Diagnosis method of hepatic steatosis using biochemical markers
a biochemical marker and steatosis technology, applied in the field of diagnosis of hepatic steatosis using biochemical markers, can solve the problem that no study has demonstrated that a single or a panel of biomarkers can be used as an alternative to liver biopsy, and achieve the effect of reducing the number of biopsy indications, reducing the cost and the risk of liver biopsy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Patients and Methods
1.1. Patients
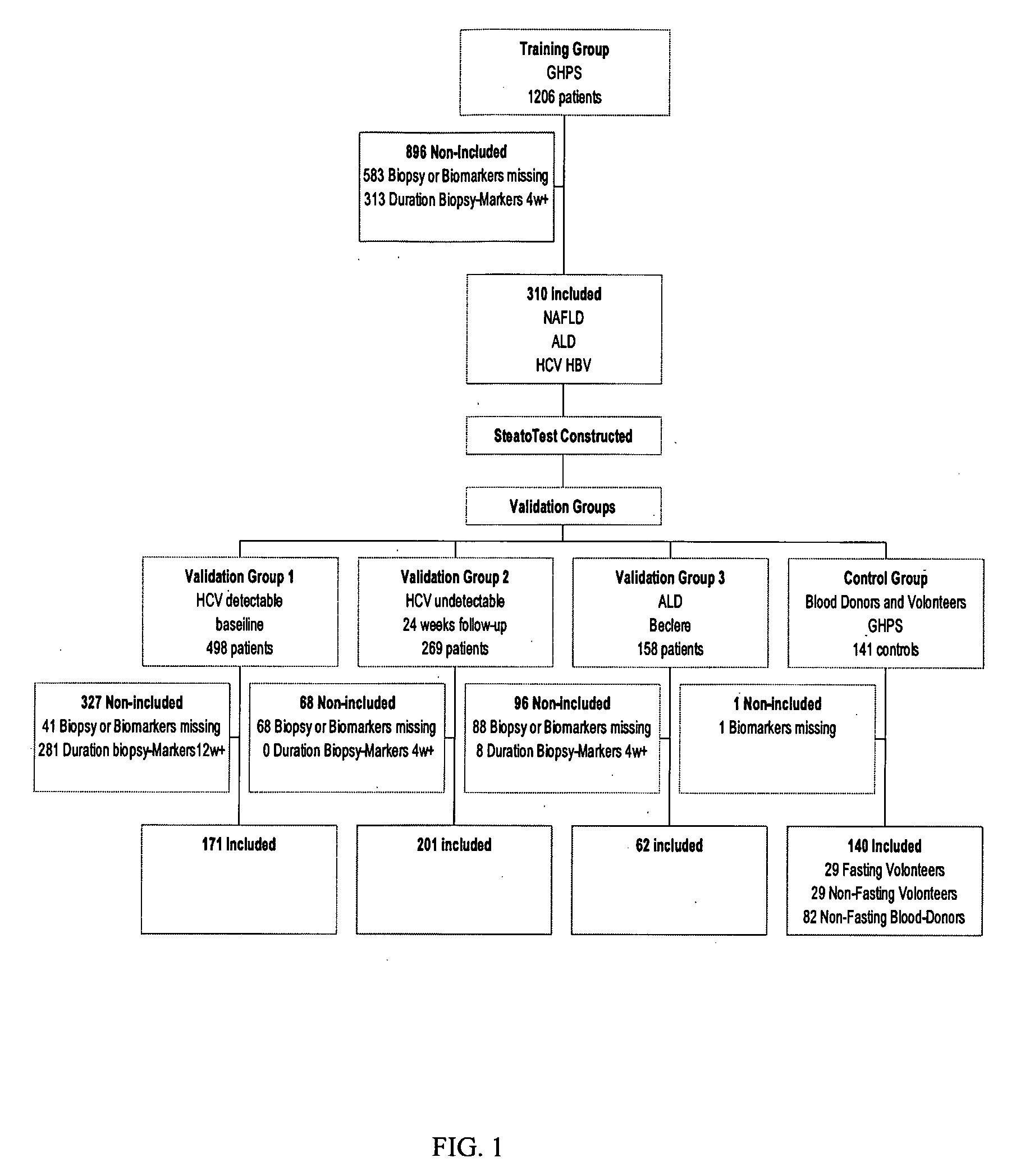
[0049]Consecutive patients with available serum, a consistent liver biopsy and a duration of time between serum and biopsy shorter than 3 months were included (FIG. 1). Non-inclusion criteria included non-available serum, and non-available biopsies and patients because biopsy and serum were collected more than 3 month apart. The analysis was performed on a first group (training group) and validated on 3 different groups (validation groups). Training group patients were retrospectively included for this specific analysis, but have been analyzed in previous prospective validation studies of Fibrotest between September 2000 and August 2004 (Poynard T, et al. Comp. Hepatol. 2004; 3:8; Myers R P, et al. J. Hepatol. 2003; 39:222-30; Ratziu V, et al. Hepatology 2003; 38:510 A). All were inpatients hospitalized in the Department of Hepato-Gastroenterology of Groupe Hospitalier Pitié-Salpêtrière for NAFLD, hepatitis C, B, and alcoholic liver disease.
[0050]Val...
example 2
Statistical Analysis
[0064]Statistical analysis used Fisher's exact test, the chi-square test, Student's t test, the Mann-Whitney test and variance analysis using the Bonferroni all-pair wise and Tukey-Kramer multiple-comparison tests to take into account the multiple comparisons and multiple logistic regression for multivariate analysis (Hintze J L. NCSS 2003 User Guide. Number Cruncher Statistical Systems 2003 software NCSS, Kaysville, Utah). The analysis was performed on a first group (training group) and validated on 3 different groups (validation groups 1, 2 and 3), in cohorts of patients as in Table 1.
[0065]According to the hepatic steatosis scoring system, patients were divided into several groups.
[0066]The primary outcome was the identification of patients with hepatic steatosis grade 2, 3 or 4 (moderate, marked or severe).
[0067]In a secondary analysis, patients were classified according to a 4 scale scoring system.
[0068]The first stage consisted of identifying factors which ...
example 3
Determination of the Logistic Function
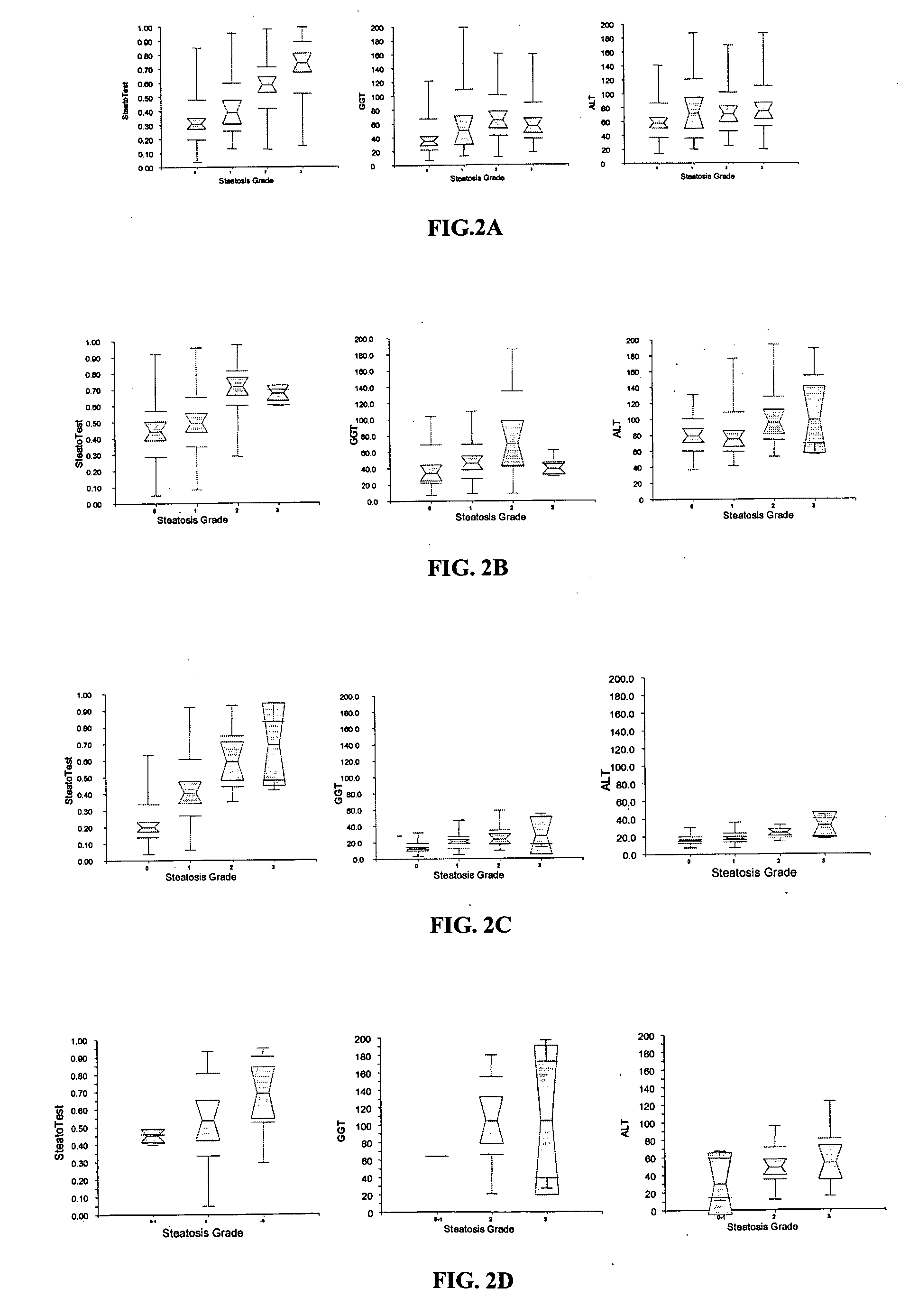
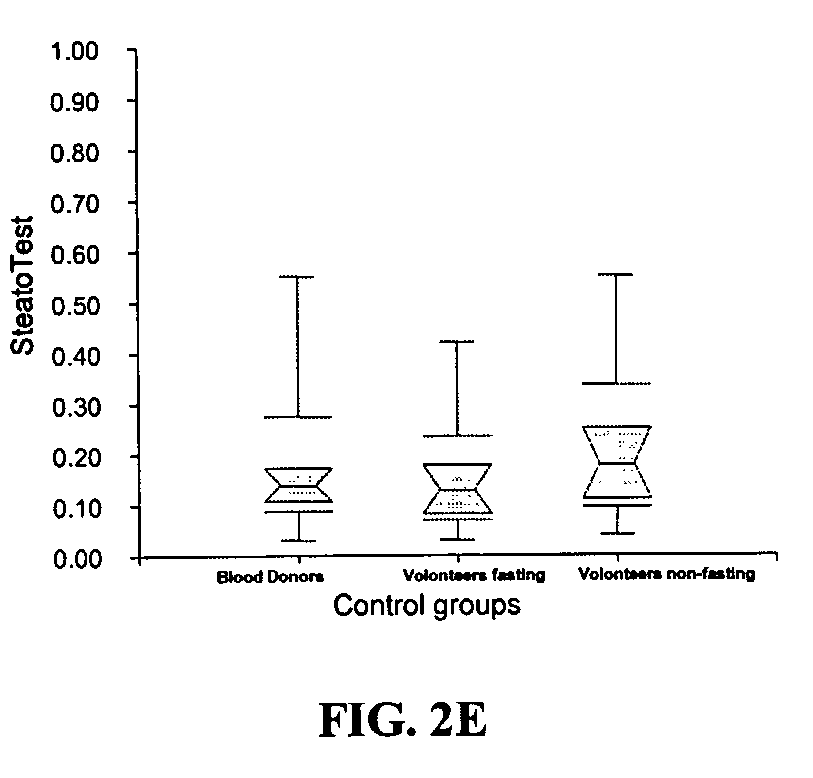
[0075]The “SteatoTest score” is defined as the logistic regression function combining the independent factors that returns the best index in term of discrimination between the presence or absence of hepatic steatosis.
[0076]In Table 2 are given the characteristics of patients according to the presence of hepatic steatosis for each of the 10 biochemical markers, the FibroTest score, and the SteatoTest score, as well as their independent association with fibrosis (P value).
[0077]In the training group the most significant components associated with the presence of grade 2-4 steatosis in univariate analysis were BMI, age, ALT, AST, GGT, glucose, and triglycerides.
[0078]In logistic regression analysis the most significant components were BMI (OR=0.89 P=0.0002), GGT (OR=0.31 P=0.002), apolipoprotein A1 (OR=3.20 P=0.01), alpha2-macroglobulin (OR=5.74 P=0.02), ALT (OR=0.38 P=0.03) and triglycerides (OR=0.31 P=0.04).
[0079]In the validation group similar d...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| body mass index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com