EUV pattern transfer with ion implantation and reduced impact of resist residue
a technology of resist residues and ion implantation, which is applied in the field of implantation post extreme ultraviolet (euv) lithography, can solve the problems of single-line opening or adjacent-line electrical shorts after etching, micro-bridging defects, and micro-bridging defects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
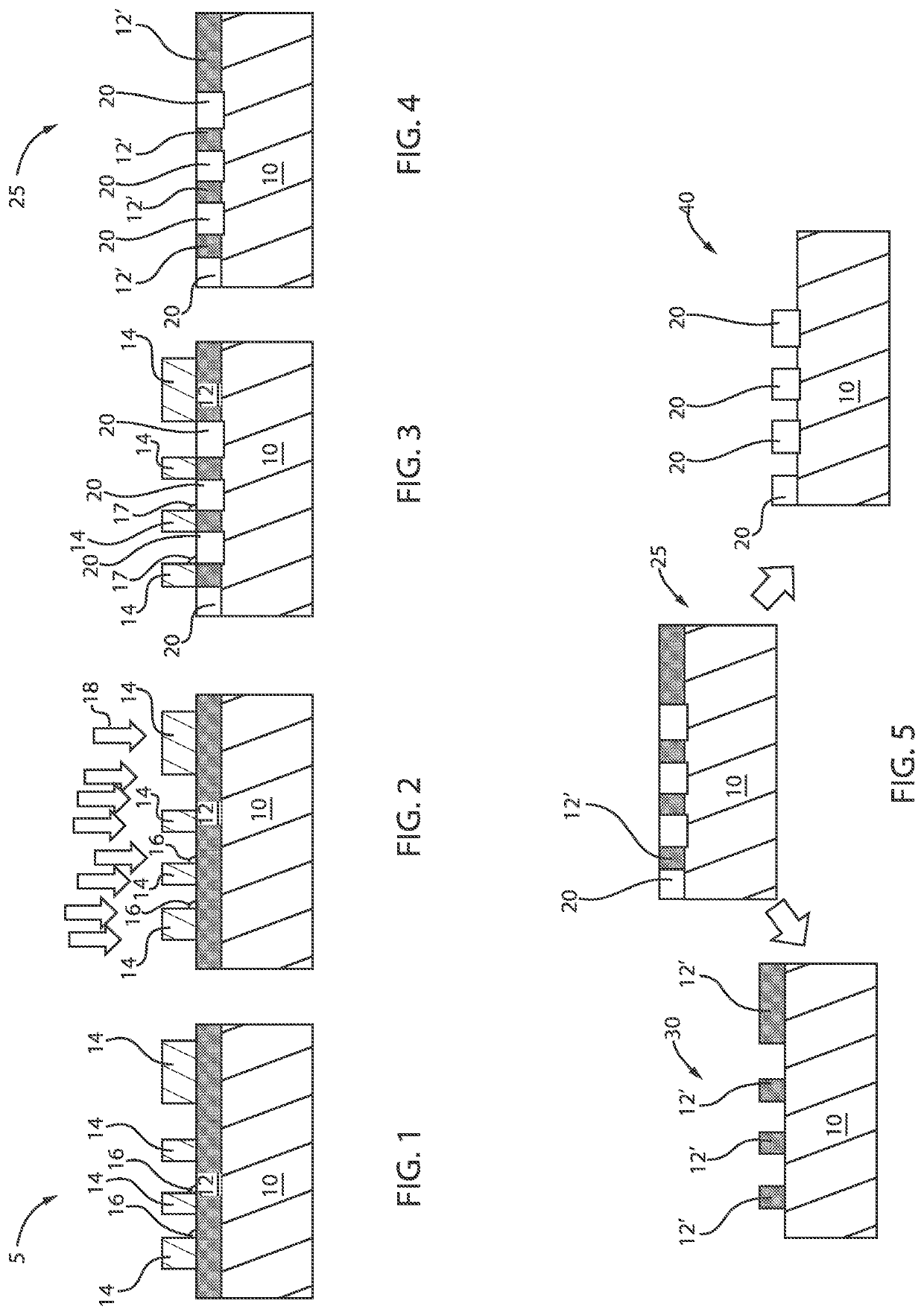
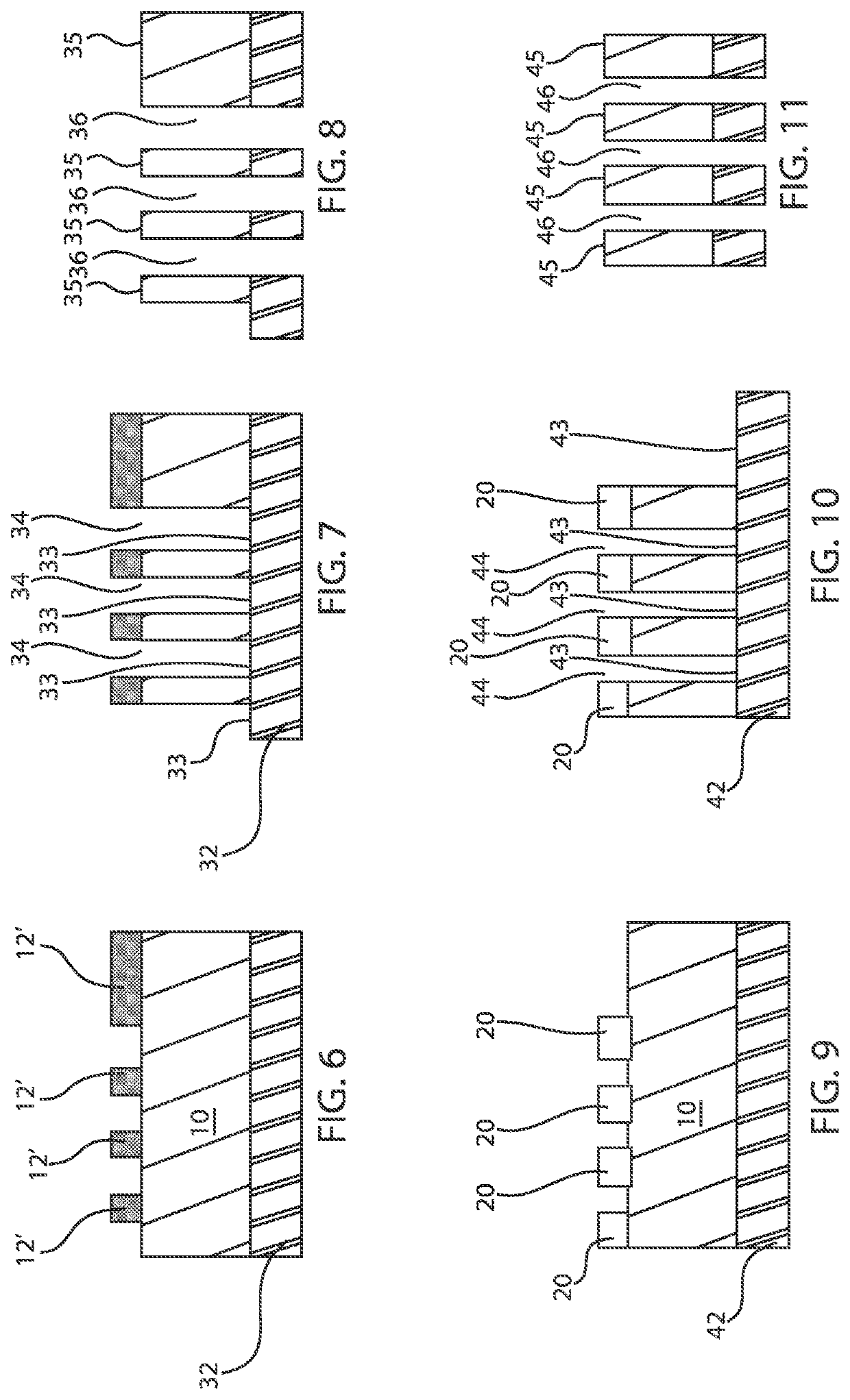
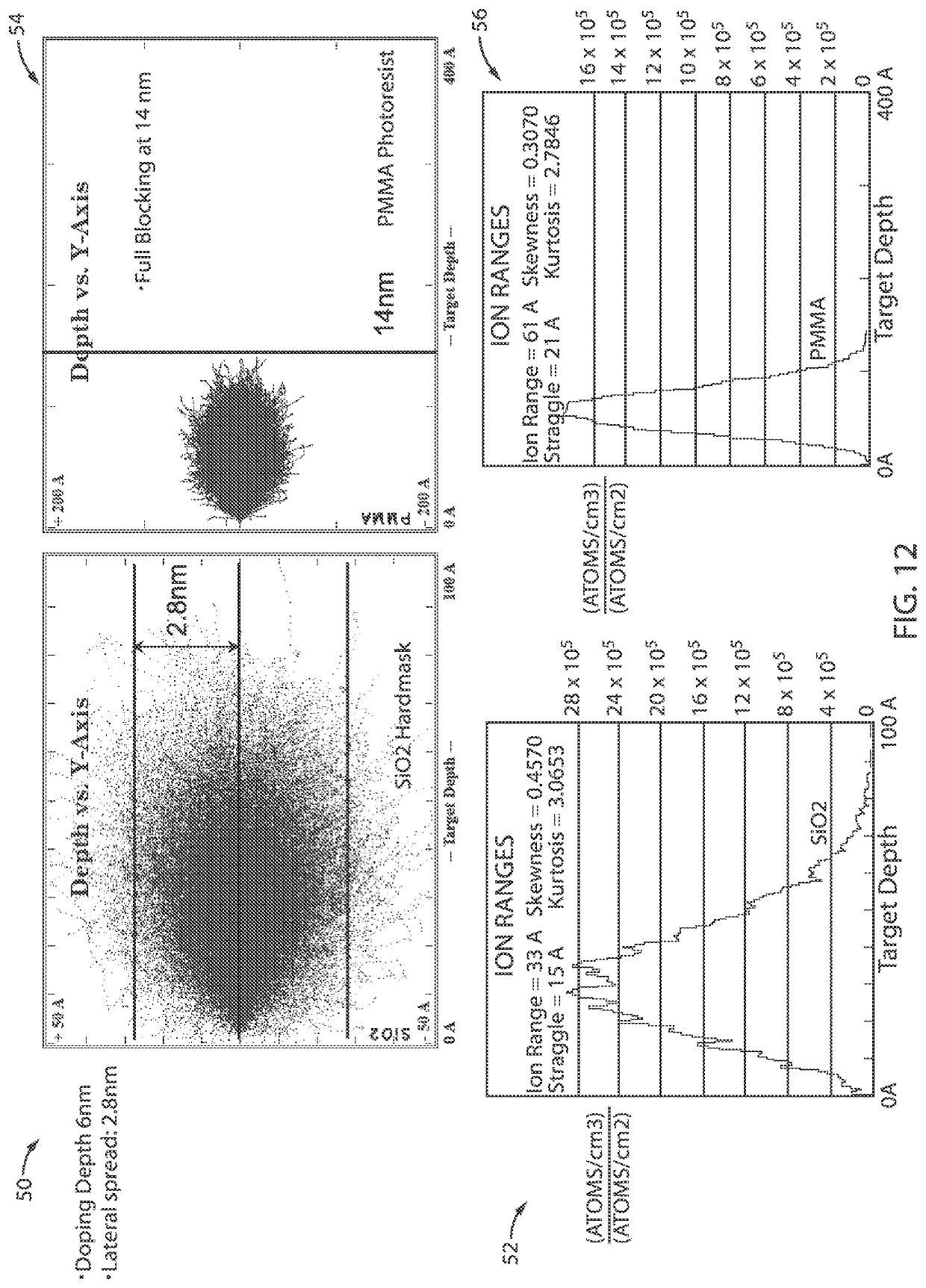
[0023]Embodiments in accordance with the present invention provide methods and devices for preventing or minimizing resist scumming and broken resist lines in semiconductor manufacturing. During the semiconductor patterning process it is common for micro-bridging defects to occur. It is particularly common for micro-bridging defects to form in the resist patterns after the EUV lithography process in advanced technology nodes, for example, nodes of approximately 7 nm and beyond. These micro-bridging or resist scumming defects are often caused by incomplete resist modification during EUV exposure processes. Micro-bridging defects include small connections between two adjacent lines in a photoresist pattern, which can connect two or more resist patterns in close proximity leading to the creation of open or short defects after etching. The open or short defects can cause a decrease in the production yield of advanced integrated circuits.
[0024]EUV lithography is a lithography technique w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com