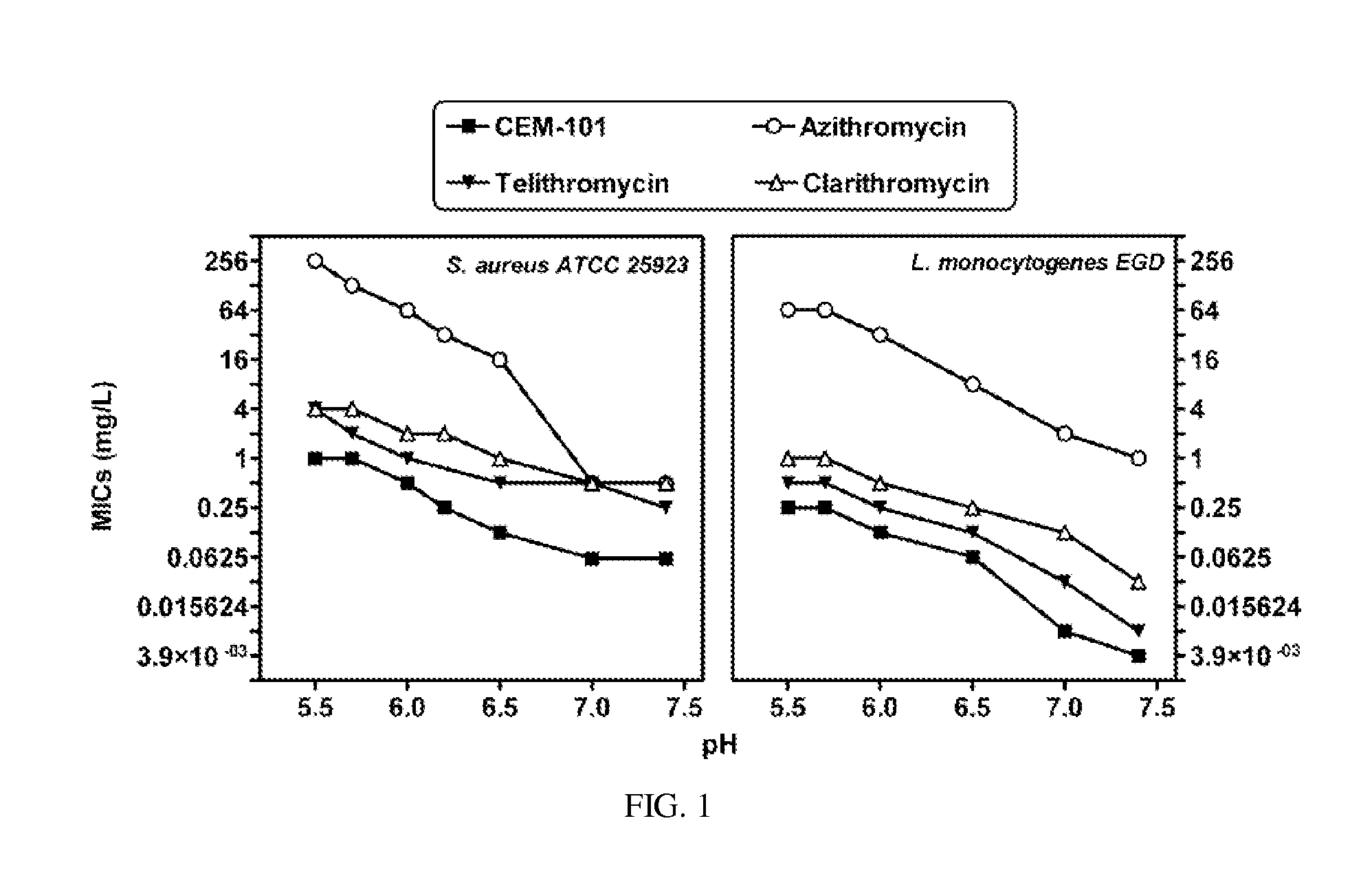
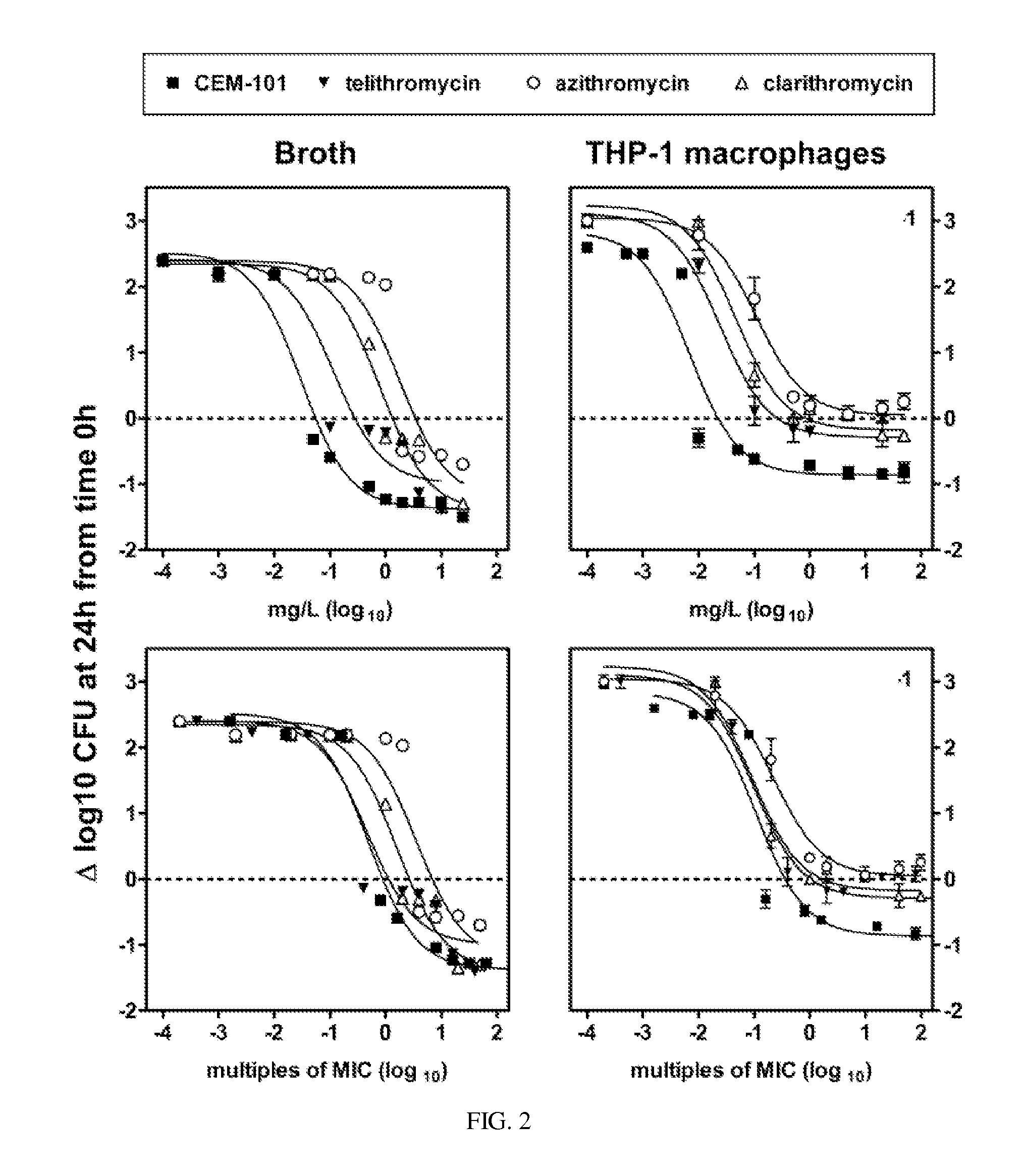
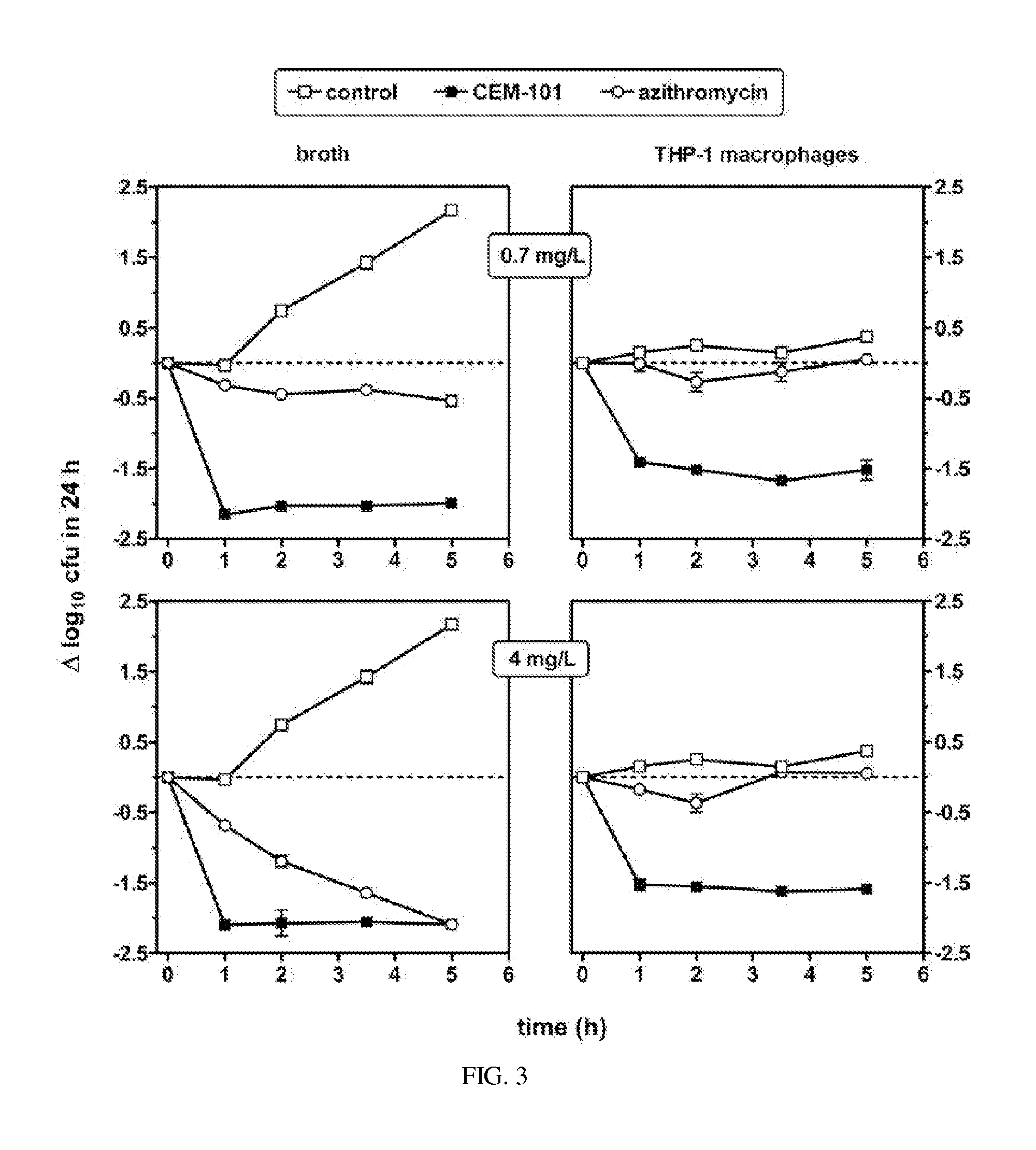
Methods for treating resistant diseases using triazole containing macrolides
a triazole and macrolide technology, applied in the field of resistant diseases, can solve the problems of limited clinical utility of this drug, inactiveness, and increased risk of pneumonia causing community-acquired respiratory infection, and achieve low resistance development potential, high activity in vitro and in vivo, and low potential
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0202]Staphylococci, β-Haemolytic and Viridans Group Streptococci. A collection of 2006-2007 clinical isolates were S tested by CLSI methods (M7-A7) with associated interpretive criteria (M100-S18) and supplements (2-5% LHB) for streptococcal tests. CEM-101, TEL (TEL) and 10 comparators were used versus 201 S. aureus (75 WT-MRSA, 75 WT-MSSA, 30 CA-MRSA, 17 VISA or hVISA, 7 VRSA), 100 coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS; 10 species), 100 β-haemolytic (BHS; 30 group A, 31 group B, 14 group C, 9 group F, 16 group G) and 51 viridans group streptococci (VGS; 5 species), see Table.
[0203]MSSA strains were slightly more CEM-101-S (MIC50, 0.06 μg / ml) that MRSA or CA-MRSA strains (MIC50, 0.12 μg / ml). VISA, hVISA and VRSA were generally more refractory to CEM-101 and TEL. CEM-101 was 2-fold more potent than TEL against all staphylococci. Streptococci were very S to CEM-101 (MIC90, 0.03-0.06 μg / ml) and TEL was 4-fold less active with non-S isolates of BHS observed. ERY-R staphylococci remain...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pKa | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com