Generation of Clonal Mesenchymal Progenitors and Mesenchymal Stem Cell Lines Under Serum-Free Conditions
a technology of mesenchymal stem cells and which is applied in the field of clonal primate mesenchymal progenitors and to mesenchymal stem cell lines under serum-free conditions, can solve the problems of limited art, inability to isolate sufficient mscs, and the risk of donors being required to isolate even a limited number of cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Generation of MSCs from Pluripotent Stem Cells Under Serum-Free Conditions
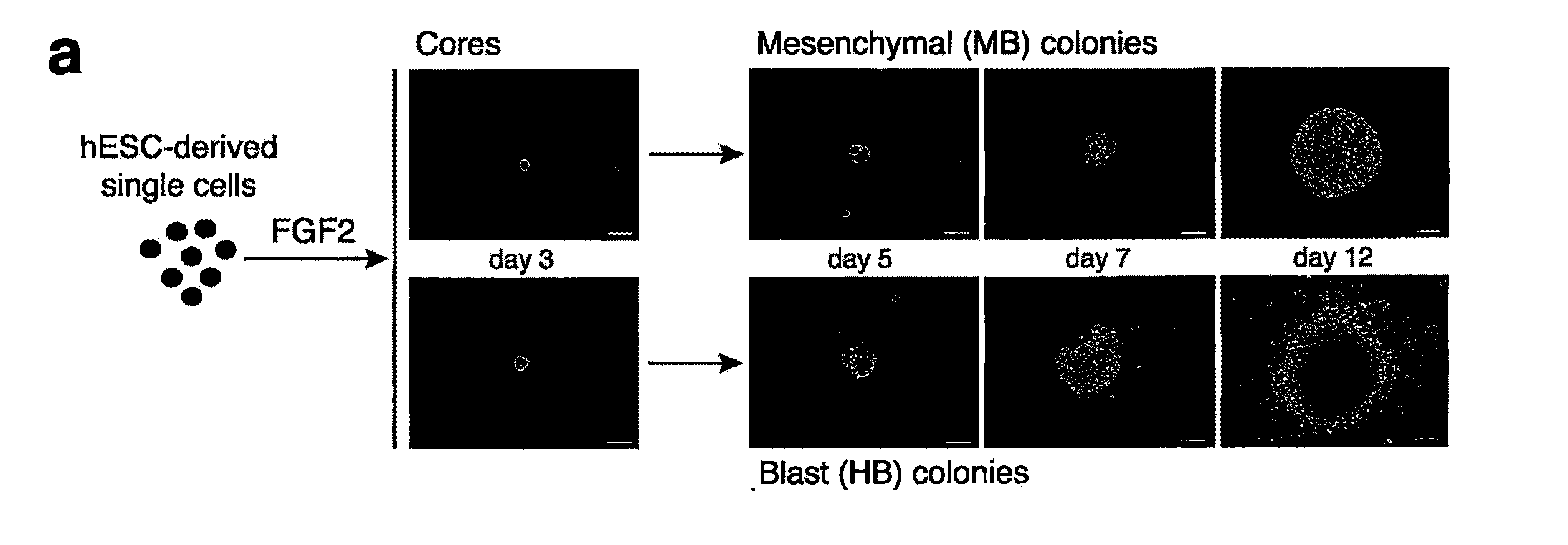
[0061] hESCs (H1; WiCell; Madison, Wis.) were maintained on irradiated mouse embryonic fibroblasts in a serum-free medium, such as DMEM / F12 medium supplemented with _20% Knockout™ serum replacer, 2 mM L-glutamine, 1×(100 μM) non-essential amino acids, 100 μM 2-mercaptoethanol and 4 ng / ml bFGF (all from Gibco-Invitrogen; Carlsbad, Calif.). See Amit M, et al., “Clonally derived human embryonic stem cell lines maintain pluripotency and proliferative potential for prolonged periods of culture,” Dev. Biol. 227:271-278 (2000), incorporated herein by reference as if set forth in its entirety. Mouse OP9 bone marrow stromal cells (kindly provided by Dr. Toru Nakano and available from ATCC, catalog # CRL-2749) were maintained by four-day subculture on gelatin-coated dishes in alpha MEM medium (Gibco-Invitrogen) with 20% fetal calf serum (FCS; HyClone; Logan, Utah).
[0062] The hESCs were induced to differentiate by co-c...
example 2
In Vitro Generation and Characterization of Mesangioblasts
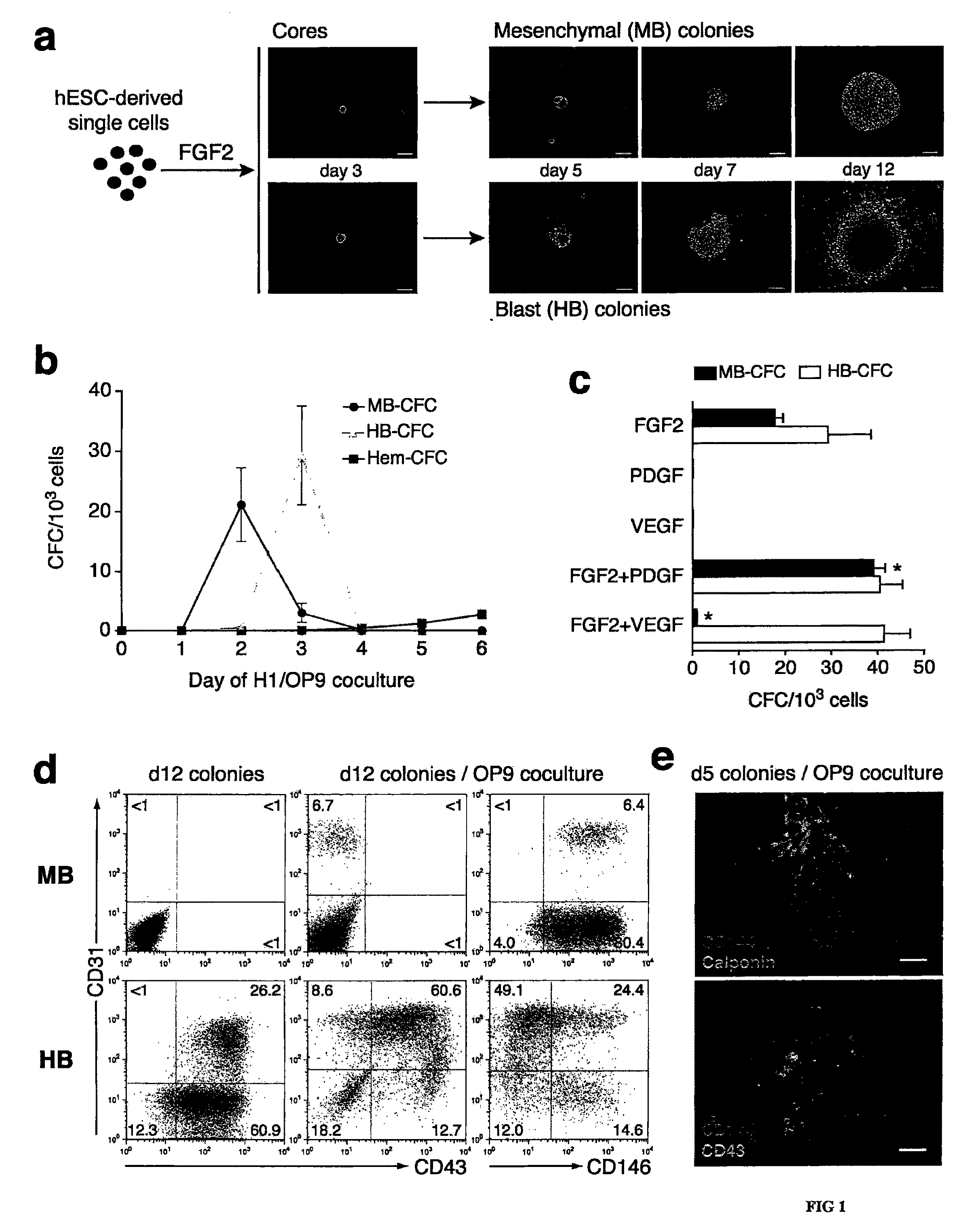
[0075] To isolate and characterize a population of mesodermal progenitors that can give rise to cells of the mesodermal lineage with hematopoietic, endothelial, and mesenchymal stem cell potentials, H1 hES cells were co-cultured with OP9 cells, as described in Example 1. After two or three days of co-culture, when genes representative of primitive streak population (mesendoderm) (MIXL1, T, EOMES) were expressed, the hESC-derived cells depleted of 0P9 cells using anti-mouse CD29 antibody were plated in semisolid, serum-free medium, essentially as described in Example 1, with 20 ng / ml bFGF (Pepro Tech; Rocky Hill, N.J.). The number of colony-forming cells (CFCs) was calculated per 1000 plated H1-derived TRA-1-85+ cells.
[0076] After 2-3 days in semisolid medium, the cells formed tightly packed structures (cores). Cores derived from hESCs that were differentiated in co-culture with OP9 cells for 2 days further grew into spheroi...
example 3
Generating and Isolating a Population of Cells Substantially Enriched in Lateral Plate / Extraembryonic Mesoderm Cells
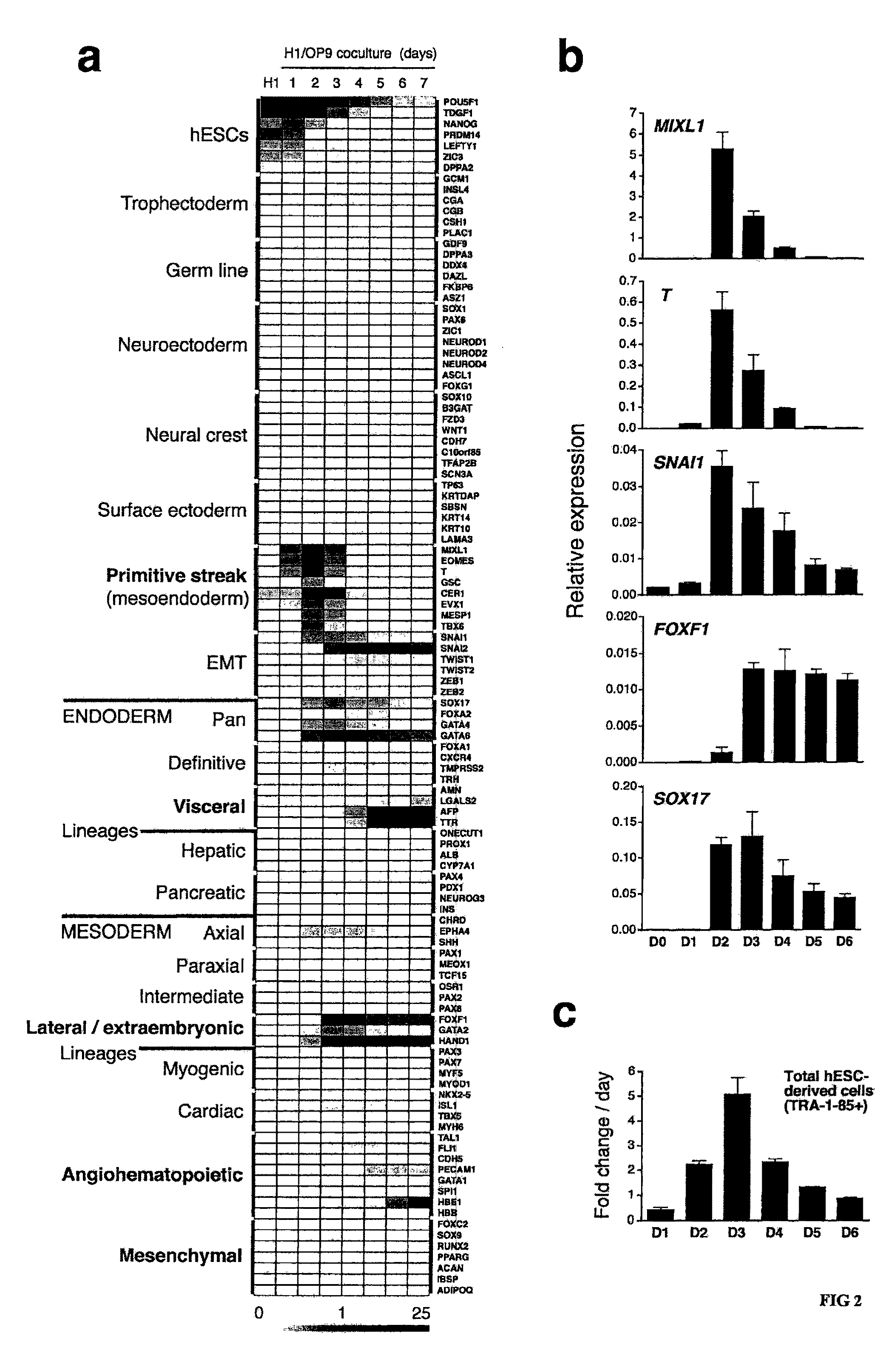
[0081] Genetic profiling of H1 hESCs differentiated in OP9 cocultures demonstrated selective commitment toward mesodermal and endodermal lineages with no detectable ectoderm (tropho-, neuro-, or surface ectoderm) (FIG. 2). The cells became committed to mesendoderm by day 2 of culture, when synchronous expression of primitive streak genes (MIXL1, T, and EOMES) was detected. At subsequent days of culture, mesoderm- and endoderm-specific genes and, eventually, endoderm- and mesoderm derivative-specific genes were expressed. Of the mesodermal genes, those characteristic of the lateral plate / extraembryonic mesodermal subset (FOXF1, HAND1, NKX2-5, GATA2) were expressed consistently, while expression of genes of the axial (CHRD, SHH), paraxial (MEOX1, TCF15), or intermediate (PAX2, PAX8) subsets was not consistent. Apelin receptor (APLNR) expression is strongly induced and u...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| paramagnetic | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| heat-inactivated | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com