Gate Leakage Based Low Power Circuits
a leakage-based, low-power technology, applied in the direction of generating/distributing signals, pulse techniques, instruments, etc., can solve the problem that continuous monitoring during low-power mcu operation may consume and achieve the effect of consuming non-trivial amounts of power and minimizing power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
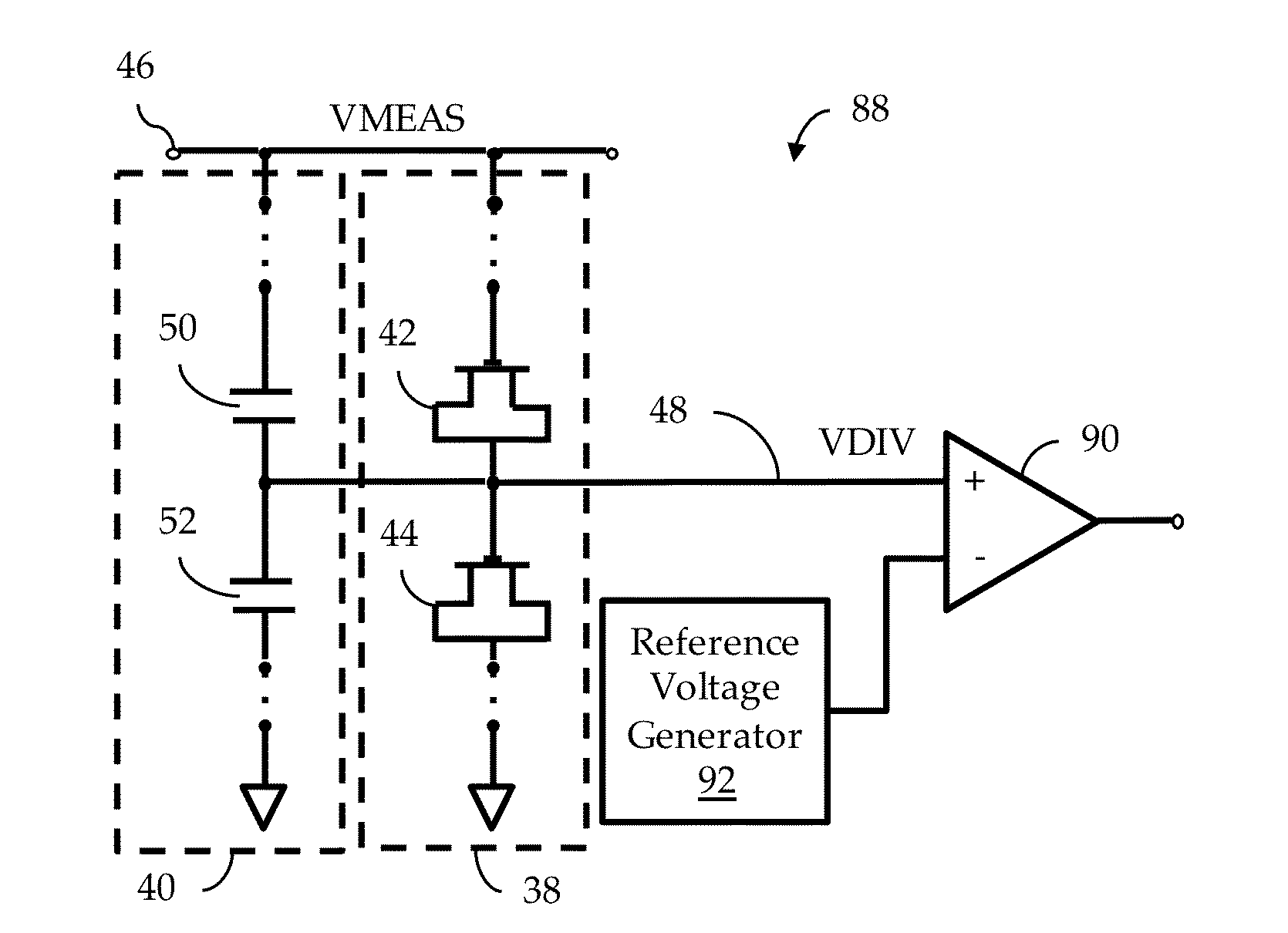
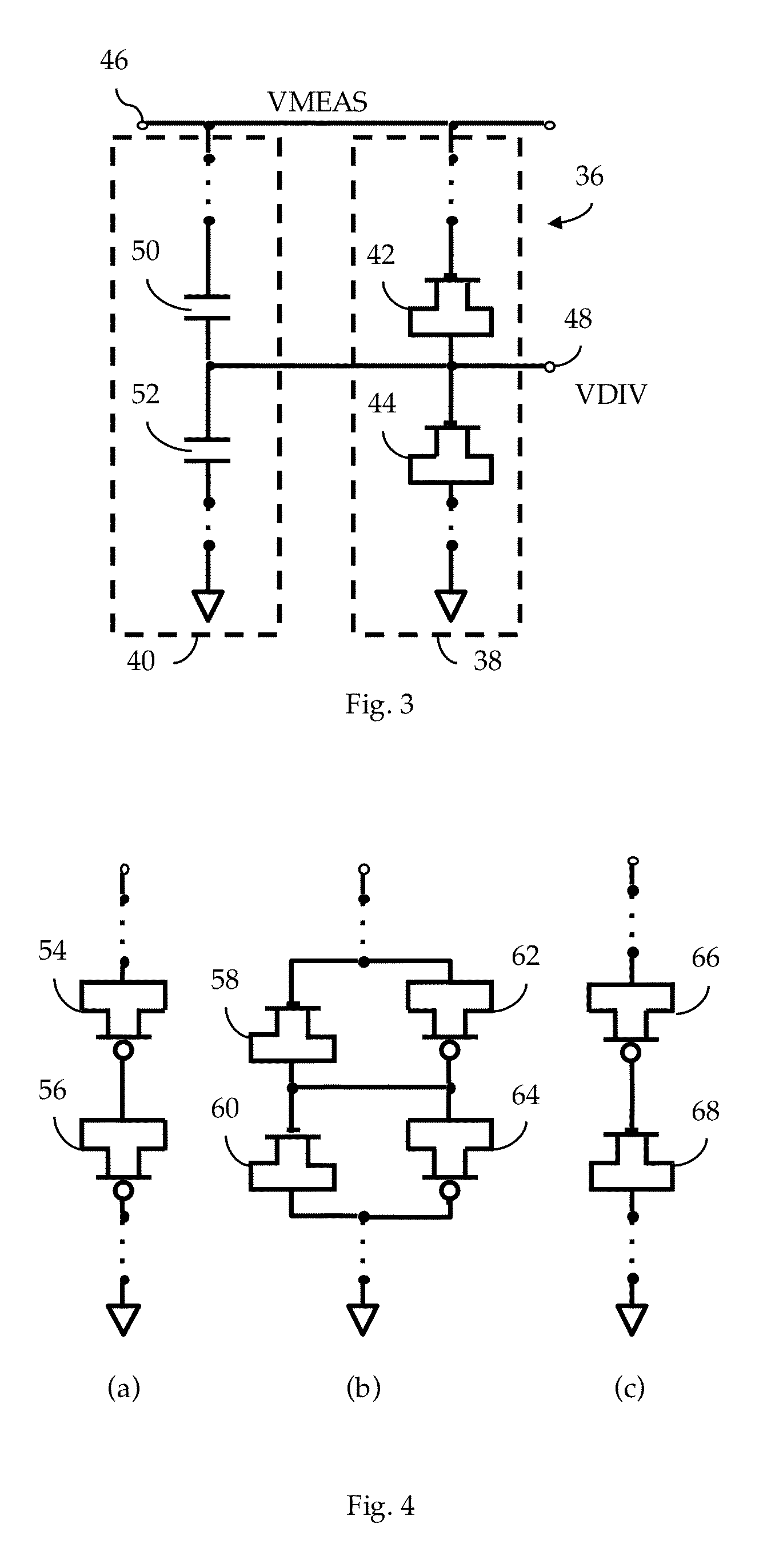
[0044]FIG. 3 illustrates, in schematic form, a voltage divider facility 36 adapted to operate in accordance to some embodiments. According to one embodiment, the voltage divider facility 36 includes a GL-based voltage divider facility 38 and a capacitive facility 40.
[0045]In the illustrated embodiment, the GL-based voltage divider facility 38 includes a stack of transistors that includes, in this simple example, a first transistor 42 and a second transistor 44. The first transistor 42 has its gate terminal coupled to a measured voltage 46, here labeled as “VMEAS”, and has both source and drain terminals shorted together. Alternatively, in a taller stack, the gate terminal of the first transistor 42 may be coupled to the measured voltage 46 via one or more additional transistors (see, e.g., FIG. 14). The shorted source and drain terminals of the first transistor 42 are coupled to the gate terminal of the second transistor 44. The gate terminal of the second transistor 44 is also coup...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com