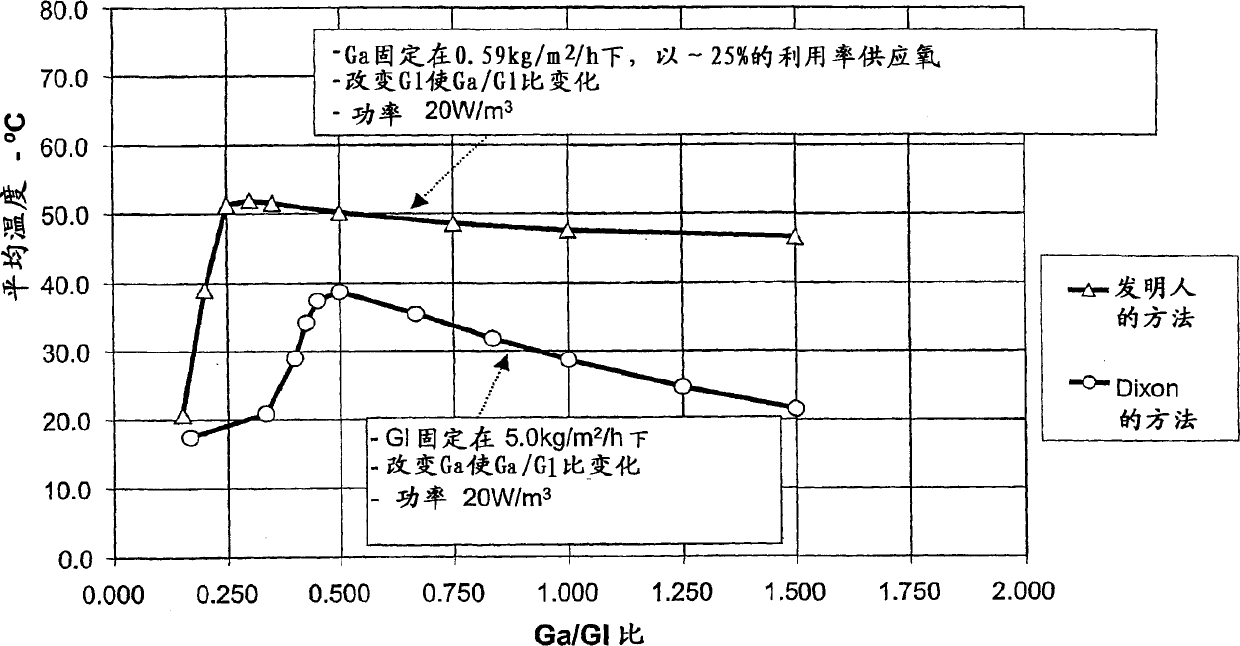
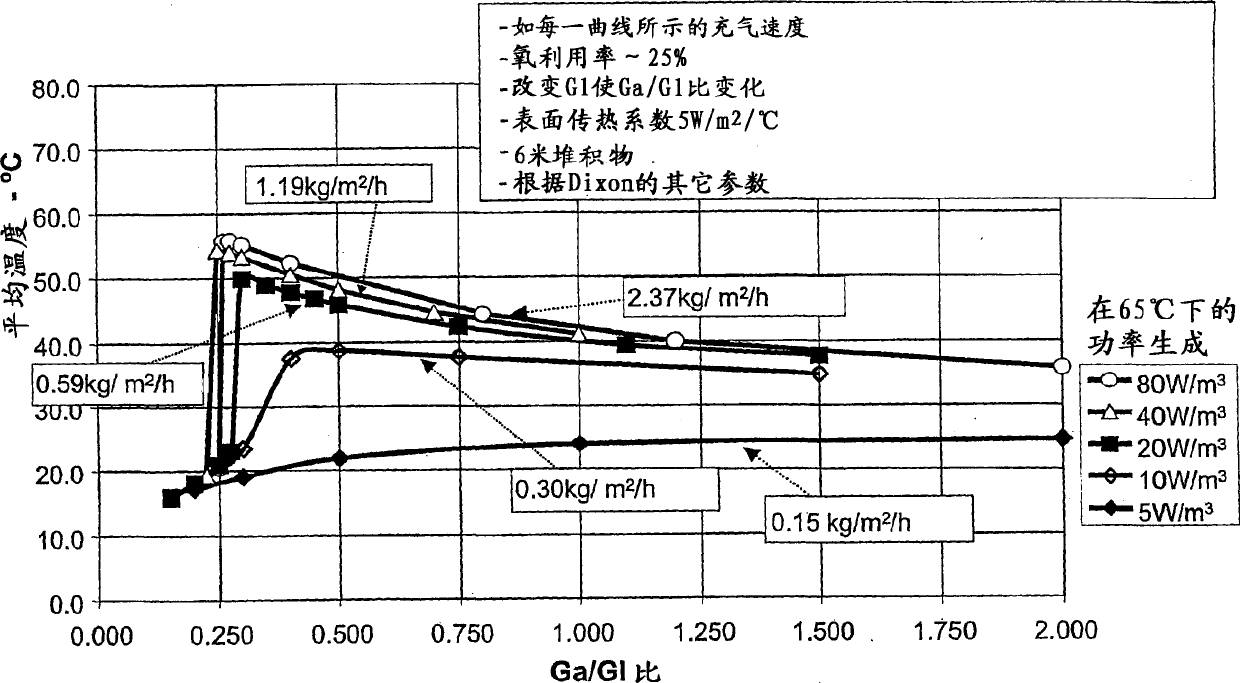
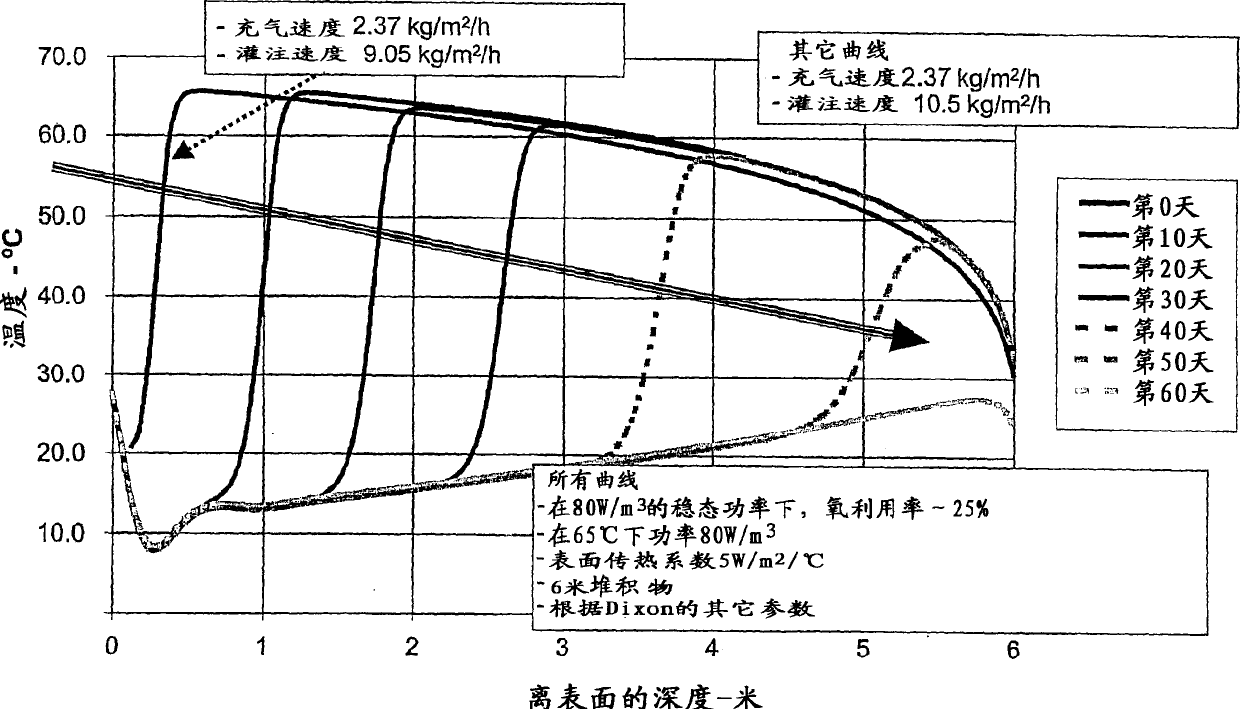
Heap leach process
A heap leaching and leaching technology, applied in the field of deposit oxidation and extraction, can solve the problems of increasing the average deposit temperature and reducing the heat loss of the surface heat transfer coefficient
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0181] Example 1 - Mixed chalcocite / chalcopyrite ore with auxiliary pyrite
[0182] Example 1 shows the case where a fixed pad, open lift system is used for a heap leaching process, the location conditions used in the simulation of the control system are those of Northern Chile in winter at an altitude of 3000m. Figure 21 of the accompanying drawings, illustrates a first heap of ore 10a placed on a pad 2a equipped with a discharge system 3a and an aeration system 4a. The ore heap 10a, when stacked, is inoculated with suitable microorganisms and at least some sulfuric acid.
[0183] The charging system 4a is supplied with atmospheric air by a variable speed air compressor 7a. The ore deposit 10a is fitted with an irrigation system 11a and a plurality of temperature probes 12a installed in a horizontal grid pattern over the area of the ore deposit 10a, which are buried approximately 3 meters below the surface of the deposit. An additional temperature probe 35a is installed t...
Embodiment 2
[0186] Example 2 - Chalcopyrite with Auxiliary Pyrite
[0187]Example 2 is the same fixed pad system as Example 1, except that the ore contains chalcopyrite and pyrite, and the location conditions used in the simulation of the control system are those of typical winter conditions in Arizona, USA. Installation and operation are the same as embodiment 1 and Fig. 21. However, the temperature probe 12a and the oxygen probe 22a are placed in this example at a depth of about 1 meter within the deposit. The operation of the control system in this case is different from Example 1. Atmospheric atmosphere 6a is supplied at such a rate that an oxygen utilization rate of 50% is obtained by varying the flow rate according to the oxygen concentration in the gas within the heap measured by the oxygen analyzer probe 22a. Depending on the pumping design size of the aeration system 4a, and / or the gas pressure, during periods of high air flow, increase the oxygen utilization setting to 65% to ...
Embodiment 3
[0188] Example 3 - Chalcocite with auxiliary pyrite
[0189] Embodiment 3 is a switch mat system, and the ore contains chalcocite and pyrite. The position conditions of the control simulation are the same as those of Embodiment 1. The installation and operation are shown in Figure 21. However, the temperature probe 12a and the oxygen probe 22a are placed at a depth of about 1.5 meters in the deposit, but the control system in this case is similar to Example 2, but not the same. Atmospheric atmosphere 6a was supplied at such a rate that an oxygen utilization rate of 25% was obtained by varying the flow rate according to the oxygen concentration in the gas within the heap measured by oxygen analyzer probe 22a. The perfusion rate was varied to maintain a suitable advective thermal efficiency coefficient 1.5 meters below the heap surface, thereby automatically maintaining the Ga / Gl ratio at the optimum level throughout the leaching cycle. The PLS in this example has an average te...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| rate of recovery | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| loose density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com