Heat exchanger
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
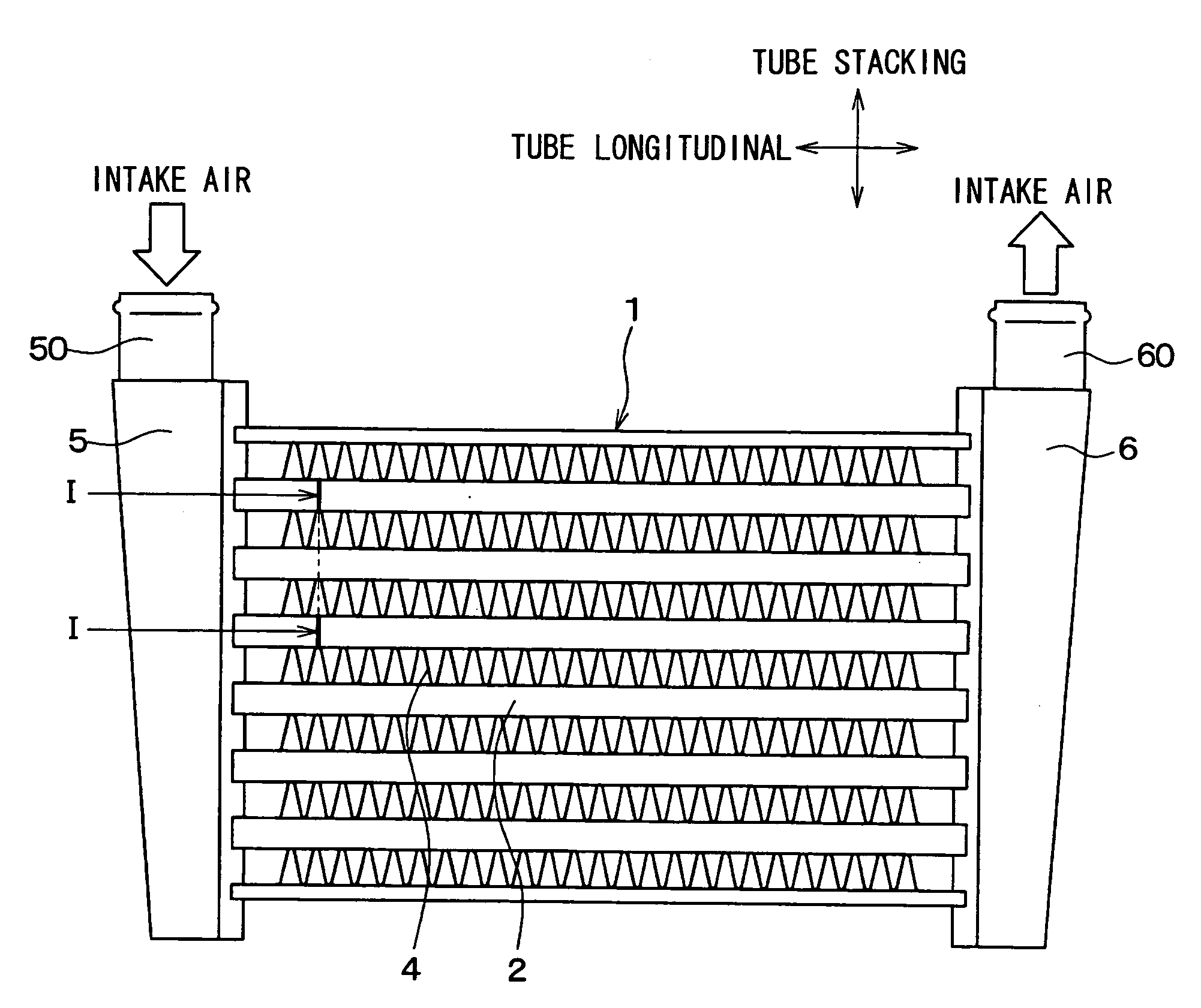
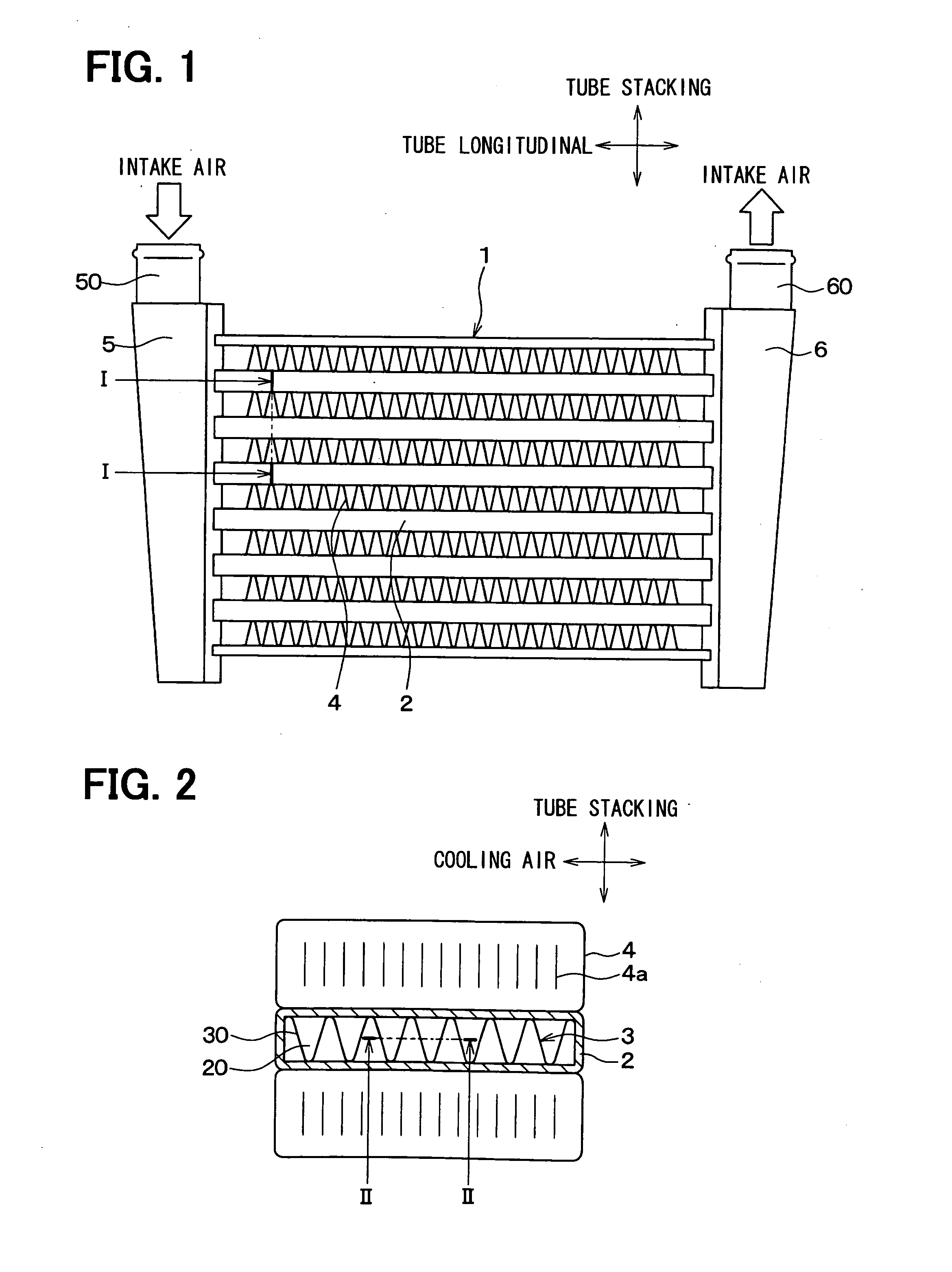
[0028]A first embodiment of the present invention will be described below with reference to FIGS. 1 to 4. A heat exchanger according to the first embodiment of the present invention is typically used for an intercooler. The intercooler is configured to perform heat exchange between outside air (cooling air) and intake air for combustion to be supplied into an internal combustion engine, thereby to cool the intake air. The intake air is an example of a first fluid of the present invention, and the cooling air is an example of a second fluid of the present invention.
[0029]As shown in FIGS. 1 and 2, a core portion 1 of the intercooler includes a plurality of stacked flat tubes 2 each having a flow passage formed therein for allowing intake air to flow therethrough, inner fins 3 disposed within the flat tubes 2, and outer fins 4 each of which is disposed between the stacked flat tubes 2. The flat tubes 2 are stacked in a tube stacking direction that is perpendicular to the tube longitud...
second embodiment
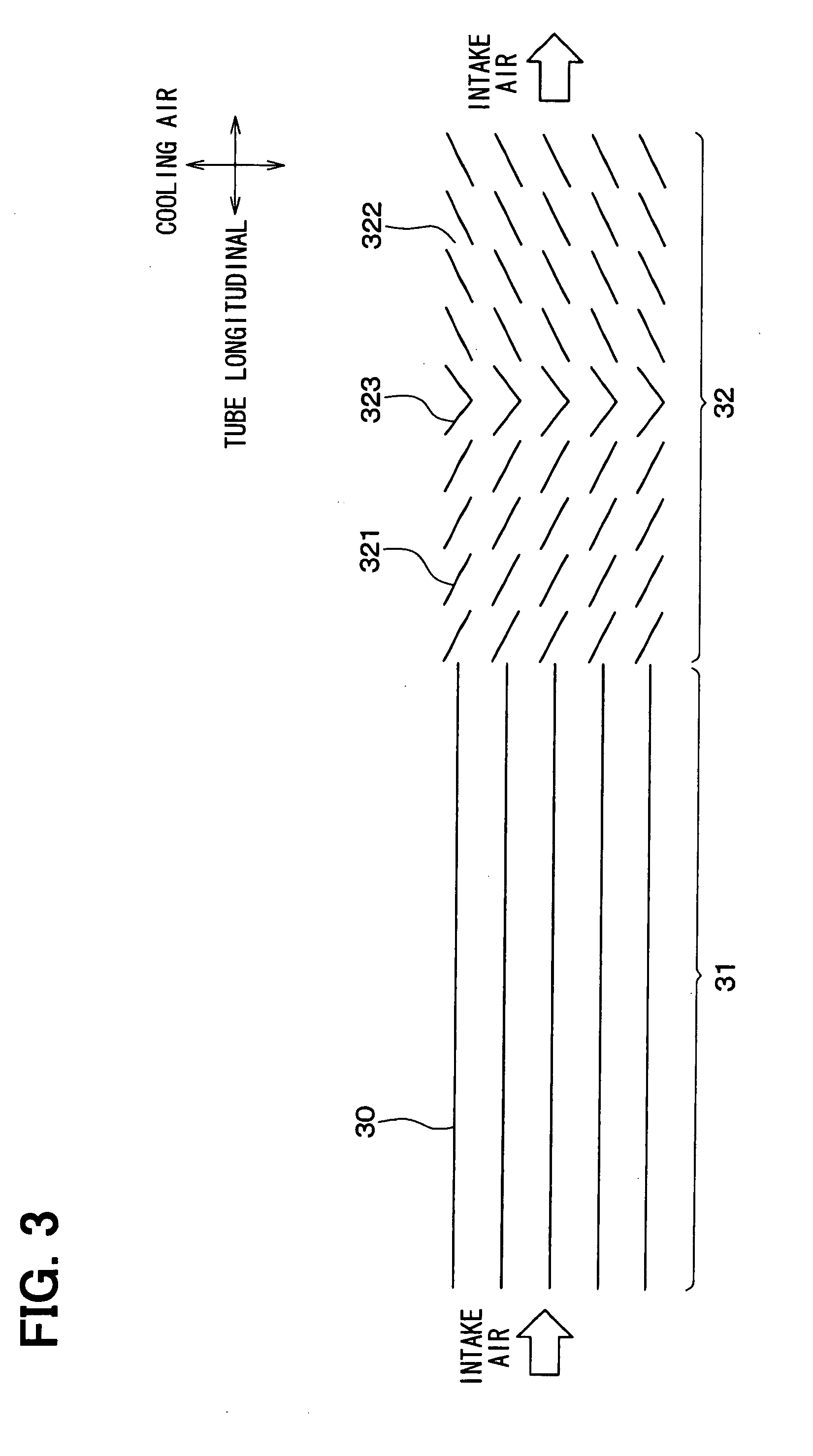
[0045]A second embodiment of the present invention will be described below based on FIGS. 5 and 6. The same components as those in the first embodiment are designated by the same reference numerals, and a description thereof will be omitted below. FIG. 5 is a sectional view of the inner fin 3 of the second embodiment when being viewed in the stacking direction of the tubes 2. FIG. 5 of the second embodiment is a drawing corresponding to FIG. 3.
[0046]As shown in FIG. 5, an inter fin 3 of the present embodiment includes three different kinds of fin portions 31 to 33. The three fin portions 31 to 33, namely, the first fin portion 31, the third fin portion 33, and the second fin portion 32 are arranged continuously in that order from the upstream side of the intake air flow. The first fin portion 31 is a straight fin similar to that in the first embodiment. The second fin portion 32 is a louver fin similar to that in the first embodiment.
[0047]FIG. 6 is an enlarged perspective view show...
third embodiment
[0051]A third embodiment of the present invention will be described below based on FIG. 7. The same components as those in the first embodiment are designated by the same reference numerals, and a description thereof will be omitted below. FIG. 7 is a sectional view showing an inner fin 3 of the third embodiment when being viewed in the stacking direction of tubes 2. FIG. 7 is a diagram corresponding to the diagram of FIG. 3.
[0052]As shown in FIG. 7, the inner fin 3 of the present embodiment includes two first fin portions 31 each of which is a straight fin similar to that of the first embodiment, and a second fin portion 32 which is a louver fin similar to that of the first embodiment. The two first fin portions 31 are disposed one by one on the upstream and downstream sides of the second fin portion 32 in the flow direction of intake air. In other words, the second fin portion 31is disposed between the two first fin portions 31 in the flow direction of the intake air.
[0053]The two...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com