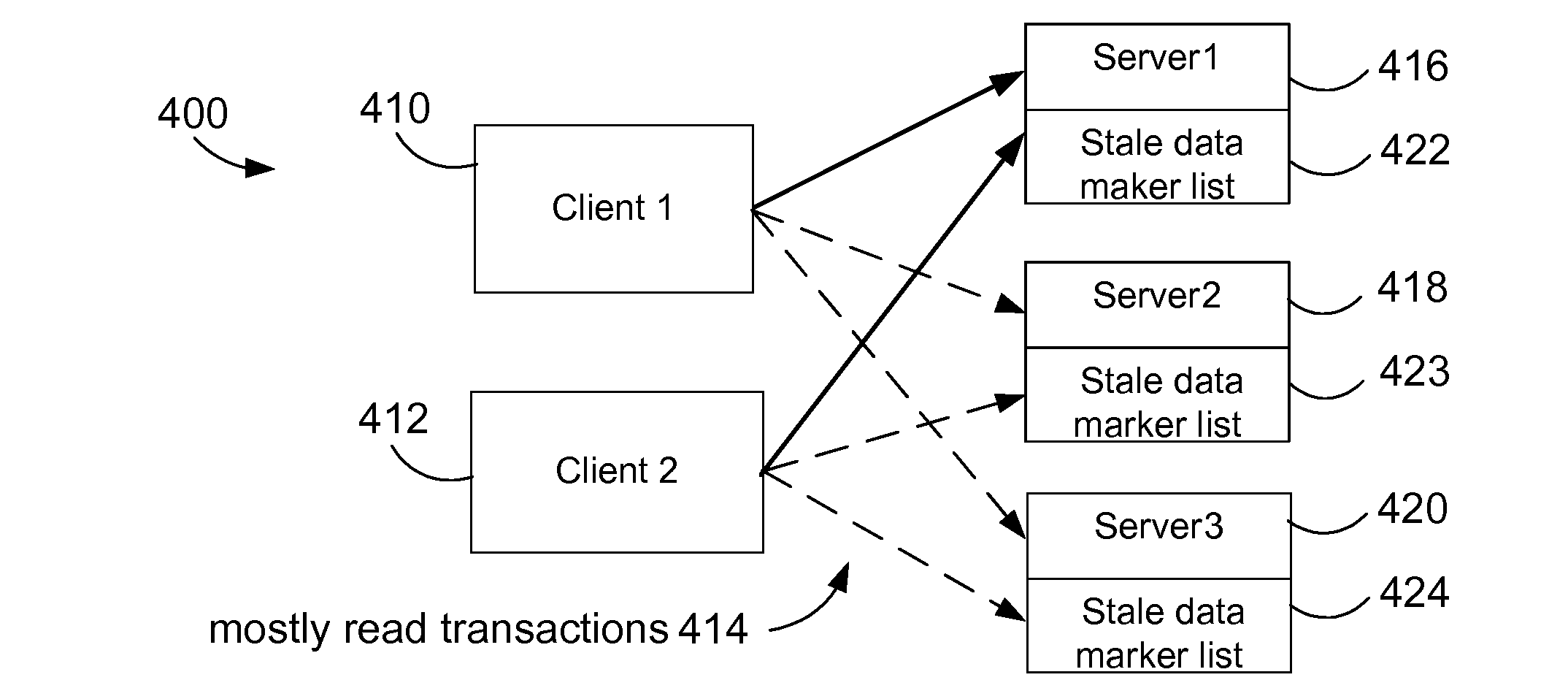
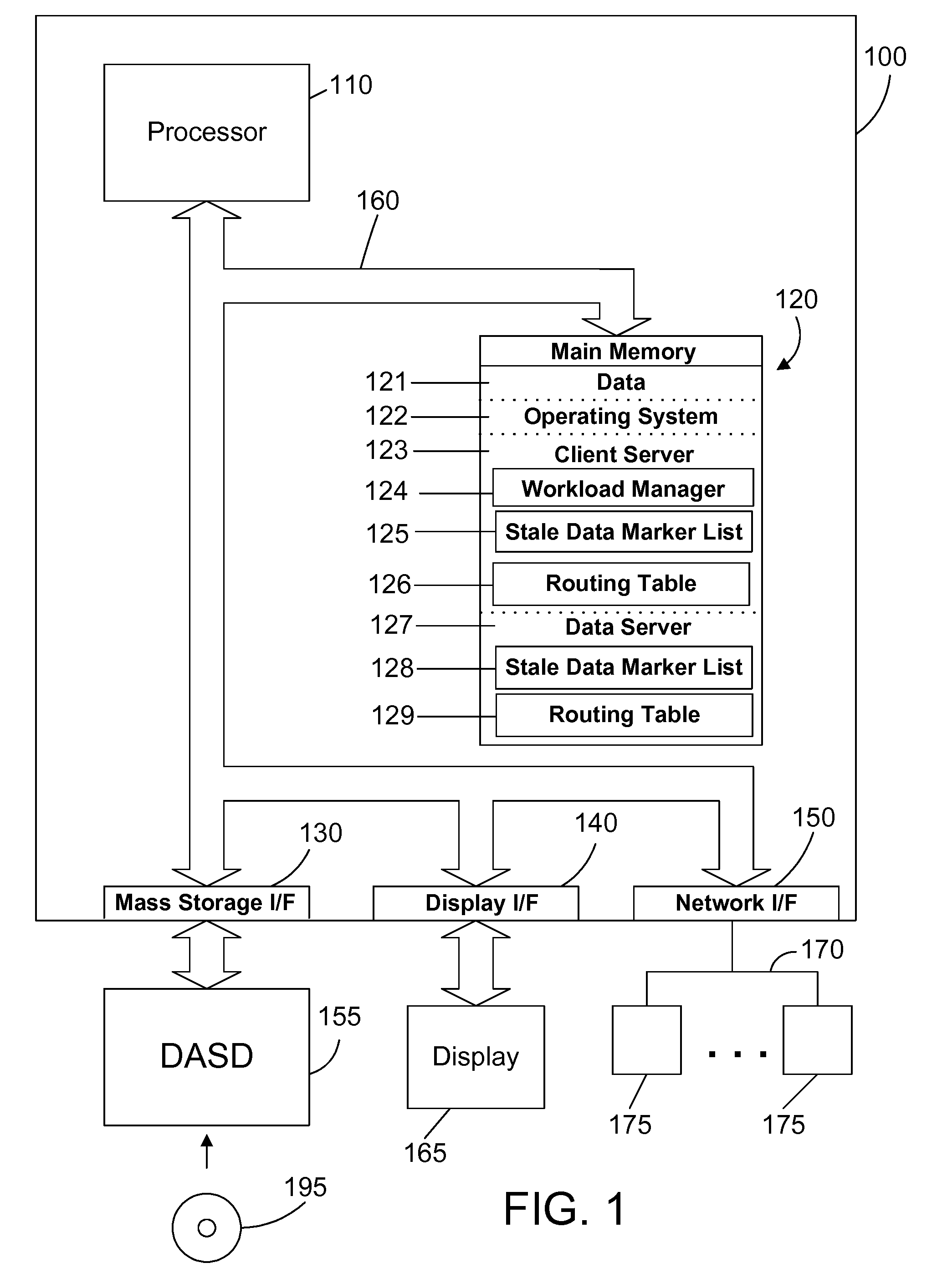
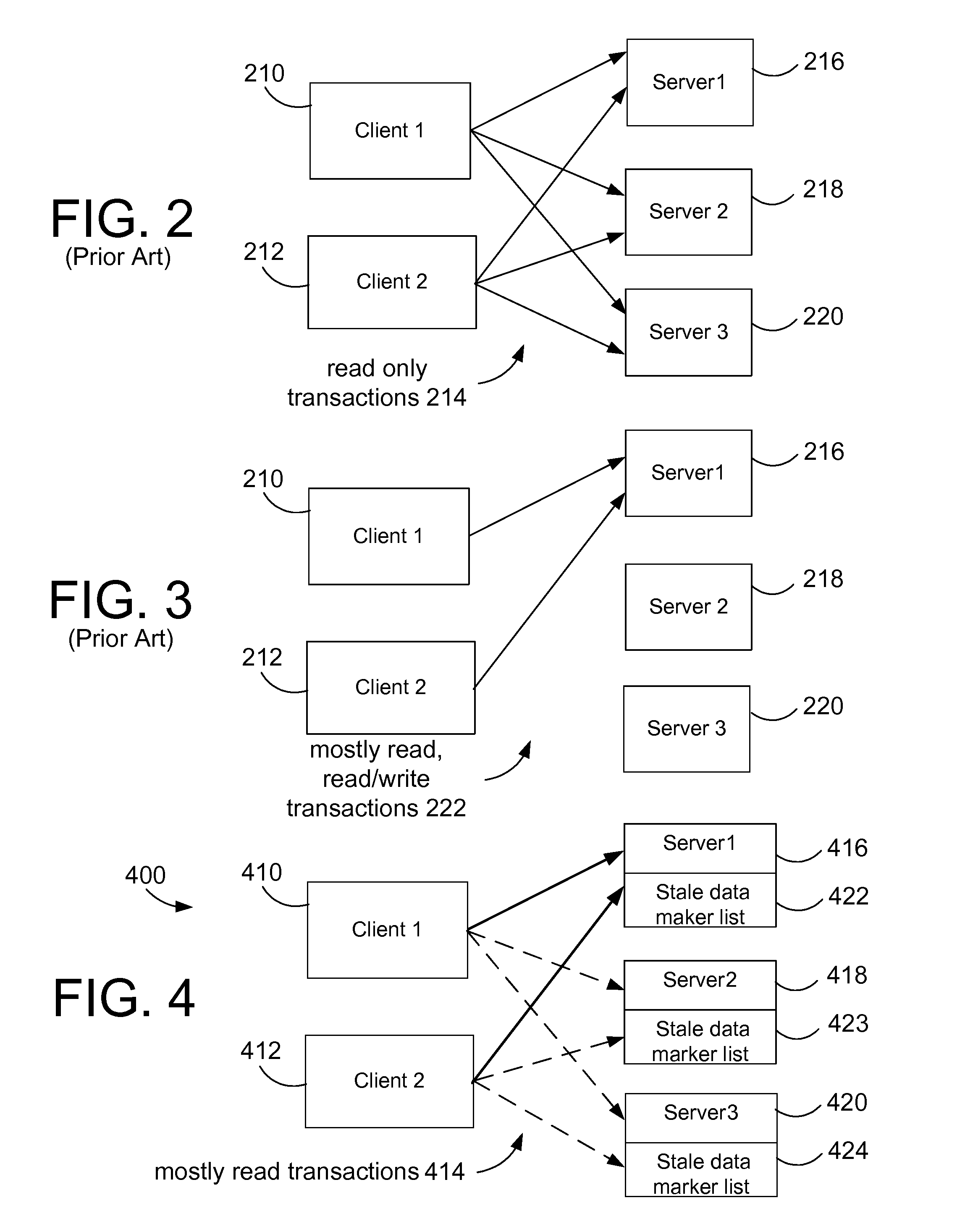
Efficient handling of mostly read data in a computer server
a computer server and data technology, applied in the field of computer servers, can solve the problems of large amount of server resources wasted, unfavorable client access utilization, and waste of servers, and achieve the effects of minimizing server response time, efficient utilization of replicated data servers, and large scalability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025]The present invention relates to application servers and in particular the WebSphere application server is used for the illustrated examples. For those who are not familiar with WebSphere and application servers, the brief overview below provides background information that will help the reader to understand the present invention.
[0026]1. OverviewWebSphere Application Server in the WebSphere Environment
[0027]WebSphere is the IBM brand of software products that are designed to work together to deliver dynamic e-business solutions for connecting people, systems, and applications with internal and external resources. The WebSphere environment of software products includes an application server. WebSphere is based on infrastructure software (middleware) designed for dynamic e-business. It delivers a secure, and reliable software portfolio. The technology that powers WebSphere products is Java™. Over the past several years, many software vendors have collaborated on a set of server...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com