Image processing apparatus, image processing method, display panel driver and display apparatus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
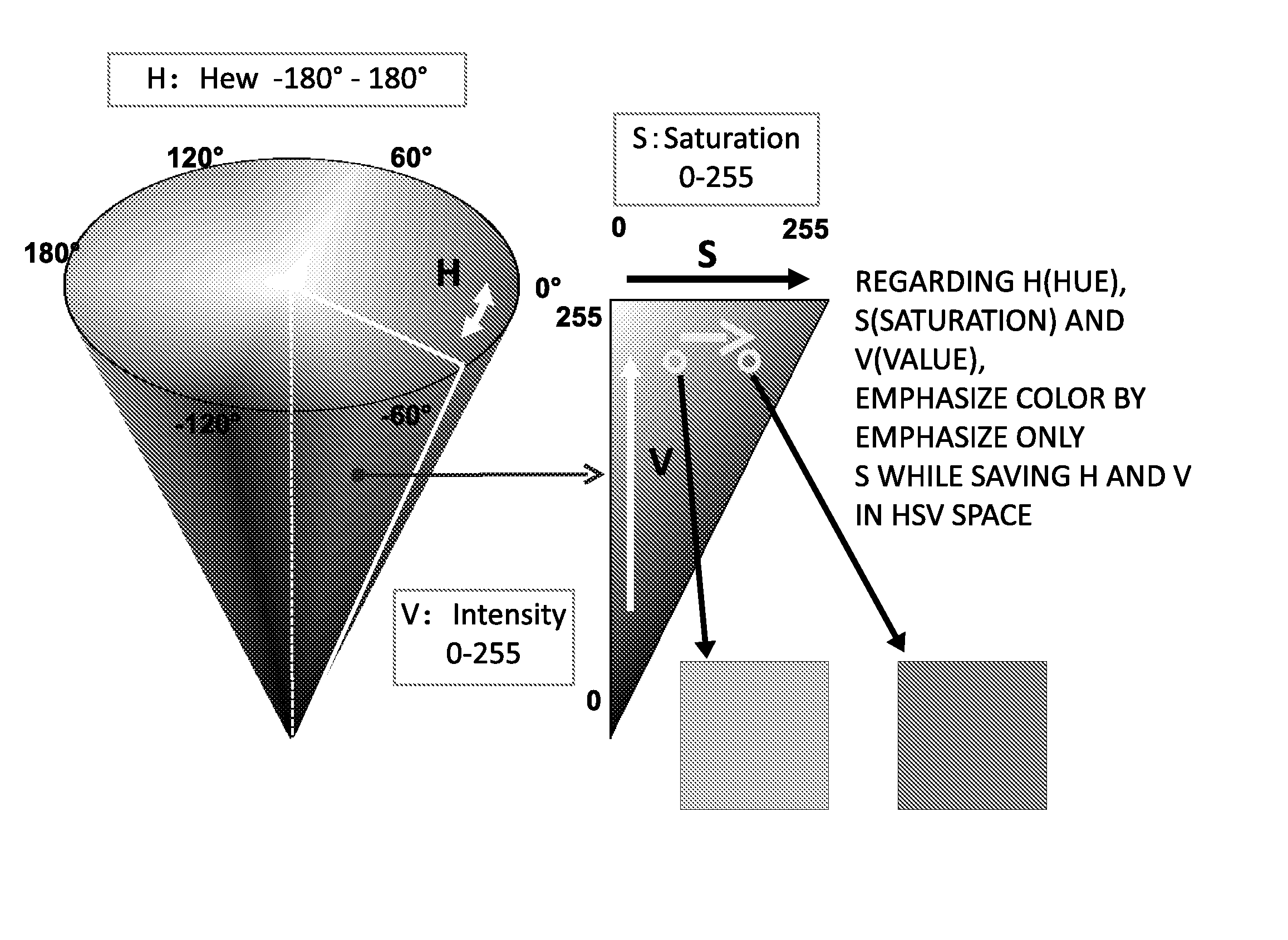
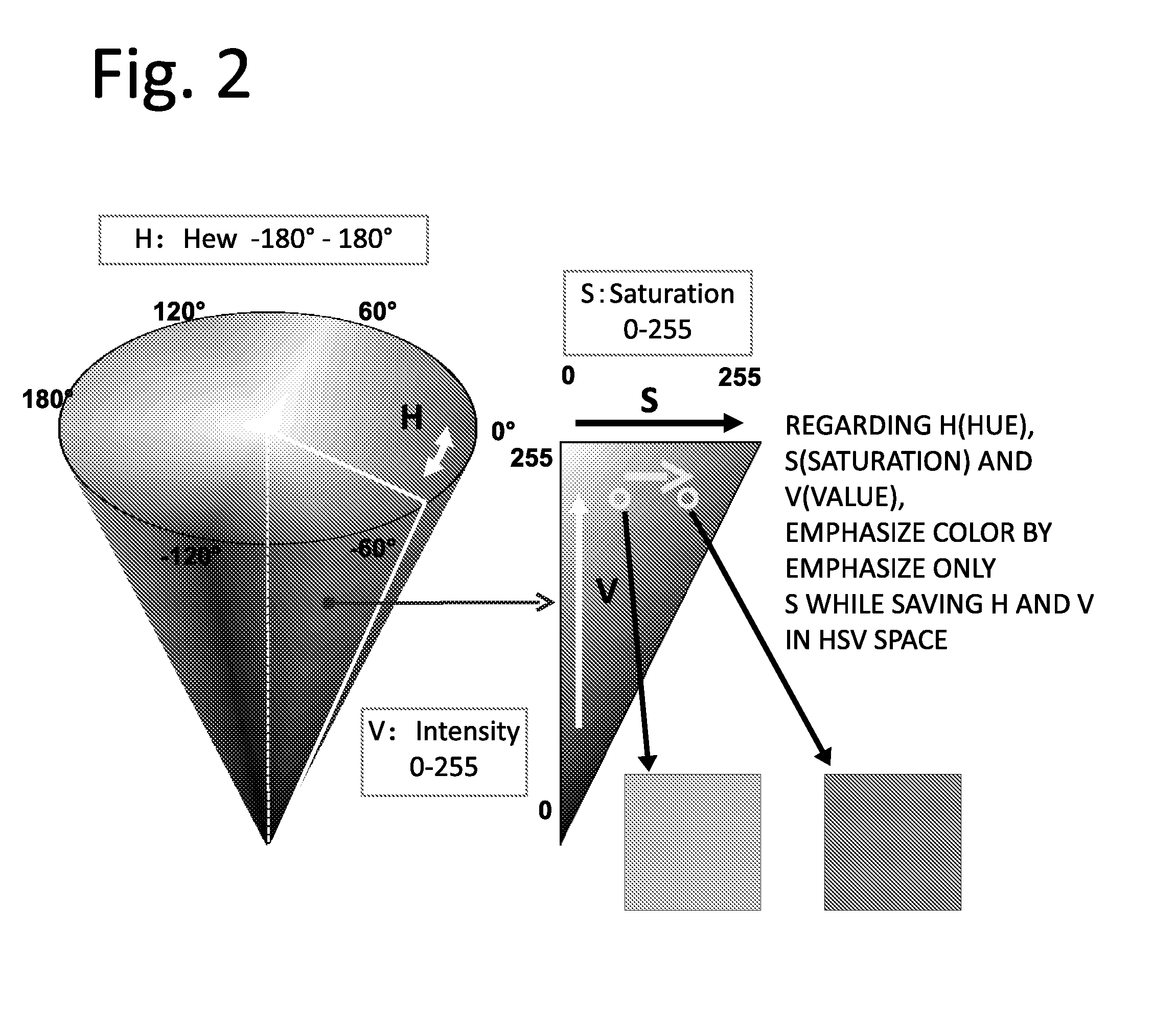
[0064]FIG. 6 is a conceptual diagram showing the saturation expansion processing that is carried out in a first, embodiment. In the saturation expansion processing of the first embodiment, the operation processing is carried out in which the saturation component S is not expanded while saving the value component V but the saturation component S is expanded while saving the brightness Y. In other words, in the first embodiment, the calculation of expanding the saturation component S is carried out while saving the reference value C, and in the calculation, the brightness Y is used as the reference value C.
[0065]FIG. 7 is a conceptual diagram showing a technical idea of the saturation expansion processing of the present embodiment. In the present embodiment, when the saturation expansion processing is carried out, the brightness compensation is carried out such that the brightness Y is saved to each of the R data, the C data, and the B data, as compared with the saturation expansion p...
second embodiment
[0099]In a second embodiment, the saturation expansion processing is carried out to expand the saturation component S while saving the reference value C. However, in the second embodiment, the reference value C is calculated as a weighted average of the value component V and the brightness Y. That is, in the second embodiment, the saturation expansion processing is carried out like the first embodiment while using the reference value C that is calculated as the weighted average of value component V and the brightness component Y instead of the brightness component Y.
[0100]In this case, the value component V is the maximum value of the R data, the G data, the B data of the RGB data (reference to equation (1-1)), and the brightness Y is calculated as the weighted average of the R data, the G data, the B data. Therefore, note that even in case that the reference value C is calculated as the weighted average of the value component V and the brightness Y, the reference value C is the wei...
third embodiment
[0122]FIG. 13 to FIG. 15 are diagrams to describe the technical features of the saturation expansion processing in a third embodiment. In the saturation expansion processing in the first and second embodiments, the values of the R data, the G data, the B data of the RGB data after saturation expansion sometimes become smaller than a lower limit value RGB_MIN or become greater than an upper limit value RGB_MAX. Here, the lower limit value RGB_MIN is “0” generally and the upper limit value RGB_MAX is a value that is determined according to the bit width of the R data, the G data, and the B data. In case that each of the R data, the G data, and the B data is n-bit data, the lower limit value RGB_MIN is “0” and the upper limit value RGB_MAX is 2n−1.
[0123]Referring to FIG. 13, for example, consider a case that each of the values of the R data, the G data, and the B data is expressed in 8 bits. In this case, each of the R data, the G data, and the B data of the RGB data is given as a valu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com