Ventilation system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
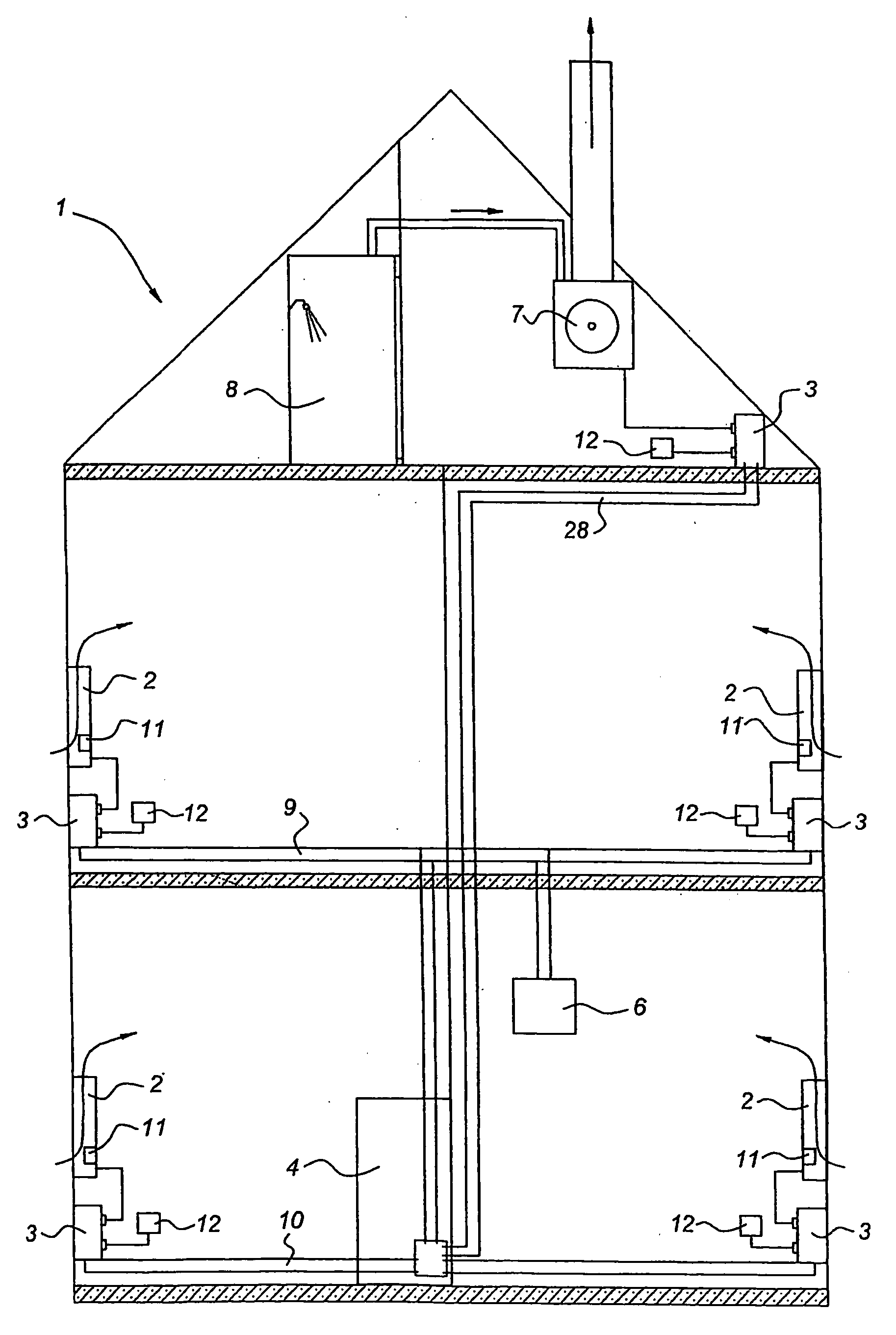
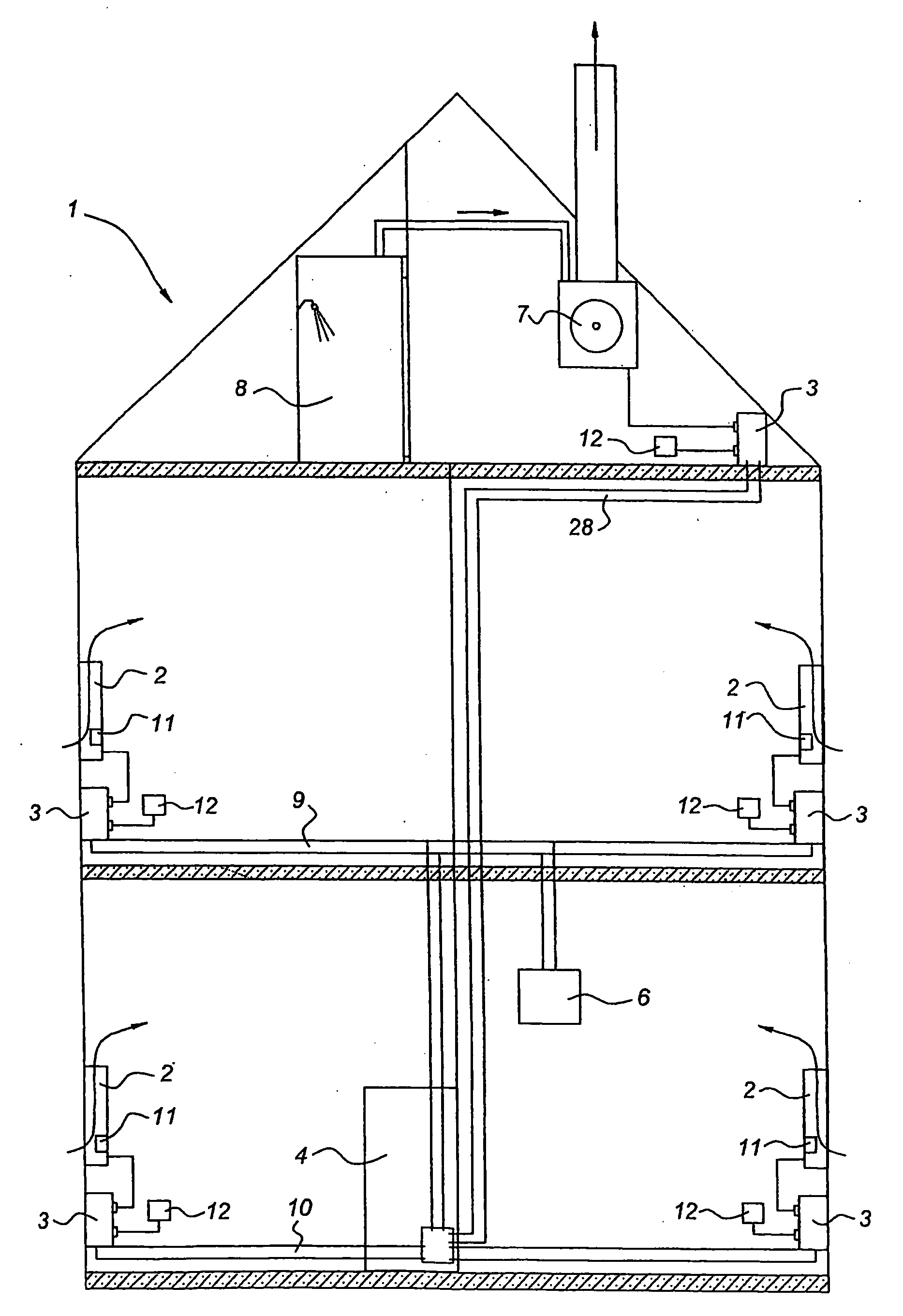
[0027] In FIG. 1 a building is indicated by 1. The blowers are indicated diagrammatically by 2. Various sockets are indicated by 3. The attic floor of the building is provided with a mains network 28, the first floor with mains network 9 and the ground floor with mains network 10. These mains network are on different phases and come together in the meter cupboard 4. An extractor 7 has been installed in the top of the building. This provides extraction for, inter alia, a shower room 8. Via the various chinks between doors and the like, extraction from the shower room 8 results in a reduced pressure in the building. However, this is negated by the action of the blowers 2. Control of the blowers 2 takes place with the aid of a control unit or central controller 6. This is likewise connected to the mains network 9. This connection of the controller 6 and of the blowers 2 to the mains network is the only connection. With the aid of the multiplexing technique it is possible to control the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com