Substrate processing apparatus and substrate processing method
a substrate processing and substrate technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurement, electric discharge tubes, decorative arts, etc., can solve the problem of large and achieve the effect of reducing the variation of incident energy of ions entering the substrate and effective reducing the voltage change of the substra
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
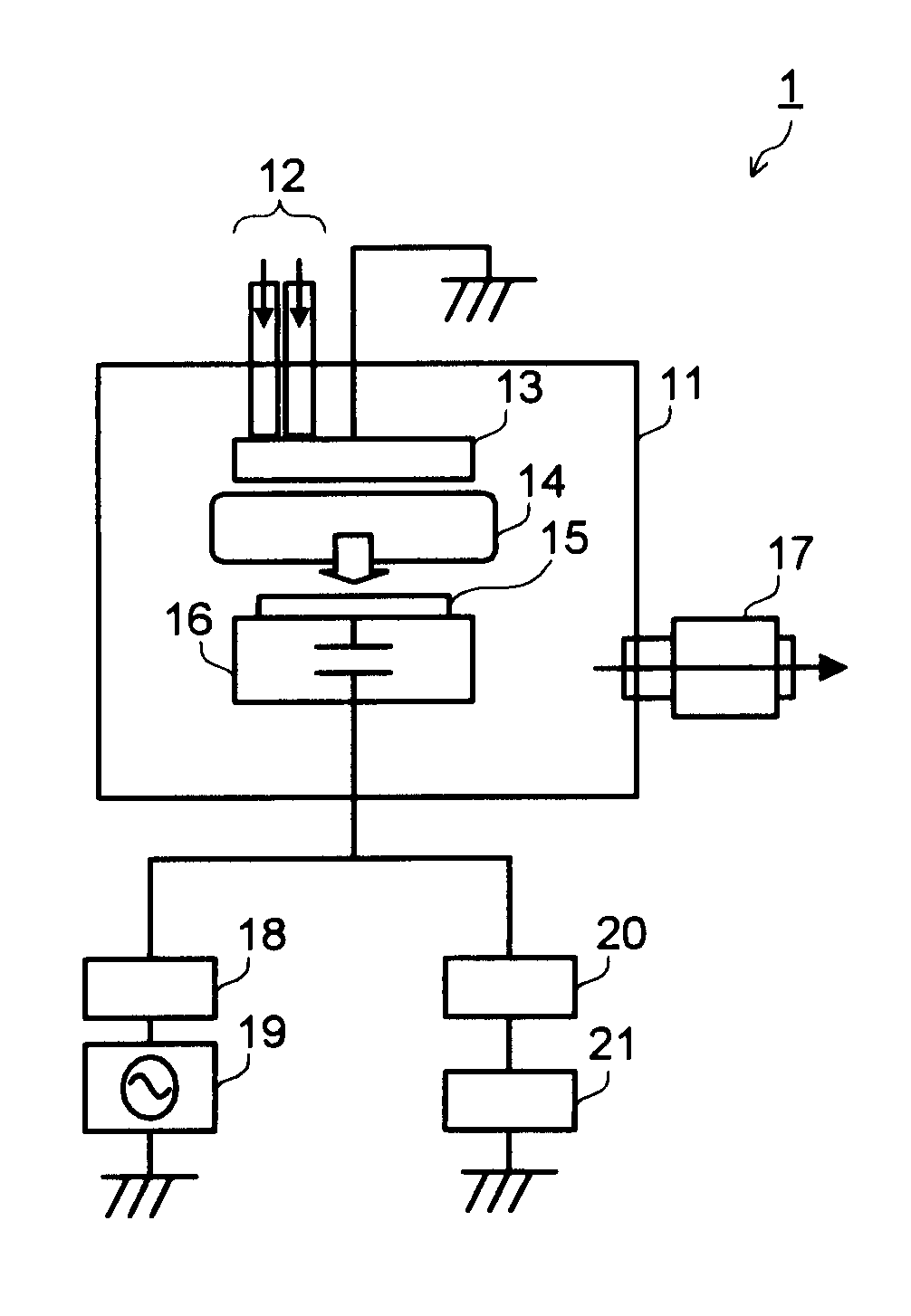
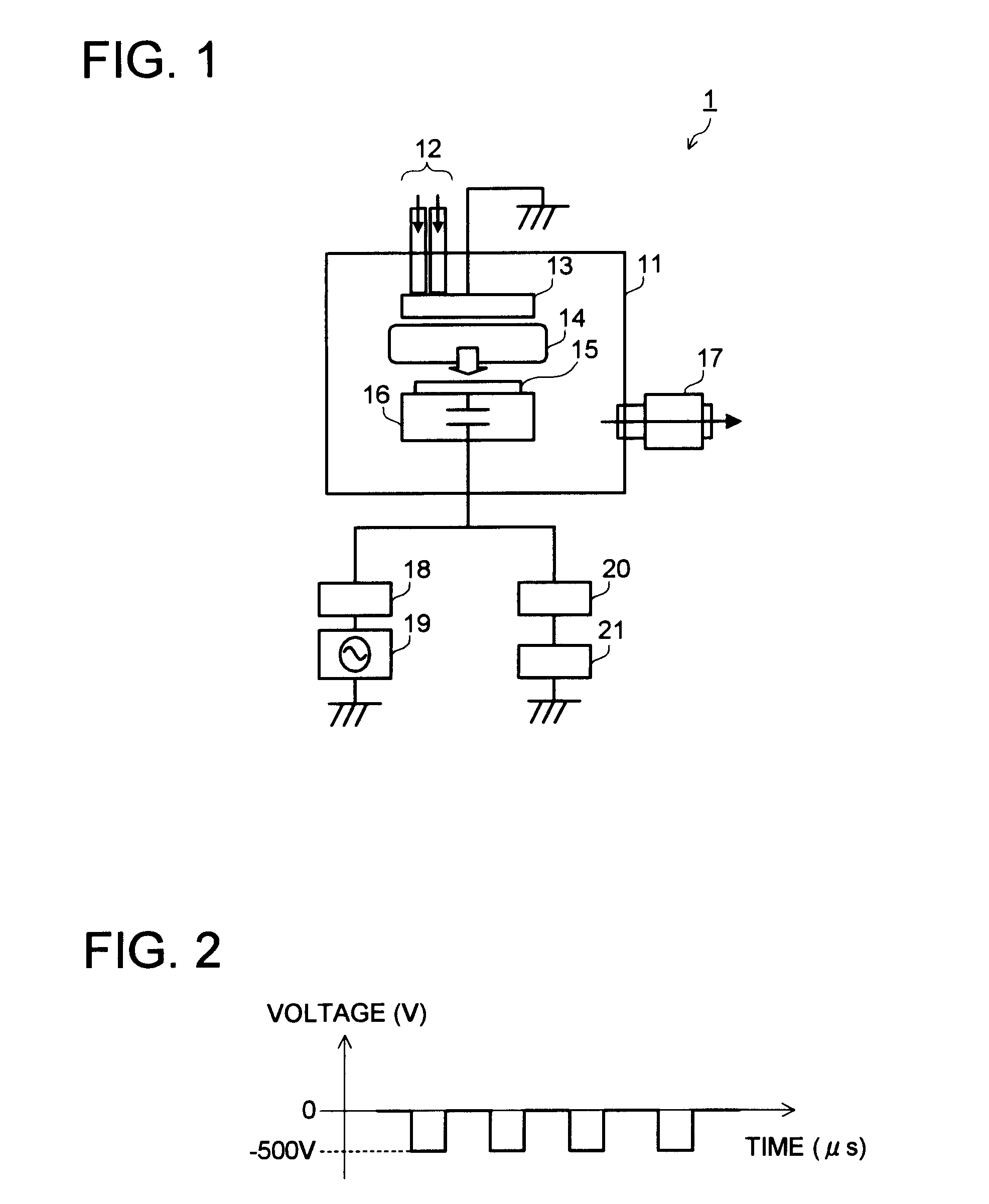
[0078]FIG. 7 is a schematic block diagram of a substrate processing apparatus 2 according to one embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 8 is a detailed block diagram of a pulse applying unit. FIG. 9 is a schematic waveform chart of a voltage applied in a superimposed manner to a lower electrode 16. In FIG. 9, the vertical axis represents voltage (Voltage) and the horizontal axis represents time (μs).
[0079]A sawtooth power source 32 outputs to a switching circuit (first switching unit) 31 a sawtooth voltage shown by a wavy line 106 in FIG. 9. Further, the sawtooth power source 32 inputs a synchronizing signal to a gate trigger 33. The synchronizing signal is input to the gate trigger 33 every arbitrary point of the sawtooth waveform shown by the wavy line 106 in FIG. 9, for example, every lowest voltage point or every highest voltage point of the sawtooth waveform.
[0080]According to the synchronizing signal input from the sawtooth power source 32, the gate trigger 33 inputs a sign...
modification examples
(Modification Examples of First Embodiment)
[0088]FIG. 11 and FIG. 12 are waveform charts of a voltage applied to the lower electrode 16 in modification examples of the first embodiment. In the first embodiment, the sawtooth voltage output from the sawtooth power source 32 as described with reference to FIG. 9 is taken out by the switching circuit 31, whereby the pulse voltage whose voltage in one pulse decreases in accordance with time is applied to the lower electrode 16.
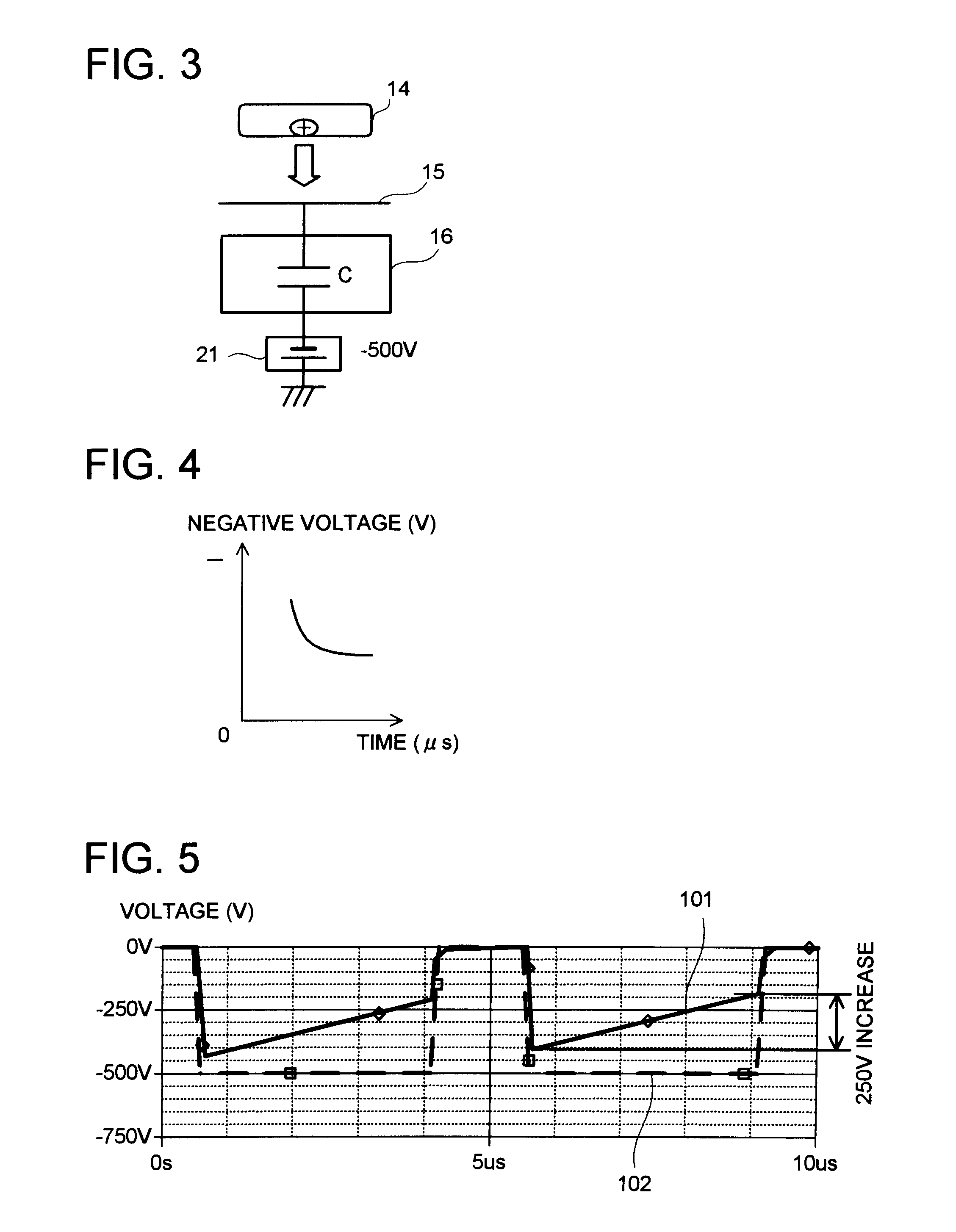
[0089]However, the use of the sawtooth voltage is not necessarily essential provided that the voltage change of the wafer 15 in the course of the etching process can be reduced to 50 V or less. Therefore, a triangular wave shown by a broken line in FIG. 11 or a sin wave shown by a broken line in FIG. 12 may be taken out by the switching circuit, whereby a pulse voltage whose voltage in one pulse decreases in accordance with time as shown by a solid line in FIG. 11 or FIG. 12 may be applied to the lower electrode 16...
second embodiment
[0091]FIG. 13 is a schematic block diagram of a substrate processing apparatus 3 according to a second embodiment. FIG. 14 is a detailed block diagram of a pulse applying unit. FIG. 15 is a schematic waveform chart of a voltage applied in a superimposed manner to a lower electrode 16. In FIG. 15, the vertical axis represents voltage (Voltage) and the horizontal axis represents time (μs).
[0092]DC power sources 42a to 42f input negative voltages different from one another to a switching circuit 41. A gate trigger 43 inputs to the switching circuit 41a signal for switching among the DC power sources 42a to 42f. The switching circuit (second switching unit) 41 includes switches 41a to 41f corresponding to the DC power sources 42a to 42f respectively.
[0093]Each of the switches 41a to 41f turns ON or OFF according to the signal input from the gate trigger 43. Concretely, when an ON signal is received from the gate trigger 43, each of the switches 41a to 41f is connected so that the voltag...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com