Screw and rod fixation system
a fixation system and screw technology, applied in the field of screw and rod fixation assemblies, can solve the problems of compromising correction, fixing points that cannot be aligned, and the doctor is unable to introduce the rod into all of the fixation points or bring,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
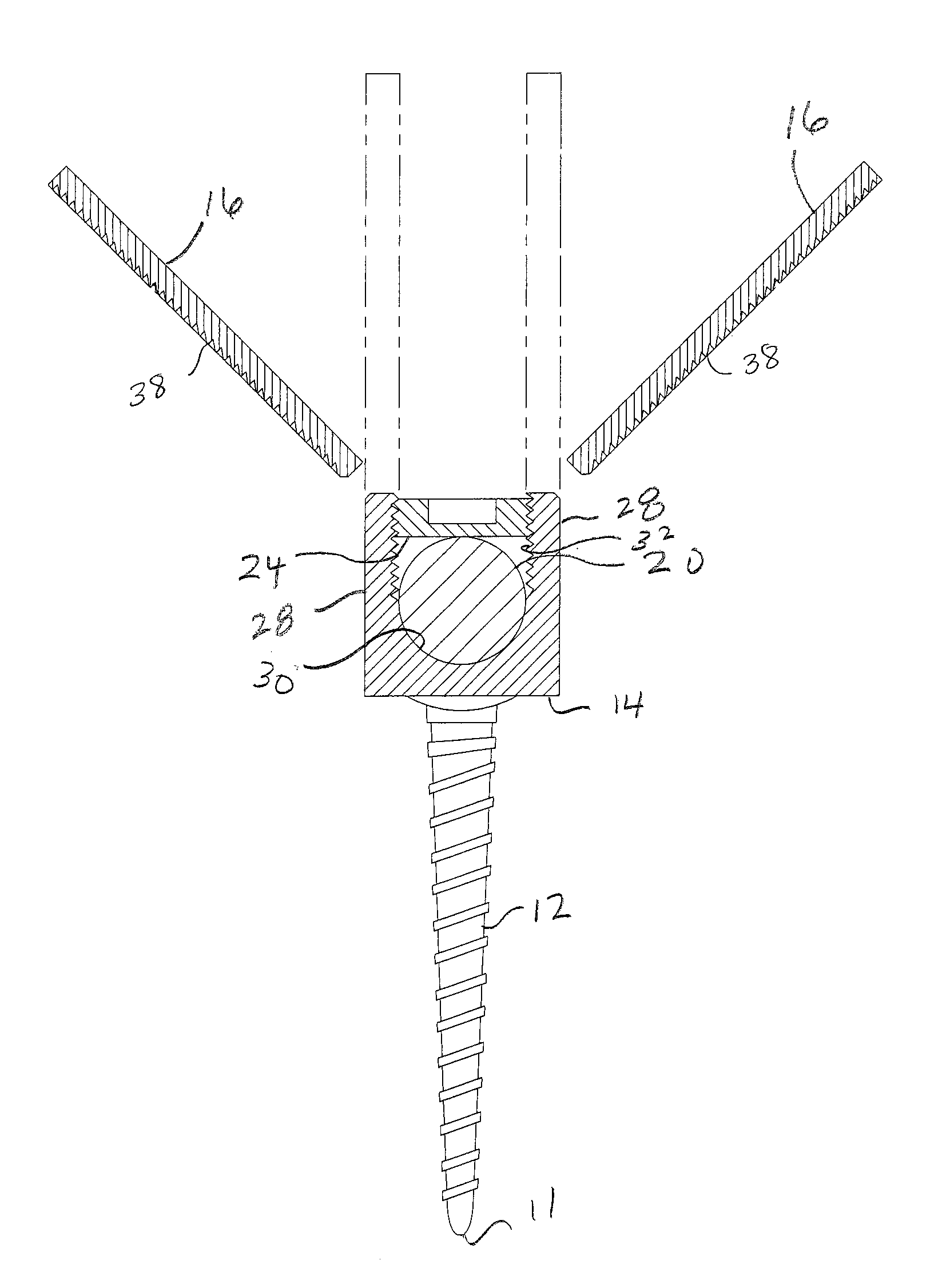
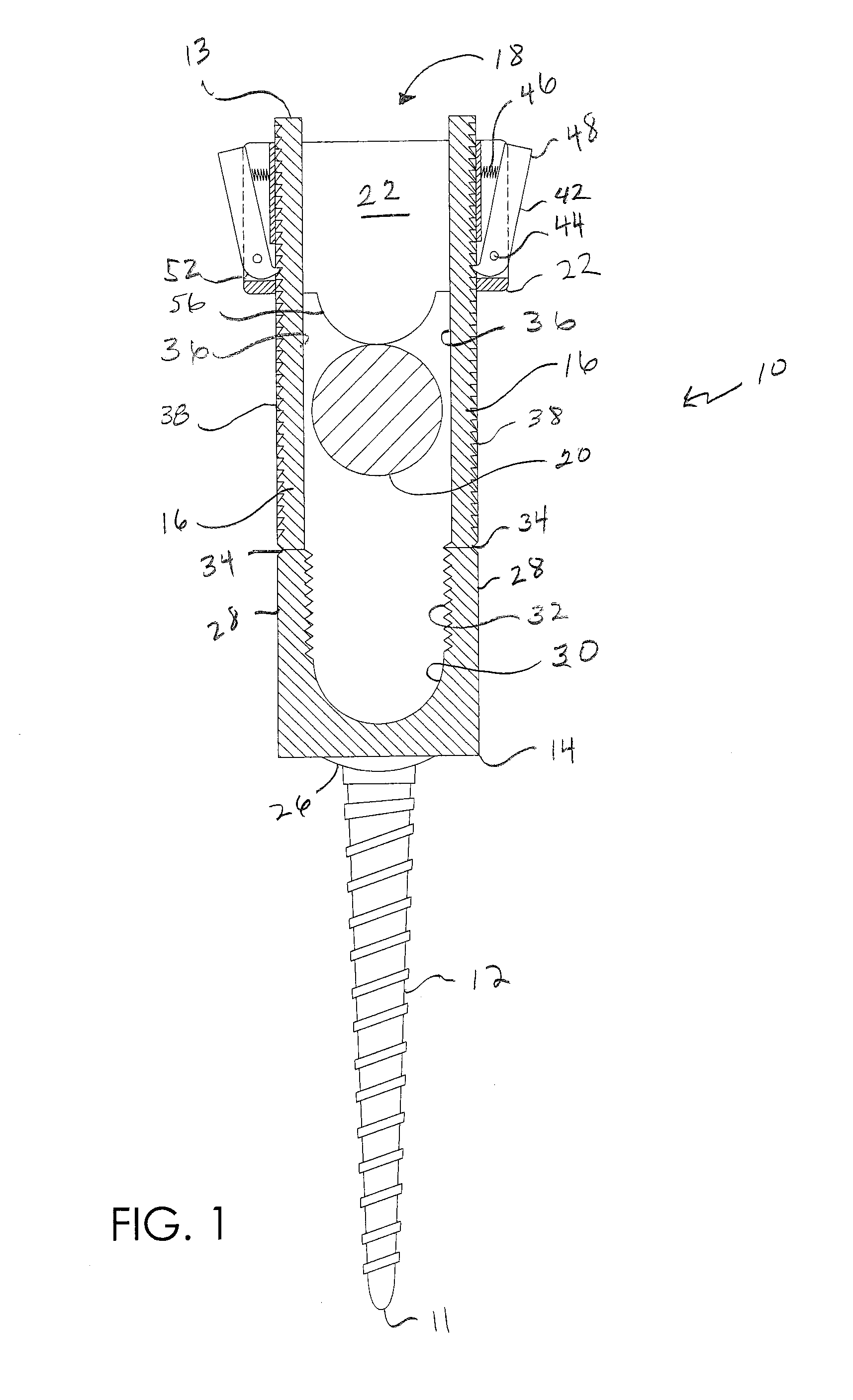
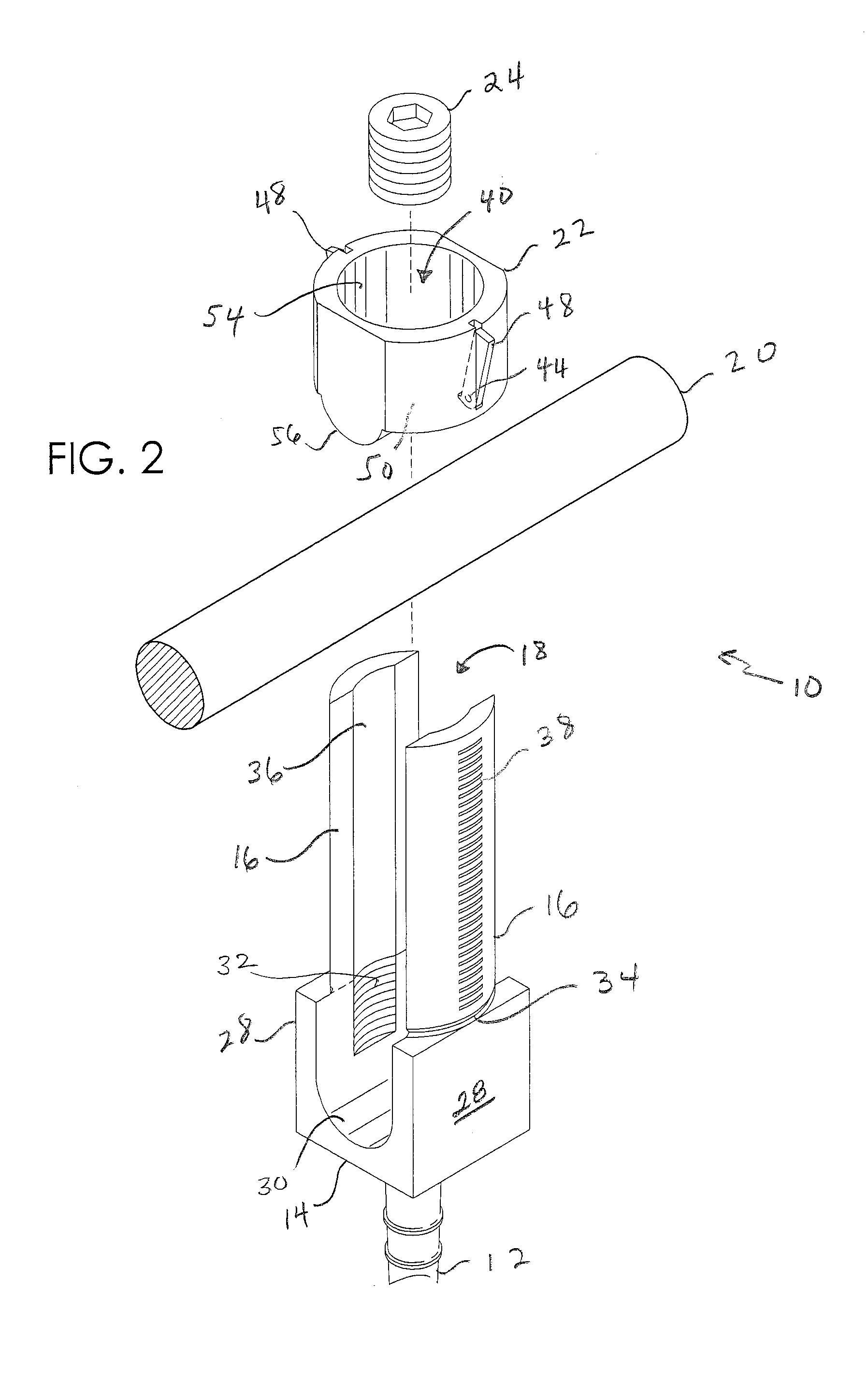
[0033]FIGS. 1 through 13 illustrate a screw and rod fixation assembly 10 and various parts thereof in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention. Generally, assembly 10 includes a distal end 11, a pedicle screw 12 having a screw head 14, a proximal end 13, a pair of opposing extension tabs 16 detachably coupled to screw head 14, a rod receiving slot 18 defined between extension tabs 16, a rod 20 slideably received within slot 18, a ratchet collar 22 pressed against rod 20 and coupled to tabs 16 in a manner allowing movement of collar 22 distally along tabs 16 while preventing movement thereof proximally and a set screw 24 for locking rod 20 within screw head 14.
[0034]More particularly, referring to FIGS. 1 and 2, screw 12 can be any size, shape or design as is known to those of skill in the art for anchoring to bone. In the preferred embodiment, screw 12 is a monoaxial pedicle screw and is therefore integrally formed with screw head 14 which is axially aligned w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| force | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flexible | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| shape | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com