Manufacturing method, golf club head, and design method
a golf club head and manufacturing method technology, applied in the field of wood-type golf club heads, can solve the problems of small spin amount of the shot, and it is difficult for the golfer to intentionally bend the shot to the left or righ
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
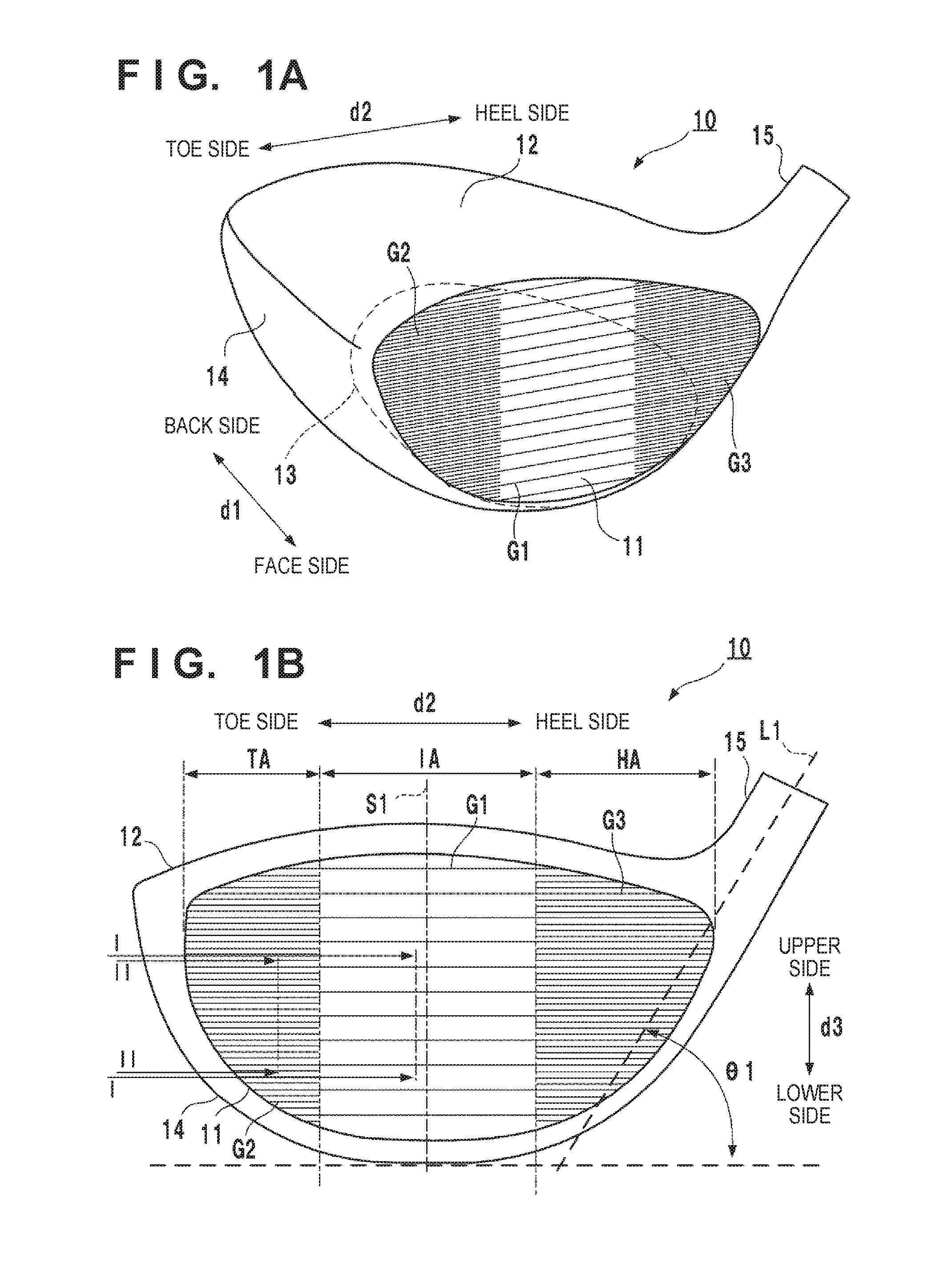
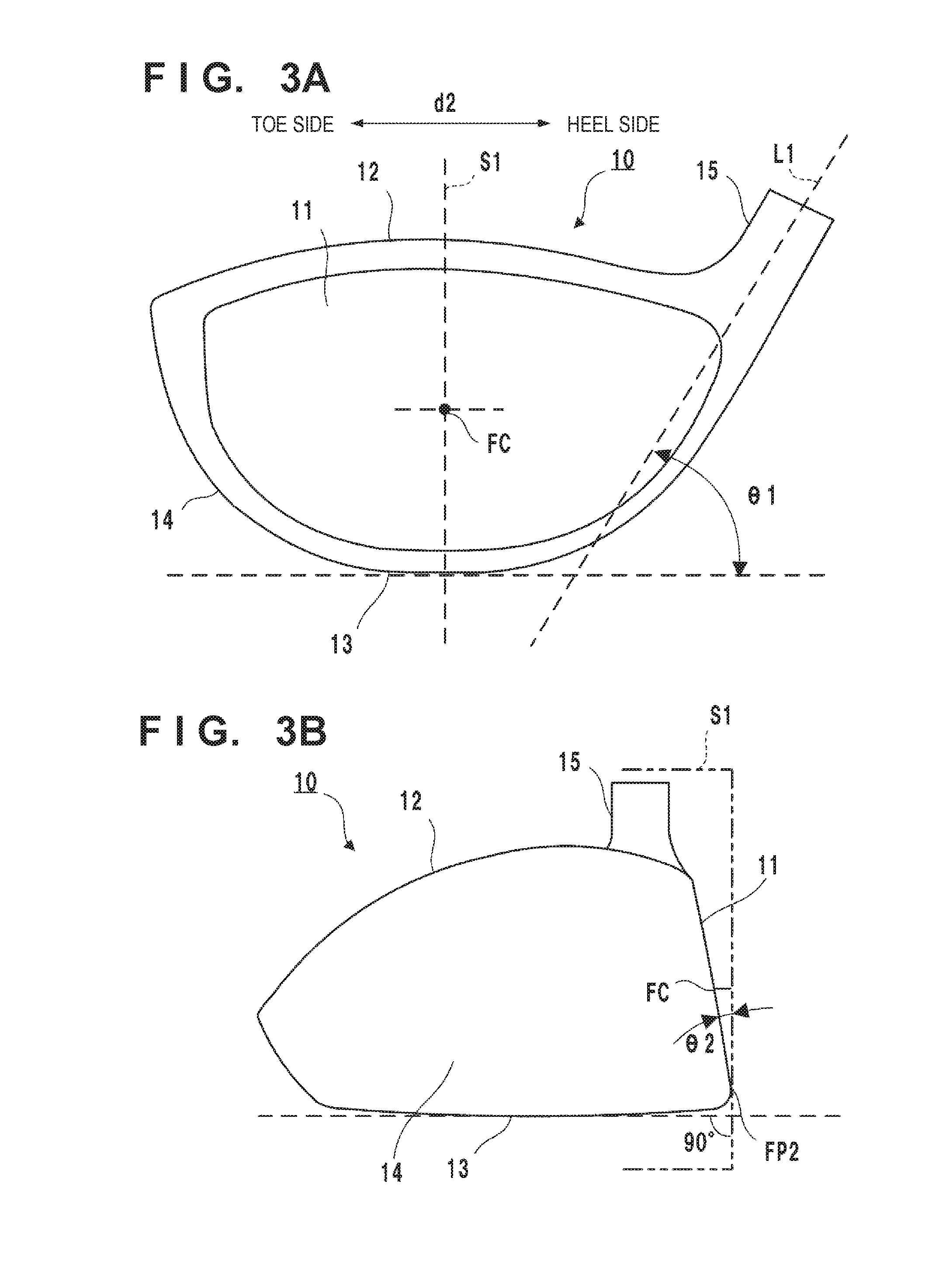
[0022]FIG. 1A is a perspective view of a golf club head 10 according to an embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 1B is a front view showing the golf club head 10 viewed from the side of a face portion 11.
[0023]The golf club head 10 forms a hollow member. Its peripheral walls form the face portion 11, a crown portion 12, a sole portion 13, and a side portion 14. The surface of the face portion 11 forms a face (striking face). A bulge and a roll are formed on the face. The crown portion 12 forms the upper portion of the golf club head 10. The sole portion 13 forms the bottom portion of the golf club head 10. The side portion 14 forms the portion between the sole portion 13 and the crown portion 12. The golf club head 10 also includes a hosel portion 15 to which a shaft is attached.
[0024]An arrow d1 in FIG. 1A indicates a face-back direction, and an arrow d2 indicates a toe-heel direction. An arrow d3 in FIG. 1B indicates the vertical direction of the face portion 11. The face-back...
second embodiment
[0067]Score lines can be formed in a face portion 11 in addition to shallow grooves G. FIG. 5B shows an example. In the example of FIG. 5B, score lines 20 are formed in areas TA and HA other than an impact area IA. The score lines 20 are straight grooves extending in the toe-heel direction and are formed in parallel to each other.
[0068]The score lines 20 may be formed in the impact area IA as well. A structure without the score lines 20 in the areas TA and HA other than the impact area IA can also be employed.
third embodiment
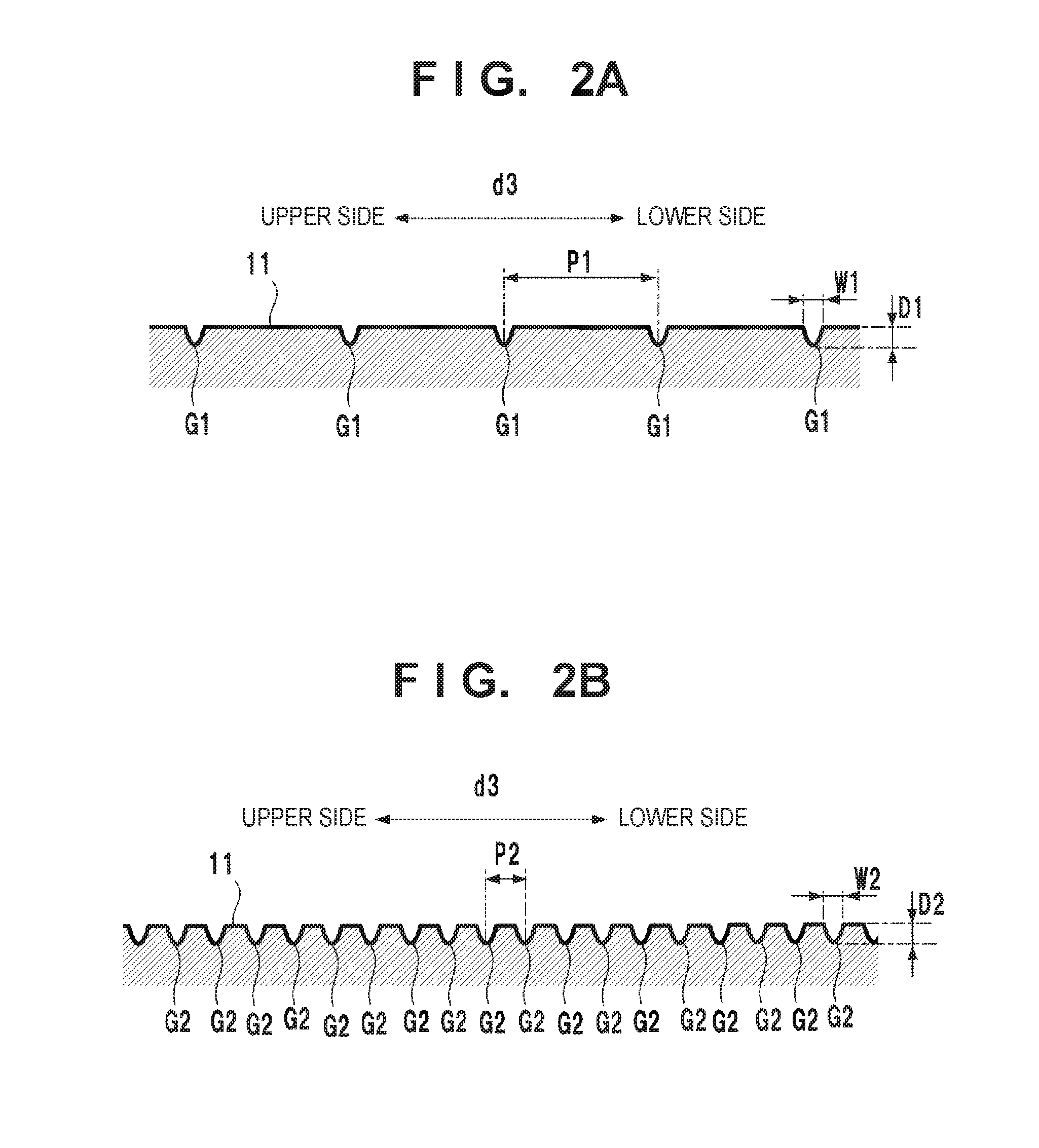
[0069]In the first embodiment, the shallow grooves G have been explained as straight grooves. However, shallow grooves G may be grooves having another shape. FIGS. 6A to 6D show examples. FIGS. 6A and 6B show examples of the shallow grooves G having wavy shapes. FIG. 6A shows a case in which the shallow grooves G are formed into a triangular wave shape, and FIG. 6B shows a case in which the shallow grooves G are formed into a sine wave shape. FIG. 6C shows an example in which the shallow grooves G are grooves having an arc shape. FIG. 6D shows an example in which shallow grooves Ga having a triangular wave shape and shallow grooves Gb having a sine wave shape are repetitively formed. As in this example, the shallow grooves G may be formed by periodically forming grooves having different shapes.
[0070]In the first embodiment, the shallow grooves G are formed so as to be level when the golf club head 10 is grounded toward the target direction. However, the shallow grooves G need not be...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com