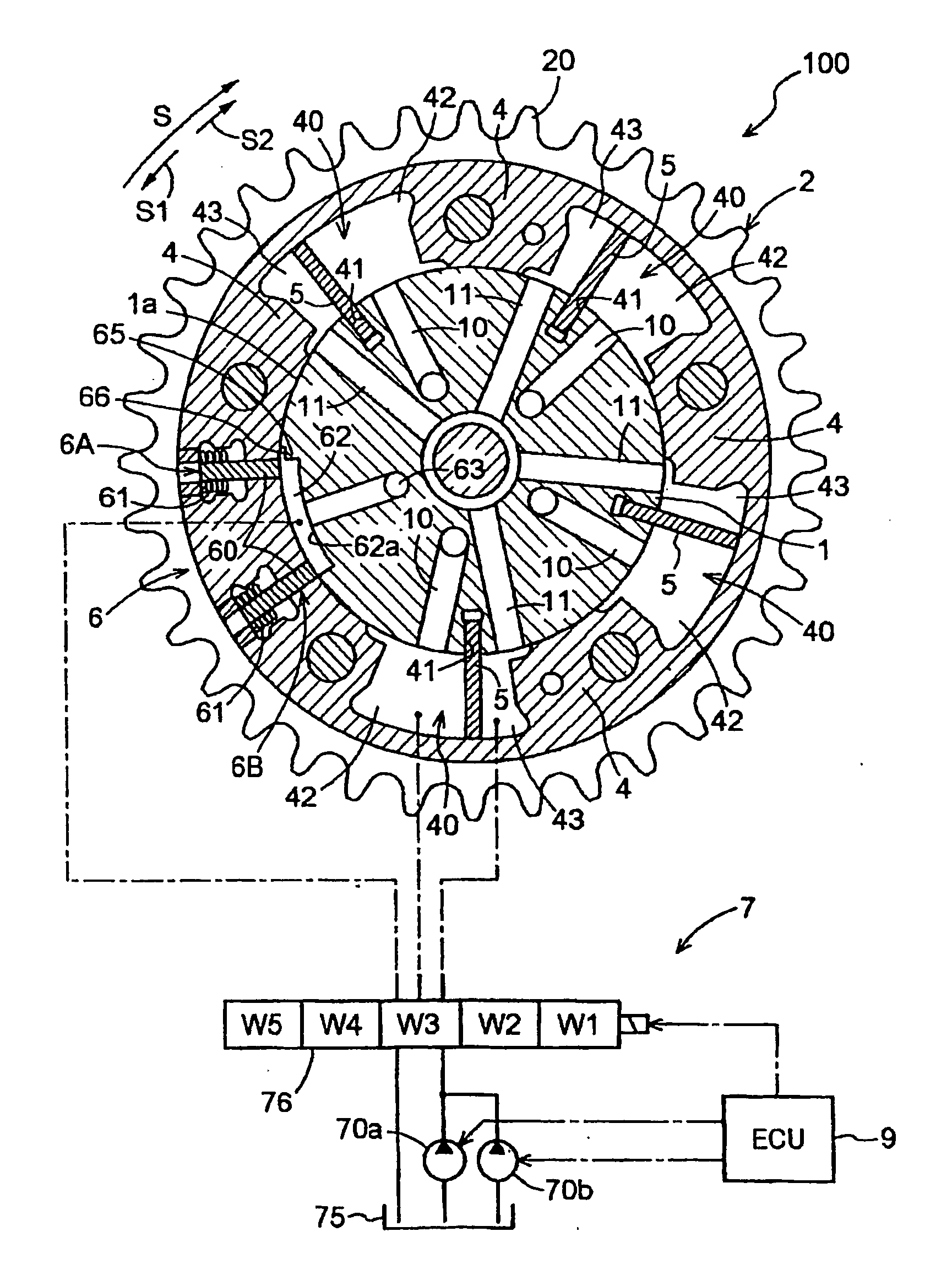
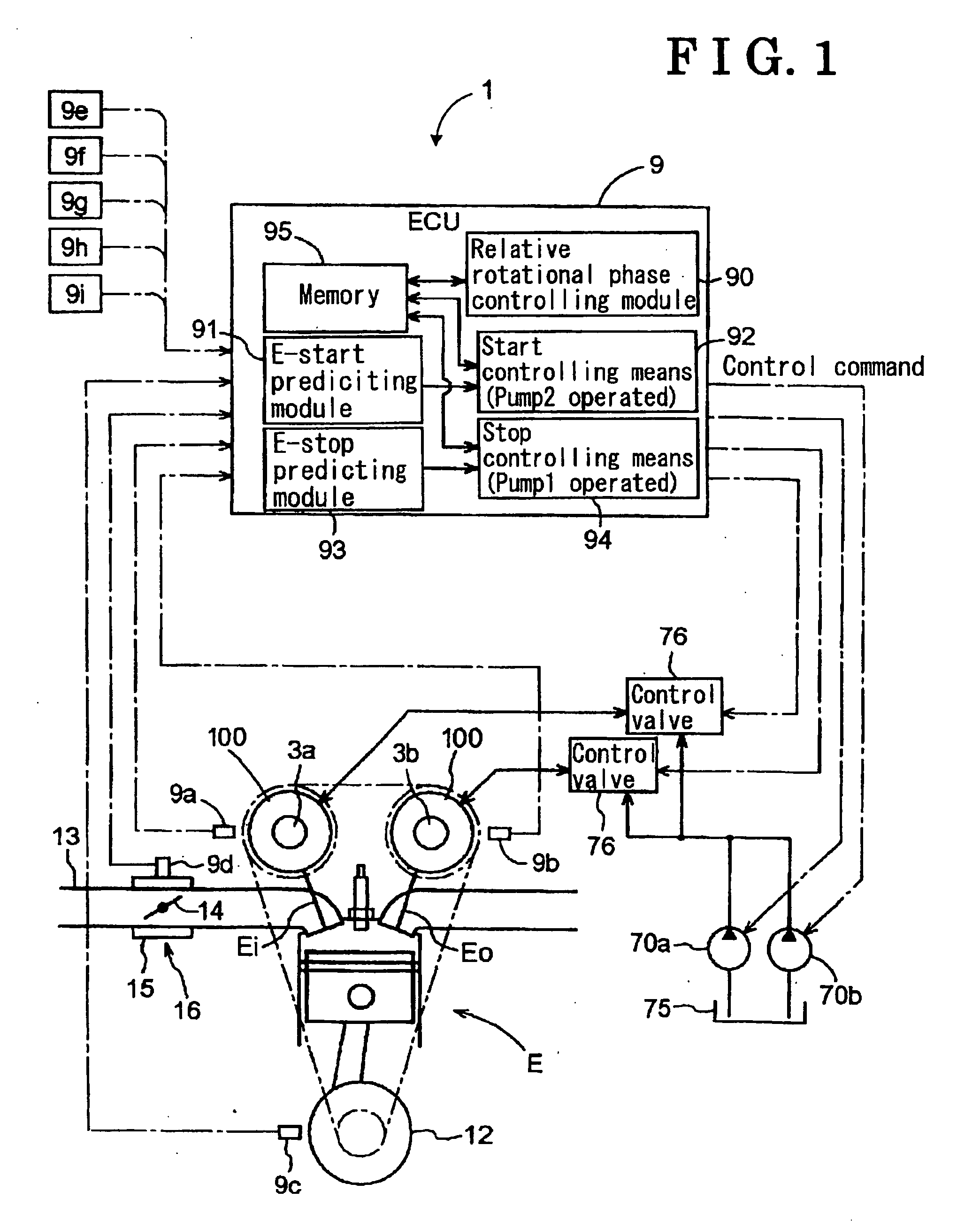
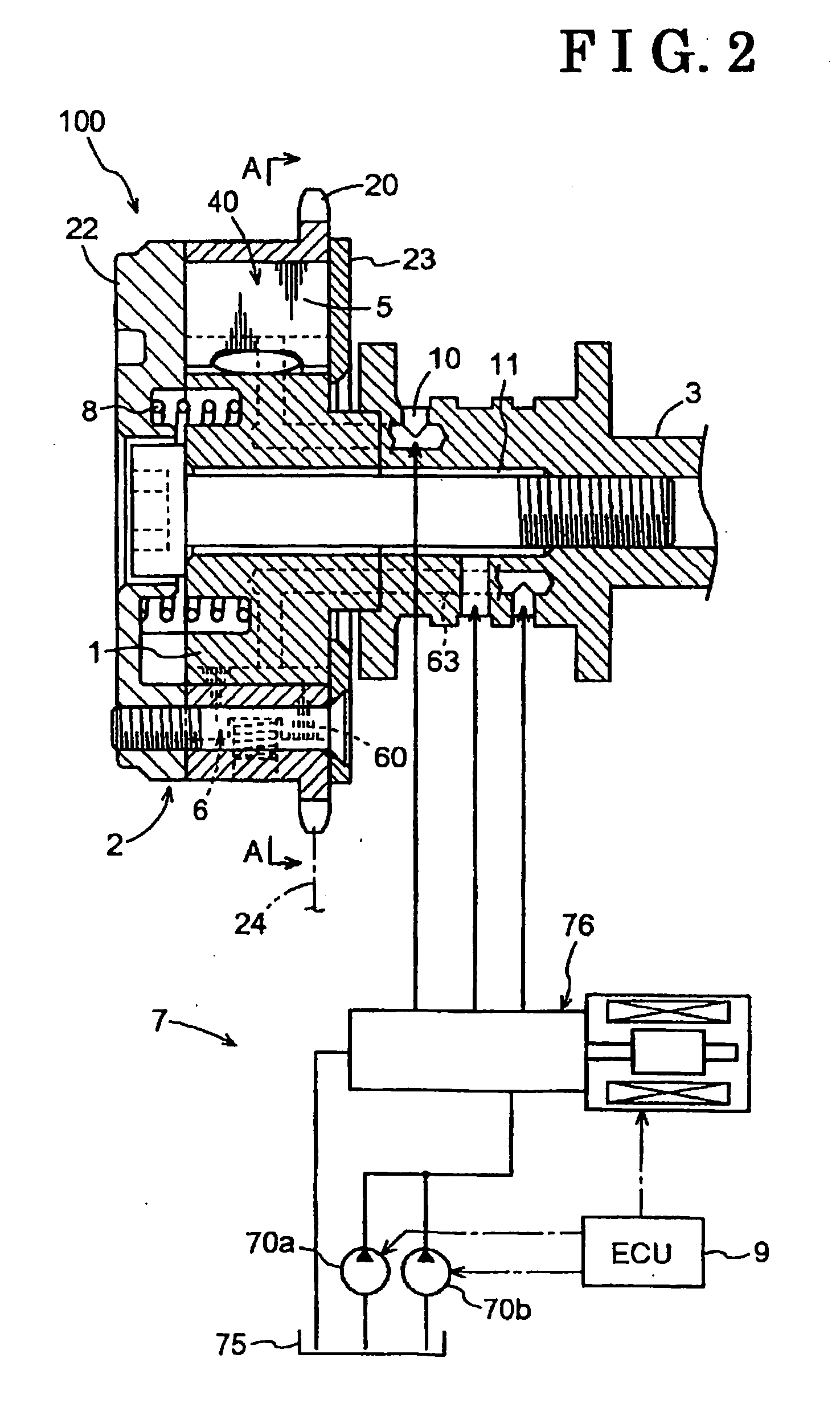
Variable valve timing control apparatus with supplementary oil pump
a technology of variable valve timing and control apparatus, which is applied in the direction of electrical control, engine starters, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of engine start-up delay, inability to control the opening and closing timing of valves, and inability to achieve reliable lock conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
second embodiment
[0136]As is illustrated in FIG. 11, in a variable valve timing control apparatus 1 according to the second embodiment of the present invention, the first pump 70a is arranged in series with the second pump 70b, while other configuration thereof is substantially identical to the first embodiment.
[0137]According to the second embodiment of the present invention, the second pump 70b is arranged in series with and on the downstream side of the first pump 70a. An oil reservoir 71 is provided between the first pump 70a and the second pump 70b. This oil reservoir 71 can store an amount of oil drawn from the oil pan 75 by the first pump 70a. When the first pump 70a is operating, oil is supplied to each portion of the engine E via a main oil passage 72 from the oil reservoir 71, and is supplied to the variable valve timing control unit 100 via the control valve 76. When the first pump 70a is inoperative in response to the halt of the engine E, the second pump 70b draws oil accumulated in the...
third embodiment
[0139]As is illustrated in FIG. 12, a variable valve timing control apparatus 1 according to a third embodiment of the present invention is provided with an engine stop delaying module (an engine stop delaying means) 96, while other configuration thereof is substantially identical to the first embodiment. Further, FIG. 12 illustrates an engine-controlling module (an engine controlling means) 110 which is not shown in other figures. However, this engine-controlling module 110 is provided in the apparatus 1 according to the other embodiments.
[0140]According to this third embodiment, in accordance with predetermined conditions described later, the engine stop control is performed in such a manner that the predetermined intermediate lock is carried out after delaying the halting of the operation of the first pump 70a. The operations relevant to this engine stop control are illustrated in the flowchart in FIG. 14. In this flowchart, the module (means), which carries out respective step, ...
fourth embodiment
[0158]As is illustrated in FIG. 13, the variable valve timing control apparatus according to the fourth embodiment of the present invention is provided with an engine stop operation predicting module (an engine stop operation predicting means) 97, while other configuration thereof is substantially identical to the first embodiment. FIG. 13 illustrates a driven system 160 which is not illustrated in other figures. However, this driven system 160 is provided in the apparatus 1 according to the other embodiments.
[0159]Here, an engine stop operation predicting control is performed by means of the engine stop operation-predicting module 97. The engine stop operation predicting control is a one implemented based on a predetermined predicted condition such as an engine stop operation (e.g. a turning of the ignition key 9e to its off position). This predetermined condition is described later.
[0160]The engine stop operation-predicting module 97 is incorporated in the ECU 9 illustrated in FIG...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com