Wind generator
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
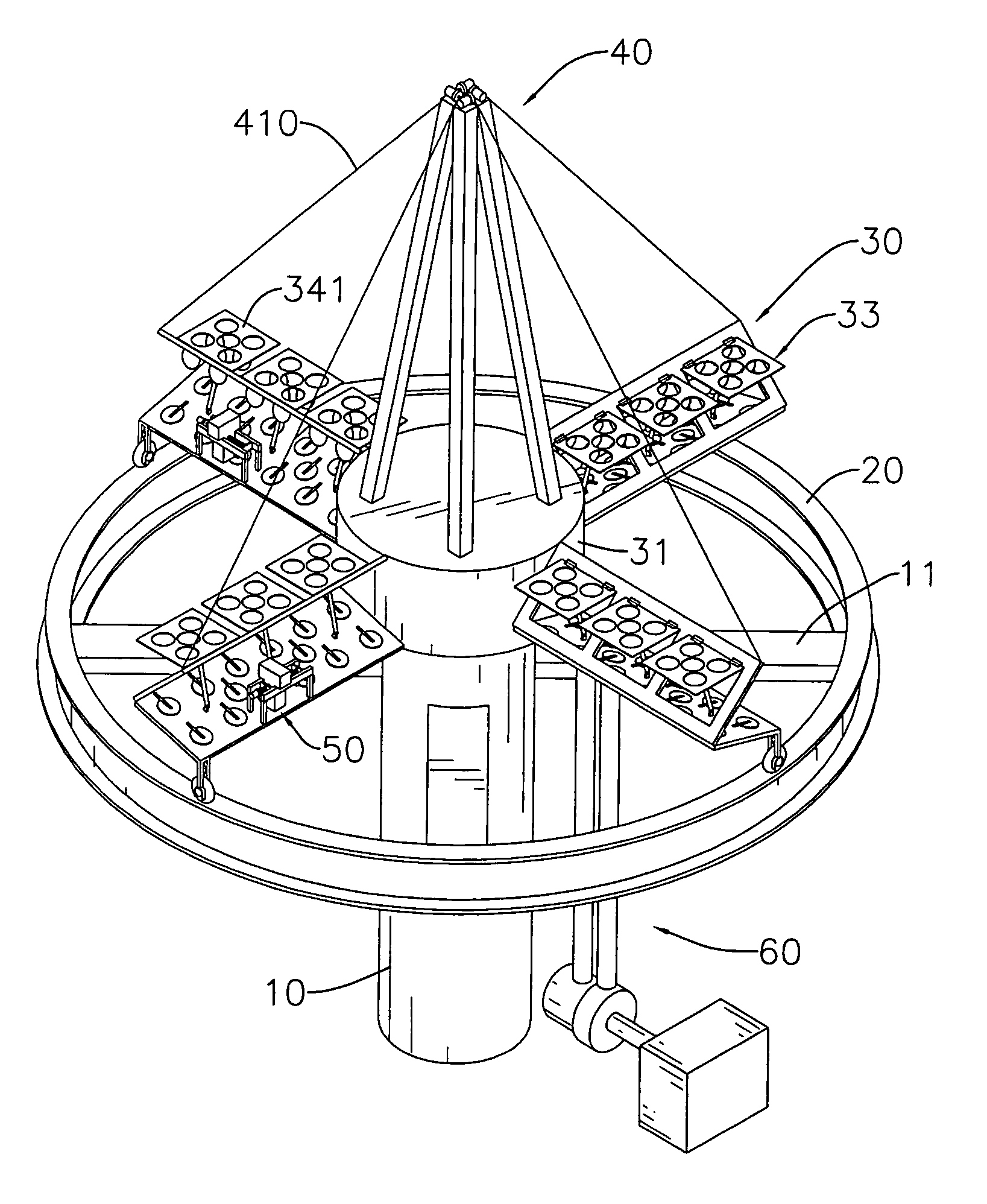
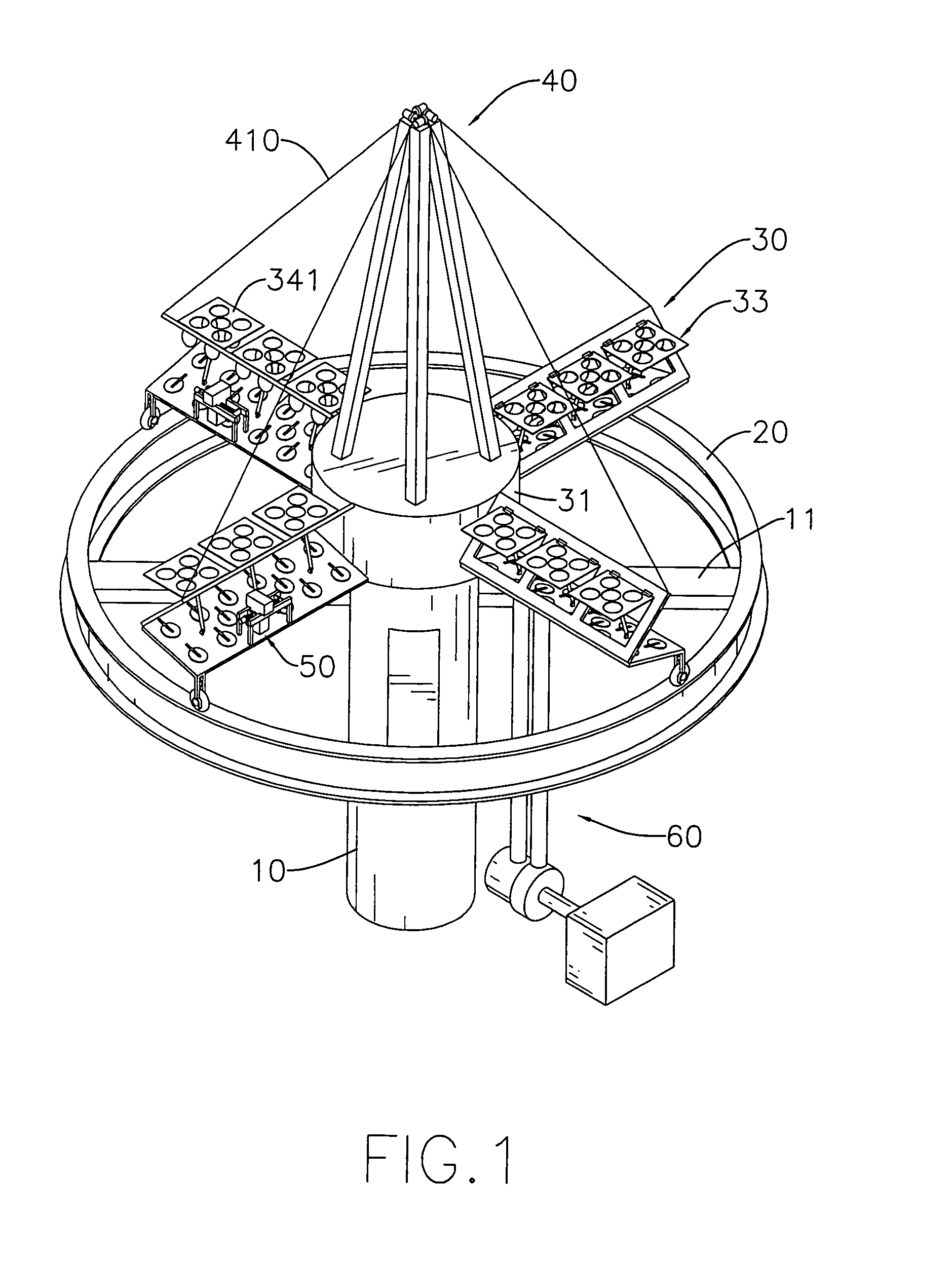
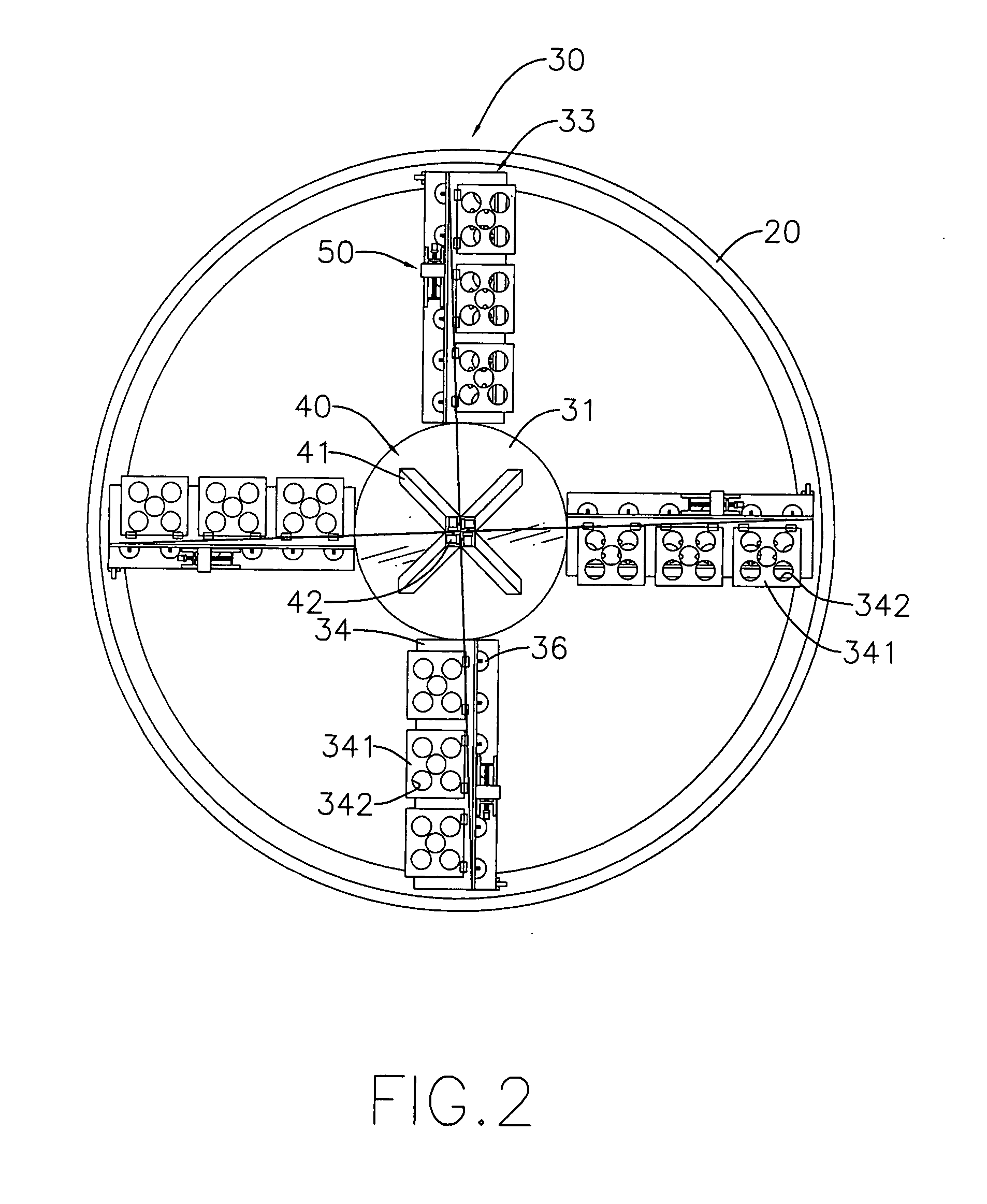
[0020]With reference to FIGS. 1, 2 and 3, the wind generator in accordance with present invention comprises a post (10), a rail (20), a blade assembly (30), a stay assembly (40), a generator assembly (60) and an optional accelerating motor (70).
[0021]The post (10) may be tubular, is securely mounted on a surface of a building, a ground or such like, and has a top and at least two support bars (11) perpendicularly attached diametrically near the top of the post (10).
[0022]The rail (20) is annular and is mounted on the support bars (11) of the post (10).
[0023]The blade assembly (30) is mounted rotatably on the top of the post (10), is pushed by the wind to rotate relative to the post (10) and has a base (31), a bearing (32) and multiple blades (33).
[0024]With further reference to FIG. 6, the base (31) is an open container, may be cylindrical and has a bottom opening (310). The bottom opening (310) is rotatably mounted around the top of the post (10) and has an inner surface and multip...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com