Method and apparatus for making nonwoven from continuous filaments
a technology of continuous filaments and nonwovens, applied in the direction of filament/thread forming, melt spinning methods, weaving, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the choice of material for the strip of nonwoven, affecting the desired soft hand of the nonwoven strip, and provisions that have not yet been proved, so as to achieve simple and cost-effective, simple and reproducible, and low material and labor costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
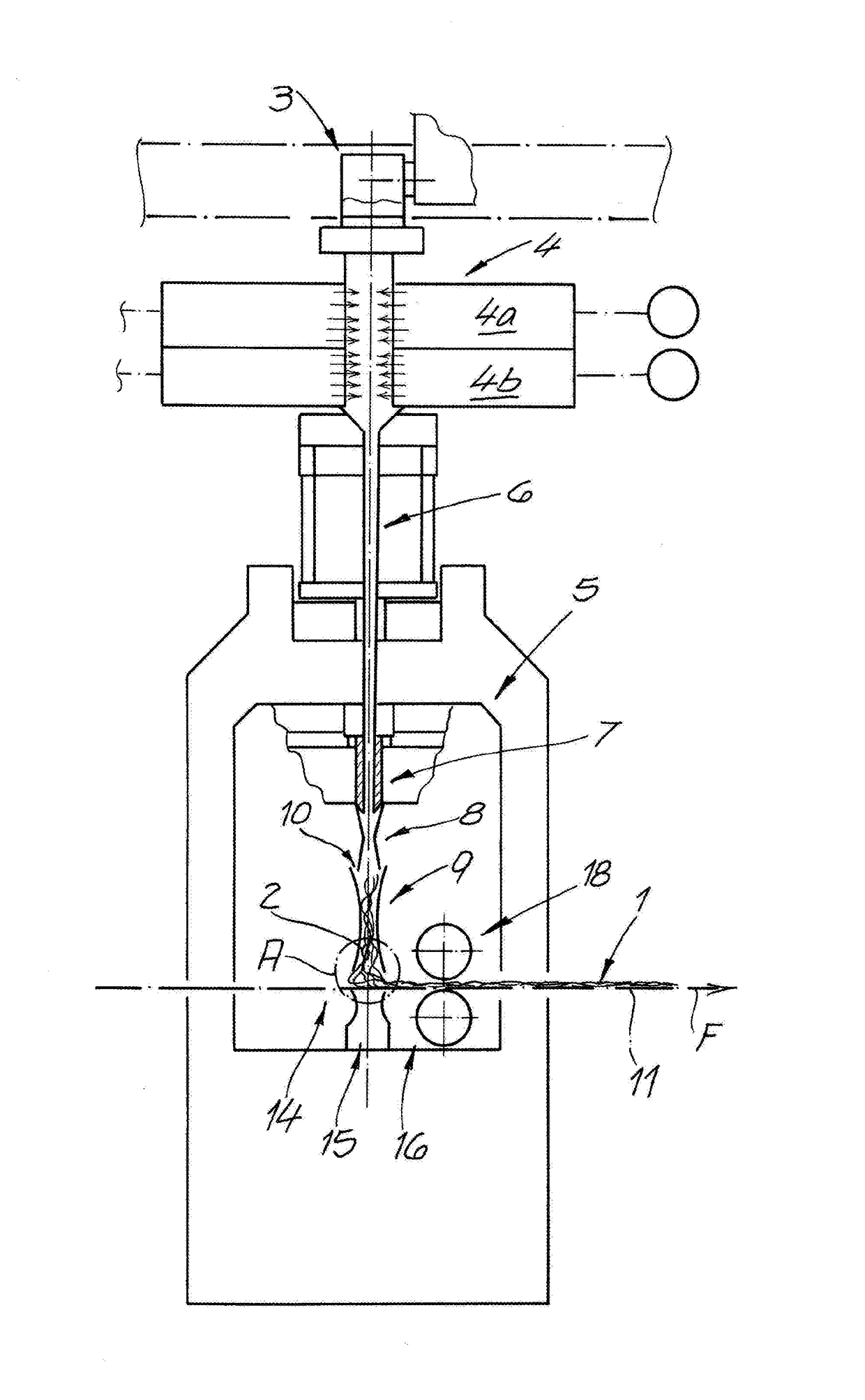
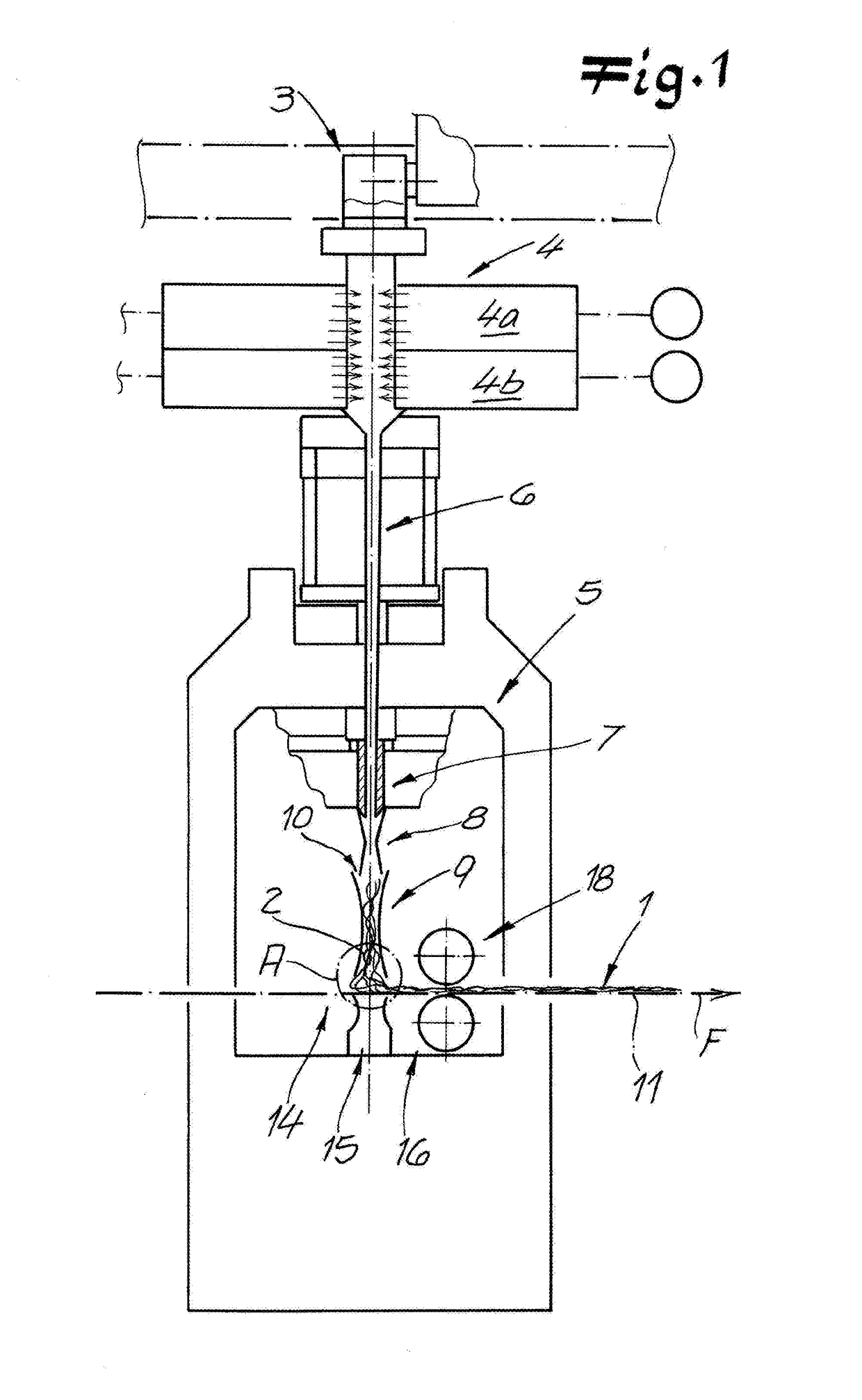
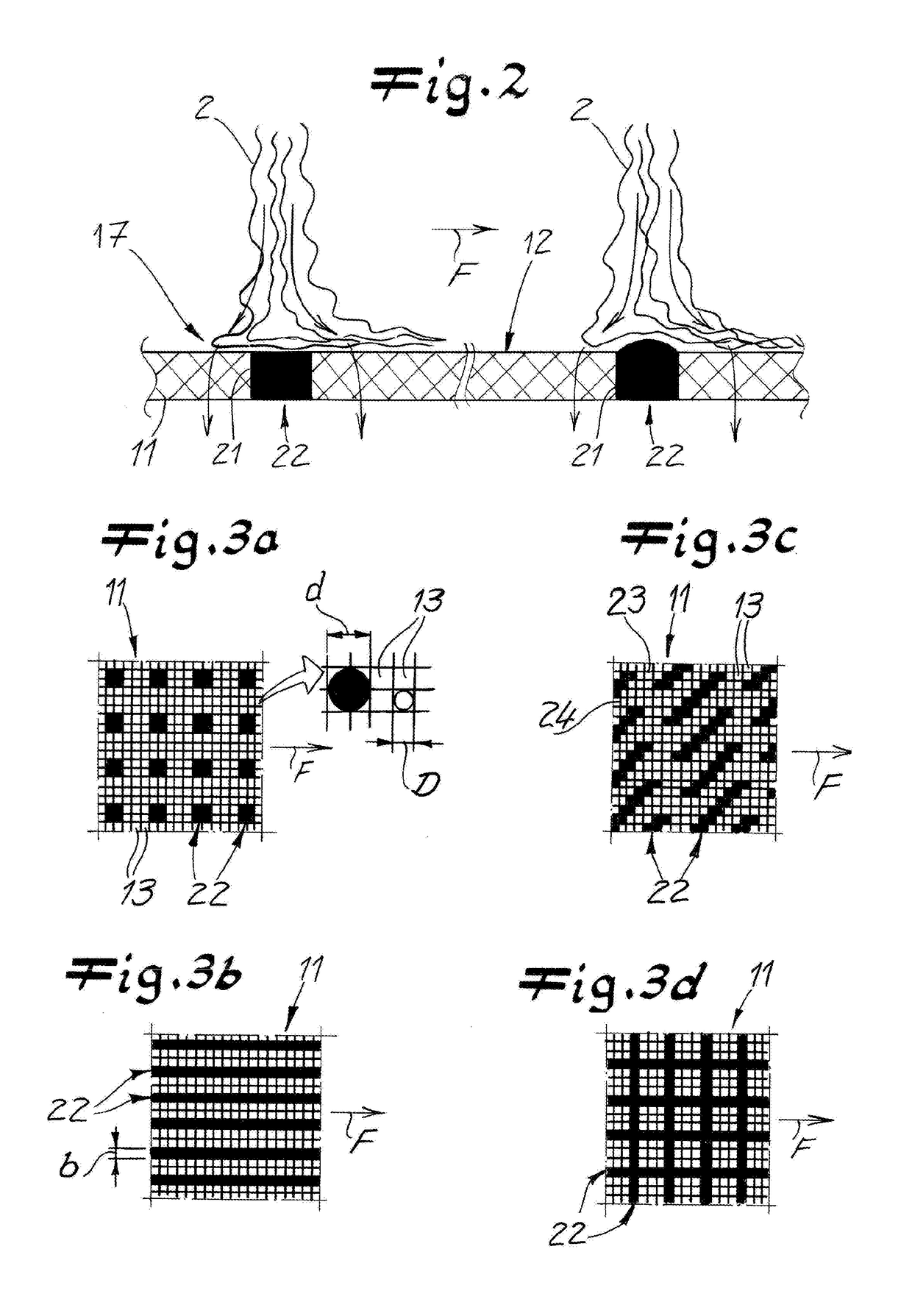
[0046]The drawings shows an apparatus according to the invention for making nonwoven 1 from continuous filaments 2. In a particularly preferred embodiment and in this illustrated embodiment, this is a spunbond apparatus for making spunbond nonwoven 1 or spun nonwoven 1. The continuous filaments 2 preferably are of thermoplastic or essentially of thermoplastic. In the apparatus of the invention, the continuous filaments 2 are spun with the aid of a spinning device a spinneret 3. After that, the continuous filaments 2 are cooled in a cooler 4. This cooler 4 preferably and in the illustrated embodiment has two compartments 4a and 4b, one above the other or one after the other in the filament-travel direction, and that introduce cooling air of a variable temperature into the filament flow chamber. Downstream of the cooler 4 in the filament-travel direction is a stretcher 5 that preferably and in the illustrated embodiment has both an intermediate passage 6 that narrows in the flow direc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| aspiration speed | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com