Multimode Heterogeneous IOT Networks
a heterogeneous iot network and multimode technology, applied in data switching networks, machine-to-machine/machine-type communication services, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of relatively high latency and intermediate bandwidth of cellular networks, and achieve the effect of maximizing signal to noise, and minimizing network induced nois
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
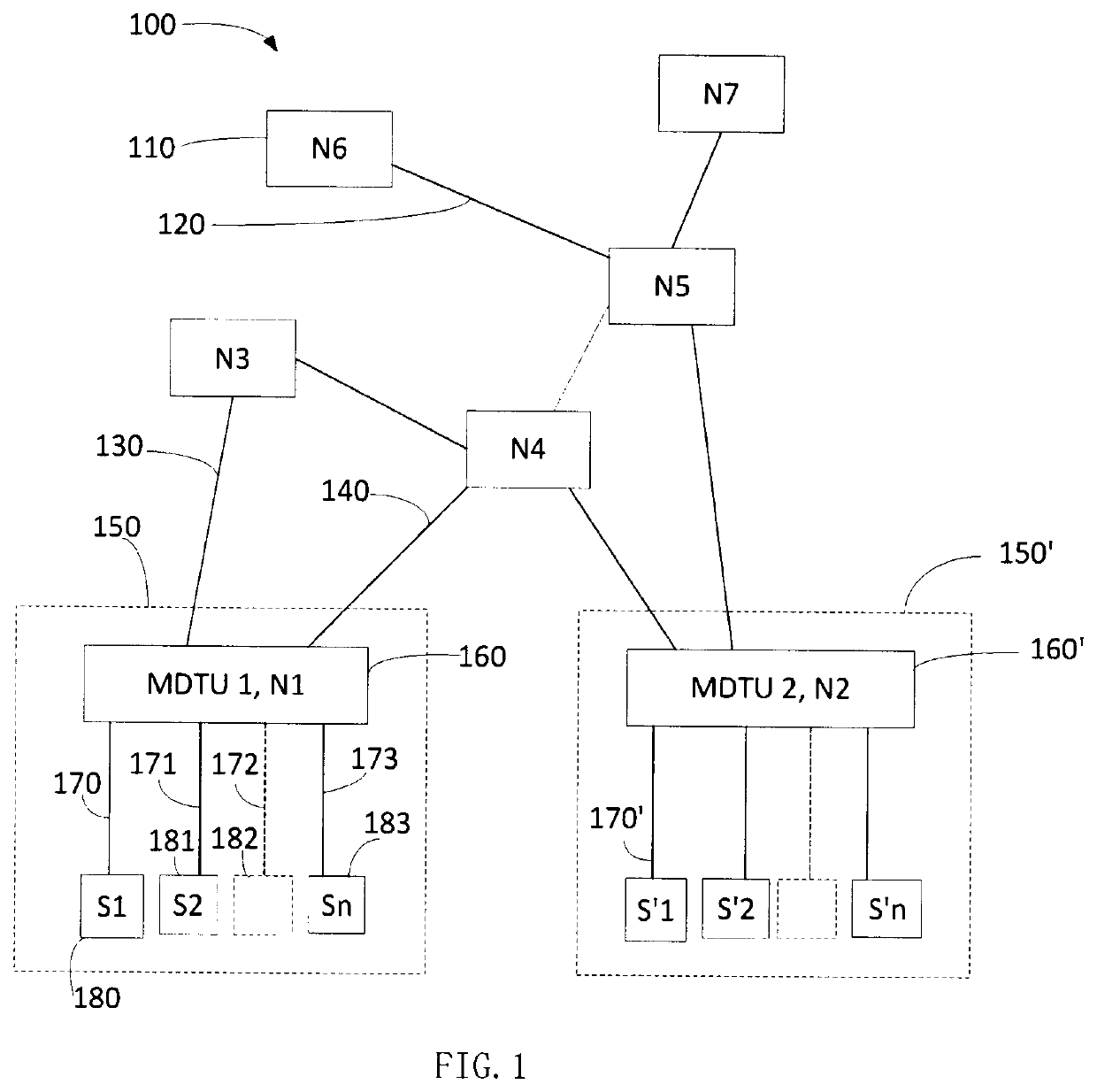
[0219]FIG. 1 shows novel IOT network 100. Network 100 is shown comprising nodes N1 to N7. Node 100, N6, is connected to Node 5, by link 120. Node N3 is connected to Node N1, that is element 1060, by link 130. Node N4 is connected to Node N1, by link 140. Element 160 is node N1, which is also an MDTU, identified as MDTU1. MDTU1 communicates with a plurality of sensors, S1, S2 to Sn (n representing an integer), numbered 180, 182, 183, and 183, by communication and / or control lines numbered 170, 171, 172, and 173. Communication and / or control line 172 and sensor 182 are shown in dashed lines indicating they may represent a plurality of sensors communicating data to node 160. FIG. 1 shows dashed box 150 representing are relatively localized region of space surrounding node 160 that contains sensors S1 to Sn, indicating that sensor data originating in the IOT network from sensors communicating with node 160 originates in the vicinity of node 160, for example within a 10 kilometers of nod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com