Antibodies to l-type voltage gated channels and related methods
a voltage gated channel and antibody technology, applied in the field of antibodies to l-type voltage gated channels and related methods, can solve the problems of undesirable side effects, incomplete characterization of the way calcium signals are generated in immune cells, etc., to reduce the survival of nave t cells, reduce the cd3/cd28 induced t cell proliferation, and reduce the t cell receptor-induced ca2+ flux
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Design and Generation of Antibodies Directed Against L-Type Voltage Gated Calcium Channels
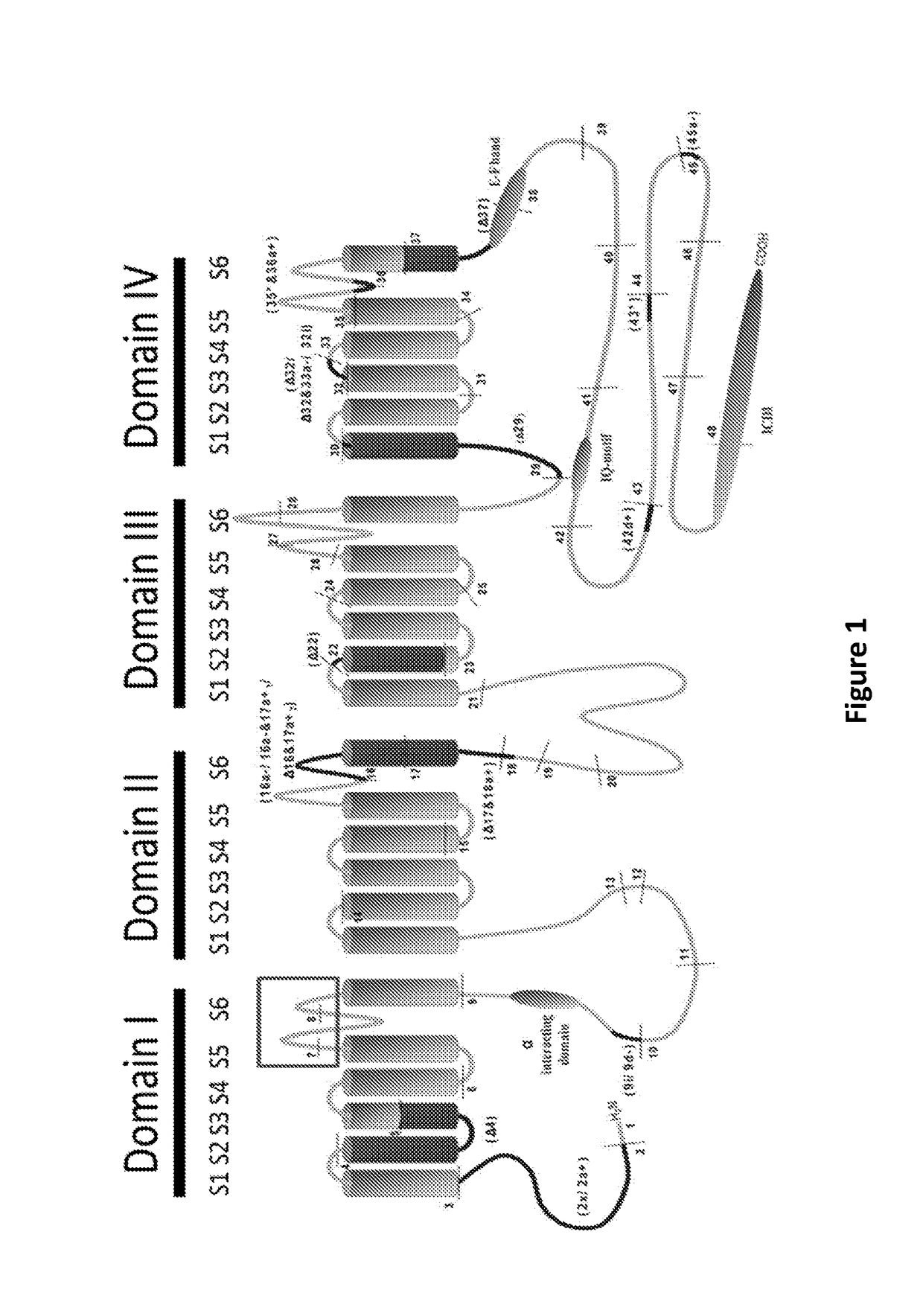
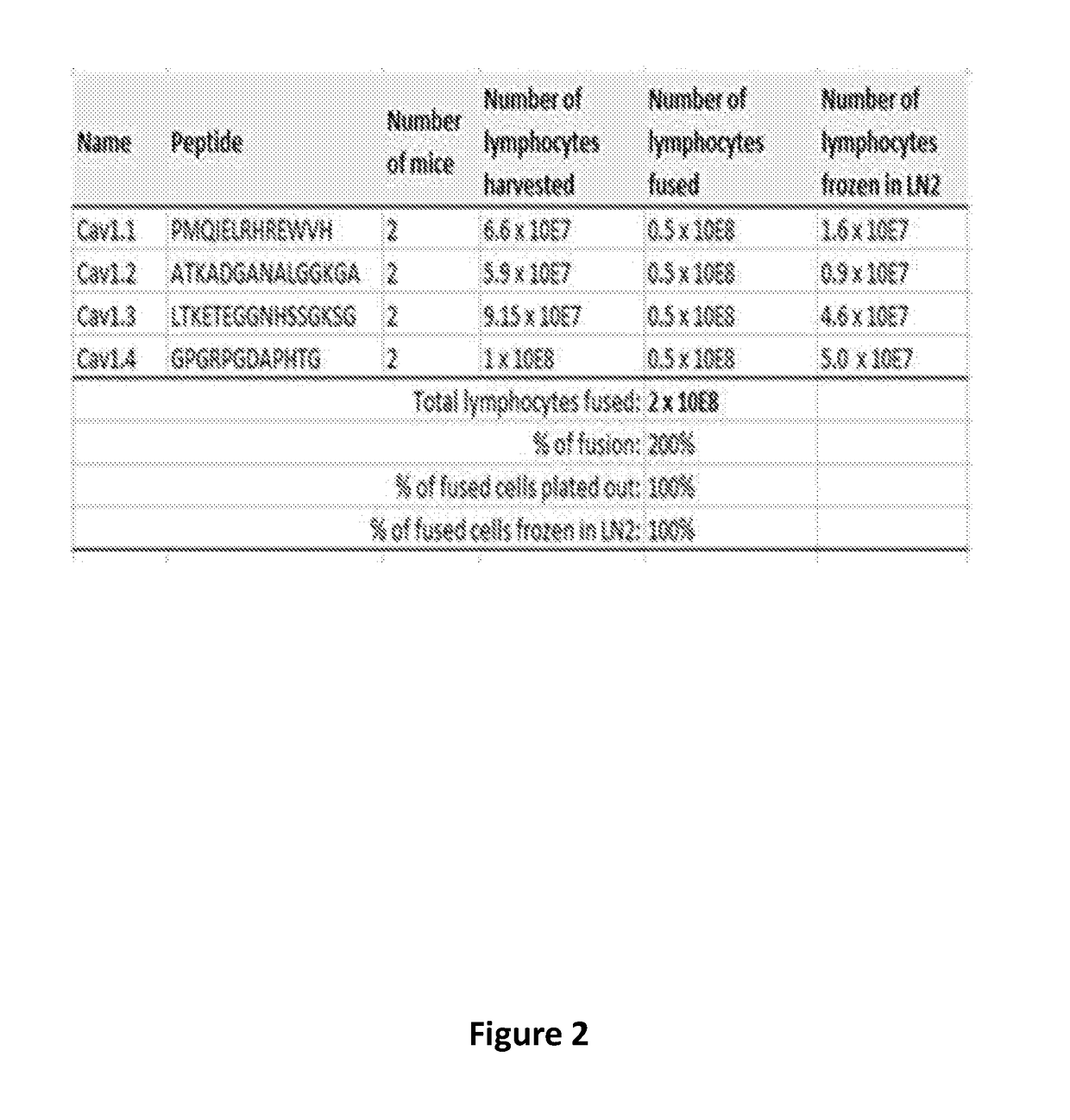
[0248]Antibodies were designed to the target L-type voltage-gated calcium channel subtypes Cav1.1, Cav1.2, Cav1.3, or Cav1.4. For each channel, an amino acid sequence was selected to use as targets for use as an antigen for generating mouse monoclonal antibodies. Amino acid sequences were selected to meet several criteria. First, the amino acid sequences had to be unique to their respective channels. Second, the amino acid sequences had to reside on an exposed portion of the channel positioned outside of the cell. Third, the amino acid sequence had to be found in both the mouse and human channel. Fourth, the sequence needed to be in a region of the channel that would affect the channel's activity when bound by an antibody.
[0249]For each of the L-type voltage-gated calcium channel subtype, an amino acid sequence located in the extracellular domain of the pore loop between transmembrane segments ...
example 2
Characterization of Hybridoma Antibody Directed Against L-Type Voltage Gated Calcium Channels
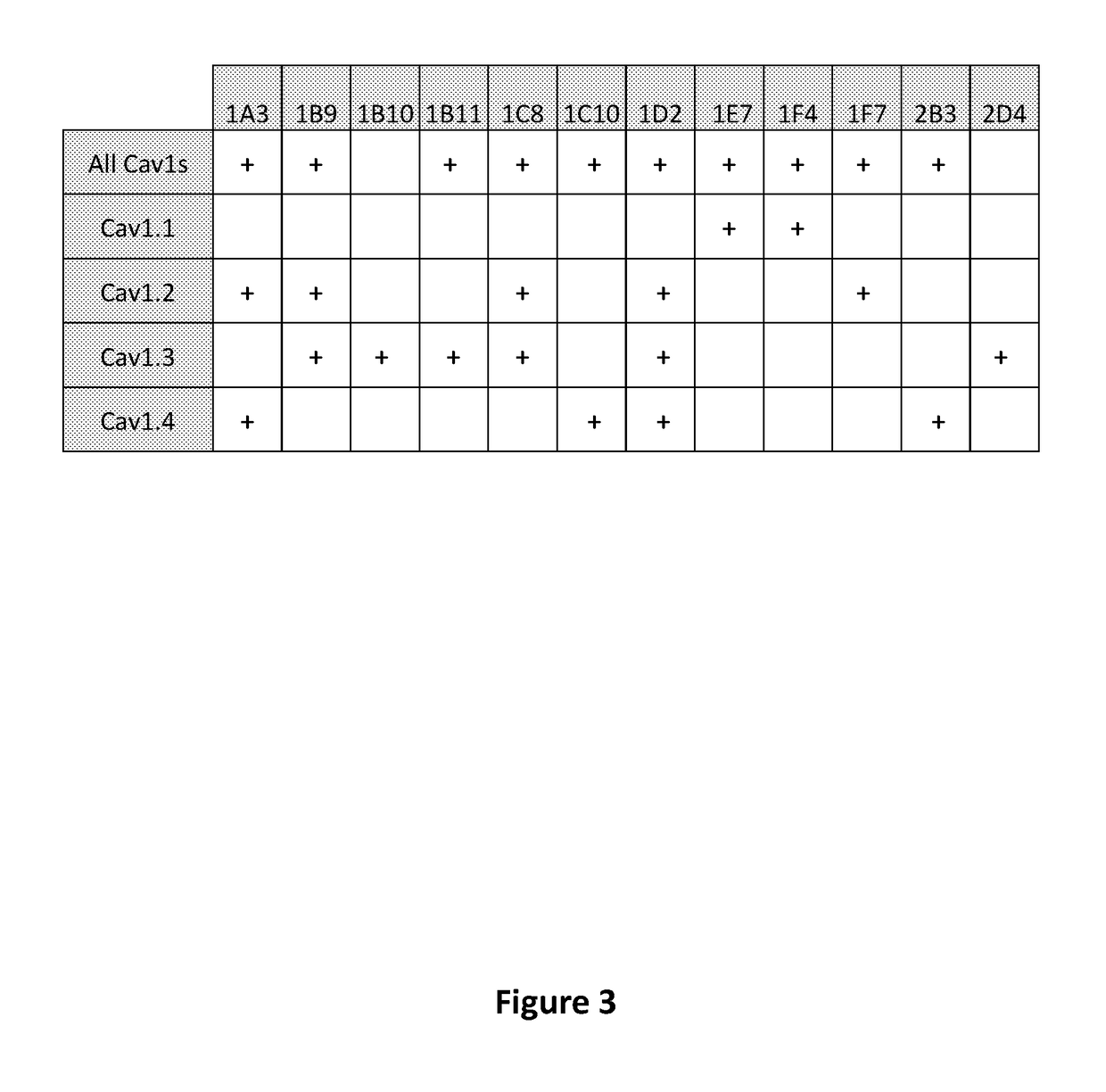
[0251]ELISA experiments were preformed to characterize monoclonal antibodies generated to target the extracellular pore domain of the L-type voltage-gated calcium channels. Sixty-three antibodies of interest were tested for their abilities to bind to the peptides with amino acid sequences from Table E1 that were used to generate the antibodies. Antibody binding was tested in wells coated with BSA and all the peptides with from each L-type voltage gated calcium channel, BSA and the Cav1.1 peptide, BSA and the Cav1.2 peptide, BSA and the Cav1.3 peptide, and BSA and the Cava.4 peptide. Binding was detected with a mixture of IgG and IgM secondary antibodies, and signal was compared to negative controls. Representative results of these experiments are presented (FIG. 3). The results indicated that the antibodies could specifically bind to the target peptides. Clones were observed that bound only ...
example 3
Hybridoma Antibodies Bind to and Inhibit Growth of Jurkat T-Cells
[0256]The hybridoma clones were additionally evaluated in a flow cytometry-based binding assay using the human Jurkat leukemia cell line (Jurkat). Cell binding and growth inhibition assays were performed using standard techniques. The results are shown in Table E2 below.
TABLE E2Jurkat Binding and Growth AssaysGrowthBinding SpecificityCell bindingInhibitionClone IDCav1.1Cav1.2Cav1.3Cav1.4IsotypeJurkat1C8YesIgGYesYes1C10YesIgGYesYes1D2YesYesYesIgMYesYes1E7YesIgMYesYes1F4YesIgGYesYes2D5YesIgGYesYes5F4YesIgGYesYes5G10YesIgGNSYes6A3YesYesIgGYesYes6C6YesIgGYesNS6E1YesIgGYesYes6H7YesIgGYesYes8G1YesIgGYesYes9C3YesIgGYesYes10E11YesIgGYesYesNS—Non-specific at time of assay.
[0257]These results show that supernatants from the hybridoma clones in Table E2 were able to bind to and inhibit the growth of human Jurkat T-cells, evidencing the therapeutic potential of these antibodies in the treatment of various cancers, including hemato...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com