Tile levelling device
a technology for levelling and spacing tiles, which is applied in the direction of roofs, roofing, roof tools, etc., can solve the problems of reducing or restricting the transfer of force between adjacent tiles, and the proportions of spacer bodies are not aligned, so as to achieve the effect of reducing or limiting the flexibility of each spacer body
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
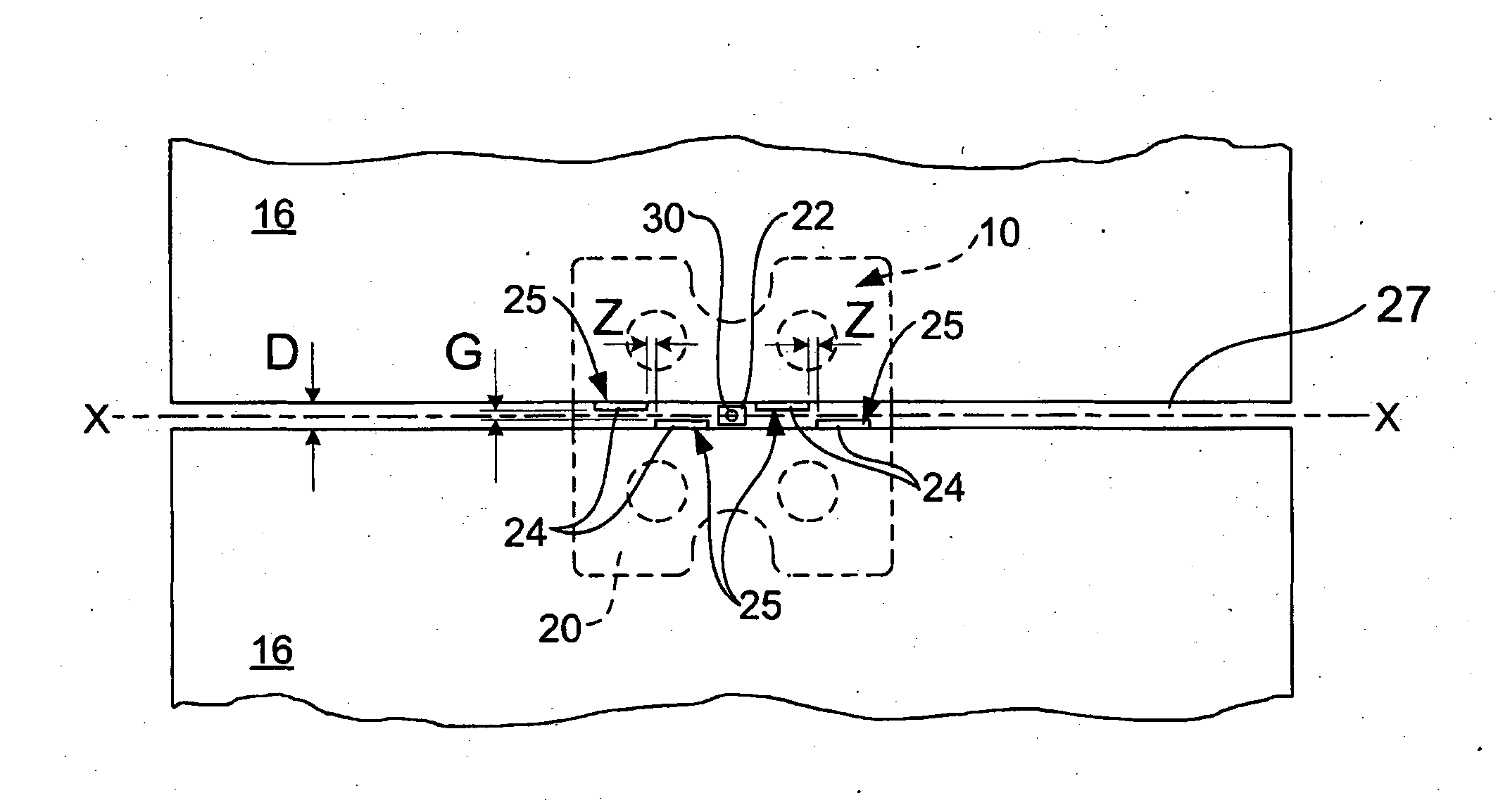
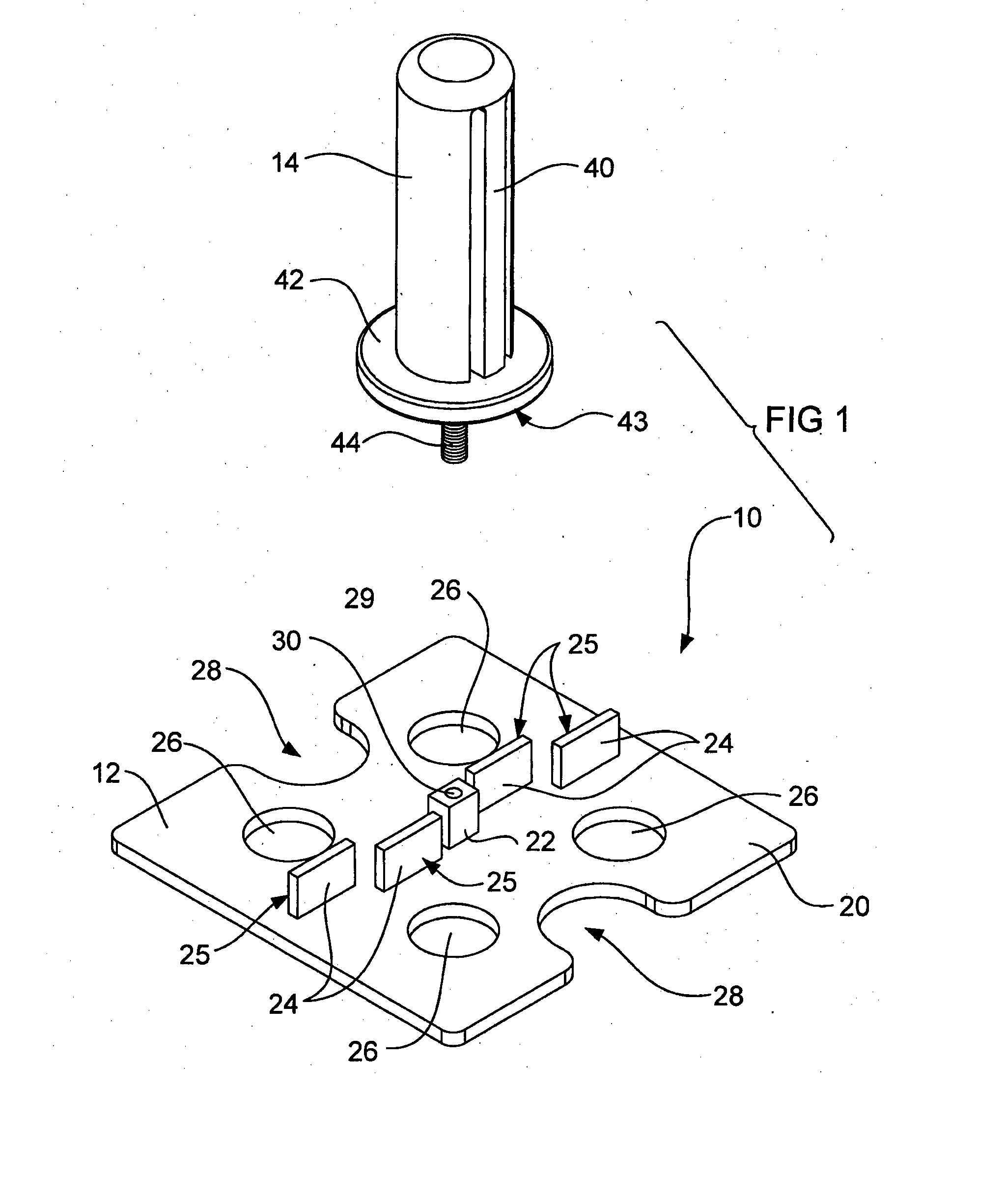
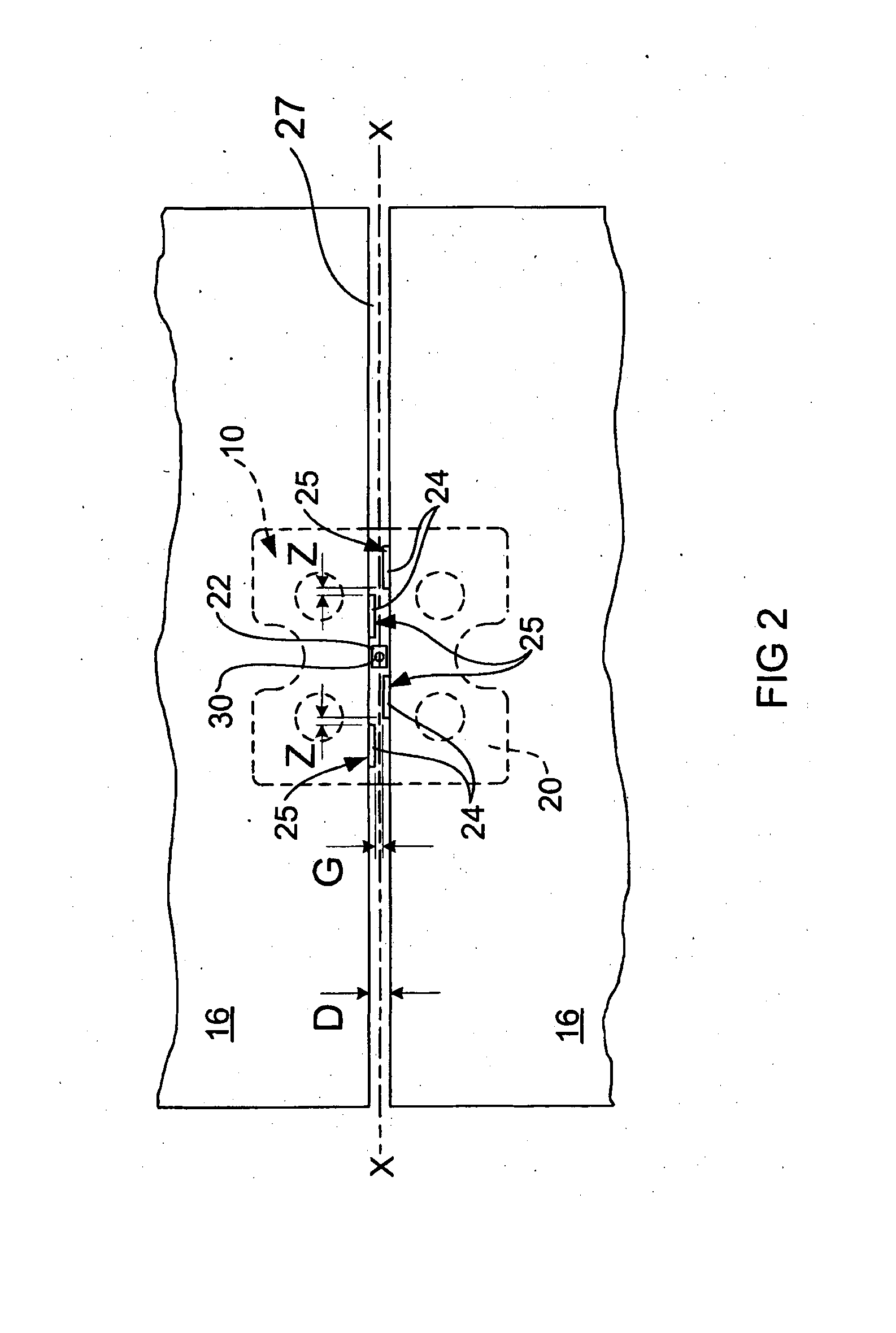
[0046]Referring firstly to FIGS. 1 and 2, there is shown a tile levelling and spacing system 10 according to a first preferred embodiment of the present invention. The tile levelling and spacing system 10 comprises a tile levelling and spacing device 12 and a clamping spindle 14. The tile levelling and spacing device 12 and a clamping spindle 14 act cooperatively to clamp around a tile 16 (FIG. 2) when in use.
[0047]The illustrated tile levelling and spacing device 12 comprises a generally square moulded body made of a plastic material fabricated in a plastic injection moulding process or similar. The device 12 includes a rectangular base plate 20, a square central connection hub 22, and four spacing tabs 24. The base plate 20, central connection hub 22 and spacing tabs are all integrally moulded as part of the device 12 during a plastic moulding process. It should be appreciated that the dimensions of the features of the device 12 can vary to suit a particular tile size and configur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com