Main heat exchanger and a process for cooling a tube side stream
a heat exchanger and side stream technology, which is applied in the direction of indirect heat exchangers, lighting and heating apparatus, stationary plate conduit assemblies, etc., can solve the problems of uneven temperature, and uneven heat transfer between the shell side and each of the first, second and third tube sides, etc., to achieve the effect of maximising the temperature of the evaporated refrigerant stream
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
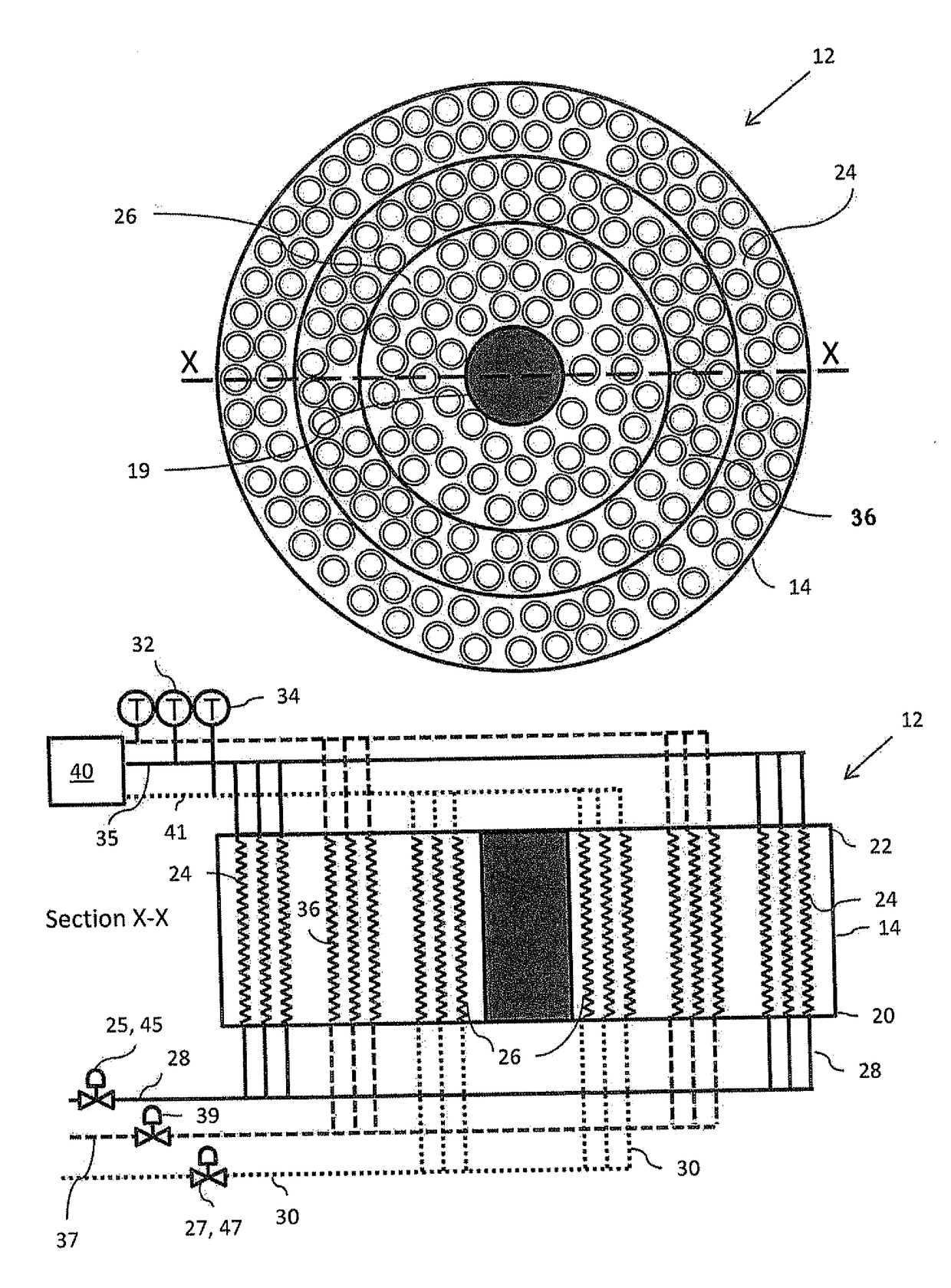
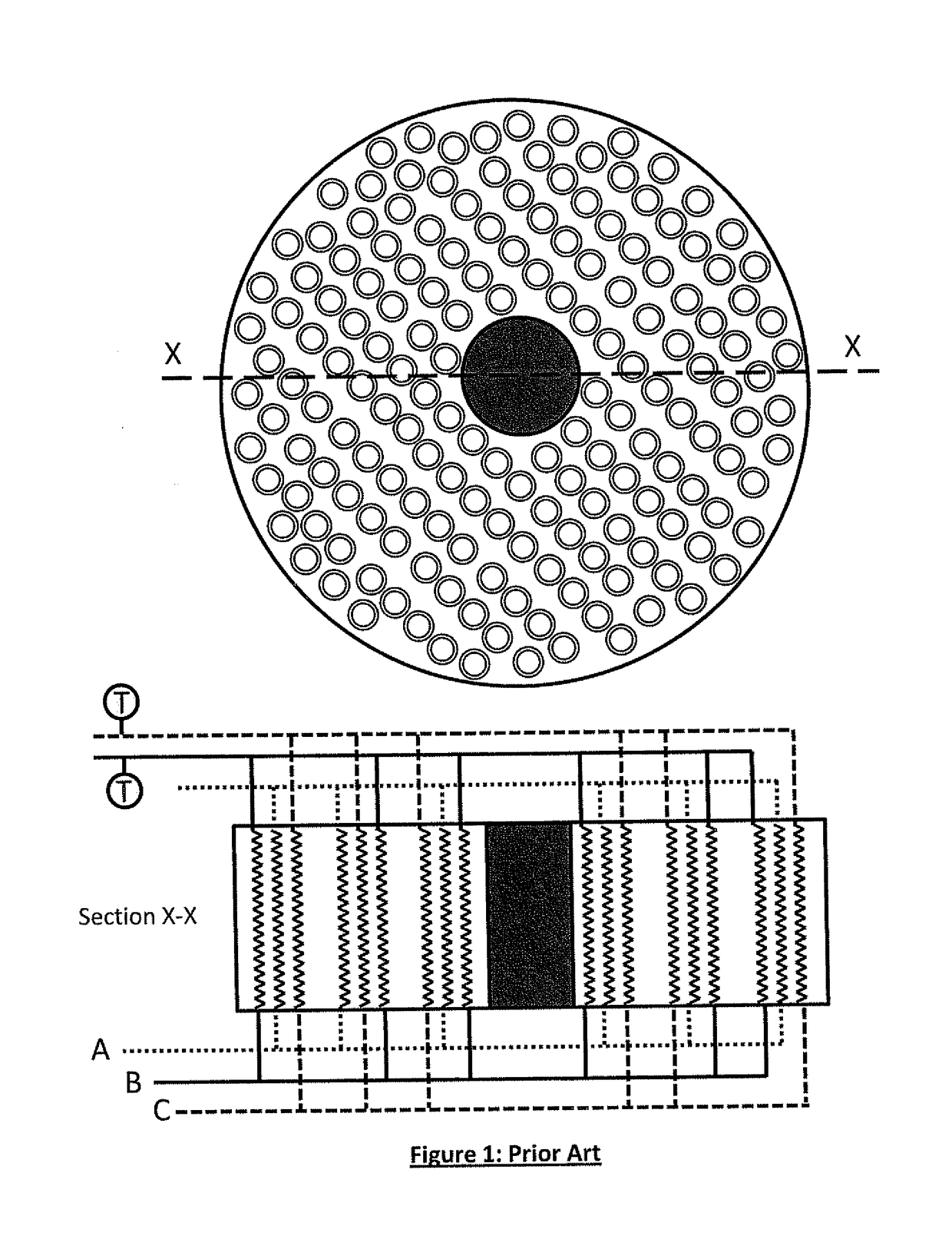
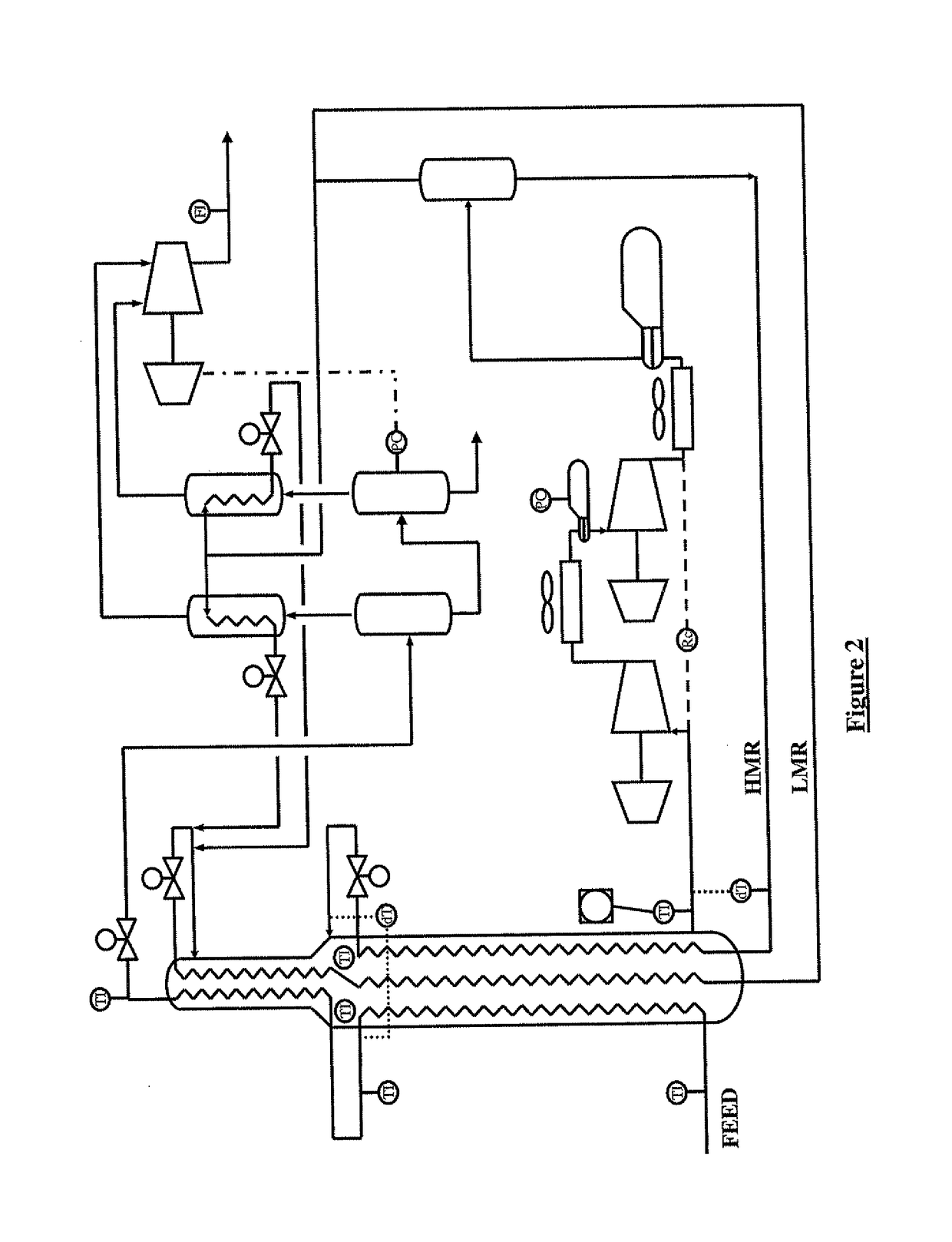
[0036]Particular embodiments of the process and apparatus of the present invention are now described, with particular reference to a plant for liquefying a gaseous, methane-rich feed gas in the form of natural gas in a main heat exchanger to produced liquefied natural gas, by way of example only.
[0037]The present invention is equally applicable to a main heat exchanger used for other applications such as the production of ethylene or other process requiring on two tube side streams instead of the three tube side streams described in detail below. The terminology used herein is for the purpose of describing particular embodiments only, and is not intended to limit the scope of the present invention. Unless defined otherwise, all technical and scientific terms used herein have the same meanings as commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the art to which this invention belongs. In the drawings, it should be understood that like reference numbers refer to like parts.
[0038]Using ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com