Optical scanning device and image forming apparatus therewith
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
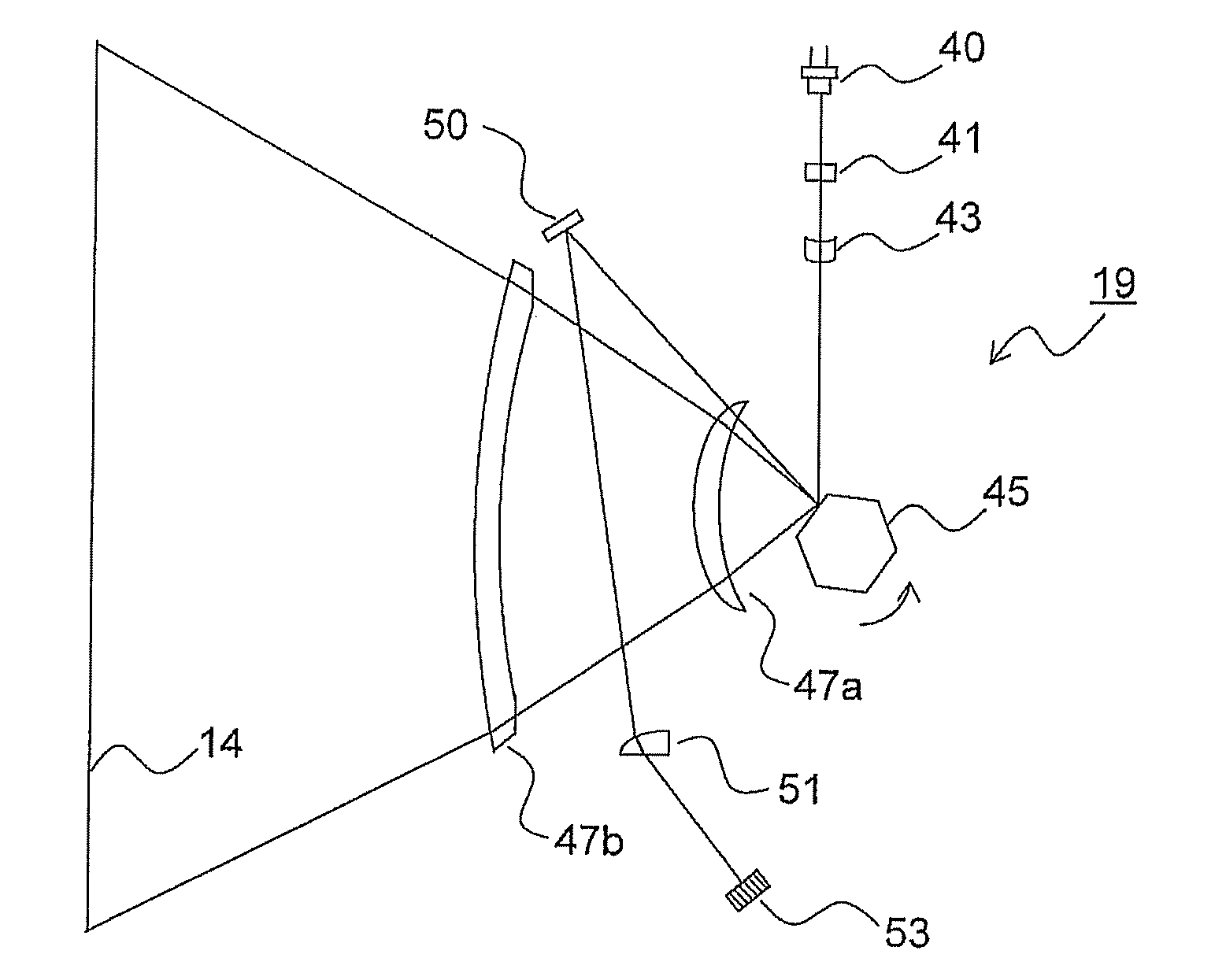
[0025]FIG. 2 is a main scanning sectional view schematically showing an internal construction of the exposure device 19 according to the present disclosure. As shown in FIG. 2, the exposure device 19 is provided with an LD unit 40, a collimator lens 41, a cylindrical lens 43, a polygon mirror 45, scanning lenses 47a and 47b, a planar mirror 50, an SOS (start-of-scan) lens 51, and a BD sensor 53.
[0026]The LD unit 40 is provided with a laser diode (LD) as a light source, and emits a light beam (laser beam) resulting from optical modulation based on an image signal. The collimator lens 41 forms the laser beam emitted from the LD unit 40 into a substantially parallel beam. The cylindrical lens 43 has a predetermined refractive power only in a sub scanning direction of the laser beam. The parallel beam having passed through the collimator lens 41 and entered the cylindrical lens 43 exits from it in the form of a convergent beam in the sub scanning direction while remaining a parallel bea...
second embodiment
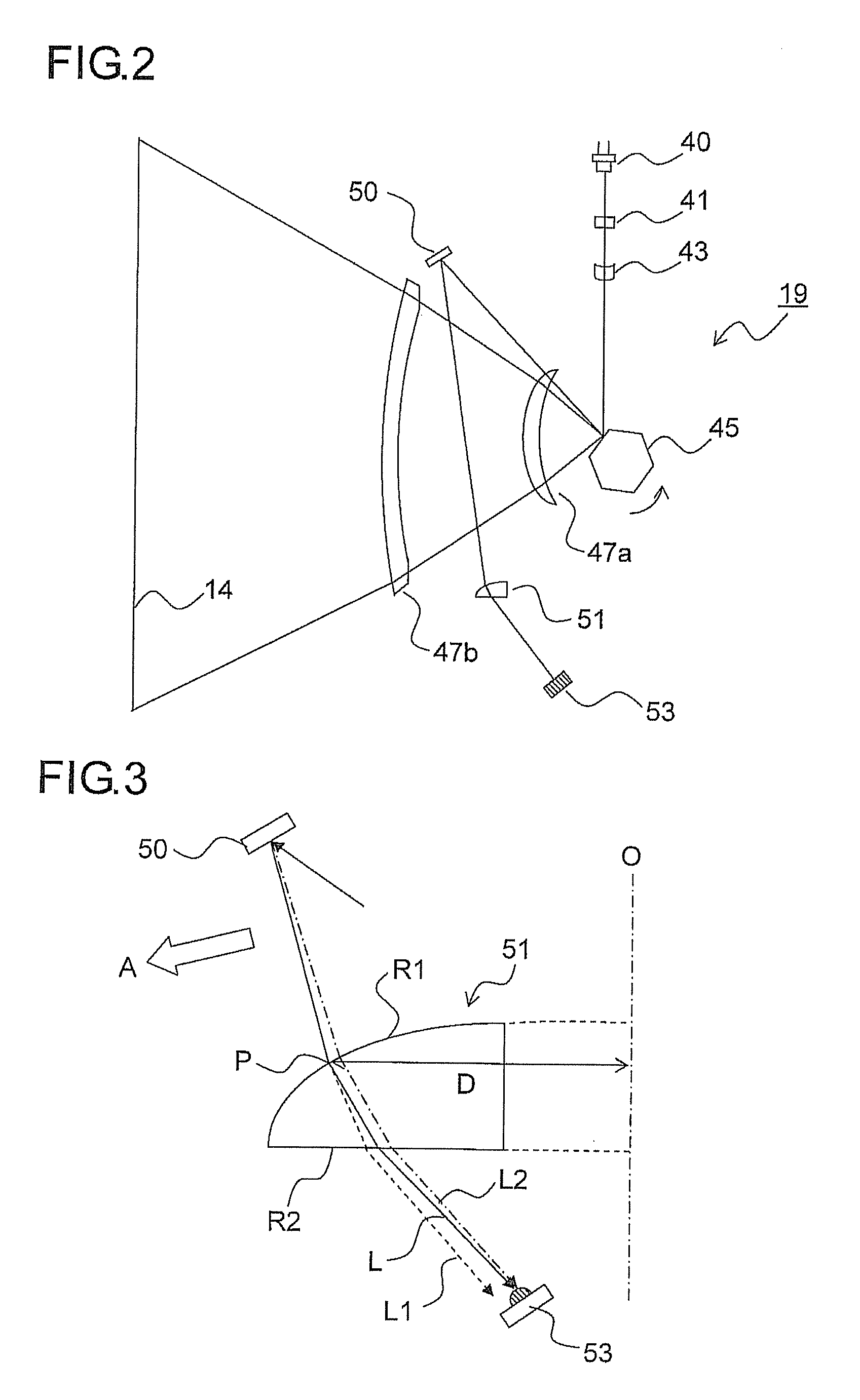
[0035]FIG. 5 is a main scanning sectional view schematically showing an internal construction of the exposure device 19 in the present disclosure. FIGS. 6 and 7 are side views showing how the laser beam reflected from the planar mirror 50 passes through the SOS lens 51 and enters the BD sensor 53.
[0036]In this embodiment, as the SOS lens 51, an aspherical lens having a negative power is used. The optical axis 0 of the lens is offset, with respect to the point of entrance P, in the advancing direction (the direction indicated by arrow A in the diagrams) in the main scanning direction. The distance (optical axis offset) from the optical axis 0 of the SOS lens 51 to the point of entrance P of the laser beam L is, for example, 20 mm. The light entrance surface (surface R1) of the SOS lens 51 is, for example, an aspherical surface with a radius of curvature of 21.075 mm and a conic constant of −0.725, and the light exit surface (surface R2) of the SOS lens 51 is a flat surface. In other ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com