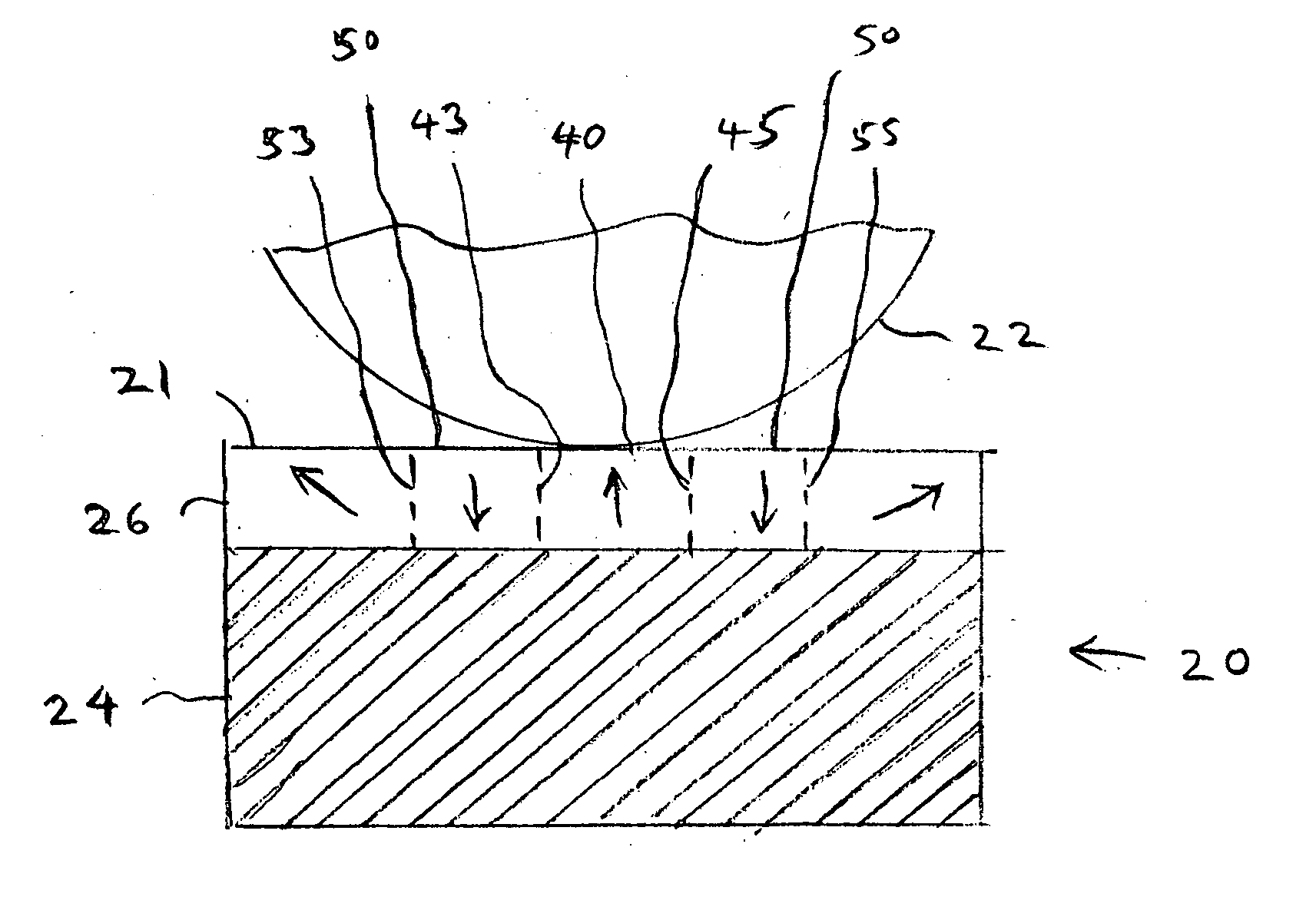
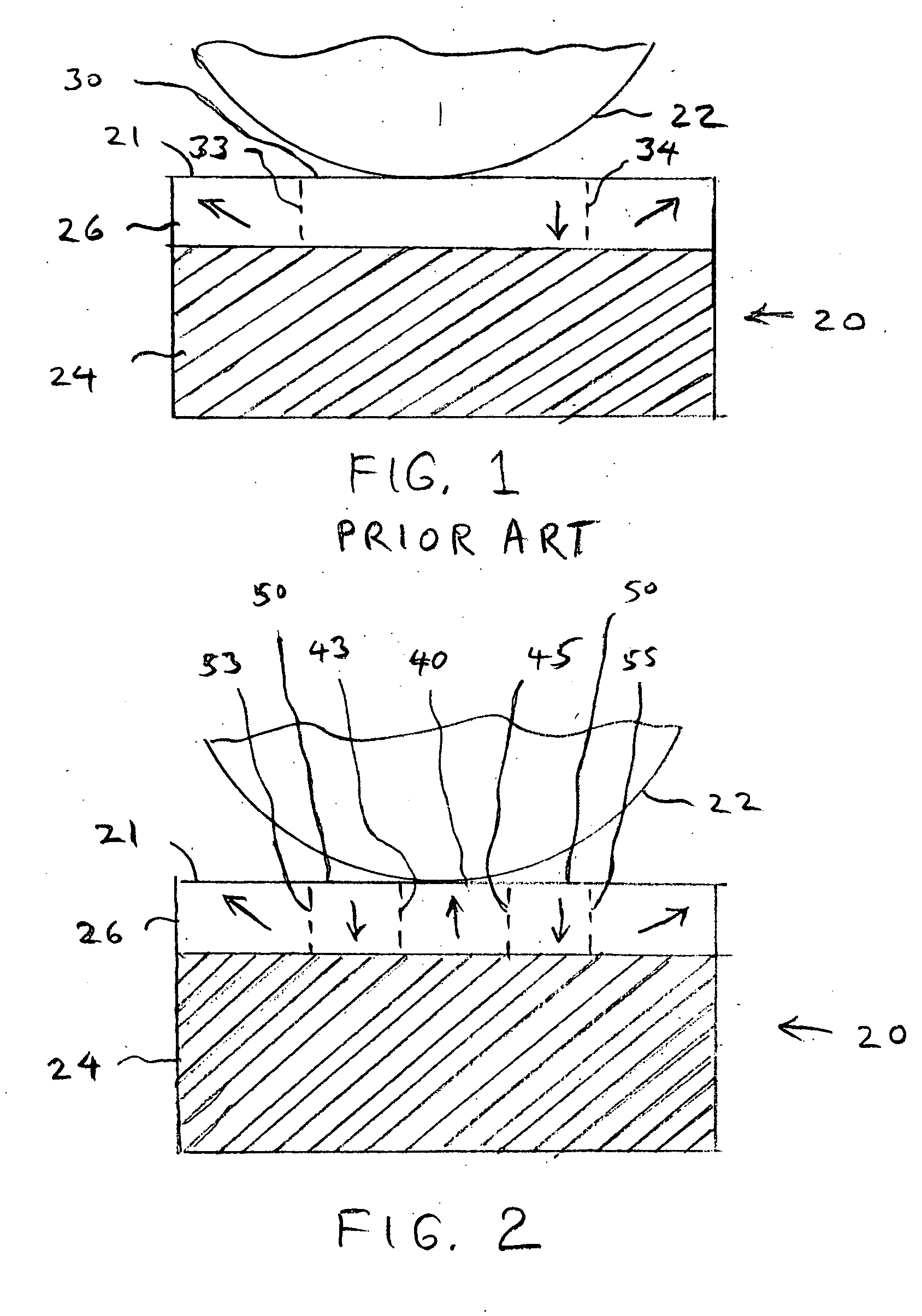
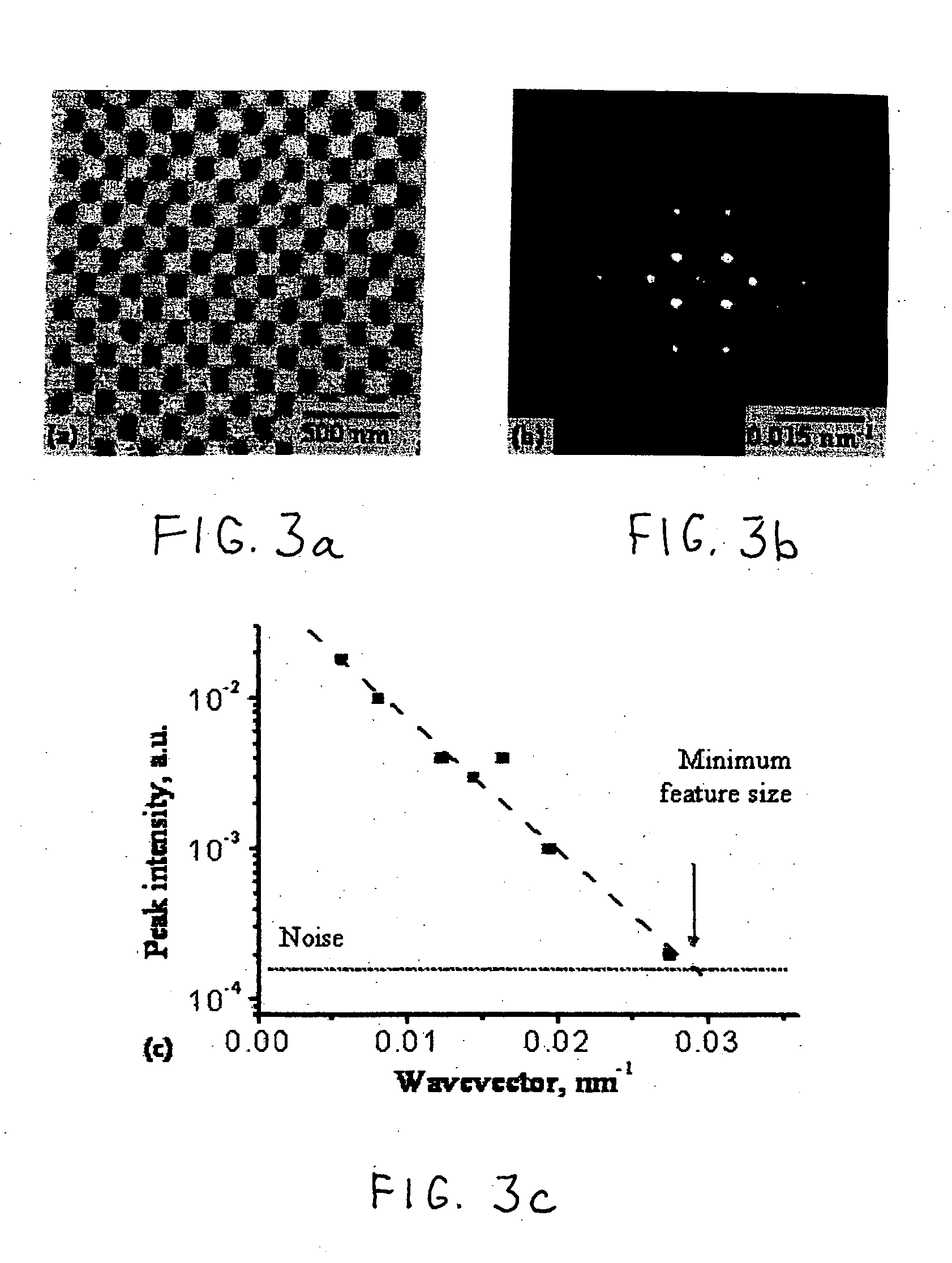
[0027] Turning now to the drawings in greater detail and considering first FIG. 1, there is illustrated a schematic representation of a ferroelectric structure, generally indicated 20, embodying a ferroelectric material whose direction of polarization can be switched with a cantilevered Atomic Force Microsocopy (AFM) tip 22 which is mounted for movement toward and away from the surface, indicated 21, of the ferroelectric structure 20 in accordance with known techniques. In this connection, the ferroelectric structure 20 includes a suitable conductive substrate 24 (e.g. silicon, germanium platinized silicon or non-ferroelectric oxide) and a thin film layer 26 of ferroelectric material which has been built up upon the substrate 24.
[0028] The material of the ferroelectric layer 26 can be any of a number of known ferroelectric materials, such as an oxide perovskite or a ferroelectric polymer. In any event, however, the polarization of the ferroelectric layer 26 (before the tip 22, when...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| ferroelectric domain size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| ferroelectric | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| polarity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com