Engineered E2 For Increasing The Content Of Free LYS11-Linked Ubiquitin
a technology of free ubiquitin and lys11, which is applied in the direction of enzyme stabilisation, peptides, fusion with degradation motif, etc., can solve the problems of inefficient solution production of free ubiquitin multimers by ube2s, which assembles k-11 linked polyubiquitin, and poor efficiency of ubiquitin transfer to proteins on their own, so as to facilitate structural studies and increase efficiency. , the effect of high-level purification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Analysis of E2 Enzymes Involved in K11 Chain Formation
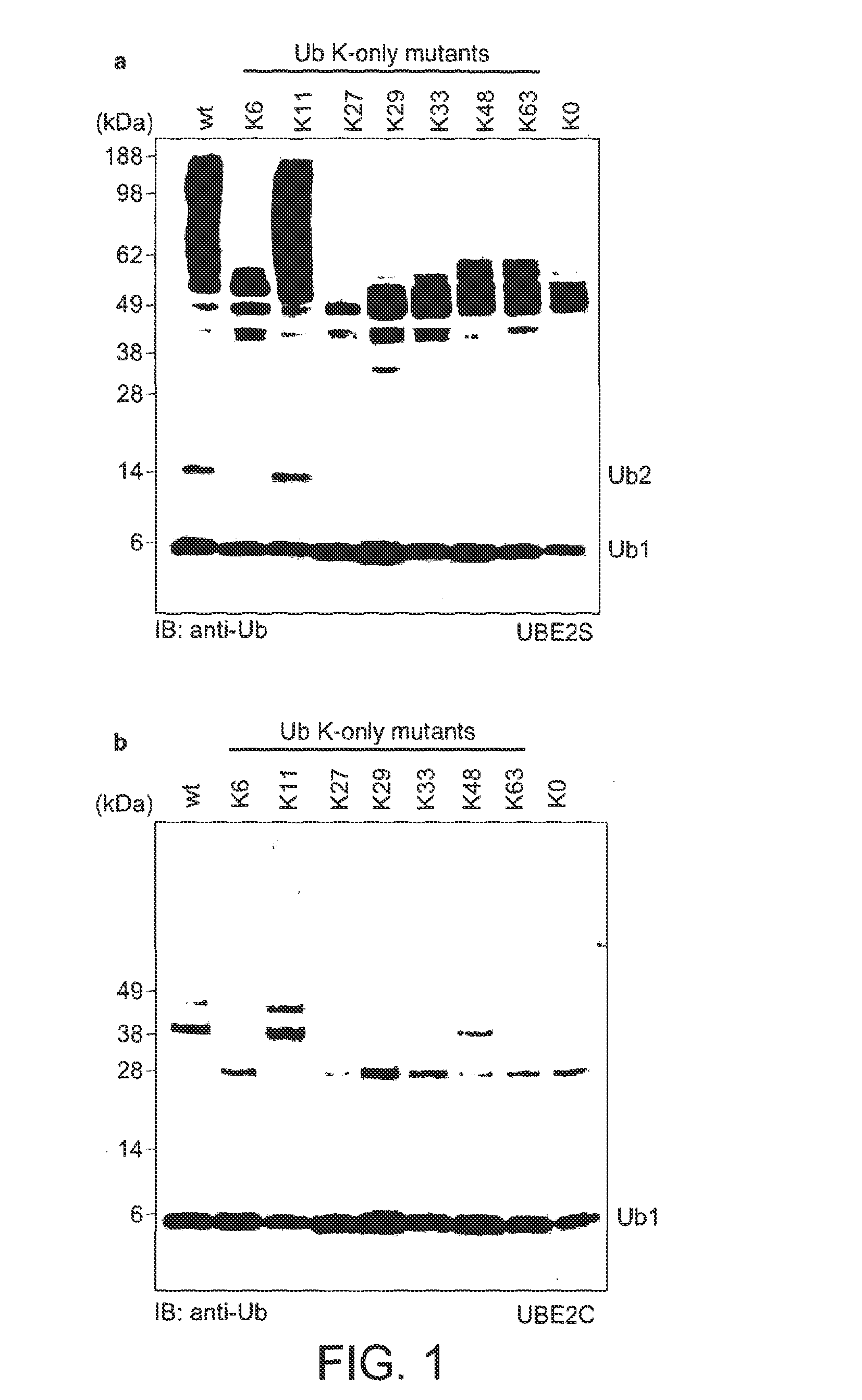
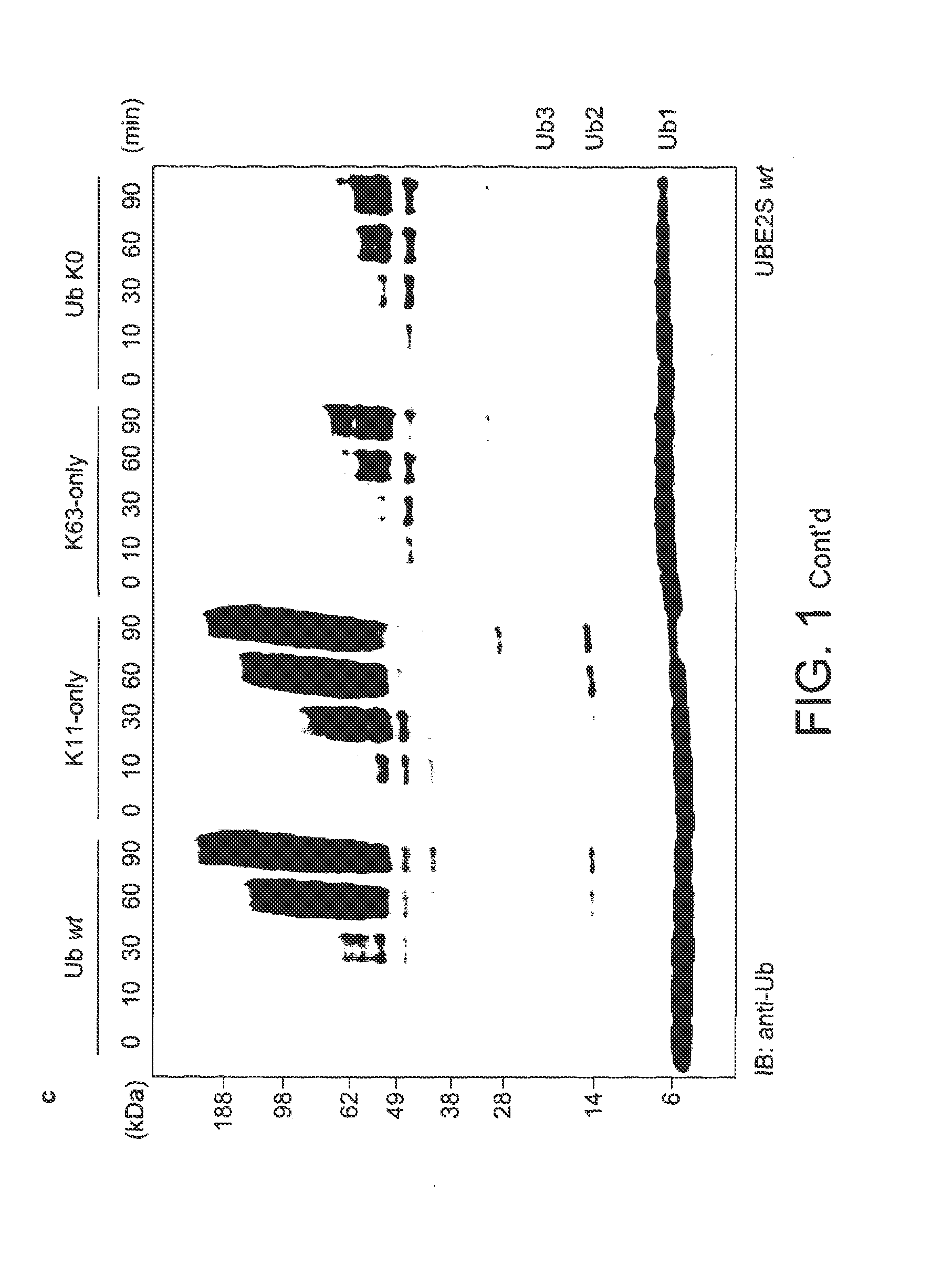
[0100]For the assembly of free K48- and K63-linked ubiquitin chains, specific E2 enzymes have been described, and the biology of these posttranslational modifications is now known in great detail. In order to study the elusive K11 linkage, Applicants analyzed the in vitro properties of two human E2 conjugating enzymes that have been associated with this chain type, namely UBE2C / UbcH10 (Jin et al., 2008) and UBE2S / E2-EPF (Baboshina & Haas, 1996). Applicants tested whether UBE2S and UBE2C would assemble unattached polyubiquitin chains in vitro in absence of an E3 ligase. Analytical assays were carried out in 30 μl reactions at 37° C. containing 250 nM ubiquitin-activating enzyme (E1), 2.8 μM (UBE2S) or 3.4 μM (UBE2C) ubiquitin conjugating enzyme (E2), 19.5 μM ubiquitin, 10 mM ATP, 40 mM Tris (pH 7.5), 10 mM MgCl2 and 0.6 mM OTT. After 1 h the reaction was stopped by addition of 10 μl 4×LDS sample buffer (Invitrogen), resolved by SD...
example 2
Generation of K11-Linked Ubiquitin Tetramers
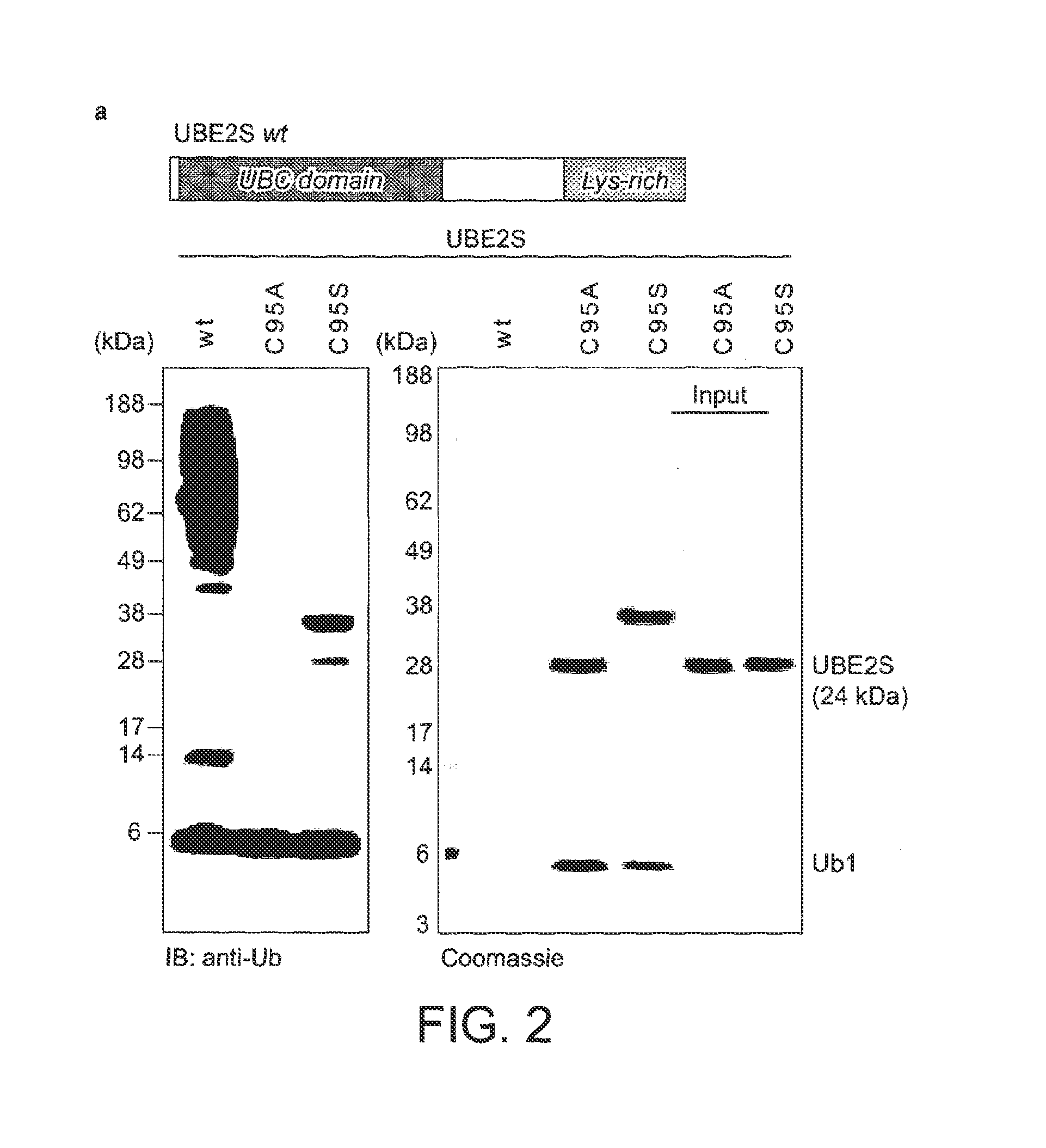
[0105]In order to increase the yields of K11-linked dimers and to obtain longer polymers, Applicants reverted to protein engineering to create an UBE2S variant with increased capability to form free ubiquitin chains. Having established that the Lys-rich tail of UBE2S is polyubiquitinated by UBE2S in a cis reaction, Applicants replaced this tail (residues 196-222) with the ubiquitin binding ZnF-UBP domain of human USP5 / IsoT (residues 173-289) (Reyes-Turcu et al., 2006; FIG. 3a). This UBD has two advantageous features: it binds ubiquitin with nanomolar affinity, and interacts with the free C-terminal tail of ubiquitin leaving the Lys11 side chain accessible for chain elongation. The UBE2S-UBD fusion protein was significantly more efficient in producing ubiquitin dimers, trimers, and tetramers.
[0106]Ubiquitin tetramers were synthesized by incubating 250 nM E1 enzyme, 4.8 μM UBE2S-UBD, 2.9 mM ubiquitin, 400 nM AMSH, 10 mM ATP, 40 mM Tris (pH 7...
example 3
Structure of K11-Linked Polyubiquitin
[0109]Generation of K11-linked ubiquitin chains in large quantities allowed detailed structural analysis of this chain type.
[0110]Large-scale ubiquitin chain assembly was carried out in 1 ml reactions. Ubiquitin dimers were synthesized by incubating 250 nM E1 enzyme, 4.8 μM UBE2SΔC, 1.5 mM ubiquitin, 10 mM ATP, 40 mM Tris (pH 7.5), 10 mM MgCl2 and 0.6 mM DTT at 37° C. overnight. Subsequently, 50 mM DTT was added to the reaction before further dilution with 14 ml of 50 mM ammonium acetate (pH 4.5) to precipitate enzymes. The solution was filtered through a 0.2 μm syringe filter and K11-linked diubiquitin was purified by cation exchange using a MonoS column (GE Healthcare) and concentrated to 5 mg / ml. Crystals formed after 1 day from 3M NaCl and 0.1 M citric acid (pH 3.5). Before freezing in liquid nitrogen, crystals were soaked in mother liquor containing 15% ethylene glycol.
[0111]Diffraction data on crystals of K11-linked diubiquitin were collect...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com