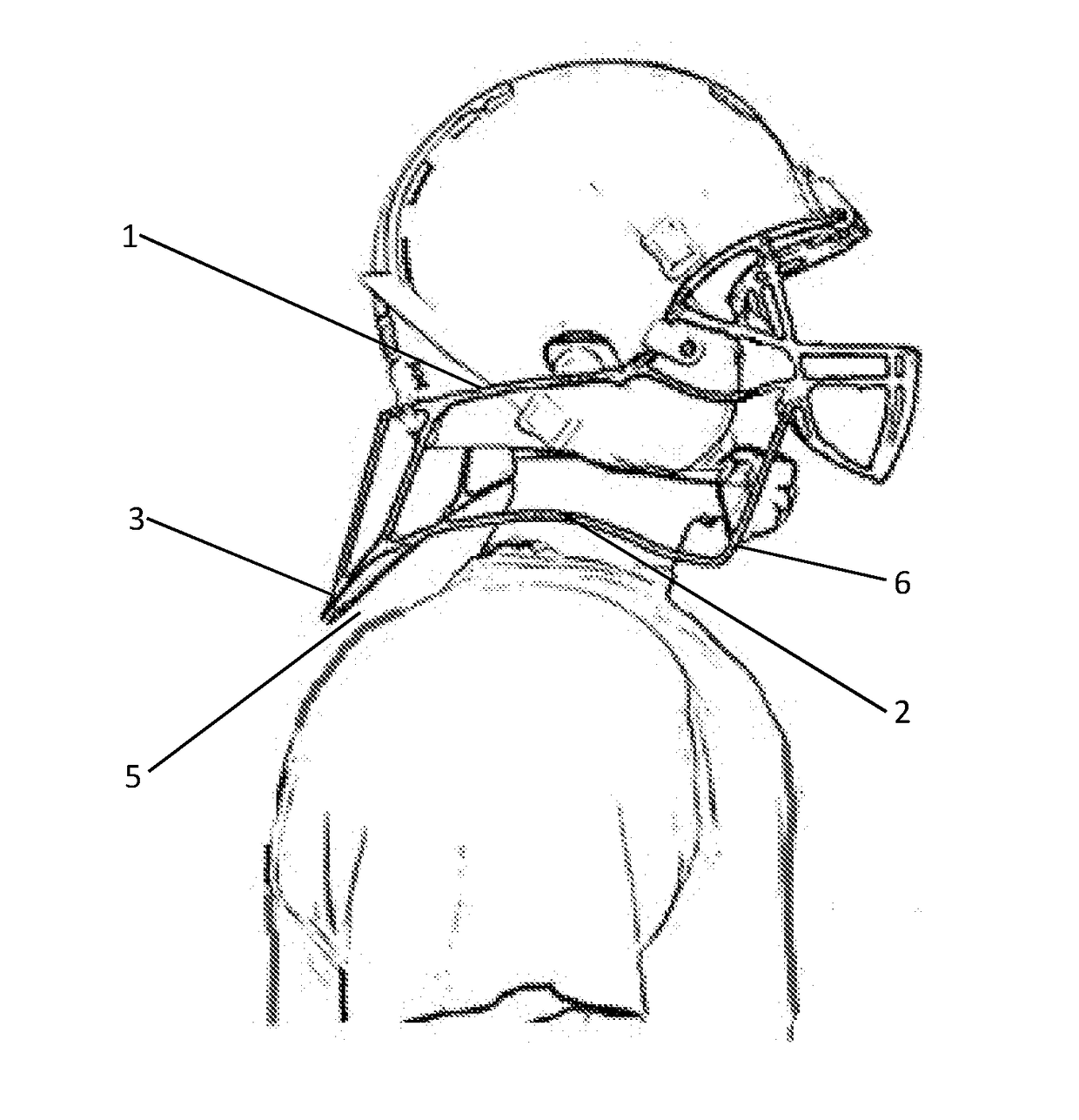
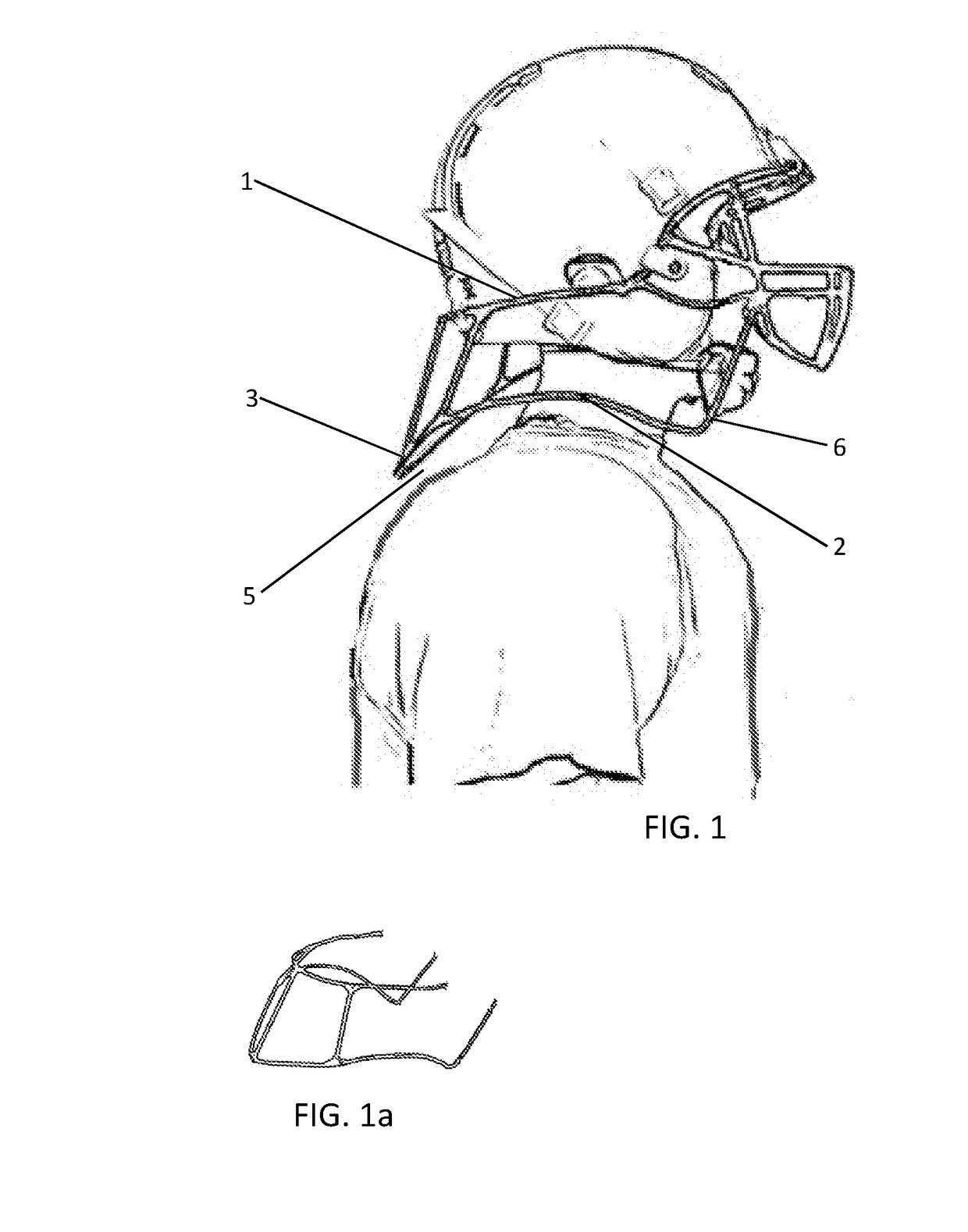
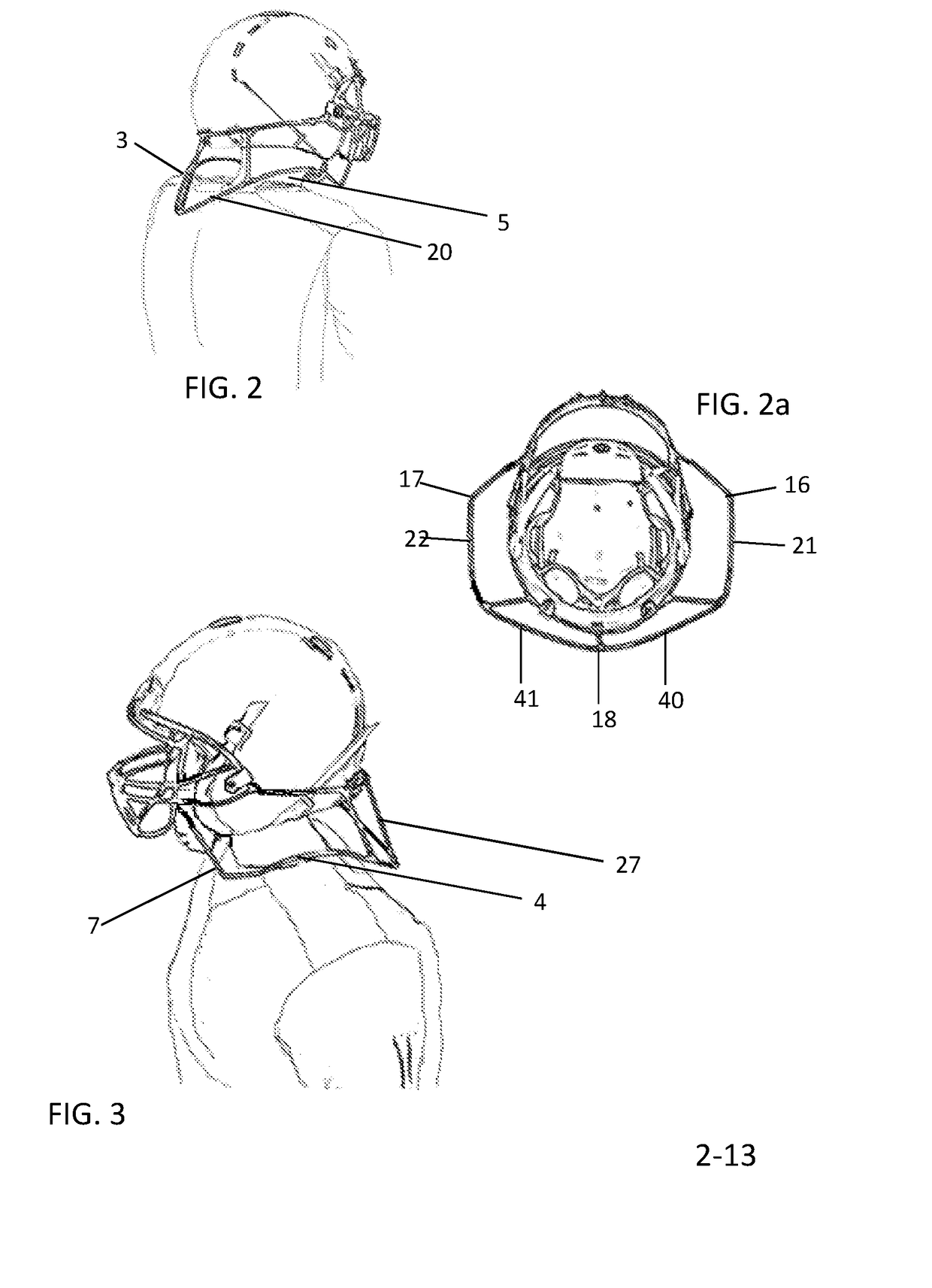
Concussive Reduction Helmet Attachment(s) Translational Axial Rotation Control and Bracing System (TARCBS).
a technology of translational axial rotation control and helmet attachment, which is applied in the direction of helmet covers, protective equipment, weapons, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the available area of acceleration potential, limiting the available space of movement, and requiring a larger magnitude of force, so as to reduce the total available space, reduce the cumulative force available, and reduce the effect of brain injury
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
second embodiment
[0108]The TARCBS attachments have two surfaces that contact the body perpendicularly to deal with accelerative forces, the contoured bracing surfaces and the rotational bracing edges. The contoured bracing surface have two embodiments the first is the contoured bracing edge with no padding and is made of the same material as the helmet is shown in FIG. 5, 26 where the contoured bracing edge is the distal portion of the TARCBS attachment which is ergonomically designed to seat upon the soldier's flax jacket. The second embodiment is a contoured bracing edge having padding FIG. 18 padding 23 or FIG. 19 where a friable material 24 on the contoured bracing surface of the shoulder attachment right, 2 is used to create a force absorbing / padded bracing surface.
[0109]Another goal of the TARCBS helmet attachments are to reduce rotational acceleration and this is where the rotational bracing edges are need. Although a large portion of rotational force is absorbed by the contoured bracing surf...
embodiment 31
[0128]FIG. 11 shows the soft mechanical multi section embodiment TARCBS attachment 30 before impact and FIG. 12 shows the soft mechanical multi sectional TARCBS embodiment 31 absorbing force from a front impact where the rotational acceleration is acing along the ZY axis pitching the head up. Additionally, the crushable component 24 is collapsed in FIG. 12 at the critical moment showing the absorbing movement of the soft mechanical multi section embodiment TARCB during impact. In this embodiment the mechanical component does not reset and is not reusable because it crushes to absorb the mechanical transfer of force at the critical moment. In this embodiment of the TARCBS attachment the mechanical crushable component would need to be replaced for successive impacts. The soft embodiment TARCBS attachment(s) are made of foam, silicone, or other resilient material that will fold in on its self to support the neck as force is absorbed as shown in the comparison between FIGS. 11 and 12 by...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com