Posterior stabilization systems with shared, dual dampener systems
a stabilization system and dampener technology, applied in the field of functional spinal implant assemblies, can solve the problems of additional stress, loss of motion, and pathologies of the spine, and achieve the effect of reducing the risk of fracture, reducing and improving the stability of the spin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
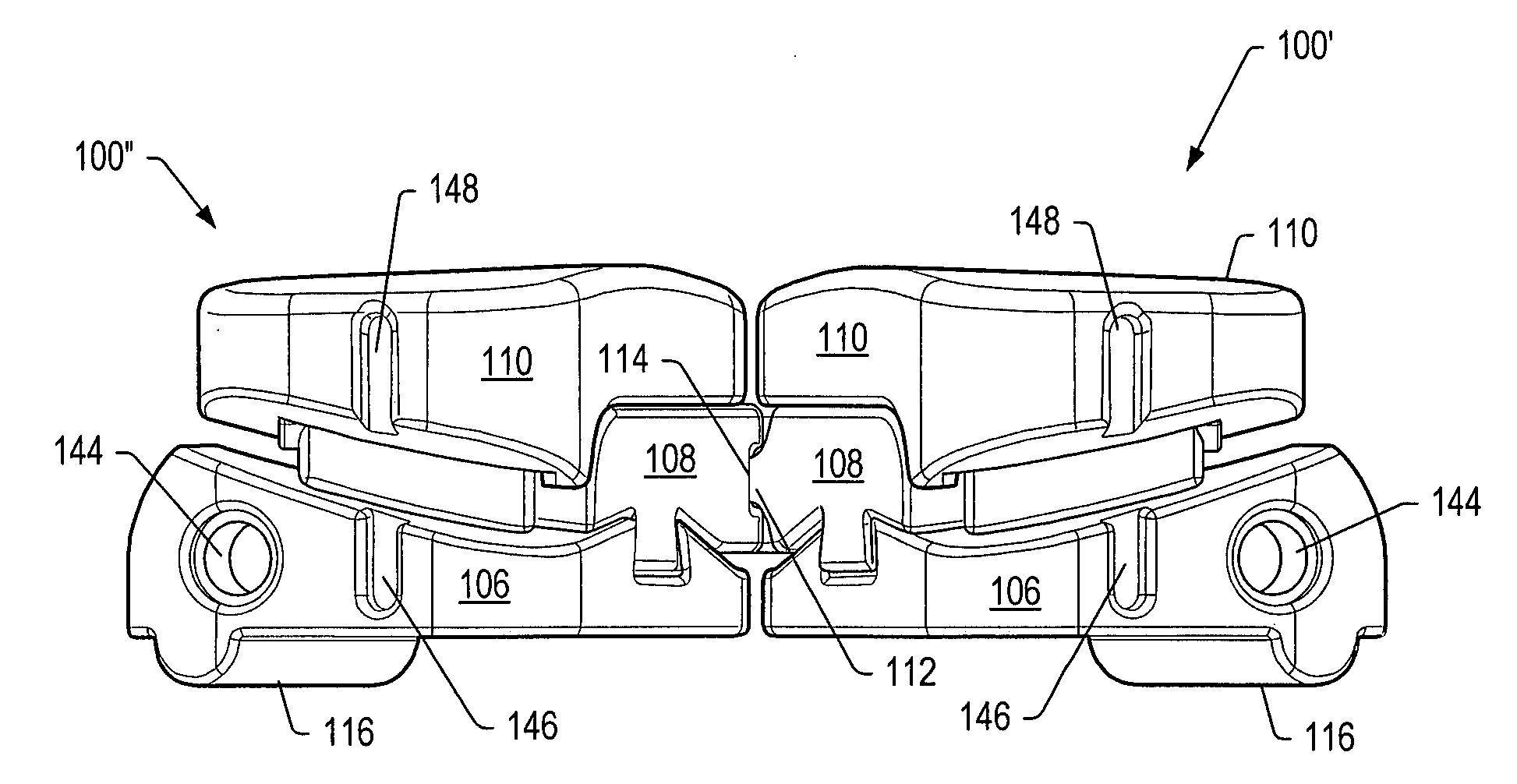
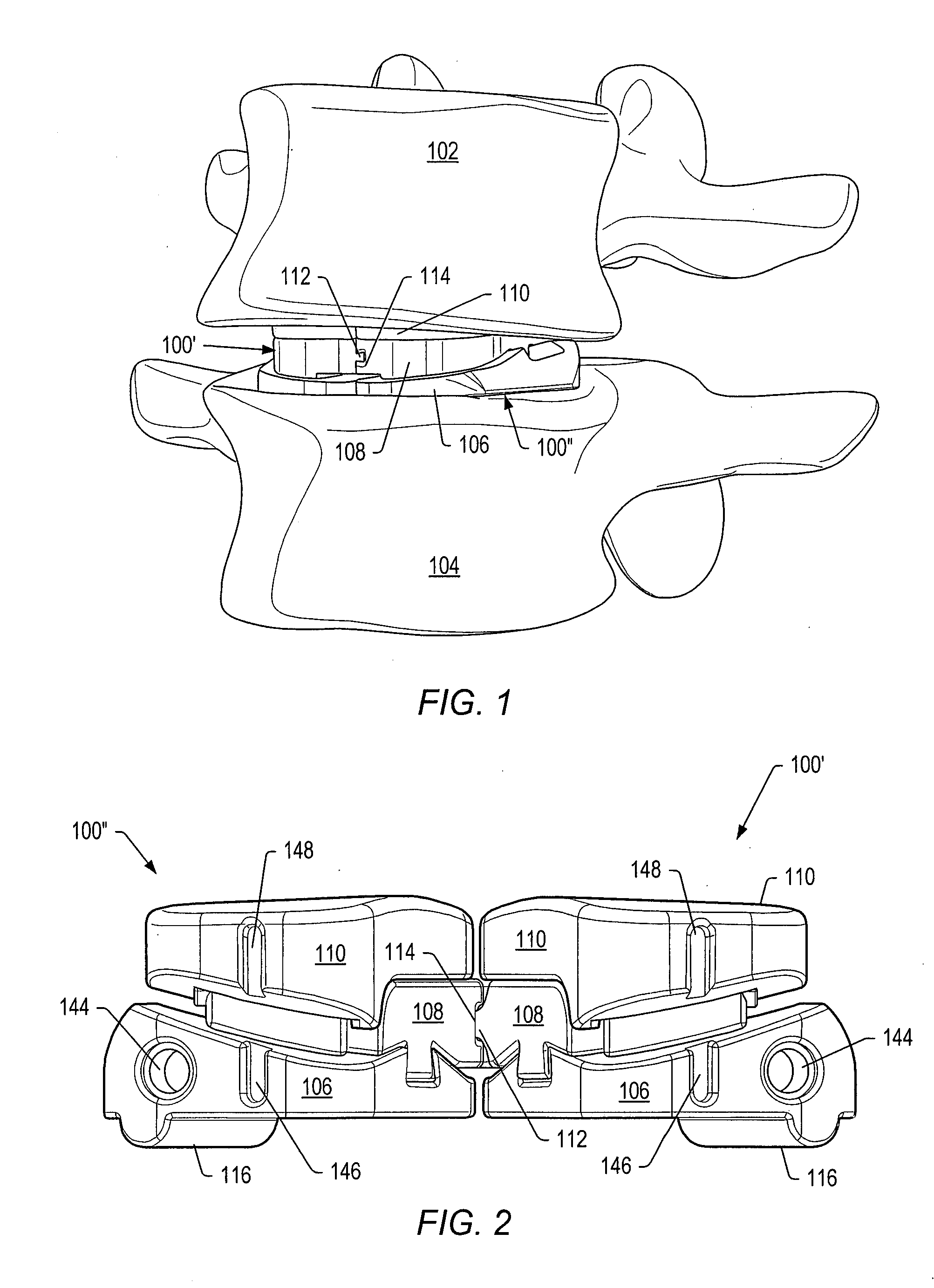
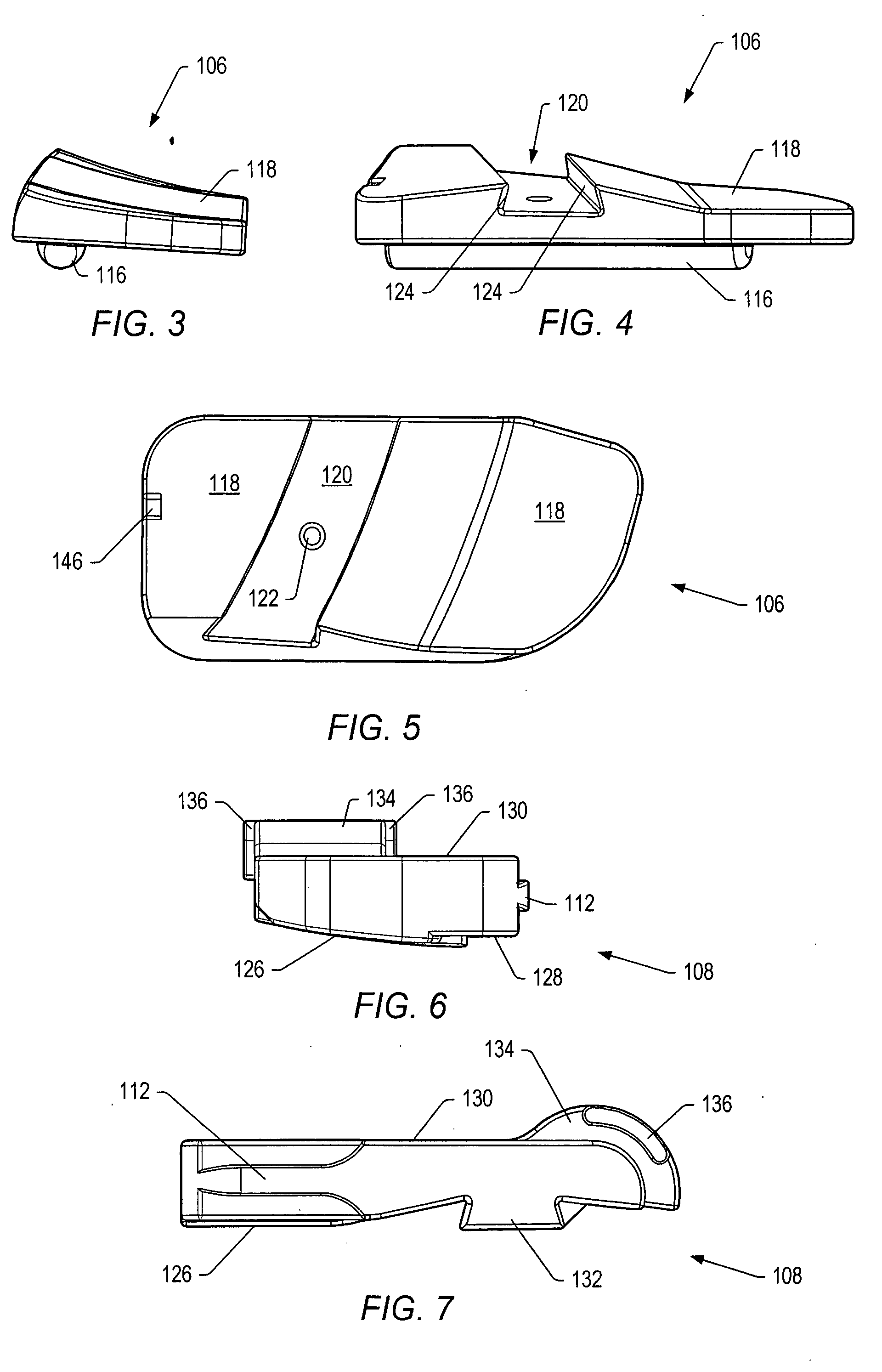
[0125]A “functional spinal unit” generally refers to a motion segment of a spine. The functional spinal unit may include two vertebrae, an intervertebral disc between the vertebrae, and the two facet joints between the vertebrae. An “artificial functional spinal unit” refers to a functional spinal unit where one or more of the components of the functional spinal unit are replaced by implants or devices that permit at least some motion of the spine. At least a portion of the intervertebral disc and / or one or both of the facet joints may be replaced by implants or devices during a spinal stabilization procedure.
[0126]As used herein, “coupled” includes a direct or indirect joining or touching unless expressly stated otherwise. For example, a first member is coupled to a second member if the first member contacts the second member, or if a third member is positioned between the first member and the second member.
[0127]A “dynamic interbody device” generally refers to an artificial interv...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Electrical resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com