Stilts
a technology for stilts and lower legs, applied in the field of stilts, can solve the problems of metal construction of 515, high production cost, and difficulty in straightening, and achieve the effect of improving the quality and improving the stability of the lower leg braces
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
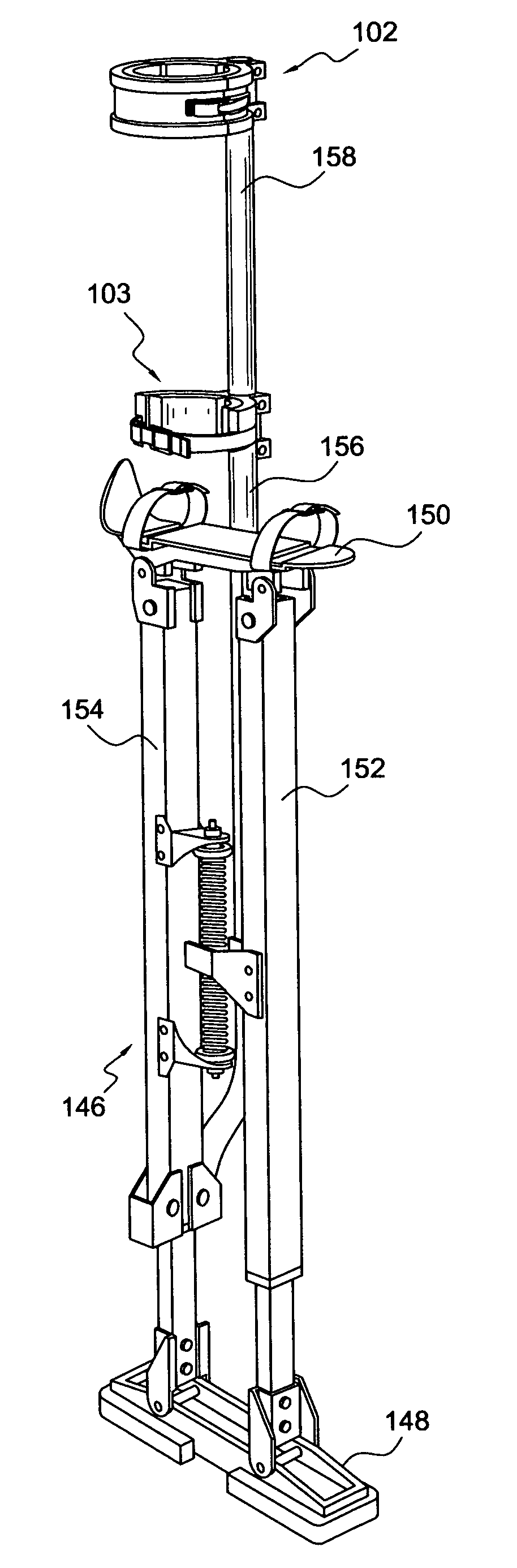
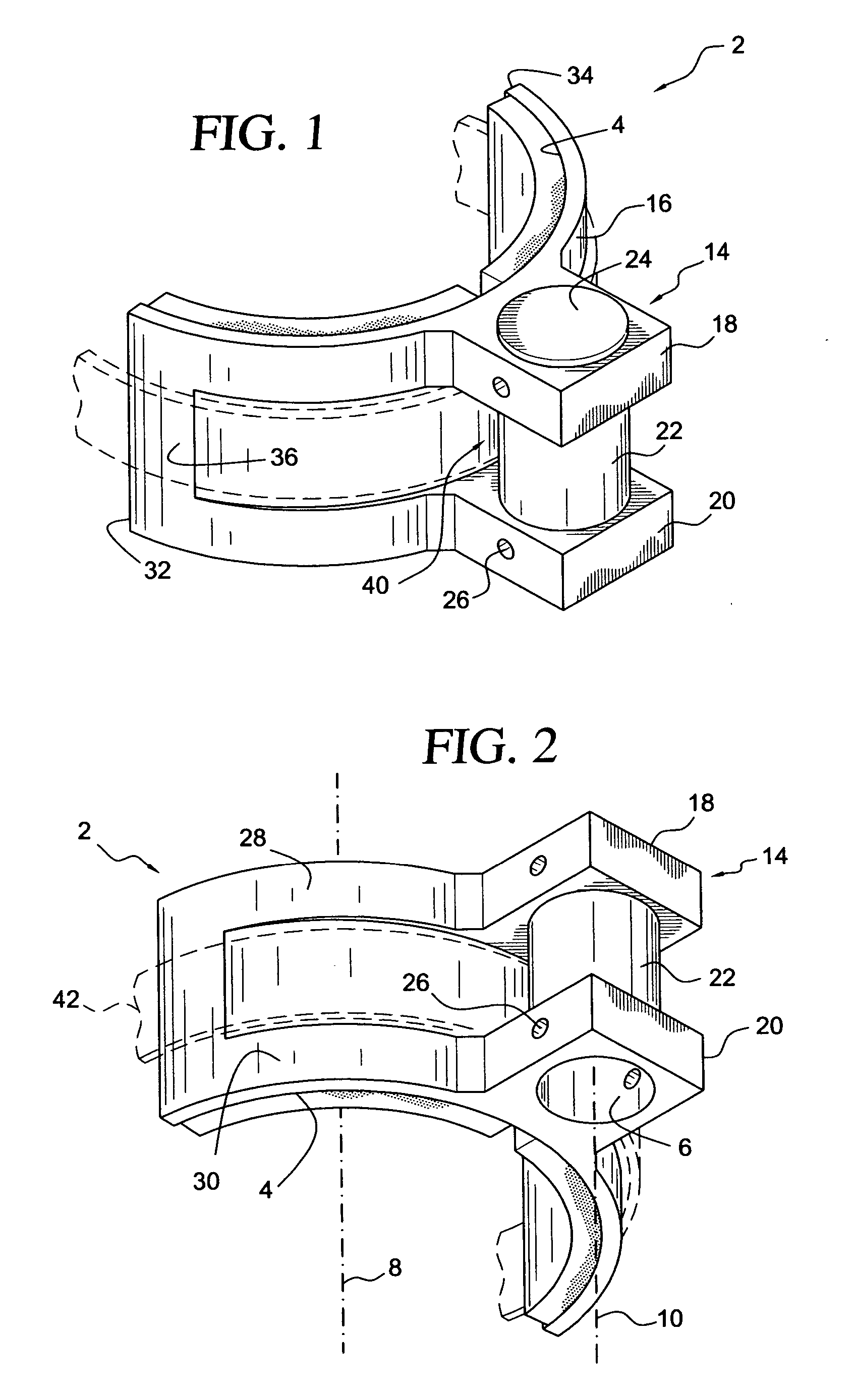
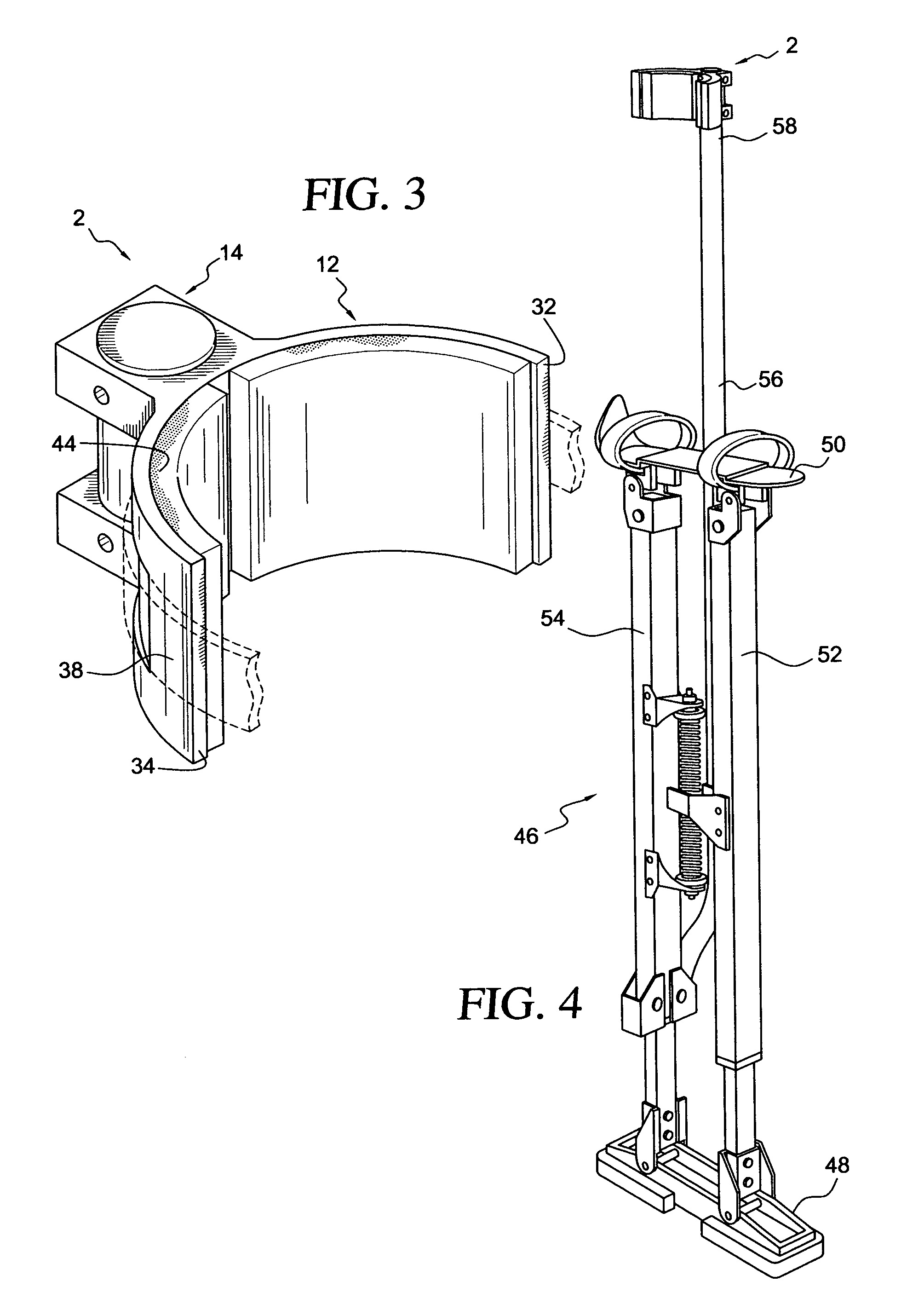
[0040] With reference to FIGS. 1 and 2, there is shown a non-flaccid lower leg brace element 2 for a stilt. The leg brace element comprises a nonflaccid body. The nonflaccid body defines a generally semi-cylindrical concave inside surface 4 for supporting a lateral side of a stilt user's leg, and a passage 6 spaced apart from the generally semi-cylindrical concave inside surface for receiving a leg support of the stilt.
[0041] A wide range of nonflaccid material is suitable for construction of the brace element 2. For cost and speed of production, a thermoplastic would be preferred. For strength, a fiber reinforced thermoplastic would be preferred. For durability, an engineering thermoplastic would be preferred. Short glass fiber reinforced polyetheretherketone (PEEK) is a suitable material, for example, as well as other nonflaccid items shown herein. The brace element 2, as well as the other nonflaccid items shown herein, is preferably produced by an injection molding process. More...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com