Methods for Determining Risk of Developing Regular Smoking Behavior
a risk and smoking behavior technology, applied in the field of human genetic polymorphisms, can solve the problems of affecting the development of regular smoking behavior, the role of high affinity nicotine receptor subunits in human smoking, and the major source of morbidity, mortality and economic loss, so as to and increase the risk of developing regular smoking behavior
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Population-Based Study of Association Between CHRNA4 Polymorphism Status and Regular Smoking
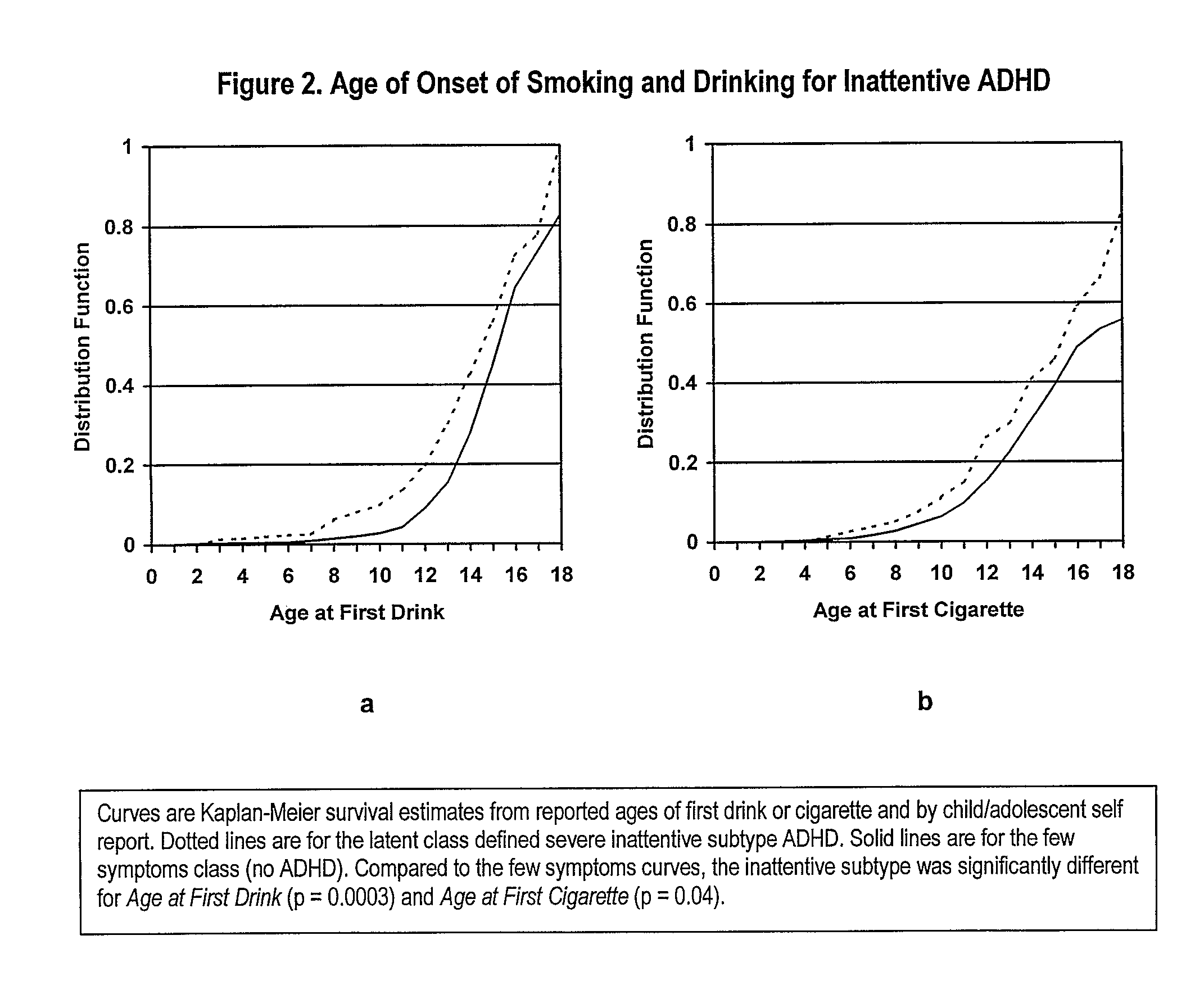
[0056]In order to attempt to link the association of a CHRNA4 polymorphism with inattentive ADHD and the previously described associations of smoking with attention problems, predictors of regular smoking were analyzed in a population-based sample of 1430. Risk for regular smoking was then analyzed for an association with CHRNA4 polymorphism status. As shown in Table 1, the sample consisted of 831 males and 509 females aged 7 to 17 years. The majority of individuals receiving a diagnosis of ADHD by either DSM-IV or latent class criteria (the inattentive and combined subtypes) were males but there was no difference in age or ethnicity by subtype. Consistent with an earlier report (Todd R D, Sitdhiraksa N, Reich W, Ji T H-C, Joyner C A, Neuman R J, Heath A C (2002), Discrimination of DSM-IV and latent class attention deficit / hyperactivity disorder subtypes by educational and cognitive performan...
example 2
Multivariate Logistic Regression Analysis of Association Between CHRNA4 Polymorphism Status and Regular Smoking
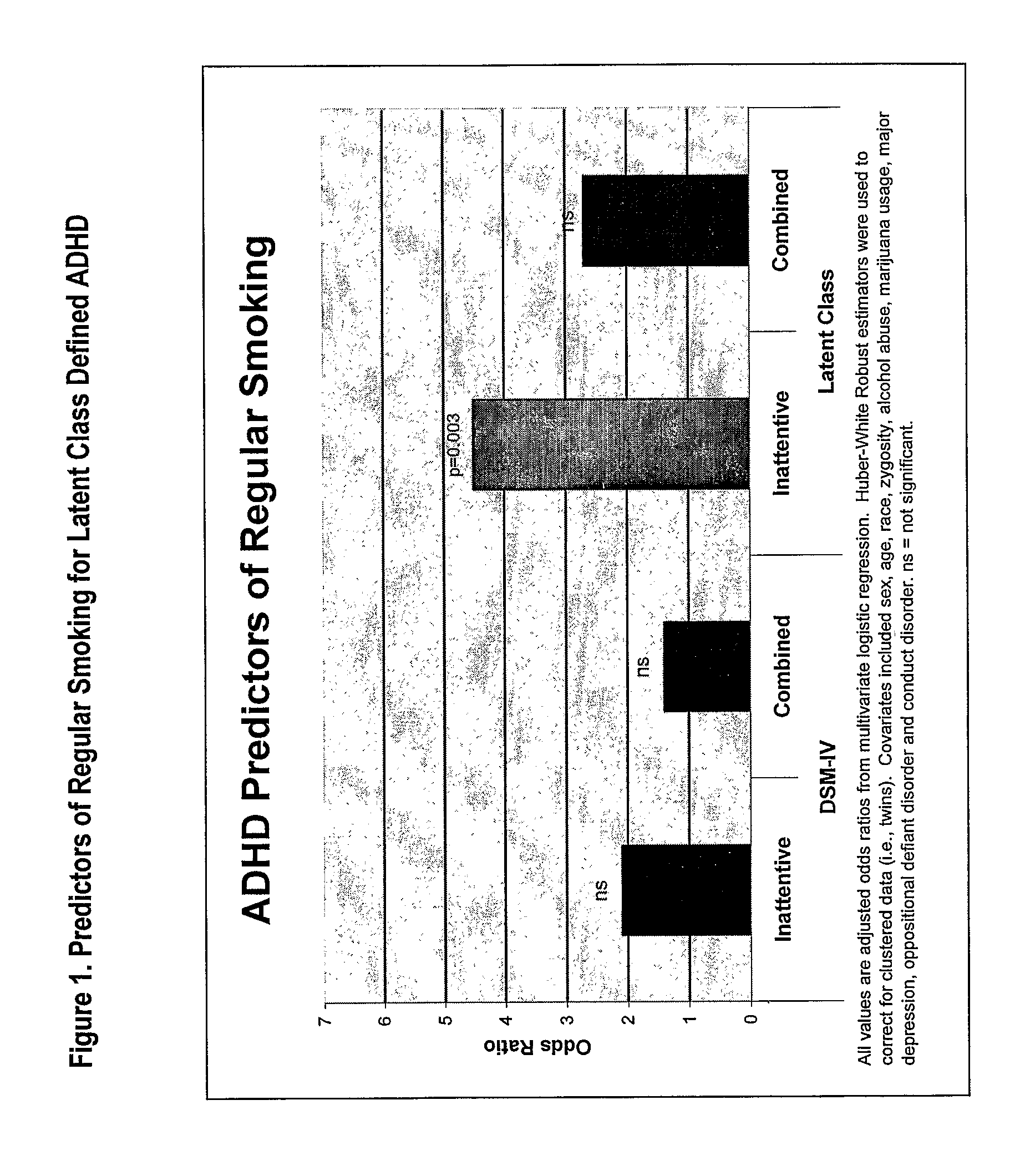
[0059]Since smoking is associated with a variety of possible confounding individual characteristics, the magnitude of ADHD predictors of regular smoking was estimated using multivariate logistic regression. Covariates included sex, age, race, zygocity, alcohol abuse, marijuana usage, major depression, oppositional defiant disorder, conduct disorder and ADHD subtype. Due to its high correlation with self-reported smoking, friend's smoking could not be included as a separate covariate. Since these were twin-based data, Huber-White Robust estimators were used to estimate confidence intervals. FIG. 1 shows that though the adjusted odds ratios for prediction of regular smoking were slightly elevated in DSM-IV ADHD subtypes, these were not significant. A significant odds ratio was only found for the inattentive latent class subtype (OR=4.5, 95% CI 1.7-11.8, p=0.003). For this sub...
example 3
Multivariate Logistic Regression Analysis of Association Between CHRNA4 Polymorphism Status and Regular Smoking
[0060]Given that smoking was predicted by latent class ADHD subtype, CHRNA4 genotyping data for the inattentive and combined ADHD subtypes was analyzed to test for association with the presence or absence of smoking. All snp genotype assignments from Todd et al. (Todd R D, Joyner C A, Heath A C, Neuman R J, Reich W (2003), Reliability and stability of a semistructured DSM-IV interview designed for family studies. Journal of the American Academy of Child &Adolescent Psychiatry. 42: 1460-8) were confirmed by genomic DNA sequencing. Analyses were restricted to those individuals who had ever smoked, reducing the sample size from 195 to 76 individuals. As shown in Table 3, there were significant associations of two exon / intron 5 snps with progression to regular smoking when all ADHD individuals were grouped together (OR=2.1, p=0.03 for each). When analyzed separately by combined...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic field | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Current | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com